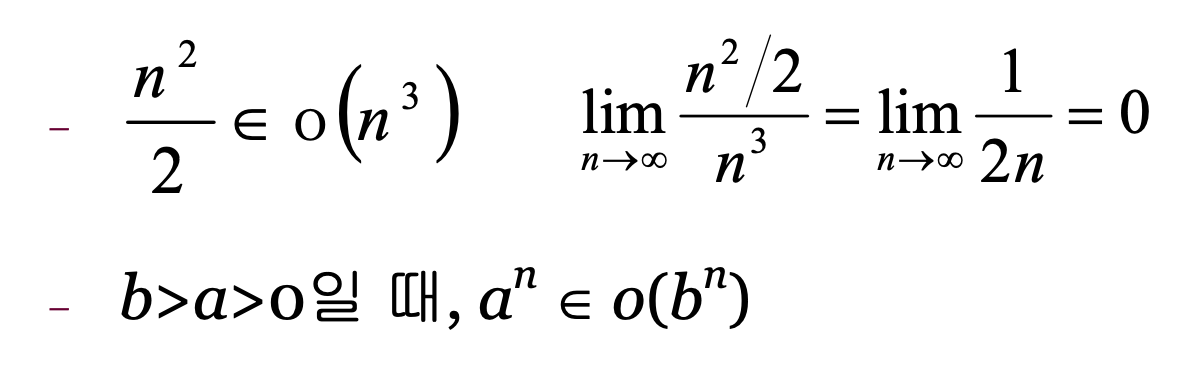⭐알고리즘(algorithm)이란?
알고리즘은 문제를 해결하기 위한 단계별 절차이다.
분석(analysis) -> (Computational(=계산))알고리즘의 복잡성 ->Order
- 문제를 얼마나 효율적으로 해결하는지 결정하는 측도
- Time - CPU cycles
- Space - memory
⭐알고리즘 분석 예시) - 피보나치 수 구하기 알고리즘
예시 1) 재귀 방식
int fib (int n) {
if (n <= 1)
return n;
else
return fib(n-1) + fib(n-2);
}Input size = n
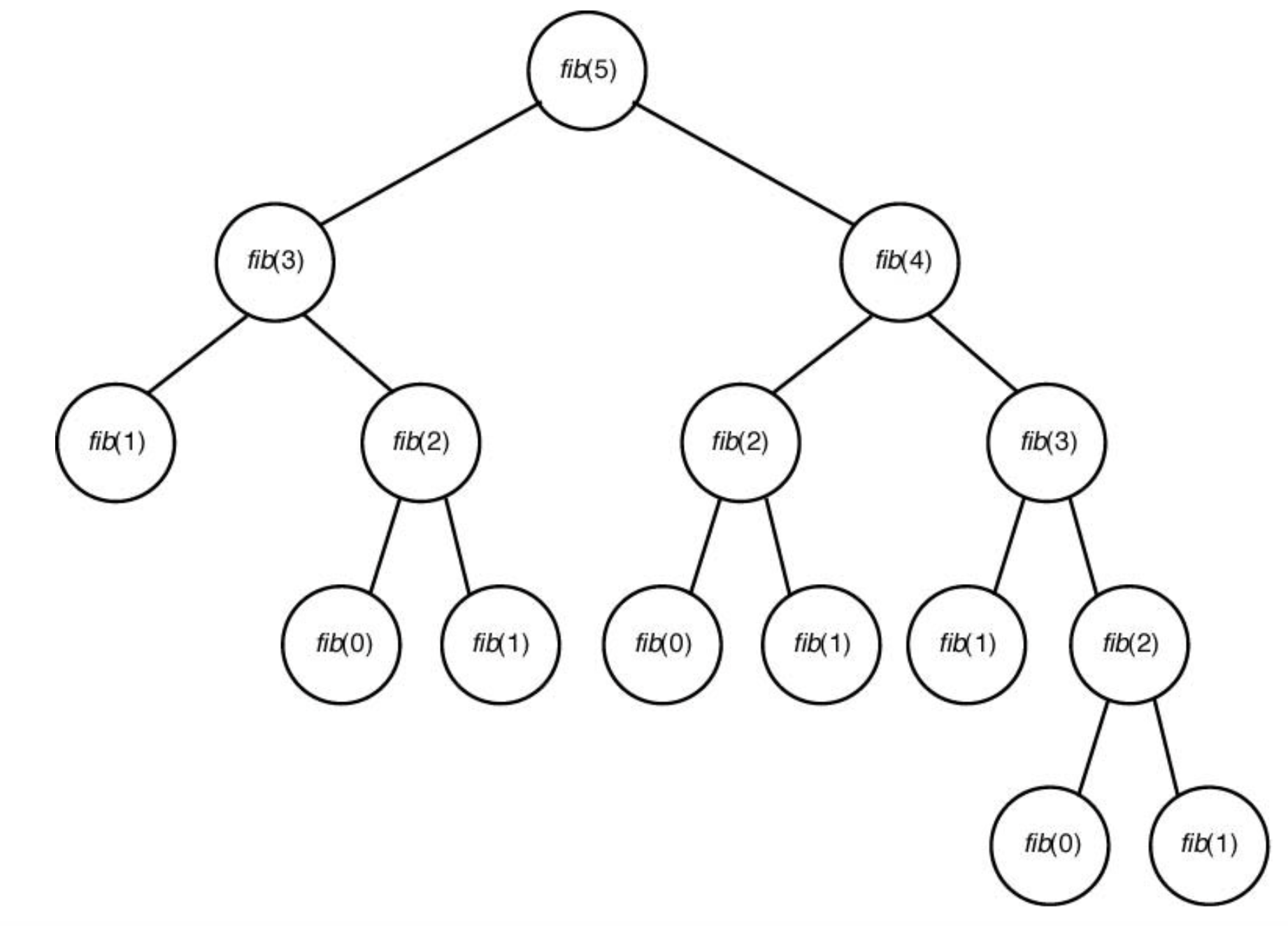
분석
T(n) = fib(n)을 계산하기 위하여 fib 함수를 호출하는 횟수
즉, 재귀 트리 상의 마디(node)의 개수가 기준이다.
T(0) = 1
T(1) = 1
- n이 2 이상일 경우T(n - 1) >= T(n - 2)이므로 둘 다 T(n-2)로 통일
증명 - 수학적 귀납법
예시 2) 반복문 방식
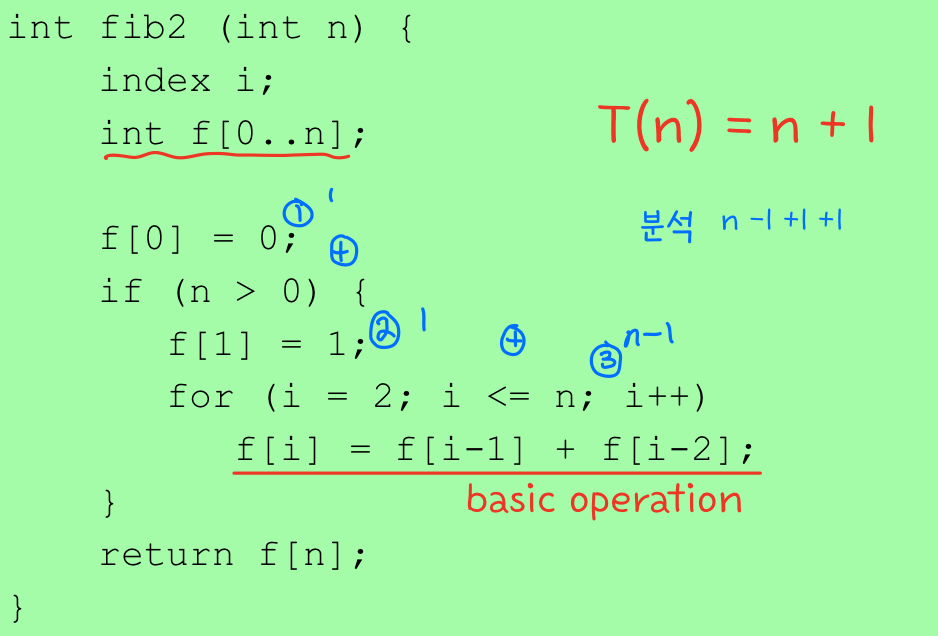
결국 반복문 방식의 알고리즘이 수행속도가 더 빠르다
이유: 중복 계산이 없이 배열에 저장하여 기억하기 때문에
⭐알고리즘을 분석 척도
- 시간 복잡도(Time Complexity) 분석
- 표현 척도
- Input size(입력 크기)
기준: 배열의 크기, 리스트의 길이, 행렬에서 행과 열의 크기, 트리에서 마디와 이음선의 수, 그래프에서는 정점과 간선의 수
- Basic operation (단위연산)
기준: 비교 (comparison), 지정 (assignment), 함수 호출 수(number of function calls)⭐알고리즘을 분석 방법의 종류
- Every-case time complexity analysis (모든 경우 분석)
- T(n) – the number of times the algorithm does the basic operation
for an instance of size n- Worst-case time complexity analysis (최악의 경우 분석)
- W(n) – the maximum number of times the algorithm will ever do
its basic operation for an input size of n- Average-case time complexity analysis (평균의 경우 분석)
- A(n) - the average number of times the algorithm does
the basic operation for an input size of n- Best-case time complexity analysis (최선의 경우 분석 )
- B(n) – the minimum number of times the algorithm will ever do
its basic operation for an input size of n
⭐ 차수(Order) - 자세한 식은 자료구조 개요
1.
- Big O, asymptotic upper bound (n이 무한으로 갈때 상한범위)
- Omega, asymptotic lower bound (n이 무한으로 갈때 하한범위)
- Theta, order, asymptotic tight bound (n이 무한으로 갈때 와 의 교집합)
- (lg n) < (n) < (n * lg n) < ()< () < () < () <
() < ()
- 여기서 k>j>2이고 b>a>1이다.
⭐ 극한(limit)를 이용하여 차수를 구하는 방법

Ex) 예시