
map이 정도 되면, BFS로 푸는 것이 낫다.
DFS
- 깊이 우선 탐색
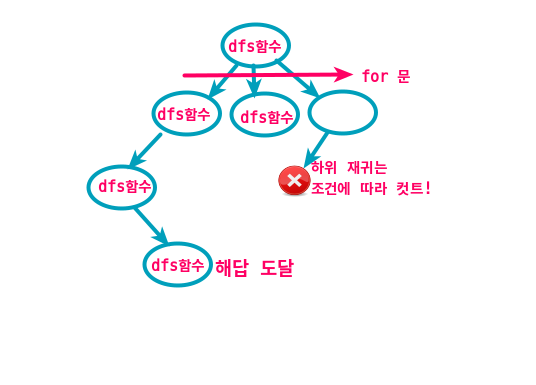
- 실행 그래프로 따지자면, 이런 느낌이다
- 일단 한 재귀를 끝까지가서 해답 도달하고 컷 시킬 조건은 알아서 해서 수행 시간을 줄인다.
- DFS도 BFS처럼 visited 배열을 두거나, 원본 배열을 훼손해도되는 경우는 그냥 원본 배열을 바꿔가며 탐색
- 일단 한 재귀를 끝까지가서 해답 도달하고 컷 시킬 조건은 알아서 해서 수행 시간을 줄인다.
- 실행 그래프로 따지자면, 이런 느낌이다
DFS Tip
- DFS의 핵심은 재귀이다!
Call-By-Value,Call-By-Reference의 특성을 잘 알자.- 무엇을 물려주고, 전역으로 둘지 잘 생각 해야한다.
- 각 노드의 공통 뷰 혹은 상관 없는 것: 전역 (어짜피 dfs는 한놈만 쭉 가니까 뭘 공유해도되는지 잘 생각)
- 물려 줄 정보: argument, return
- 선 visited
후 dfs
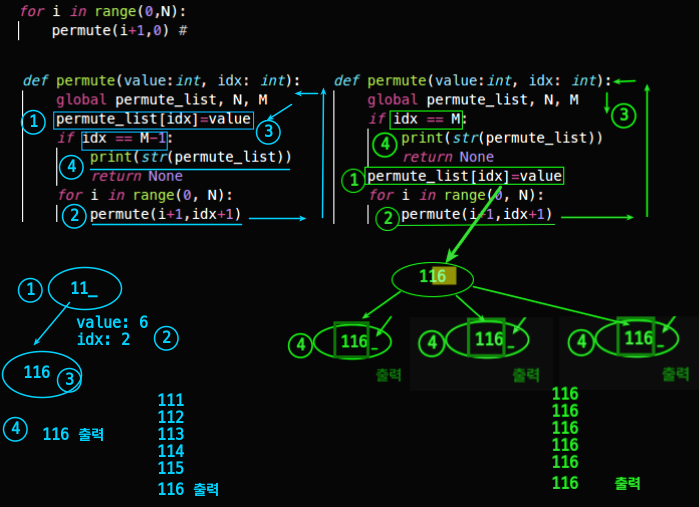
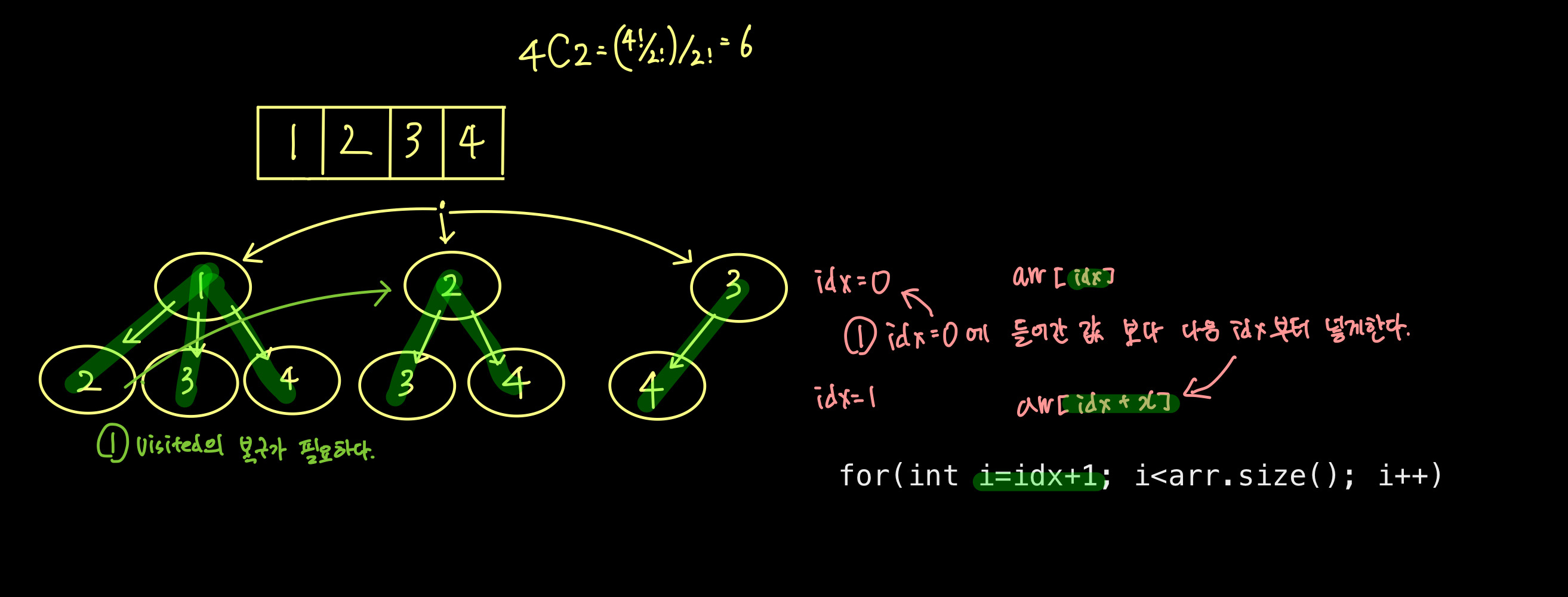
순열(Permutation)
- 순열(Permutation)
(1,2,3)과 (1,3,2)는 다름. 즉 element 값, 순서 다 중요
- =
- =
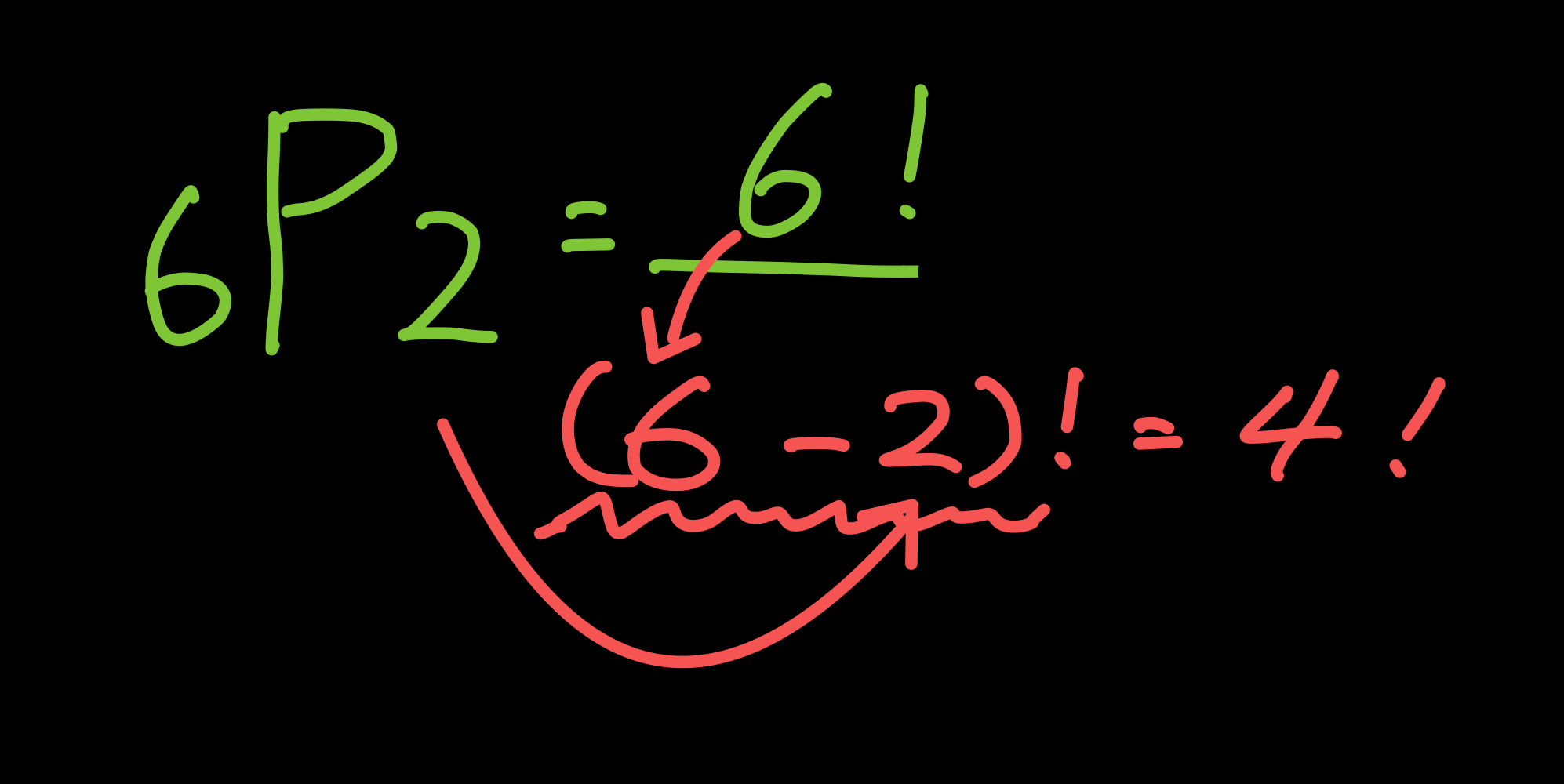
일반 순열
- element 값, 순서 다 중요,
값 중복 허용 (X) - 즉, 주사위(6가지 경우의 수)를 3번 던지는데, 각각 다른 value 가 나오는 경우
- 1,2,3 (O)
- 3,1,2 (O)
- 1,1,3 (X): 1의 중복
즉, =
- 주사위(6가지 경우의 수)를 6번 던지되, 각각 다른 value가 나오는 경우
- Time Complexity 를 참고하자 링크
- 일반 순열() 의 Time complexity에서 1s 시간 제한일 경우, 가능한 의 값은 10
python code
- code
d=[]
rec=[]
visited=[]
N=0
def dfs(idx, val):
global d, rec, visited, N
rec[idx]=val
if idx+1 == N:
print(*rec)
return
for i in range(0,len(d)):
if visited[d[i]]:
continue
visited[d[i]]=True
dfs(idx+1,d[i])
visited[d[i]]=False
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=3
d=[2,5,7]
rec=[0,0,0]
visited={2:False, 5:False, 7:False}
for i in range(0,len(d)):
visited[d[i]]=True
dfs(0,d[i])
visited[d[i]]=False
itertools.permutations() 사용
import itertools
d=[]
rec=[]
visited=[]
N=0
def gen(max_dep):
for i in (itertools.permutations(d,max_dep)):
yield i
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=4
d=[6,5,3,1]
max_depth=4
for i in gen(max_depth):
print(i)
# 혹은 하나 빼고 출력
get=gen(max_depth)
print(get) # <generator object gen at 0x1234578>
pring(next(get)) # (0,1)
# ===== 출력 ===== #
(6, 5, 3, 1)
(6, 5, 1, 3)
(6, 3, 5, 1)
(6, 3, 1, 5)
(6, 1, 5, 3)
(6, 1, 3, 5)
(5, 6, 3, 1)
(5, 6, 1, 3)
(5, 3, 6, 1)
(5, 3, 1, 6)
(5, 1, 6, 3)
(5, 1, 3, 6)
(3, 6, 5, 1)
(3, 6, 1, 5)
(3, 5, 6, 1)
(3, 5, 1, 6)
(3, 1, 6, 5)
(3, 1, 5, 6)
(1, 6, 5, 3)
(1, 6, 3, 5)
(1, 5, 6, 3)
(1, 5, 3, 6)
(1, 3, 6, 5)
(1, 3, 5, 6)중복 순열
- TimeComplexity:
- 주사위 1번 던질 때 경우의 수: : 6
- 시도 횟수 : 3
e.g., 4 -> 4 -> 4
bigO: =
- visited 가 필요가 없다.
python code
d=[]
rec=[]
N=0
def dfs(idx, val):
global d, rec, N
rec[idx]=val
if idx+1 == N:
print(*rec)
return
for i in range(0,len(d)):
dfs(idx+1,d[i])
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=3
d=[2,5,7]
rec=[0,0,0]
for i in range(0,len(d)):
dfs(0,d[i])itertools.product()
- 중복 순열은
itertools.permutations()itertools.products(d,repeat=' ')!!!
import itertools
d=[]
rec=[]
visited=[]
N=0
def gen():
for i in (itertools.product(d,repeat=4)):
yield i
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=4
d=[6,5,3,1]
for i in gen():
print(i)
# === 출력 === #
(6, 6, 6, 6)
(6, 6, 6, 5)
(6, 6, 6, 3)
(6, 6, 6, 1)
(6, 6, 5, 6)
(6, 6, 5, 5)
(6, 6, 5, 3)
(6, 6, 5, 1)
(6, 6, 3, 6)
(6, 6, 3, 5)
(6, 6, 3, 3)
(6, 6, 3, 1)
(6, 6, 1, 6)
(6, 6, 1, 5)
(6, 6, 1, 3)
(6, 6, 1, 1)
(6, 5, 6, 6)
(6, 5, 6, 5)
(6, 5, 6, 3)
(6, 5, 6, 1)
(6, 5, 5, 6)
(6, 5, 5, 5)
(6, 5, 5, 3)
(6, 5, 5, 1)
(6, 5, 3, 6)
(6, 5, 3, 5)
...중략...
(1, 1, 3, 5)
(1, 1, 3, 3)
(1, 1, 3, 1)
(1, 1, 1, 6)
(1, 1, 1, 5)
(1, 1, 1, 3)
(1, 1, 1, 1)
조합(Combination)
- 조합
(1,2,3)이나 (1,3,2)나 똑같음. 즉 element 값만 중요.순서(X)
- =
- = () = 20
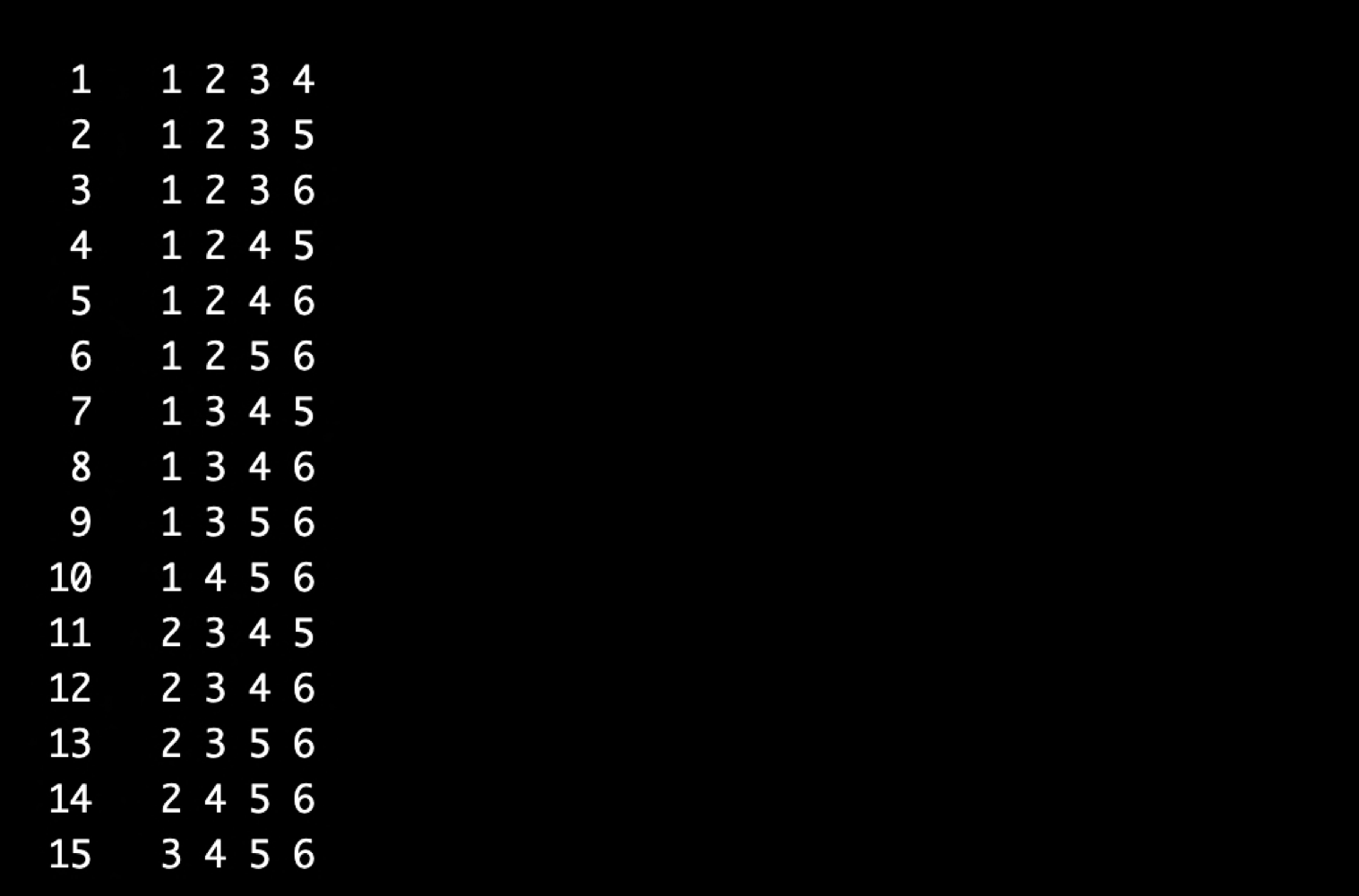
일반 조합
- (1,2,3)과 (1,3,2) (3,2,1) 등 똑같다. '값'만 중요
- 1,2,3만 만들어내면 된다.
- 이전 idx의 value 현재 idx의 value
- =
- = () = 20
- 1)배열을 오름차순 정렬 후, -> 2)이전 idx의 value < 현재 idx의 value 하면 됨
- 굳이 어렵게 하지말고.. 오름차순으로 정렬 한번 해서,
c++

python code

- max dep을 지정하는 일반 조합
- 그냥 depth 깊이를 정하여, 적절히 return 하자.
itertools.combinations() 사용
itertools를 import 할 수 있으면 제일 편하다.
import itertools
d=[]
rec=[]
visited=[]
N=0
def gen(max_dep):
for i in (itertools.combinations(d,max_dep)):
yield i
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=4
d=[6,5,3,1]
max_depth=2
for i in gen(max_depth):
print(i)
# ====== 출력 ====== #
(6, 5)
(6, 3)
(6, 1)
(5, 3)
(5, 1)
(3, 1)
itertools + generator 사용
- generator를 사용하는 이유는 꼭 (list) 결과를 다 받아 볼 필요는 없기 때문

중복 조합
- (2,1,1), (1,2,1) 같이 element 값 중복허용.
순서(X)- 그래서 (2,1,1), (1,2,1), (1,1,2) 다 같으니까 애초에
(2,1,1),(1,2,1)은 컷 컷 시키자.
(1,1,2)만 실행 하도록! - 이전 idx의 value <= 현재 idx의 value
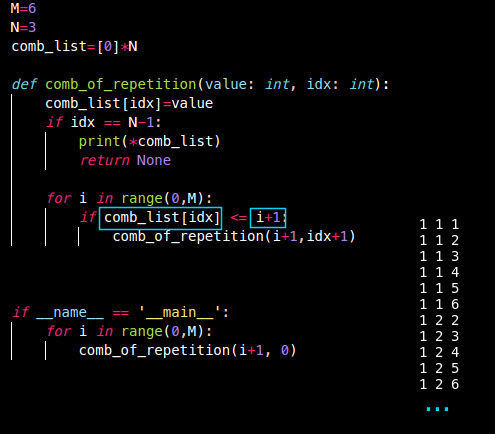
- 그래서 (2,1,1), (1,2,1), (1,1,2) 다 같으니까 애초에
itertools.combinations_with_replacement() 사용
import itertools
d=[]
rec=[]
visited=[]
N=0
def gen(max_dep):
for i in (itertools.combinations_with_replacement(d,max_dep)):
yield i
if __name__ == '__main__':
N=4
d=[6,5,3,1]
max_depth=2
for i in gen(max_depth):
print(i)
# ====== 출력 ====== #
(6, 6)
(6, 5)
(6, 3)
(6, 1)
(5, 5)
(5, 3)
(5, 1)
(3, 3)
(3, 1)
(1, 1)여객선
- http://jungol.co.kr/bbs/board.php?bo_table=pbank&wr_id=1983&sca=9040
- 첫 번째 줄에는 배의 수 B와 승객의 수 N이 주어진다. (1 ≤ B ≤ 16, 1 ≤ N ≤ 100,000) 두 번째 줄부터 B개의 줄에는 각 배의 최대수용무게가 주어진다. 최대수용무게는 100,000,000 이하의 자연수이다. 그 다음 줄부터 N개의 줄에는 각 승객의 몸무게가 줄 선 순서대로 주어진다. 몸무게는 10,000 이하의 자연수이다. 전체 데이터의 40%는 B ≤ 10 이고 N ≤ 5,000을 만족한다.
- 출항하지 않는 배들의 수용무게의 합의 최댓값을 출력한다. 만약 모든 배를 출항해도 승객들을 모두 태울 수 없다면 -1을 출력한다.
- 입력
3 6
12
15
10
6
3
3
2
3
7- 출력
12tips
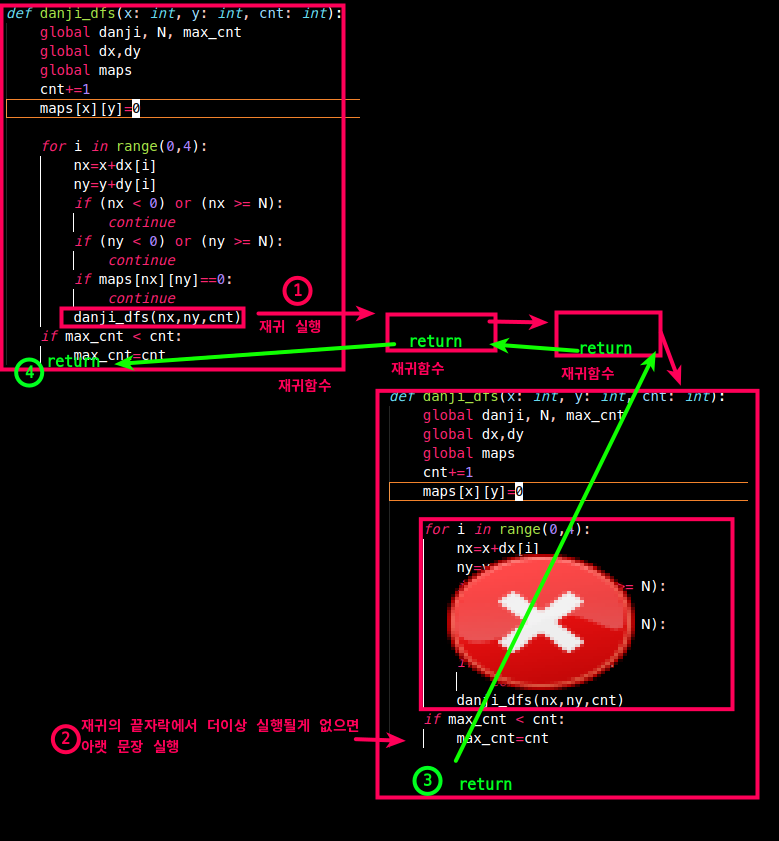
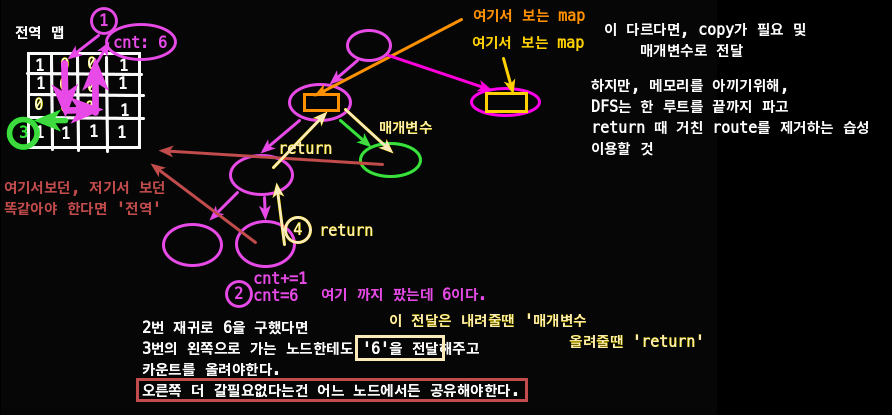
 어떤 것을 공유하고 물려줄 지 잘 생각해보자..
어떤 것을 공유하고 물려줄 지 잘 생각해보자..
- 전 노드가 공유해서 볼것 = 전역
- 전달 내려줄 때: 매개변수, 올려줄 때: return
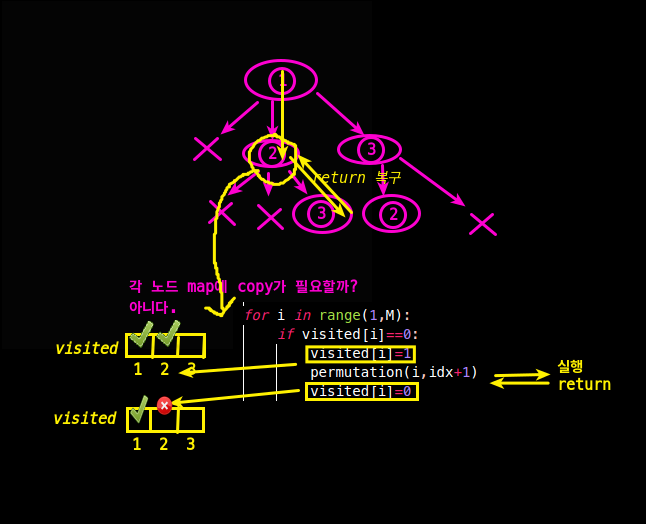
3. 뭘 표시하고, 복구 시킬지 생각하자.
- 아래 그림처럼 dfs전 할 행동과, 다음 노드를 위해 '복구'해야하는 것들을 생각
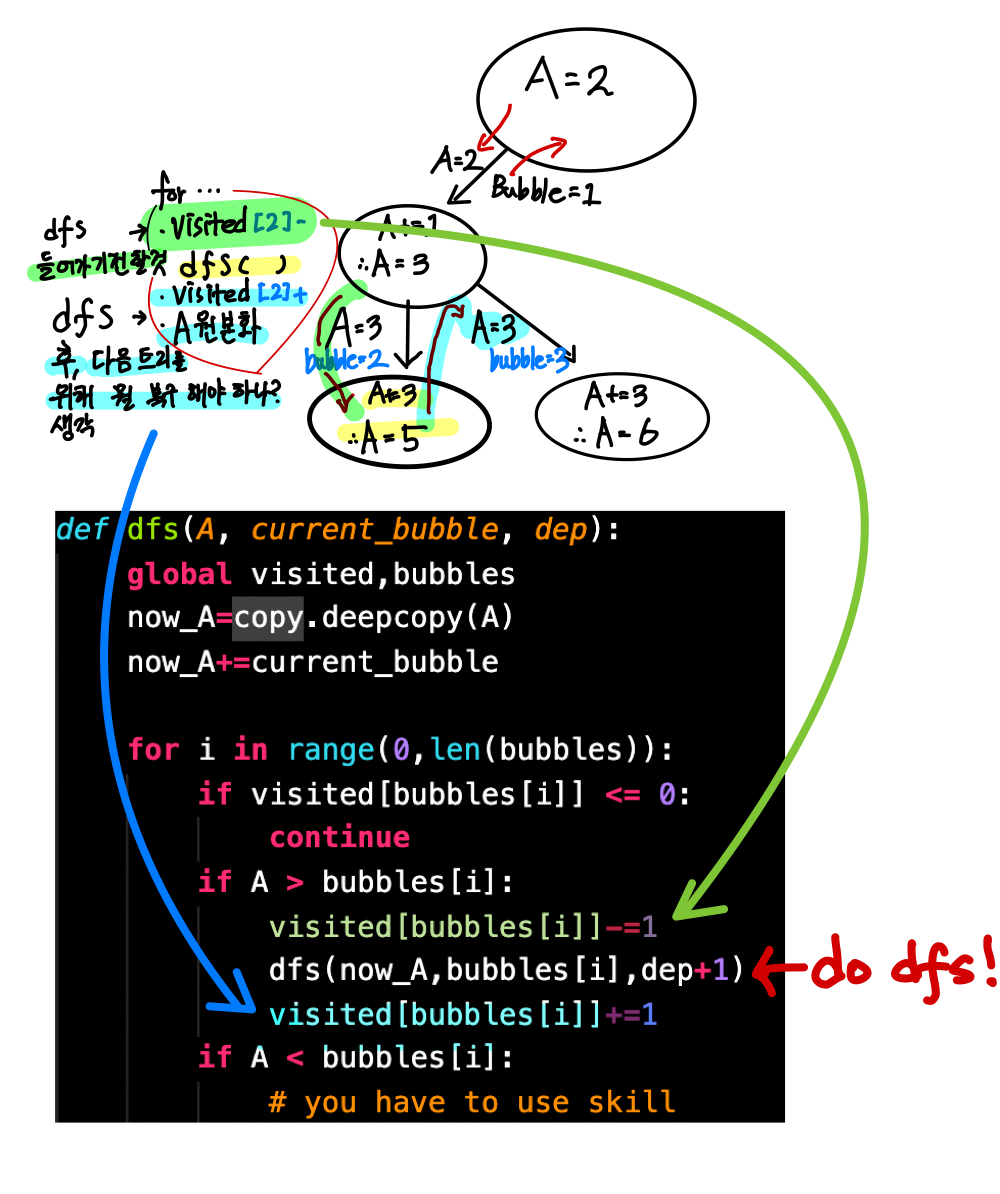
- 아래 모습이 더 이해하기는 편할 것 같다.
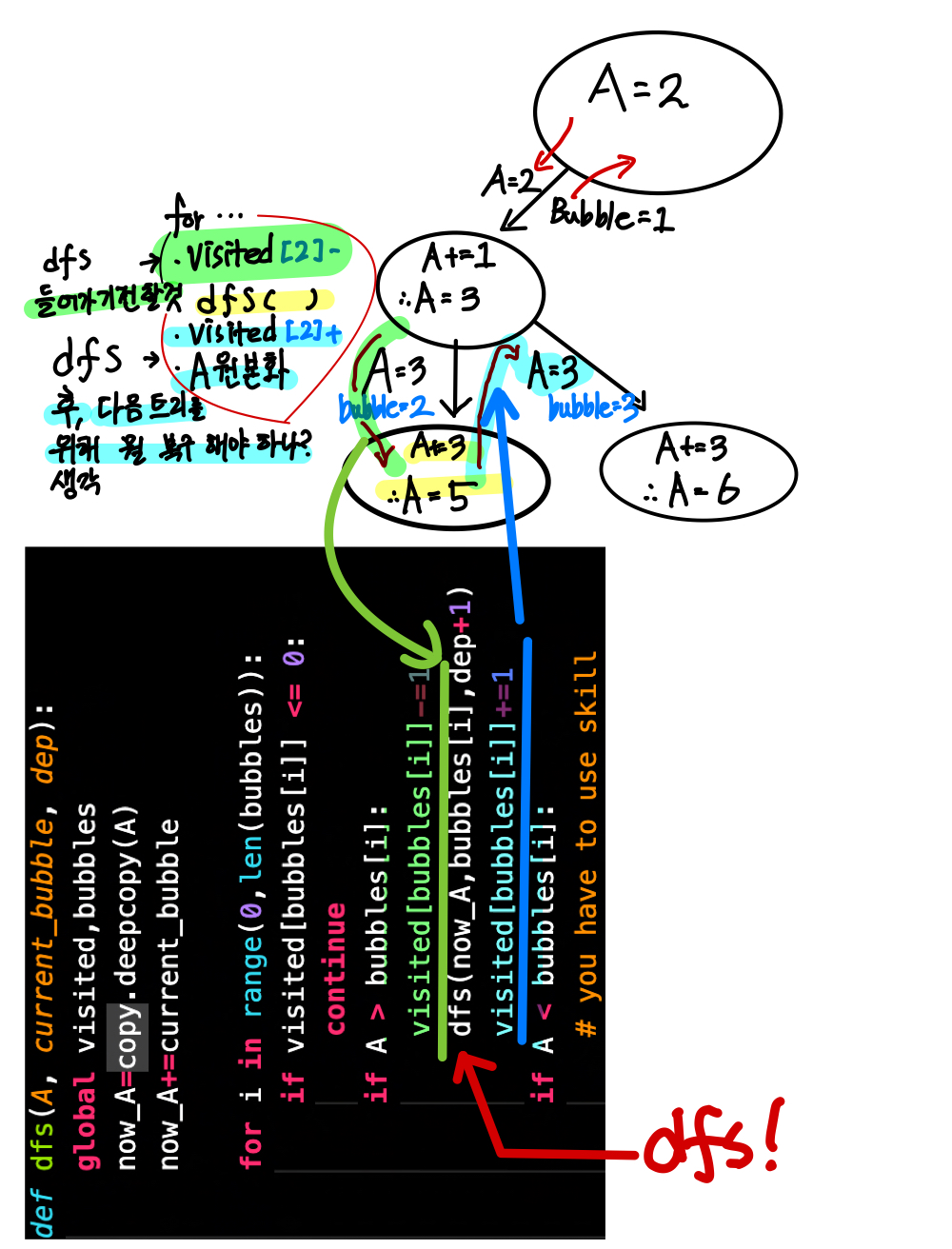
backtrack
페그 솔리테어
- ansPin
- ansMove

벽장문 이동
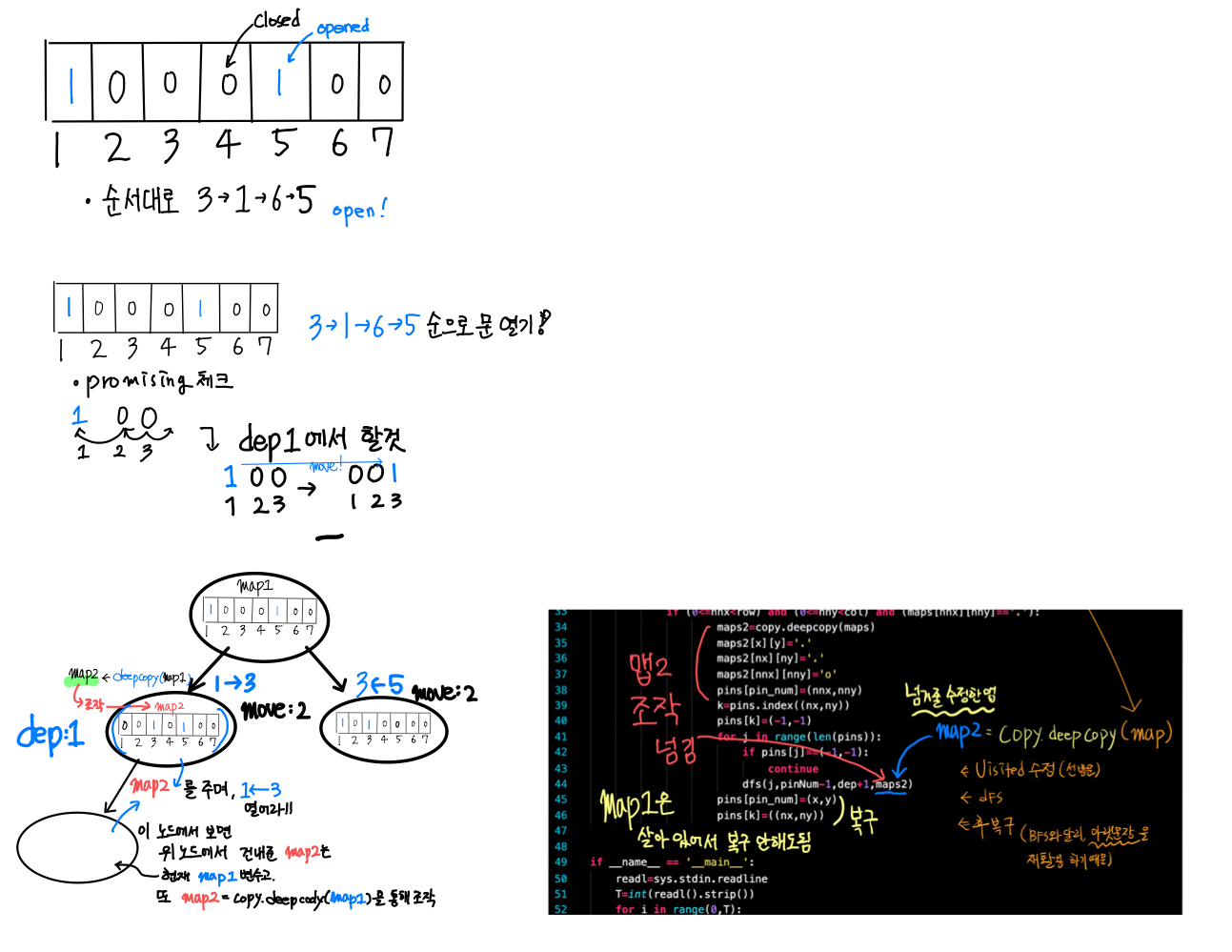
외판원순회2
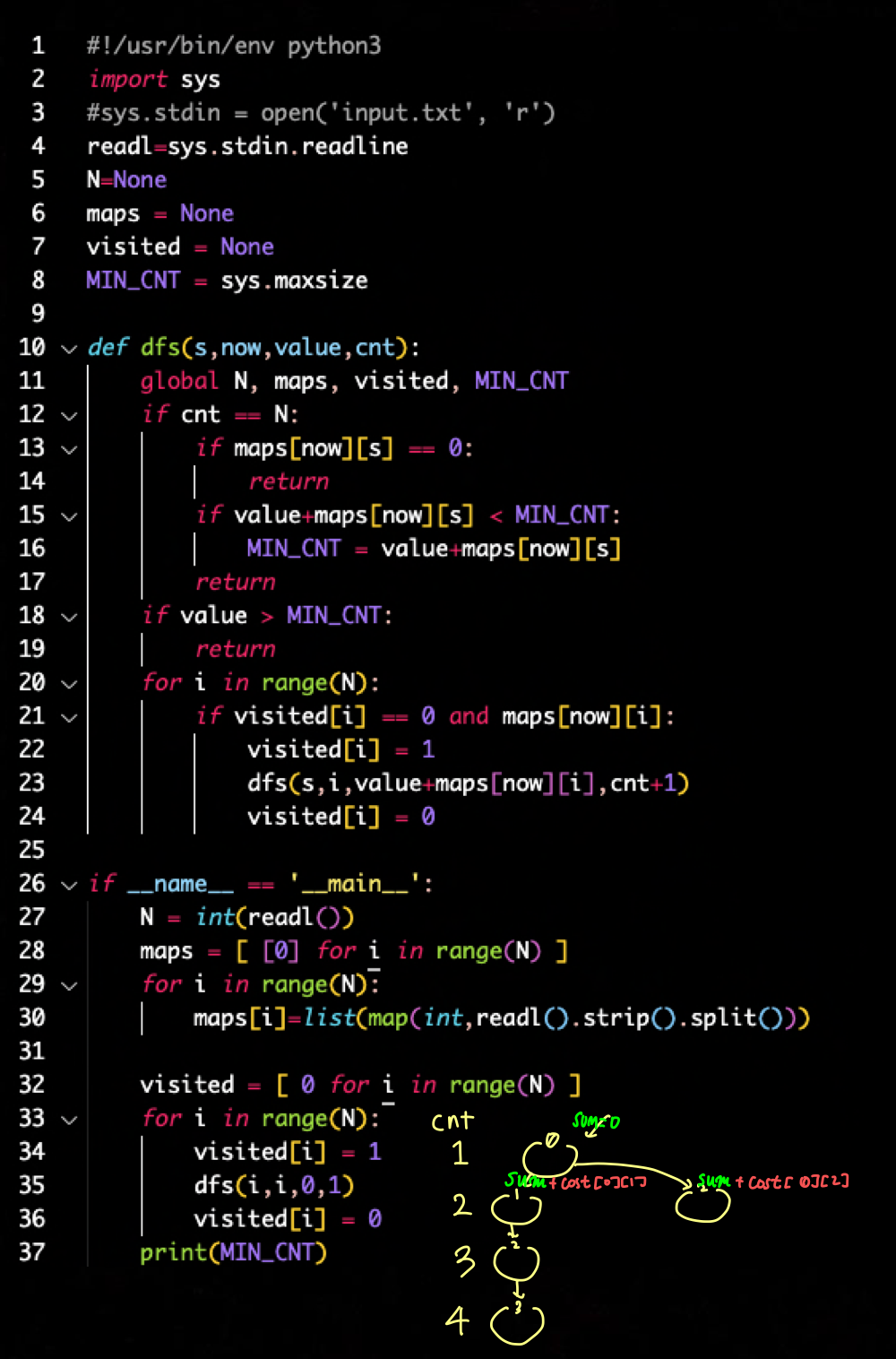
BFS
미로탐색
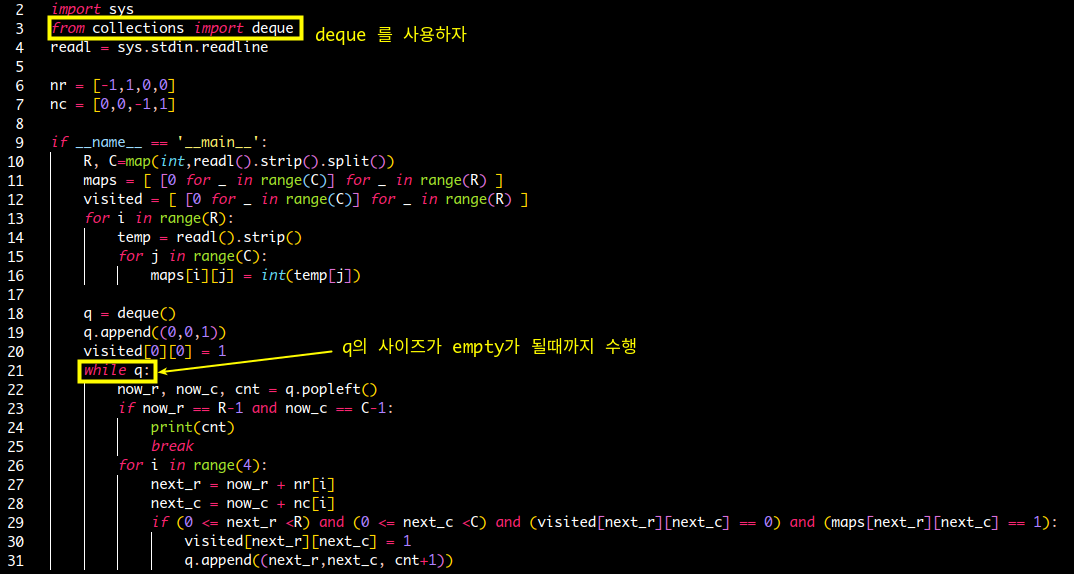
- BFS 특징
- visited를 기록하여, 큐에 넣을 때 보고 중복 방지: (Vertex1 -> Vertex2 등 모든 그래프의 가중치가 1인 경우)
- 중복방문이 오히려 더 효율적인 경우(Vertex1 -> Vertex2에 가중치가 있는 경우) 이를 고려해야한다.
- 이럴 땐 visited 에 단순히 방문 여부가 아닌!! 현재 까지 가중치를 넣어 pruning!
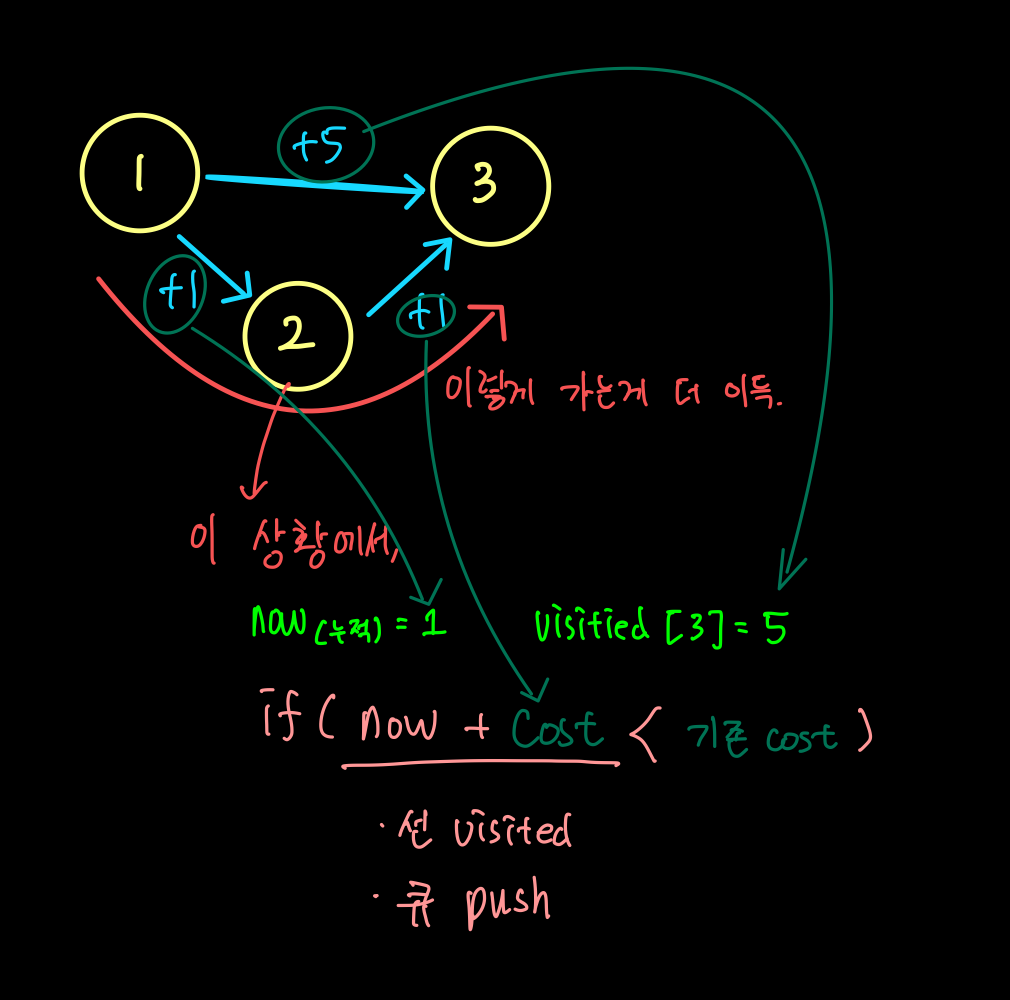
- 이럴 땐 visited 에 단순히 방문 여부가 아닌!! 현재 까지 가중치를 넣어 pruning!
- 중복방문이 오히려 더 효율적인 경우(Vertex1 -> Vertex2에 가중치가 있는 경우) 이를 고려해야한다.
- 미로에서 목표까지 최단거리의 거리 수 구하기 용이함(지나간 경로는 DFS)
- priority queue를 사용하여 시간 단축 가능
- 큐에 넣는 순서가 실행 순서와 상관 있음
- visited를 기록하여, 큐에 넣을 때 보고 중복 방지: (Vertex1 -> Vertex2 등 모든 그래프의 가중치가 1인 경우)

 1. 선 방문
1. 선 방문
2. 후 큐 넣기
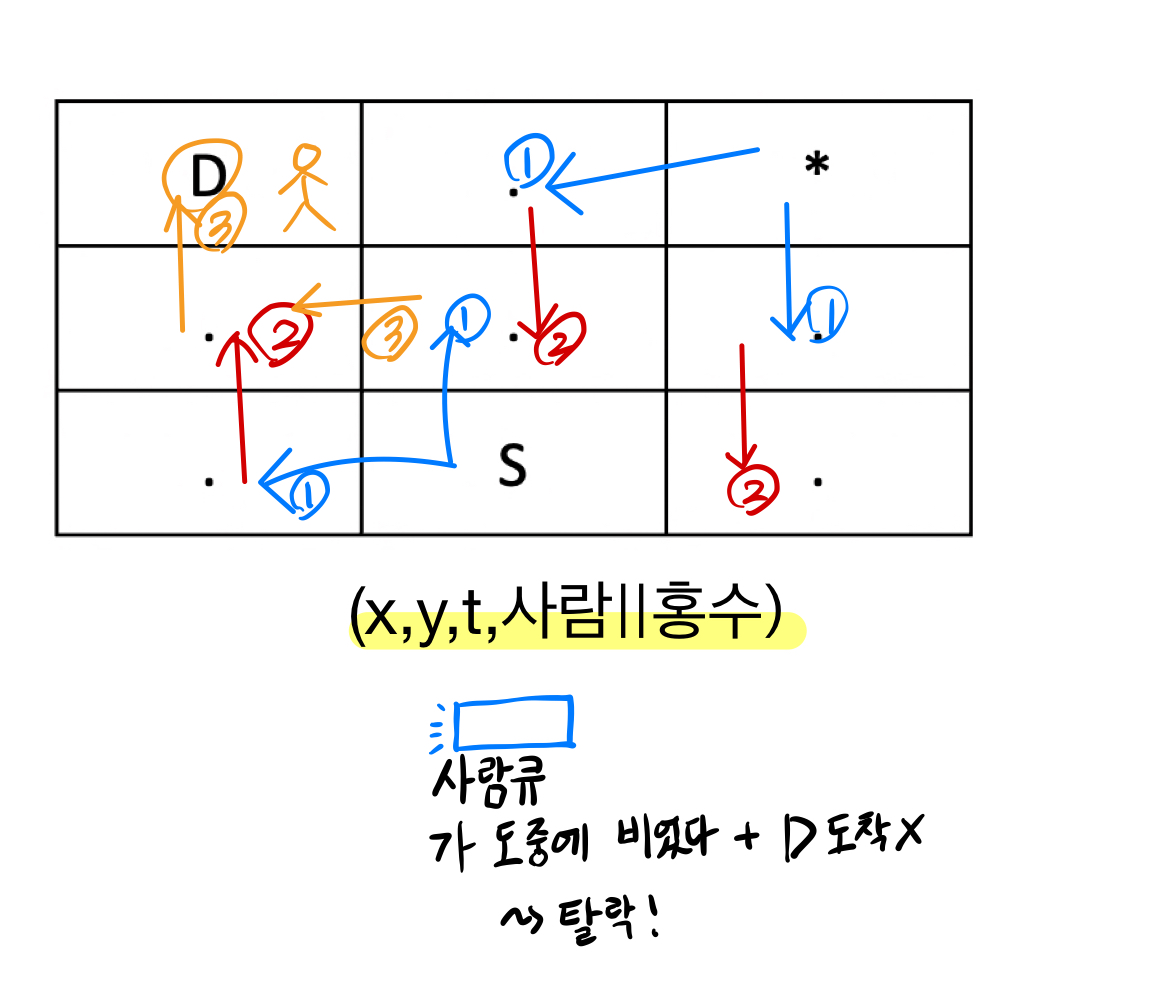
BFS 에서 경로가 필요한 경우
- BFS는 그때 그때 '최단 거리'길이는 잘 구하지만 경로까지 알기위해, 큐에 모든 경로를 다 넣긴 용량이 부족하다.
- path배열 혹은 스택을 추가한다!!
- 답을 찾아 역추적하는 것은 쉽다.

- path 의 idx는 vertex번호이고, path[4]=3 인데, 이는 '4' vertex 도착하기 전에 '3' vertex에서 왔다는 기록이다.
- 답을 찾아 역추적하는 것은 쉽다.
- 이 경우, 큐에 이전 방문 idx도 넣어야한다!
- path[idx] 에 update는 visited 가 갱신될 때!
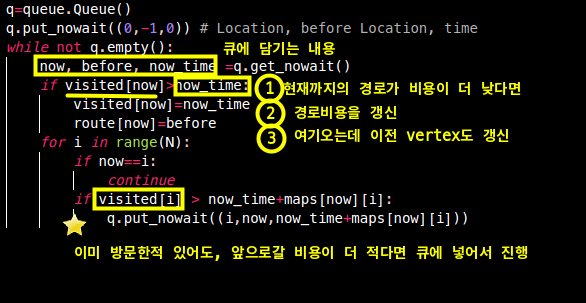
while not q.empty():
now, before, now_time=q.get_nowait()
if visited[now] > now_time: # 현재 경로에 도착하는데 더 낮은 가중치로 가능하는 '갱신' 프로시저
visited[now]=now_time # 현재 경로에 도착하는데 더 낮은 가중치 갱신
path[now]=before # path[현재 vertex]=이전vertex 담기
....가중치 + 경로
BFS의 경우 가지치기가 관건
최장이자 최단경로
- 최장 경로이자 최단 경로
최장 경로이자 최단 경로의 경우 '최장'의 조건 때문에 Edge to Edge이다.
그러니 BFS의 시작을 Edge에서 해야한다.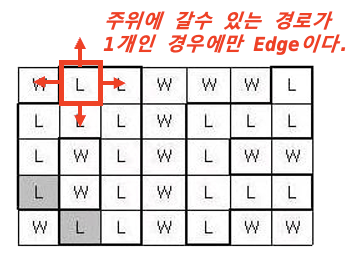
시작노드 여러개 -> 목표 한개
- 첫 시작에 3개의 노드면 관리하기 까다롭다.
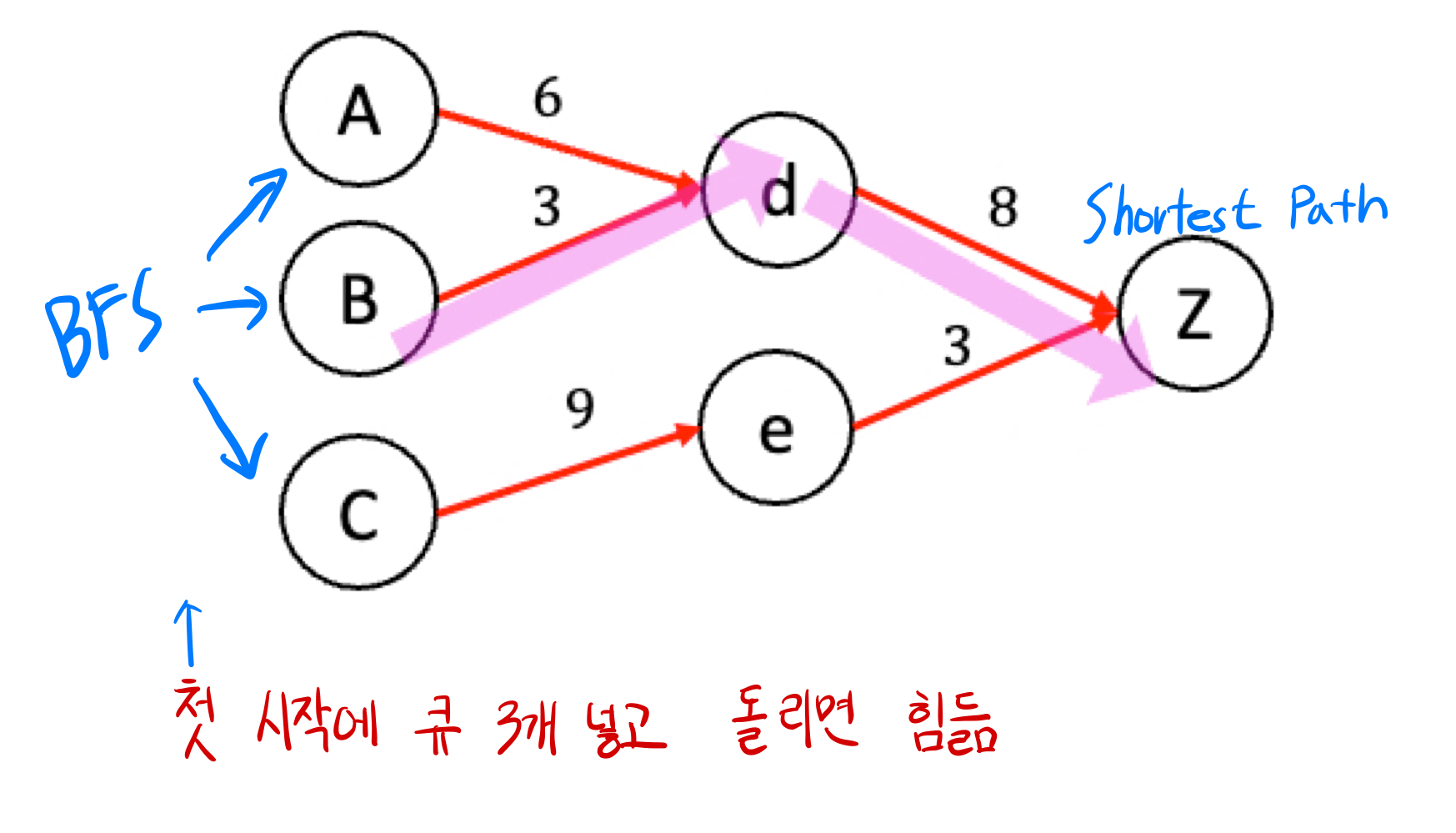
- 역으로 도착지점은 하나니까 역 그래프로 탐색한다.


- 역 그래프 그렸는데, 도착점이자 역 그래프의 시작점인 Z에서 출발하는게 없다면, 어쩔 수 없이
visited에서 하나 시작해야함.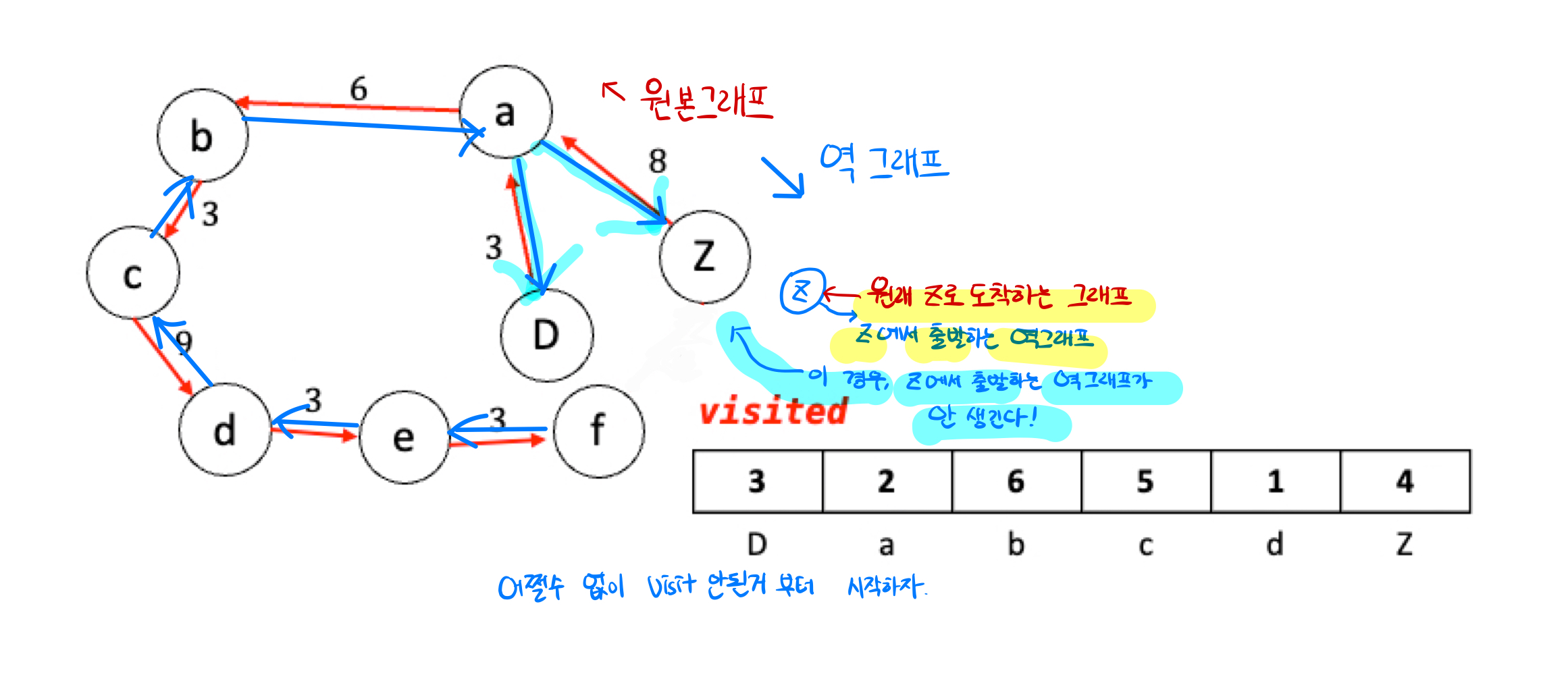
Flood Fill
- BFS특성을 잘 이해해야한다.

https://paris-in-the-rain.tistory.com/m/89?category=819756
https://hooongs.tistory.com/264
치즈
쌍 큐 (큐 두개)
파도 모래성
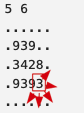 모래성 지도
모래성 지도- 숫자에 표시된
.만큼 버틸 수 있다. - 8방면을 봐야한다.
- 위의 3같은 경우는
.을 5개 만나므로 다음 파도가 치면 무너진다. map에서0(.)일 경우만 Q에 넣는다.
- 숫자에 표시된
8이하의 값을 가진 모래성을 관리하며,dfs로 풀면 될 줄 알았으나, map이 이므로 너무 많은 수가 요구된다.- BFS로 외벽햝기 방식으로 풀어야한다.
.일때는0으로 다시 삽입하자!
if maps[i][j] == '.':
maps[i][j]=0
Q.append((i,j)) <-- "0"일 경우만 Q에 넣는다.
else:
maps[i][j] = int(maps[i][j])
ans = 0
while Q:
x,y = Q.popleft()
if maps[nx][ny] != 0:
maps[nx][ny] -=1
if maps[nx][ny] == 0:
visited[nx][ny] = visited[x][y]+1
ans = max(ans, visited[nx][ny])
Q.append((nx,ny))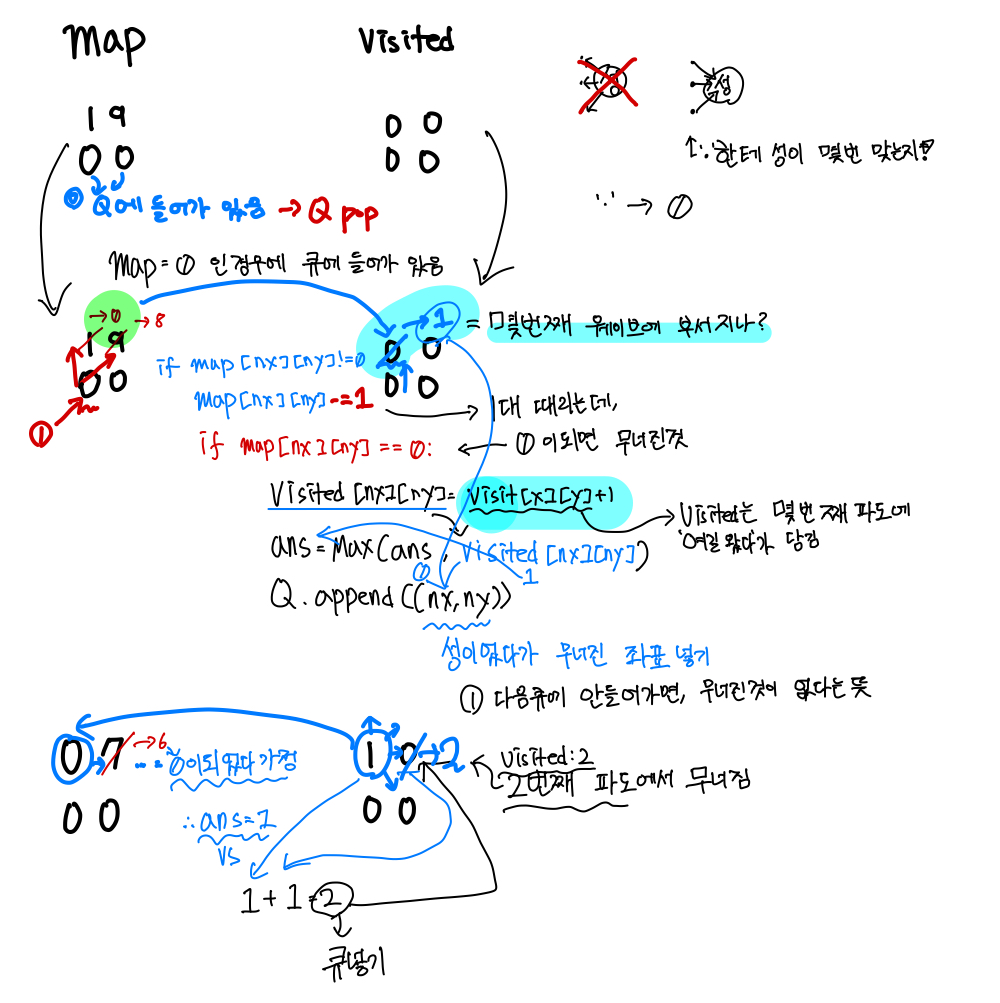


2022-08-31 출쳌 ..👼