Chapter 01. Understanding large language models

https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main
목차
- Preface
- Acknowledgments
- About this book
- About the author
- About the cover illustration
- Understanding large language models
- What is an LLM?
- Applications of LLMs
- Stages of building and using LLMs
- Introducing the transformer architecture
- Utilizing large datasets
- A closer look at the GPT architecture
- Building a large language model
- Working with text data
- Understanding word embeddings
- Tokenizing text
- Converting tokens into token IDs
- Adding special context tokens
- Byte pair encoding
- Data sampling with a sliding window
- Creating token embeddings
- Encoding word positions
- Coding attention mechanisms
- The problem with modeling long sequences
- Capturing data dependencies with attention mechanisms
- Attending to different parts of the input with self-attention
- Implementing self-attention with trainable weights
- Extending single-head attention to multi-head attention
- Implementing a GPT model from scratch to generate text
- Coding an LLM architecture
- Normalizing activations with layer normalization
- Implementing a feed forward network with GELU activations
- Adding shortcut connections
- Connecting attention and linear layers in a transformer block
- Coding the GPT model
- Generating text
- Pretraining on unlabeled data
- Evaluating generative text models
- Training an LLM
- Decoding strategies to control randomness
- Loading and saving model weights in PyTorch
- Loading pretrained weights from OpenAI
- Fine-tuning for classification
- Different categories of fine-tuning
- Preparing the dataset
- Creating data loaders
- Initializing a model with pretrained weights
- Adding a classification head
- Calculating the classification loss and accuracy
- Fine-tuning the model on supervised data
- Using the LLM as a spam classifier
- Fine-tuning to follow instructions
- Introduction to instruction fine-tuning
- Preparing a dataset for supervised instruction fine-tuning
- Organizing data into training batches
- Creating data loaders for an instruction dataset
- Loading a pretrained LLM
- Fine-tuning the LLM on instruction data
- Extracting and saving responses
- Evaluating the fine-tuned LLM
- Conclusions
- Appendices
- Introduction to PyTorch
- References and further reading
- Exercise solutions
- Adding bells and whistles to the training loop
- Parameter-efficient fine-tuning with LoRA
1. What is an LLM?
LLM이 성공할 수 있었던 건 트랜스포머 아키텍처가 언어의 뉘앙스나 문맥이나 패턴의 다양성을 포괄했기 때문이다.
- LLM은 인간의 텍스트를 이해하고 생성하고 반응하기 위해 디자인된 신경망이다.
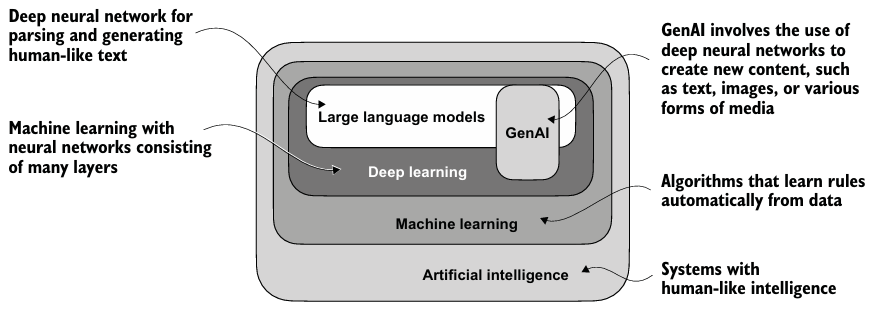
- 딥러닝은 3개 이상의 layer를 가진 신경망에 중점을 둔 머신러닝으로 Deep neural networks로도 불린다.
- 전통적인 머신러닝은 수동적인 특징 추출을 필요로 하여 가장 관련있는 특징(e.g. 스팸 메일 분류 시 특정 trigger 단어 선택)을 직접 선택해줘야 하지만, 딥러닝은 필요하지 않다 (여전히 스팸인지 논스팸인지에 대한 label은 필요하다).
- 머신러닝과 딥러닝 이외에도 AI는 rule-based systems, genetic algorithms, expert systems, fuzzy logic, or symbolic reasoning 등의 접근 방식들도 활용되었다.
2. Applications of LLMs
- LLM은 거의 모든 분야에서 전문적으로도 사용가능하며, 텍스트를 분석하고 만들어내는 모든 일을 자동화할 수 있다.
3. Stages of building and using LLMs
- custom LLM을 만드는 것이 기존 범용 LLMs보다 성능이 좋을 수 있으며, 데이터 보안성과 업데이트 및 수정에 대한 자율성을 가지고 서버 비용도 줄일 수 있다.
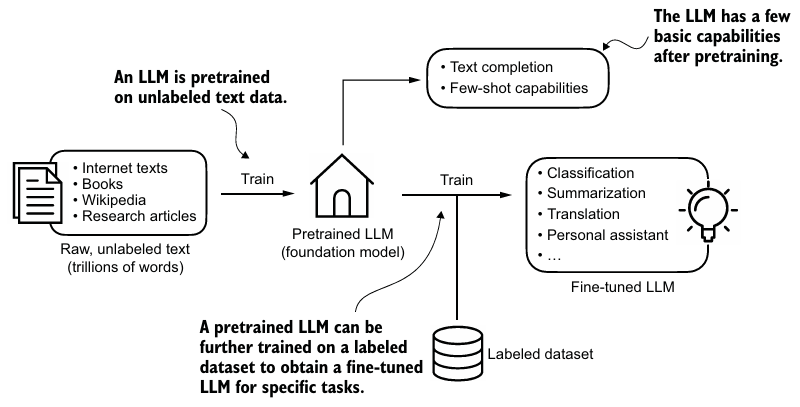
- Pretraining 단계에서 대형 corpus 텍스트 데이터를 훈련한다. 이 과정에서 self-supervised learning을 사용한다.
- Pretrained model은 base or foundation model로 부른다. 이후, labeled data로 fine-tuning 한다.
- query와 label을 가지는 instruction fine-tuning과 텍스트와 해당 class label을 가지는 classification fine-tuning으로 나뉜다.
4. Introducing the transformer architecture
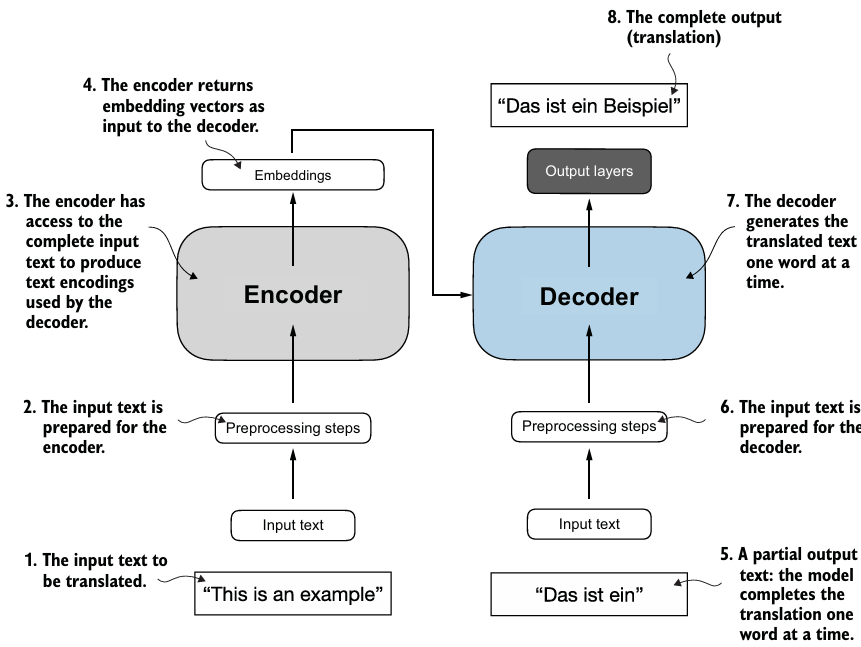
- 트랜스포머는 디코더와 인코더로 구성된다.
- 각각은 많은 layer가 연결된 self-attention mechanism으로 구성된다.
- 인코더는 input 텍스트를 맥락과 관련한 정보를 가진 vector로 인코딩한다.
- 디코더는 인코딩된 vector로 output text를 만든다.
- self-attention mechanism
- 모델이 서로 다른 토큰 별로 중요도에 따라 가중치를 부여하도록 한다.
- 모델이 input 데이터에서 멀리 떨어져있는 의존성과 문맥 상의 관계를 잡도록 도와준다.
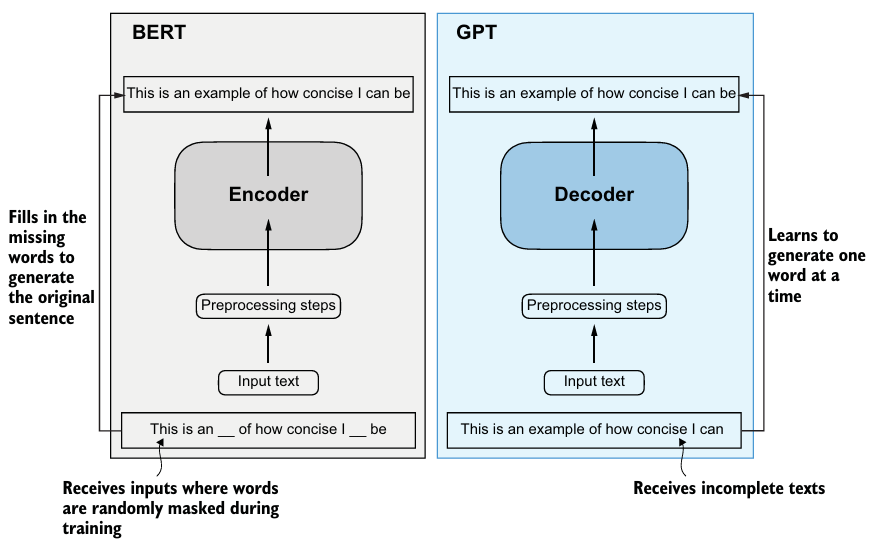
- BERT는 기존 트랜스포머의 인코더 submodule을 기반으로 만들어져 mask된 단어 예측을 통해 훈련한다. 이로 인해 텍스트 분류 task에 강하다.
- GPT는 텍스트 완성 task에 강하며, zero-shot과 few-shot learning tasks에 능숙하다.
5. Utilizing large datasets
- BERT나 GPT 훈련에 사용된 large training datasets은 다양하고 포괄적인 수 억개의 단어를 가지는 text corpora이다.
- Pretraining은 막대한 비용이 들지만, 많은 모델이 오픈소스로 이용이 가능하다. 이 모델을 fine-tuning하여 특정 task에 사용할 수 있다.
6. A closer look at the GPT architecture
- GPT는 next-word prediction task로 pretrain하였다.
- next-word prediction task는 self-supervised learning의 형태이다.
- 다음 단어를 label로 사용하기 때문이다.
- GPT는 트랜스포머의 decoder만 존재하며 한 번에 한 단어만 예측하여 텍스트를 생성한다.
- 이는 이전 output을 예측에 필요한 input으로 포함하는 autoregressive model 유형이다.
- 이를 통해 일관성을 유지한다.
- GPT-3은 96개의 트랜스포머 layer를 가진다.
- 기존 트랜스포머 모델은 언어 번역을 위해 디자인되었다.
- GPT도 예상과 달리 번역과 관련한 좋은 성능을 가지고 있다.
- 이러한 명시적으로 훈련되지 않은 작업을 수행하는 능력을 emergent behavior라고 한다.
- 이는 모델이 막대한 양의 다국어 데이터를 다양한 문맥에 대해 노출되면서 생기는 자연스러운 결과이다.
7. Building a large language model
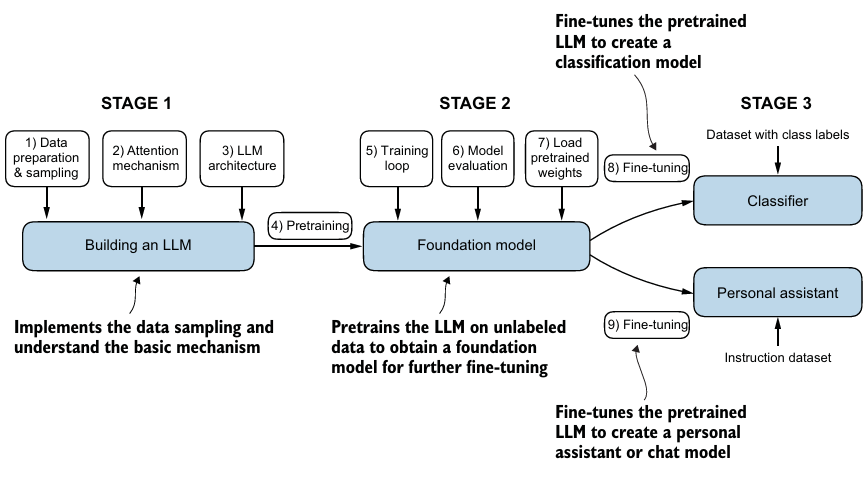
- 핵심적인 데이터 전처리와 attention mechanism을 코딩한다.
- GPT같은 텍스트 생성 LLM을 어떻게 pretrain하는지 배우고, LLM을 평가하는 것의 핵심을 조사한다.
- 텍스트 분류나 질의응답같은 명령에 따라 LLM을 fine-tuning한다.
