[Programming Language week3] Structured data types, Vectors, Records, Pointers
Computer Science
Characters
-
Sequence of characters are often processed as a unit
-
Specification
-- Value : set of possible character values that are language-defined enumeration, and supported by underlying hardware -
Implementation
-- Directly supported by underlying hardware
-- Converted from input-output system to the character-set representationAssignment
-
Basic operation for changing the binding of a value to a data object

-
Forms of Assignment Statements

-
Schizophrenic Representation
-- lvalue(location attribute) and rvalue (value attribute)
-- ex) X = X + 1

-
Variation on assignment
-- The updating assignment

-- Multiple target assignment
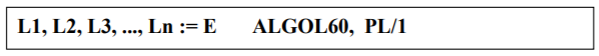
-- Multiple assignment statement

-- Aliasing, Different number of variables on LHS and RHS
Storage models
- Value semantics : assigned to immutable value
- Pointer semantics : assign the location

- Storage insecurities
-- Use before initialization
-- Dangling reference

Structured data types
Structured data Object
- Aggregate data object
- Component
-- Elementary object
-- Another data structure
Issues about data structures
- Maintaining specification of the structural information
- Indicating the component data objects
- Managing the storage
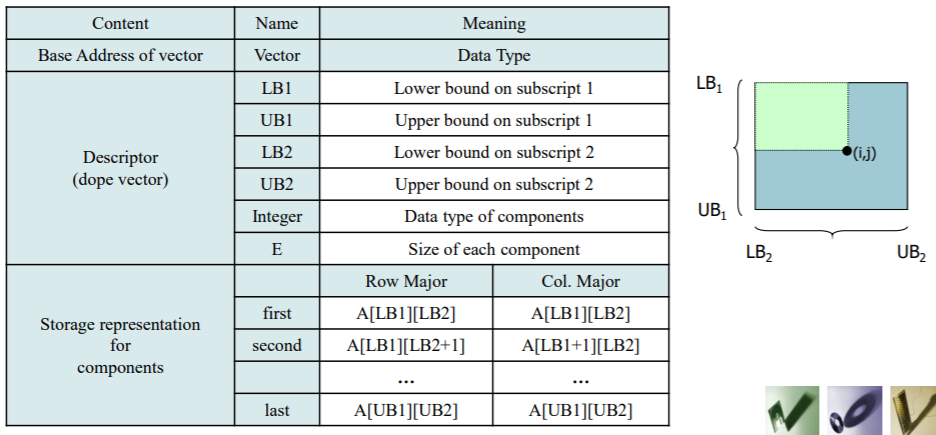
Specification of structured data types
-
Major attributes
-- Number of components
: Fixed size - array, record
: Variable size - lists, stacks, files, sets
-- Type of each component
: Homogeneous - array
: Heterogeneous - record
-- Names to be used for selecting components
: Homogeneous type may use integer subscribt or sequence of subscript
: Heterogeneous type use programmer defined identifier
-- Maximum number of components
: Only for the cariable size data strucr=ture
-- Organization of the components
: Simple linear sequence is the most common organization
: Multi-dimension forms are used to extend sequences -
New classes of operations on data structures
-- Component selection operations
: Random selection
: Sequential selection
-- Whole-data-structure operations
: Addition of two arrays
: Assignment of one records to another
: Union operation on sets
-- Insertion/Deletion
: Storage representation and management problems related
: Not allowed for sequentially allocated memory
-- Creation/destruction of data structure
: Storage management problems related
Implementation of data structures types
-
Storage representation
-- Storage for data + optional descriptor
-- Usually S/W simulated
-- Basic representation
: Sequential representation
: Linked representation -
Implementation of operation on data structures
Sequential representation
-- Using accessing formula to locate the component
: Location = base address + offset
e.g. A[10] = lvalue(A) + 10* sizeof(A[0]) (homogeneous)Linked representation
-- Following a chain of pointers
-
Type checking issues
-- Existence of a selected component
-- Type of a selected components
-
Name equivalance VS structural equivalence
-- Name equivalence
: Same name
-- Structural equivalence
: Same structureVectors
-
Linear arrays
: Composed of a finite number of homogeneous components
: Selected by using its subscripts -
Attributes of a vector
: Number of components
: Data type of each component
: Subscripts to be used to select each component(Could be an integer value or enumerated value)

-
Operations of vectors
-- Subscripting
-- Creation
-- Destroying
-- Assigning a value to a component
-- Arithmetic operation on two vectors

-
Implementation
-- For efficiency
: Homogeneity
: Fixed size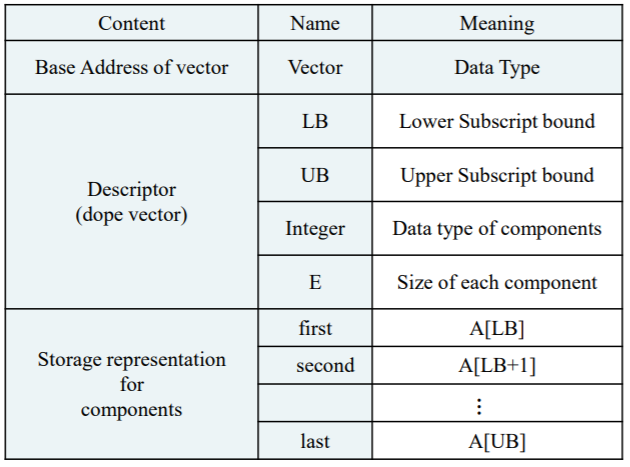
-- Accesing formula
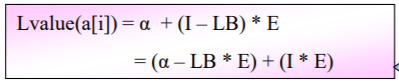
VO = (a - LB * E )
-- Packed storage representation
: Create issues like boundary crossing
-- Whole vector operation -
Multi-dimensional arrays
-- Specification
: Extension of vector array with multiple subscripts
-- Implementation
: A vector of vectors
: Storage representation
: Row-major order
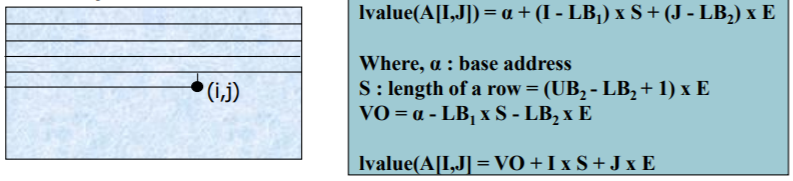
: Column-major order

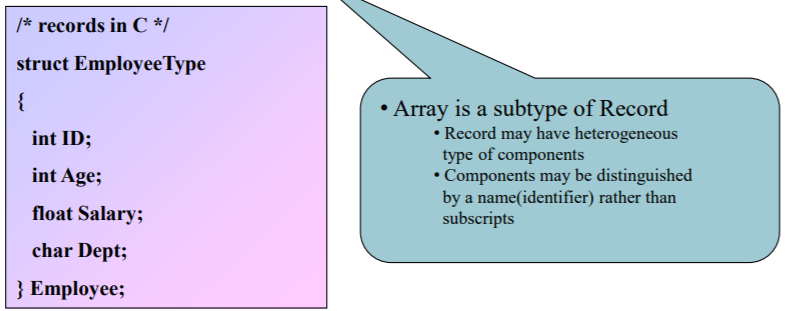
Records
-
A data structure of a fixed number of components of different typed
-
Specification
-- The attribute of components
: The number of components
: The data type of each component
: The selcetor used to name each component
-- Operations on entire structure is not common -
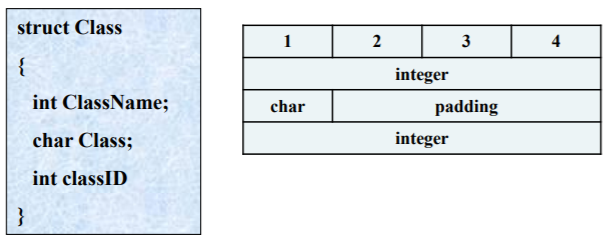
Implementation
-- Mapping into an offset
: the distance from the base
: Padding occurs for data alignment
Variant Records
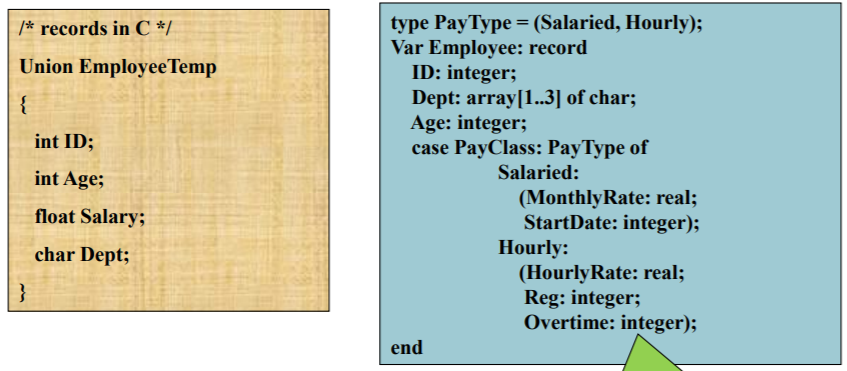
-
Union type in C
-
Implementation
: Allocate largest storage for the variant record
: Dynamic checking is provided for range error
Lists
- Similar to vectors except
: Variable length
: Heterogeneous components
: Usually implicit declaration is used
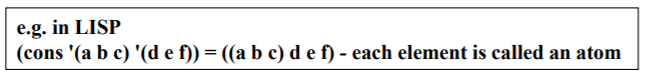
- Operation
: Selector, Insert, Append, Delete, etc. - Variation of lists
: Stack, queue, tree, etc.
Character Strings
-
Specification
-- Operation
: Concatenation
: Relational operations on string
: Substring selection
: I/O formatting -
Implementation
-- S/W simulated for the part that H/W does not support
-- Implementation manner
: Fixed declared length
: Variable length to a declared bound
: Unbounded length
( C uses a null terminator to indicate the end of a string )Pointers
-
An object that contains the location of another data object
-
Its rvalue is lvalue of another object ( or itself)
-
Specification
: Pointers may reference data object of a single type
: Pointers may reference data object of any type -
Operations
: Creation
: Dereferencing -
Implementation
-- Storage representation
: Absolute address
: Relative address
-- Issues
: Garbage
: Dangling reference
: OptimizationSets
-
Containing unordered collection of distinct values
-
Operations
: Membership
: Insertion/deletion
: Union
: Intersection
: And/or -
Implementation
: Bit string representation
: Hash-coded representation
