[Network Week1] Switched networks, Packet switching, Datagram, Virtual Circuit
Computer Science

| Contents |
|---|
| 1. Network model |
| 2. Switched Networks (Circuit Switching, Packet Switching) |
| 3. Packet Switched Networks |
| 4. Datagram vs Virtual Circuit |
1. Network model
1-1. Data communications model
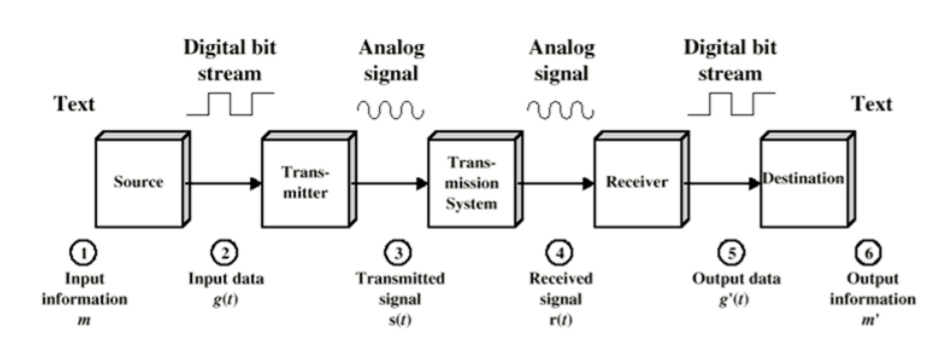
- Telecommunication
: Communication at a distance - Data
: Information presented in whatever form is agreed upon by the parties - Data communications are the exchange of data between two devices via some form of trasmission medium such as a wire cable and wireless
1-2. Networks
- A set of devices (often referred to as nodes) connected by communication links
(즉 커뮤니케이션 링크로 연결된 노드)
Node can be a computer, printer, or any other device capable of sending and/or receiving data generated by other nodes on the network
(그럼 노드란..? 노드는 네트워크에서 다른 노드에 의해 생성된 데이터를 주고 받을 수 있는 컴퓨터, 프린터 등의 장치)

1-3. Simplified Network Model
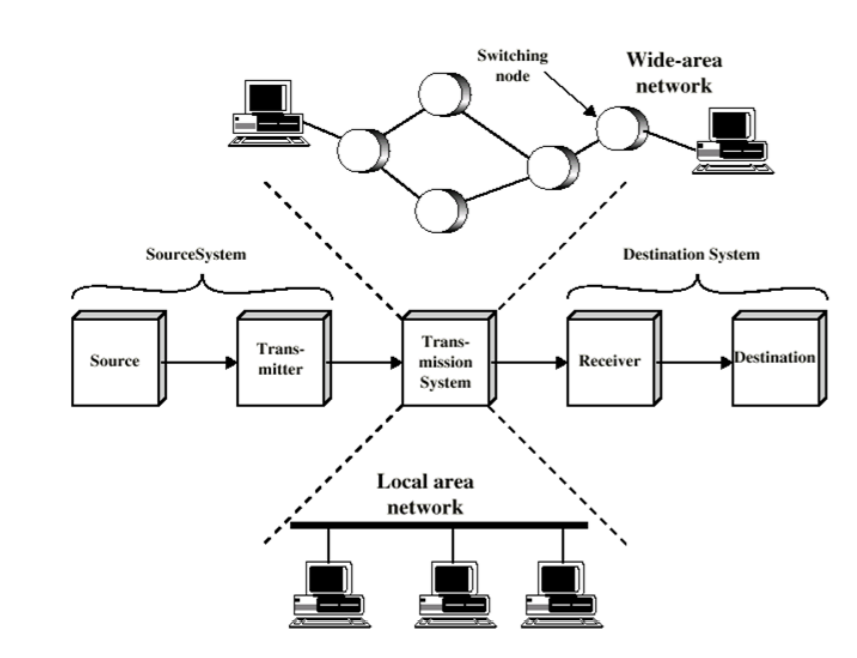
2. Switched Networks
2-1. Switched Communication Network
- Transmitting data from SRC to DST thru a network of intermediate network nodes (routers)
- Long distance transmission is typically done over a network of switched nodes
(Nodes are not concerned with content of data) - End devices are stations
(Computer, terminal, phone, etc.) - A collection of nodes and connections is a communications network
- Data routed by being switched (forwarded) from node to node
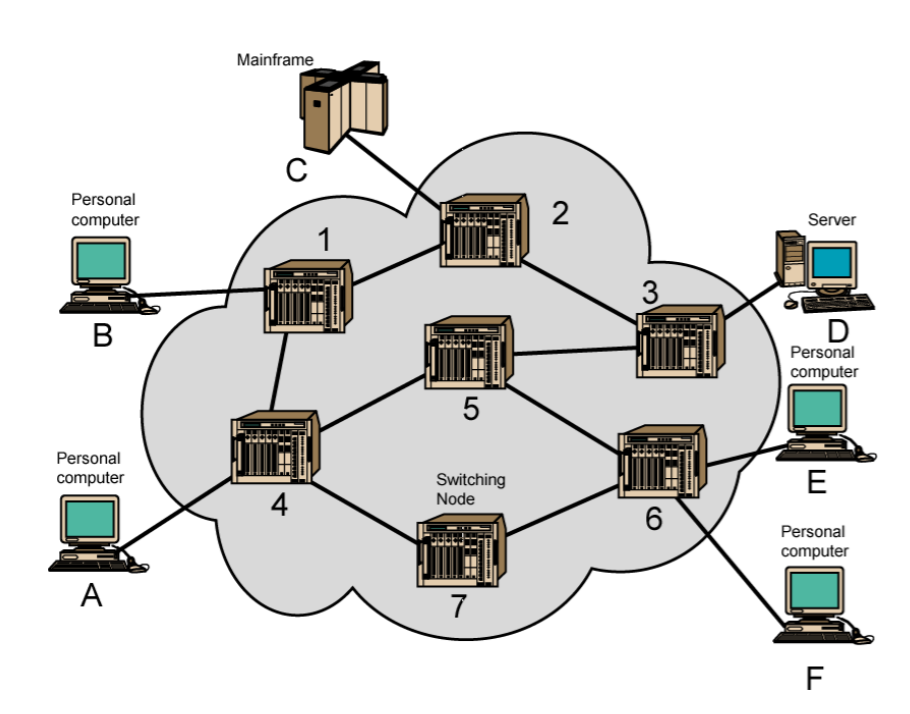
2-2. Simple Switched Network
(최적의 경로를 찾으며 경로를 바꾸어 주는 것)
ex. 6 devices, 7 routers
2-3. Two switching Technologies
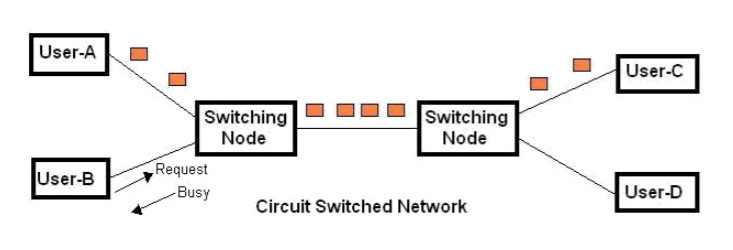
- Circuit Switching
- Packet Switching
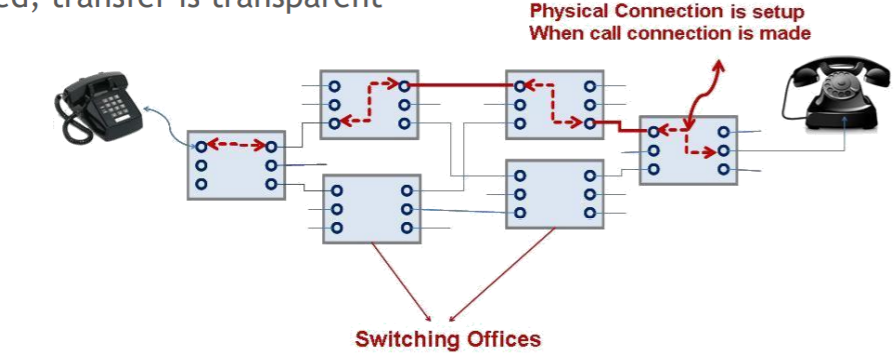
2-4. Circuit Switching
- Dedicated communication path between two stations physically and logically
- Path is established before data transmission
- Three phases
(Establish -> Transfer -> Disconnect) - Must have switching capacity and channel capacity to establish connection
- Must have intelligence to work out routing (Centralized)

2-4. Circuit switching applications
- Inefficient
- Channel capacity dedicated for duration of connection
- If no data, capacity wasted
- Setup (connection) takes time
- Delay prior to data transfer
- Once connected, transfer is transparent
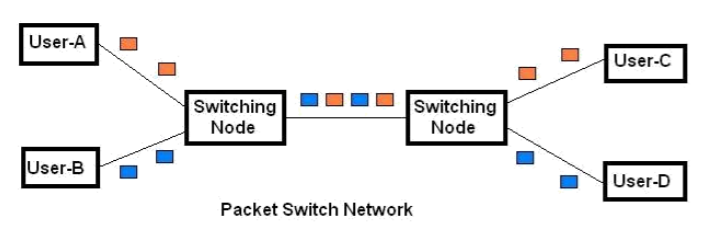
2-5. Packet switching Principles
- Circuit Switching designed for voice
-- Resources dedicated to a particular call
-- Much of the time a data connection is idel
-- Data rate is fixed(CBR : Constant Bit Rate)
-- Both ends must operate at the same time) - Packet swtiching are shared, channelized
-- A link between switch may carry several packets at the same time, each sent by a different source and going to different destination
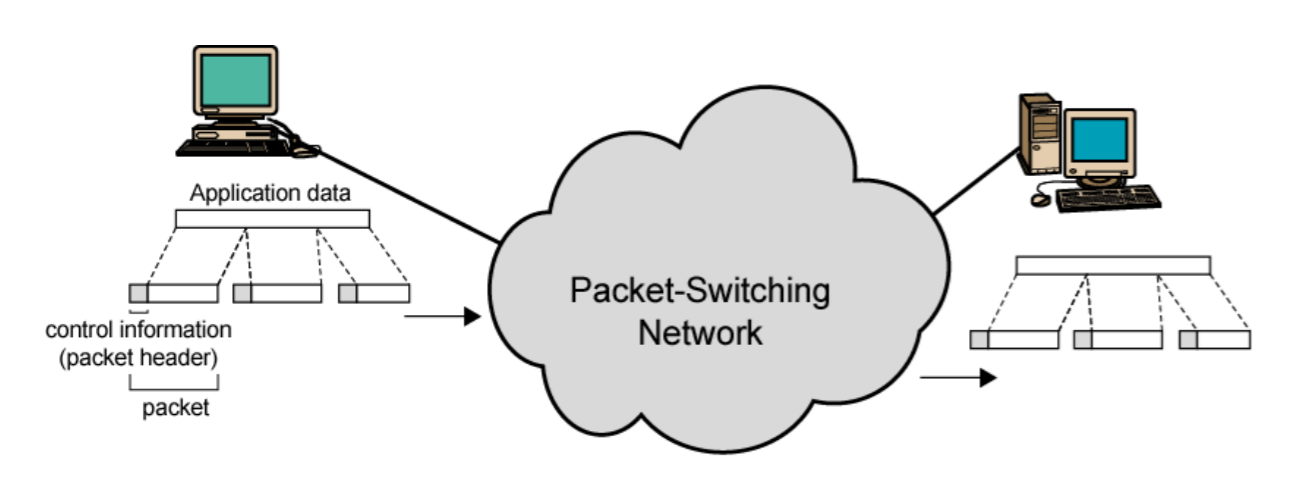
2-6. Basic operation of Packet Switching
- Data transmitted in small packets
-- Typically 1000 octets
-- Longer messages split into series of packets
-- Each packet contains a portion of user data plus some control information - Control info
-- Routing (addressing) info - Packets are received, stored briefly (buffered) and past on to the next node
-- Store and forward
2-7. Use of Packets
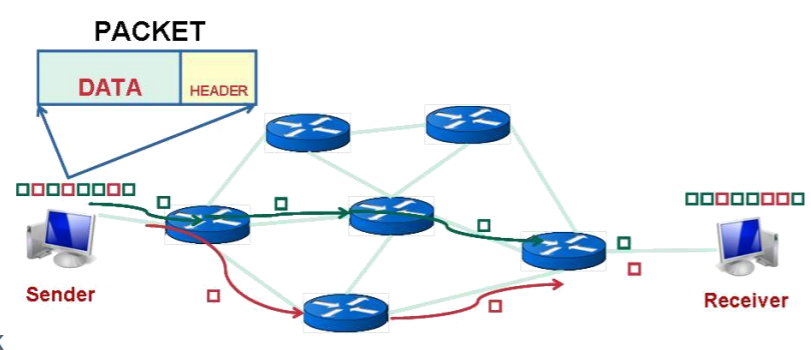
2-8. Packet Switching Advantages
-
Line efficiency
-- Single node to node link can be shared by many packets over time
-- Packets queued and transmitted as fast as possible -
Data rate conversion (VBR : Variable Bit Rate)
-- Each station connects to the local node at its own speed
-- Nodes buffer data if required to equalize rates -
Packets are accepted even when network is busy
-- Delivery may slow down -
Priorities can be used
3. Packet Switched Networks
3-1. 5 Layers in Packet Switched Networks
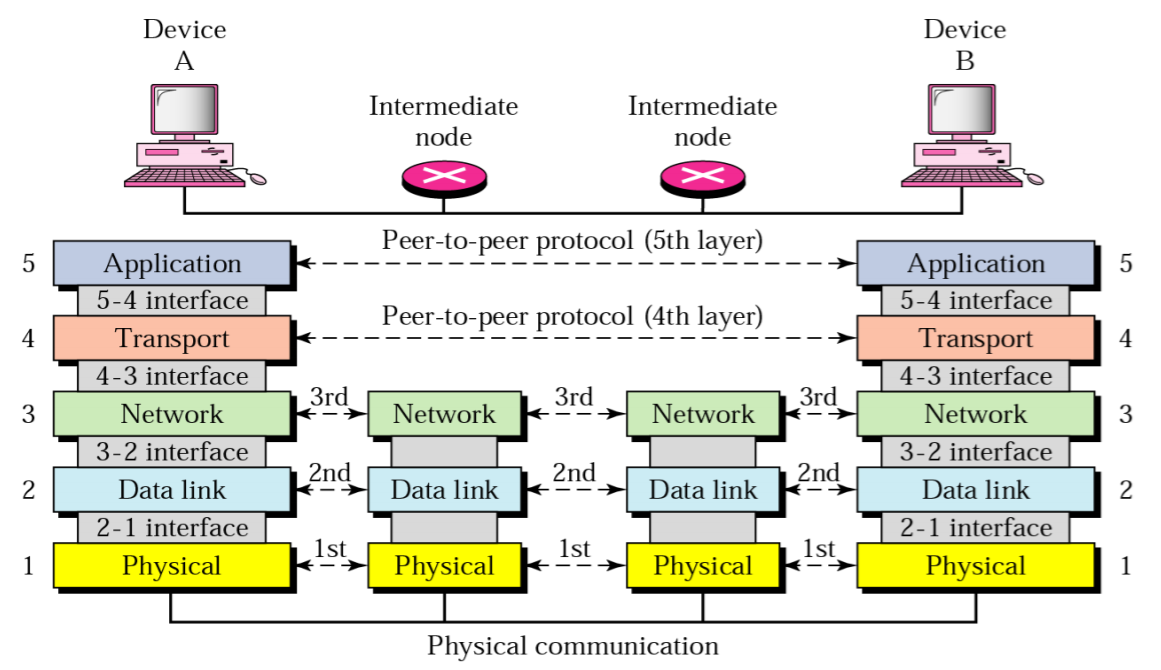
3-2. Network Layer (3rd Layer)
- Goal
-- Allow packets to be forwarded from any source to any destination through heterogeneous networks and routers - Services
-- Unreliable connectionless service
-- Reliable connection-oriented service
3-3. Transport Layer
- Goals
--Imporves the service by the network
(Reliability, Multiplexing) - Transport layer services
-- Unreliable connectionless service
-- Reliable connection-oriented service
3-4. Routers in Routing
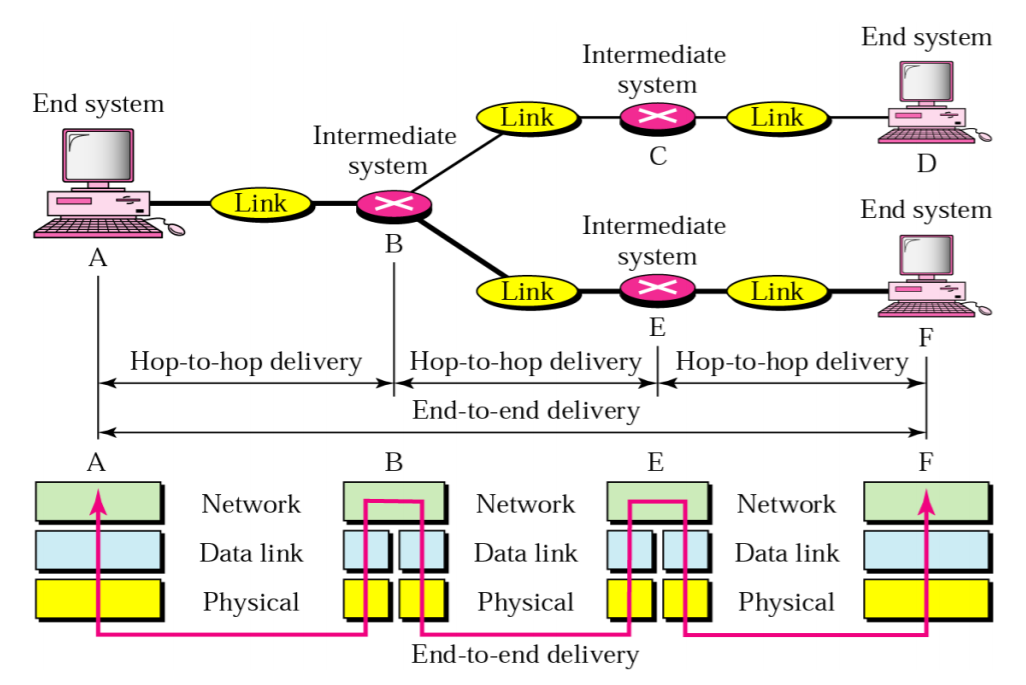
3-5. Network Layer Basic Principles
- Each host/router must be identified by a network layer address
-- Independent from its datalink Layer address (MAC) - Network layer forwards packets from source to destination through multiple routers
- Network layer service must be completely independent from the service provided by the datalink layer
(Hop by hop) - Network layer user should not need to know anything about the internal structure of the network layer to be able to send packets
4. Datagram vs Virtual Circuit
4-1. Two services in Packet Switching
- Two possible nodes
-- Datagrams
-- Virtual Circuits - Datagram mode is used to provide a connectionless ervice
-- There is no "network-layer-connection" between two hosts - Virtual circuits are used to provide a connection-oriented service
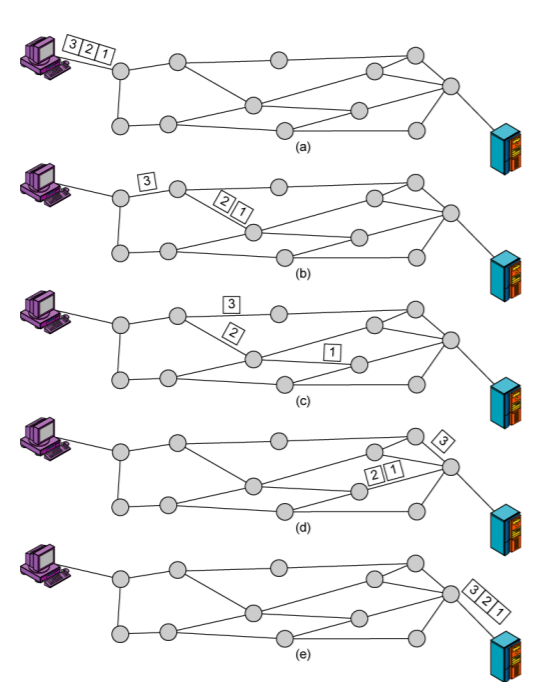
4-2. Datagram
- Each packet treated independently
- Packets can take any practical route
- Packets may arrive out of order
- Packets may go missing
- Up to receiver to re-order packets and recover from missing packets
- Used in the network layer
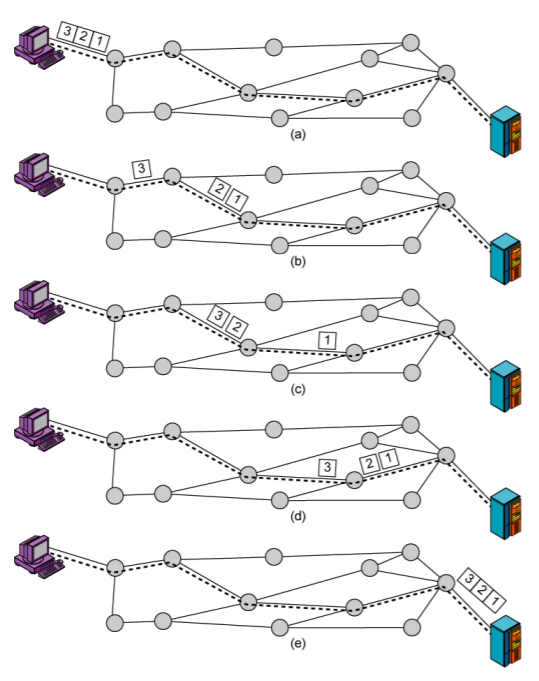
4-3. Virtual Circuit
- Preplanned route established before any packets sent
- Call request and call accept packets establish connection (handshake)
- Each packet contains a virtual circuit identifier instead of destination address
- No routing decisions required for each packet
- Clear request to drop circuit
- Not a dedicated path
4-4. Virtual Circuits vs. Datagram
- Virtual circuits
-- Network can provide sequencing and error control
-- Packets are forwarded more quickly
: No routing decisions to make
-- Less reliable
: Loss of a node loses all circuits through that node - Datagram
-- No call setup phase
(Better if few packets)
-- More flexible
(Routing can be used to avoid congested parts of the network)
- Key Points
- Circuit switching is used in public telephone networks
(Designed to handle voice traffic) - With circuit switching, a dedicated path is established between two stations
-- Switching and transmission resources within network are reserved for exclusive use of circuit for duration of connection
-- Connection is transparent
(Once established it appears as if direct connection) - Packet switching was designed for more efficient facility than circuit switching for bursty data traffic
- With Packet switching, a station transmit data in small blocks, called packet
- Virtual circuit and datagram
-- A route is defined between two endpoints and all packets follow the same route
-- Each packet is treated independently and packet for the same destination may follow different path
