Appendix A. Introduction to PyTorch

https://github.com/rasbt/LLMs-from-scratch/tree/main/appendix-A
PyTorch의 사용법과 Tensor, 자동 미분 엔진에 대해서 먼저 배우자.
1. What is PyTorch?
The three core components of PyTorch
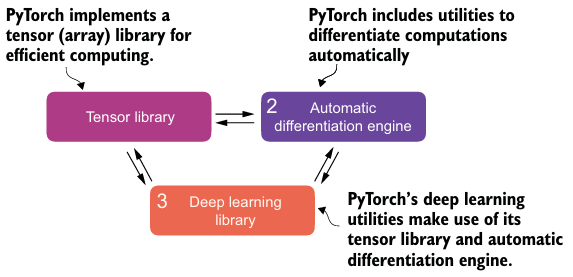
- tensor library는 array-oriented programming library인 Numpy에 GPU를 통한 계산 가속을 더하였다.
- autograd(automatic differentiation engine)는 역전파와 모델 최적화를 간단화했다.
- deep learning library는 유연하고 효율적인 block 설계와 사전 훈련된 모델, 손실 함수, 옵티마이저 등을 제공한다.
Defining deep learning
- AI는 인간 지능을 필요로 하는 task를 할 수 있는 computer system이다.
- 머신러닝은 컴퓨터가 명시적인 프로그래밍 없이 예측과 의사결정을 하는 것을 데이터로부터 배우도록 하는 알고리즘과 관련된 것이다.
- 딥러닝은 Deep neural networks를 훈련시키고 적용하는데 집중하는 머신러닝의 하위 개념이다.
- 수많은 hidden layers는 데이터 내 비선형적 관계를 모델링한다.
Installing PyTorch
- GPU가 사용 가능한 버전과 only CPU인 버전이 있다.
- Torch는 Lua 언어로 만들어진 머신러닝 알고리즘을 광범위하게 지원하는 scientific computing framework에서 유래한다.
2. Understanding tensors
Tensor는 차원(rank, order)에 대한 특징을 갖는 수학적 객체이다.
- Tensor는 데이터 컨테이너 역할을 하여, array를 효율적으로 만들어 조작하고 계산한다.
- Numpy array에 자동 미분 엔진과 GPU 연산을 더한다.
- e.g. 스칼라는 0차원, 벡터는 1차원 행렬은 2차원 텐서이다.
- PyTorch는 64비트 integer 데이터 type, float로 32비트 precision을 기본값으로 가진다.
- GPU도 32비트 floating-point에 최적이다.
.to로 데이터 type을 바꿀 수 있다.
- GPU도 32비트 floating-point에 최적이다.
- Methods
.shape,.reshape,.view(원본 데이터가 연속적이면 reshape),.T,.matmul,@(.matmul과 동일)
3. Seeing models as computation graphs
- computational graph는 수학적 표현을 나타내는 걸 허용하는 방향성이 있는 그래프이다.
- 신경망의 출력을 계산하는 데 필요한 computation sequence를 나타낸다.
- PyTorch의 자동 미분 엔진(autograd)은 background에 computational graph를 만들어서, 우리는 모델 파라미터의 손실 함수에 대한 미분을 계산할 수 있다.
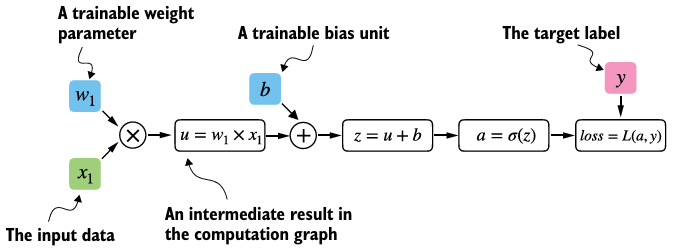
4. Automatic differentiation made easy
requires_grad가 True인 terminal node에 computational graph를 짓는다.- chain rule을 통해 역전파 알고리즘을 통한 미분이 계산된다.
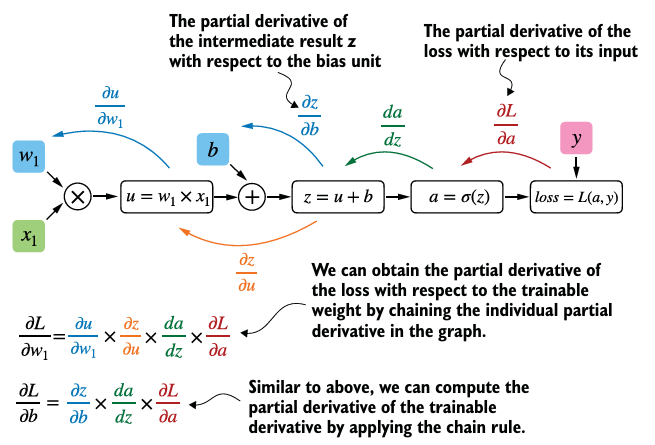
- 각 변수에 대한 변화율이 편미분이고, gradient은 다변수 함수의 편미분을 모두 포함하는 벡터이다.
- 이 값이 손실함수를 최소화하는 방향으로 각 파라미터를 업데이트할 때 필요한 정보를 제공한다.
grad함수를 호출하여 각 파라미터의 손실의 gradient를 계산할 수 있다.- 손실 함수에
.backward를 호출하여 모든 leaf node의 gradient를 계산할 수 있으며, 결과는 텐서의.grad에 저장된다.
5. Implementing multilayer neural networks
torch.nn.Modulebase class로 model을 build하고 train한다.__init__생성자에서forwardmethod와 layer가 어떻게 상호작용할지를 정의한다.- 우리가 구현하지 않는
backwardmethod는 손실함수의 gradient를 계산한다.
- 비선형 활성화 함수가 은닉층 사이에 놓인다. 마지막 layer의 output은 logits으로 불린다.
- 이를 출력하면, computational graph에서 마지막으로 사용된 함수를 나타내는
grad_fn을 알 수 있다.
- 이를 출력하면, computational graph에서 마지막으로 사용된 함수를 나타내는
Sequentialclass는 필수는 아니지만, 특정 순서에 실행시킬 때 유용하다.torch.no_grad()로 훈련 이후 예측 때 불필요한 학습을 막을 수 있다.- 마지막 layer의 output은 비선형 함수를 통과하지 않고 따로 softmax나 sigmoid 함수를 사용하여 class-membership 확률을 얻는다.
6. Setting up efficient data loaders
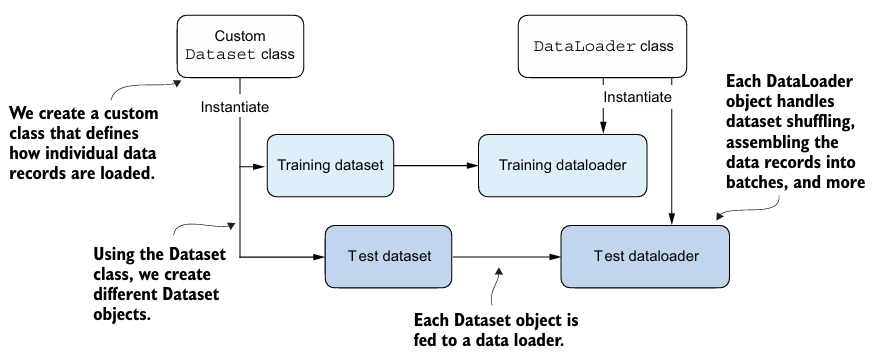
- Dataset
- torch.utils.data.Dataset에서
__init__,__getitem__,__len__가 필수이다. __getitem__에서는 인덱스를 통해 데이터셋에서 정확히 하나의 항목만 반환한다.__len__은 데이터셋의 길이를 반환한다.
- torch.utils.data.Dataset에서
- Dataloader가 훈련 동안 반복해서 돌아간다.
- dataset을 자동으로 shuffling해서 iterate한다.
drop_last = True를 통해 마지막 batch가 나누어 떨어지지 않으면 drop할 수 있다.num_workersCPU의 서브 프로세스 수를 지정하여 병렬적인 data 적재를 할 수 있다.- 프로세스를 생성하고 시작하는 데 드는 오버헤드를 발생시킬 수 있기 때문에, 적절한 수로 지정해야 한다.
7. A typical training loop
- Optimizer
.zero_grad()를 통해 의도하지 않은 gradient 축적을 막는다.- learning rate를 조정하여 loss가 적절히 수렴할 수 있도록 한다.
.step()을 통해 gradient를 사용하여 모델 파라미터를 업데이트한다.
.train()과.eval()로 훈련과 추론 모드를 설정한다. 이러한 구분은 dropout이나 batch normalization layers를 다르게 두기 위해서는 필수적이다.softmax대신torch.argmax로 예측한 결과값이 어떤 클래스에 속하는지 return 받을 수 있다. 이때dim=1이면 각 행에 대한 최대값이다.
- Tensor끼리
==와torch.sum통해 예측과 실제값이 같은지를 T/F로 확인하거나 count할 수 있다.
8. Saving and loading models
model.save()로 모델을 저장하고,model.load_state_dict(torch.load("model.pt"))로 모델을 파이썬 딕셔너리 형태로 load한다.- 저장된 매개변수를 적용하려면 메모리에 모델의 인스턴스가 필요하다.
9. Optimizing training performance with GPU
torch.cuda.is_available()로 GPU 사용을 확인하며,.to()로 GPUs 간 이동이 가능하다. 하지만, 같은 device에 존재해야만 한다.
# device를 정의하고 모델이나 메소드에 적용한다.
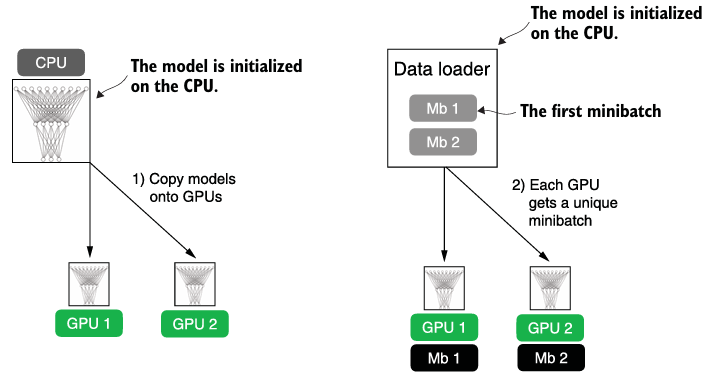
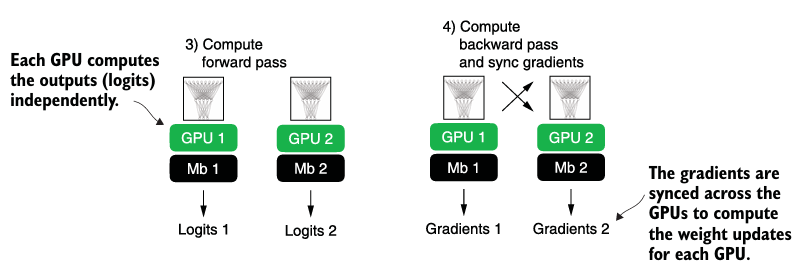
device = torch.device("cuda" if torch.cuda.is_available() else "cpu")- Distributed DataParallel (DDP)는 input data를 가용가능한 devices에 쪼개어 병렬 실행을 가능하게 한다.
- DDP는 멀티 프로세스를 필요로하며 각 프로세스는 각자의 파이썬 인터프리터 인스턴스를 가져야한다. 따라서, 모듈로 import하는 게 아니라 script 환경에서 실행되어야 한다.
Code (중요 부분만)
import torch
import torch.nn.functional as F
from torch.utils.data import Dataset, DataLoader
# NEW imports:
import os
import platform
import torch.multiprocessing as mp
from torch.utils.data.distributed import DistributedSampler
from torch.nn.parallel import DistributedDataParallel as DDP
from torch.distributed import init_process_group, destroy_process_group
def ddp_setup(rank, world_size):
"""
Arguments:
rank: a unique process ID
world_size: total number of processes in the group
"""
# rank of machine running rank:0 process
# here, we assume all GPUs are on the same machine
os.environ["MASTER_ADDR"] = "localhost"
# any free port on the machine
os.environ["MASTER_PORT"] = "12345"
if platform.system() == "Windows":
# Disable libuv because PyTorch for Windows isn't built with support
os.environ["USE_LIBUV"] = "0"
# initialize process group
if platform.system() == "Windows":
# Windows users may have to use "gloo" instead of "nccl" as backend
# gloo: Facebook Collective Communication Library
init_process_group(backend="gloo", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
else:
# nccl: NVIDIA Collective Communication Library
init_process_group(backend="nccl", rank=rank, world_size=world_size)
torch.cuda.set_device(rank)
def prepare_dataset():
train_ds = ToyDataset(X_train, y_train)
test_ds = ToyDataset(X_test, y_test)
train_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=train_ds,
batch_size=2,
shuffle=False, # NEW: False because of DistributedSampler below
pin_memory=True, # 훈련 동안 빠른 메모리 전송 허용
drop_last=True,
# NEW: chunk batches across GPUs without overlapping samples:
sampler=DistributedSampler(train_ds) # NEW
)
test_loader = DataLoader(
dataset=test_ds,
batch_size=2,
shuffle=False,
)
return train_loader, test_loader
# NEW: wrapper
def main(rank, world_size, num_epochs):
ddp_setup(rank, world_size) # NEW: initialize process groups
train_loader, test_loader = prepare_dataset()
model = NeuralNetwork(num_inputs=2, num_outputs=2)
model.to(rank)
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.5)
model = DDP(model, device_ids=[rank]) # NEW: wrap model with DDP
# the core model is now accessible as model.module
for epoch in range(num_epochs):
# NEW: Set sampler to ensure each epoch has a different shuffle order
train_loader.sampler.set_epoch(epoch)
model.train()
for features, labels in train_loader:
features, labels = features.to(rank), labels.to(rank) # New: use rank
logits = model(features)
loss = F.cross_entropy(logits, labels) # Loss function
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
print(f"[GPU{rank}] Epoch: {epoch+1:03d}/{num_epochs:03d}"
f" | Batchsize {labels.shape[0]:03d}"
f" | Train/Val Loss: {loss:.2f}")
model.eval()
train_acc = compute_accuracy(model, train_loader, device=rank)
print(f"[GPU{rank}] Training accuracy", train_acc)
test_acc = compute_accuracy(model, test_loader, device=rank)
print(f"[GPU{rank}] Test accuracy", test_acc)
destroy_process_group() # NEW: cleanly exit distributed mode
if __name__ == "__main__":
print("Number of GPUs available:", torch.cuda.device_count())
# NEW: spawn new processes
# note that spawn will automatically pass the rank
num_epochs = 3
world_size = torch.cuda.device_count()
mp.spawn(main, args=(world_size, num_epochs), nprocs=world_size)
# nprocs=world_size spawns one process per GPUmultiprocessesing.spawn으로 새로운 프로세스를 GPU 수만큼 생성한다. multiple input에 함수를 병렬적으로 적용한다.rank는 GPU ID로 사용하는 프로세스 ID를 의미하고 자동으로 pass한다.model은 DDP로 감싸서 훈련 동안 모든 process에서의 gradient를 동기화한다.ddp_setup에서 IP와 port를 정의 후 GPU간 소통을 위해 만들어진 NCCL backend에서 프로세스 group을 초기화한다.CUDA_VISIBLE_DEVICES=0, 2를 통해 사용할 GPU를 지정할 수 있다.- test도 모든 GPU가 진행하기 때문에 한 번만 진행하기 위해서 rank로 test할 GPU를 지정한다.
