백준 9375 java : Map
Map 자료구조를 복습한다. 항상 키값과 value 값을 꺼내서 나열하는걸 까먹었는데 다시 정리해본다.
for (String key : clothes.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + clothes.get(key));
}또한 getOrDefault라는 메서드로 키값과 value값을 자유자재로 저장해보자.
clothes.put(kind, clothes.getOrDefault(kind, 0) + 1);import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class bj9375 {
static Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
public static void main(String[] args) {
int T, N;
T = sc.nextInt();
for (int i = 0; i < T; i++) {
N = sc.nextInt();
Map<String, Integer> clothes = inputClothes(N);
System.out.println(findAnswer(clothes));
}
sc.nextLine();
}
public static Map<String, Integer> inputClothes(int N) {
Map<String, Integer> clothes = new HashMap<>();
String kind;
String name;
for(int i = 0; i < N; i++) {
name = sc.next();
kind = sc.next();
//맵에 kind 키가 존재하면 그 값 반환, 없으면 내가 지정한 defaultValue 반환
clothes.put(kind, clothes.getOrDefault(kind, 0) + 1);
}
return clothes;
}
public static int findAnswer(Map<String, Integer> clothes){
int answer = 1;
/*
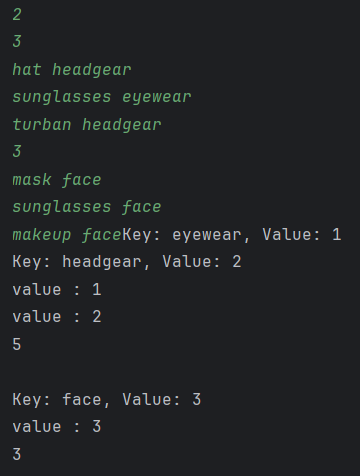
hat headgear
sunglasses eyewear
turban headgear
clothes[headgear] == 2
clothes[eyewear] == 1이니까
headgear 안입거나 입는 경우 3
eyewear 안입거나 입는 경우 2
조합의 경우 3 * 2 - 1 = 5
*/
for (String key : clothes.keySet()) {
System.out.println("Key: " + key + ", Value: " + clothes.get(key));
}
for (int count : clothes.values()) {
System.out.println("value : " + count);
answer *= (count + 1);
}
return answer - 1;
}
}