
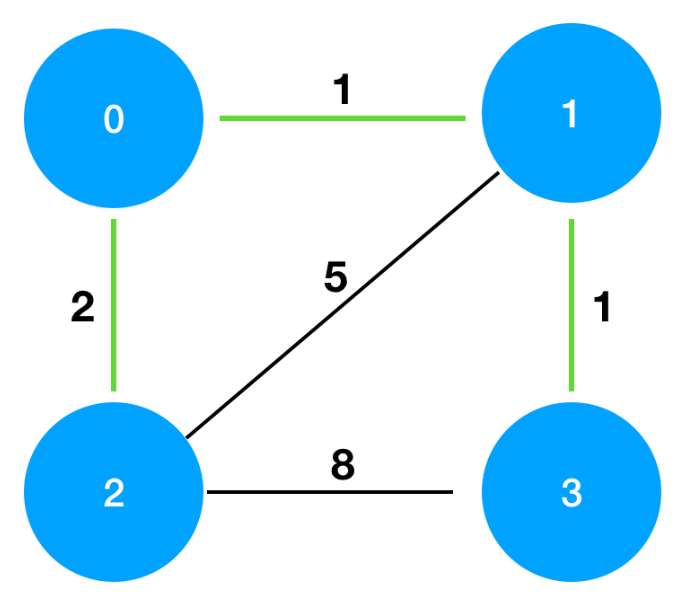
다른 분들이 많이 사용한 Kruskal 알고리즘
def solution(n, costs):
answer = 0
costs.sort(key = lambda x: x[2])
link = set([costs[0][0]])
while len(link) < n:
for cost in costs:
if cost[0] in link and cost[1] in link:
continue
if cost[0] in link or cost[1] in link:
answer += cost[2]
link.update([cost[0], cost[1]])
break
return answerKruskal 알고리즘을 알고나면 어렵지 않게 풀 수 있는 문제이다.
알고리즘 자체도 이해하기 쉬운 편이였다. 하지만 처음 떠올린 다익스트라 알고리즘으로 풀고 싶었다.
from heapq import heappush, heappop
def solution(n, costs):
answer = 0
graph = [[] for _ in range(n)]
for cost in costs:
graph[cost[0]].append((cost[1], cost[2]))
graph[cost[1]].append((cost[0], cost[2]))
h = [(0,0)]
visited = [False] * n
while h:
c, node = heappop(h)
if visited[node]:
continue
visited[node] = True
answer += c
for next_node, next_c in graph[node]:
if not visited[next_node]:
heappush(h, [next_c, next_node])
return answer다익스트라 알고리즘으로 해결한 코드
기본적인 다익스트라와 다른 점은 시작점에서의 거리를 누적?해서 저장하지 않고 graph를 순환하며서 해당 간선의 크기만 저장한다.
