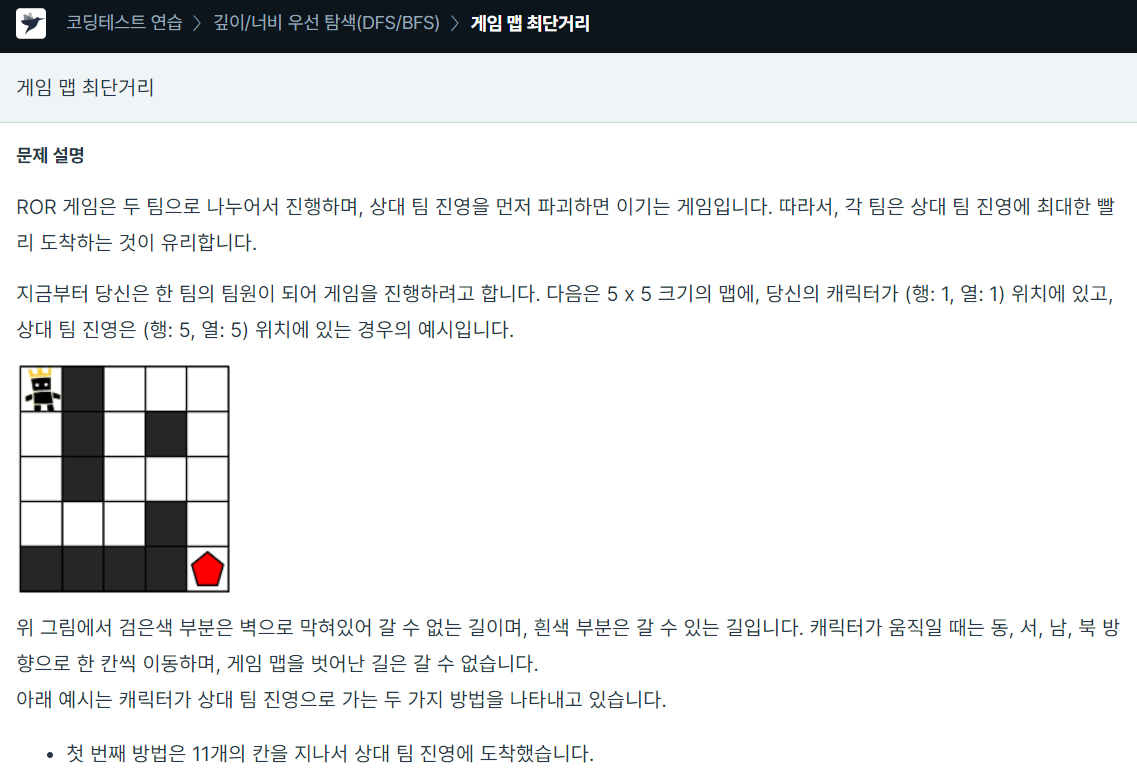


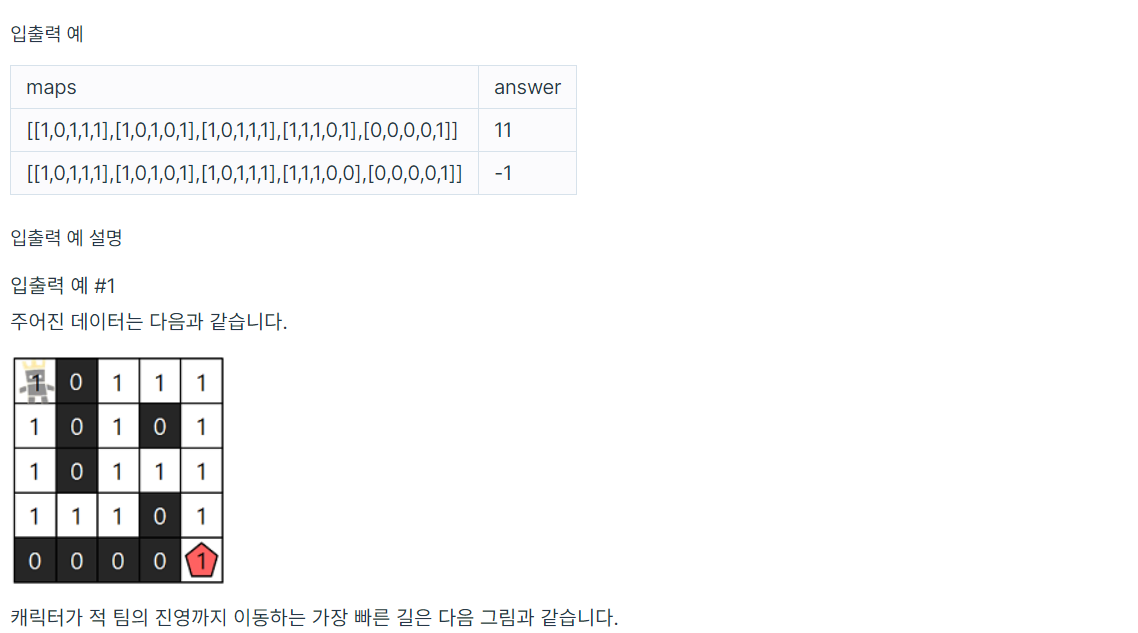

import math
answer = math.inf
direction = [[1,0], [-1,0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]
dp = []
def dfs(deph,n, m, x, y, visited, maps):
global answer
if deph > answer:
return
if x == n-1 and y == m-1:
answer = min(answer, deph+1)
return
for d in direction:
nx, ny = x + d[0], y + d[1]
if 0 <= nx < n and 0 <= ny < m:
if not visited[nx][ny] and maps[nx][ny] == 1:
visited[nx][ny] = True
dfs(deph+1, n,m, nx, ny, visited, maps)
visited[nx][ny] = False
return
def solution(maps):
global answer
global dp
visited = [[False]* len(maps[0]) for _ in range(len(maps))]
visited[0][0] = True
dfs(0, len(maps), len(maps[0]), 0, 0, visited, maps)
if answer == math.inf:
return -1
return answer정확성 테스트의 경우 전부 정답이였지만
효율성 테스트에서 전부 오답이 나왔다.
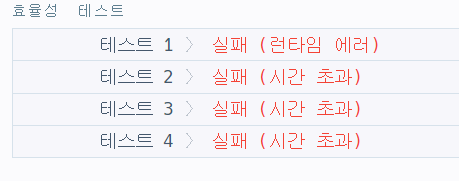
...
from collections import deque
import math
direction = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]
def solution(maps):
q = deque([[0,0,1]])
n, m = len(maps), len(maps[0])
while q:
x, y, deph = q.popleft()
maps[x][y] = 0
for d in direction:
nx, ny = x+d[0], y+d[1]
if nx == n-1 and ny == m-1:
return deph+1
else:
if 0 <= nx < n and 0<= ny <m and maps[nx][ny]:
q.append([nx, ny, deph+1])
return -1dfs가 아닌 bfs를 통해 시도했지만 이번에도 효율성 테스트에서 전부 실패했다.
결국 스스로 해결하지 못하고 인터넷에서 참조해서 풀었다.
from collections import deque
direction = [[1, 0], [-1, 0], [0, 1], [0, -1]]
def solution(maps):
q = deque([[0,0,1]])
n, m = len(maps), len(maps[0])
while q:
x, y, deph = q.popleft()
maps[x][y] = 0
for d in direction:
nx, ny = x+d[0], y+d[1]
if nx == n-1 and ny == m-1:
return deph+1
else:
if 0 <= nx < n and 0<= ny <m and maps[nx][ny]:
q.append([nx, ny, deph+1])
maps[nx][ny] = 0
return -1q에 저장할때 다음에 갈 map에 대해서도 미리 0으로 만듬으로써 해결
