0. 개념
Recursive Call : A Method call in which the method being called is the same as the one making the call (=자기 자신을 호출하는 메소드)
- Direct 는 f->f 형태, Indirect는 f->g->f 형태이다.
- 단점 : 무한 루프에 빠질 수 있다, iterative(반복문)보다 덜 효율적(실행속도, 메모리)일 수 있다.
- 장점 : simple & elegant. 간단하므로 프로그램 읽기가 쉽다(readability 향상). 따라서 소스 코드 관리 비용을 절감할 수 있다.
1. 원칙 : Divide and Conquer
recursive의 가장 큰 원칙은 문제를 쪼개서 풀고 확인하는 작업을 반복하는 것이다.
- Base case: recursive call을 언제 끝낼지에 대한 조건을 명시해준다. 반드시 존재해야 한다.
- General(recursive) case : 더 작게 쪼개지는. 재귀 호출 상황.
if (some condition for which answer is knonw) // base case
solution statement
else // general case
recursive function call2. Factorial Recursion Function : 팩토리얼 재귀 함수
n! = n * (n-1)! 이므로 재귀로 표현될 수 있다.
재귀를 반복하다가 1!=1 x 0!에 이르면 0!일 때가 base case로 재귀 호출을 종료하면 된다.
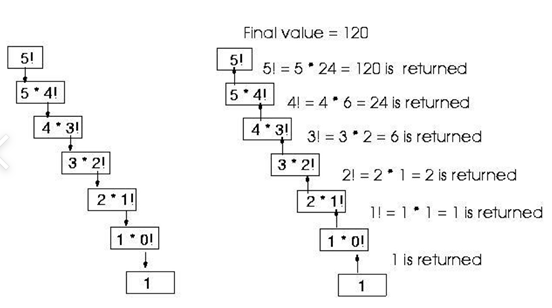
int Factorial(int number)
// Pre: number is assigned and number>=0.
{
if(number==0) // base case
return 1;
else // general case
return number*Factorial(number-1);
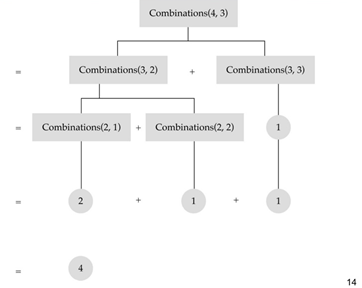
}3. Combination Recursion Function : 조합 재귀 함수
nCk = n-1Ck + n-1Ck-1 로 나타낼 수 있으므로 재귀로 표현될 수 있다.
- Base case 1 : nC1=n ( k==1 )
- Base case 2 : nCn=1 ( k==n )
int Combinations(int n, int k)
{
if(k==1) // base case 1
return n;
else if (n==k) // base case 2
return 1;
else
return (Combinations(n-1, k)+Combinations(n-1,k-1));
}
4. 재귀 함수 검증하는 3가지 방법

5. x의 n승을 재귀 함수로 표현하기
x^n = x * x^n-1이므로 n제곱승은 재귀 함수로 표현될 수 있다.
x^0=1일 때가 base case가 된다.
int Power(int x, int n)
// Pre : n>=0. x, n are not both zero.
// Post : Function value = x raised to the power n.
{
if(n==0) // base case
reutnr 1;
else // general case
return (x*Power(x,n-1));6. struct ListType ValueInList 함수
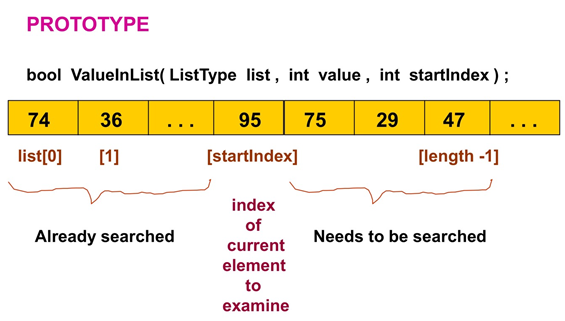
- struct type의 List에서 값을 찾는 함수를 재귀 함수로 구현한다.
- 기존에는 length-1 까지 iteration을 하는 형태로 구현했다.
- 이제 시작 인덱스를 Parameter로 받는다.
- 찾았을 때와 끝까지 갔을 때(마지막까지 확인했는데 없을 때)가 Base case가 된다.
만약 Base case에 해당하지 않으면 다음 칸(startIndex+1)부터 시작하는 재귀 함수를 호출하는 General case가 된다.
struct ListType
{
int length; // number of elements in the list.
int info[MAX_ITMES];
};
ListType list;
bool ValueInList(ListType list, int value, int startIndex)
{
if (list.info[startIndex] == value) // base case 1
return true;
else if (startIndex == list.length-1) // base case 2
return false;
else // general case
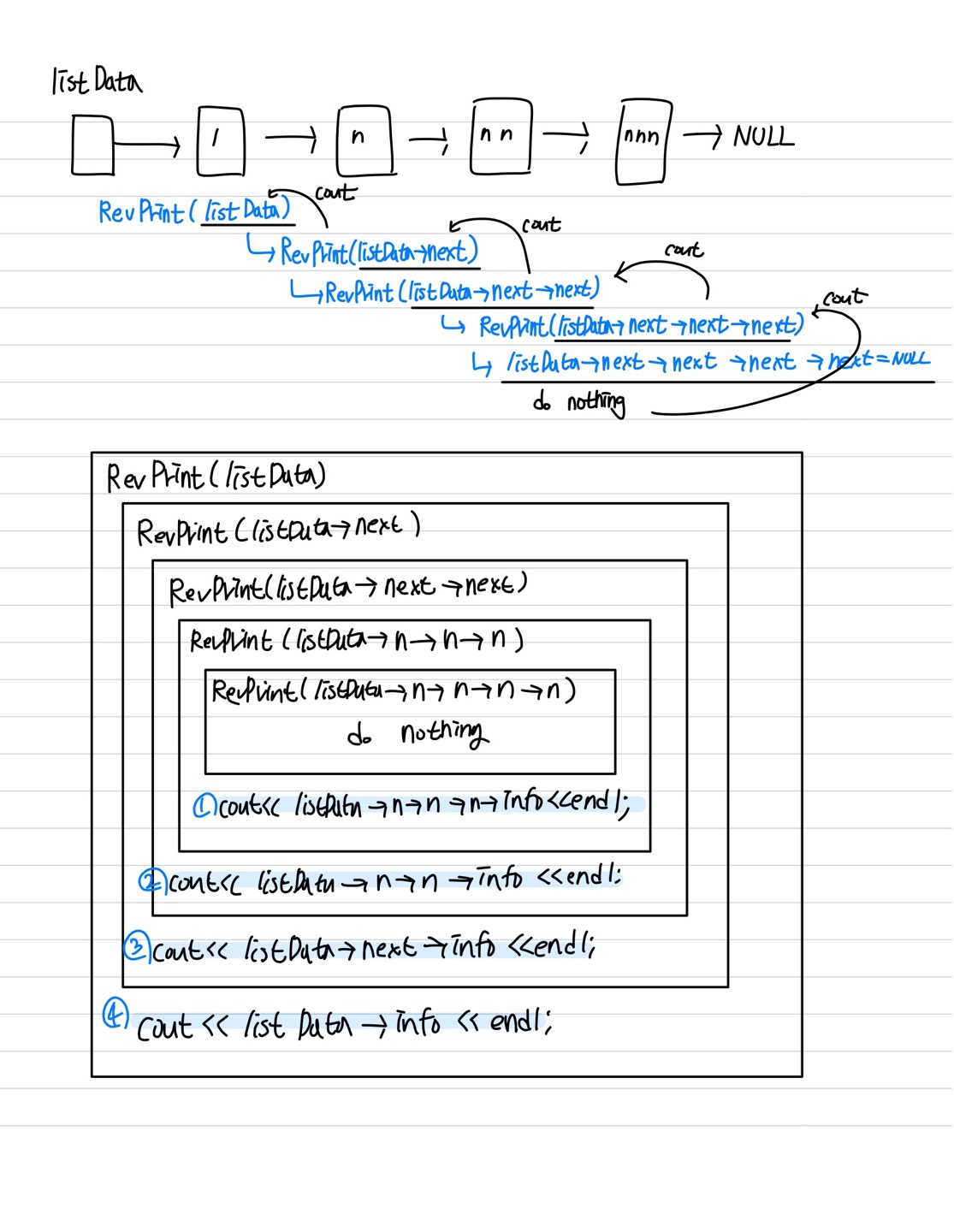
return ValueInList(list, value, startIndex+1);7. struct ListType RevPrint 함수
제일 뒤로 간 다음, 나오면서 Print를 하면 역순으로 출력이 된다. 일반적과 달리
재귀호출을 한 다음 Print를 하는 방식이다.
struct NodeType
{
int info;
NodeType* next;
}
class SortedType
{
public:
private:
NodeType* listData;
};
void RevPrint(NodeType* listPtr)
{
if(listPtr!=NULL) // general case
{
RevPrint(listPtr->next);
std::cout<<listPtr->info<<std::endl; //print this element
}
// base case : if the list is empty, do nothing
}
8. BinarySearch() Recursion Function
// Non Recursive Implementaion
template<class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::RetrieveItem(ItemType& item, bool& found)
{
int midPoint;
int first=0;
int last=length-1;
found false;
while( (first<=last) && !found )
{
midPoint = (first+last)/2;
if (item<info[midPoint])
last=midPoint-1;
else if (item>info[midPoint])
first=midPoint+1;
else
{
found=true;
item=info[midPoint]
}
}
}Recursive Binart Search
- size factor : the number of elements in ( info[first] ... info[last] )
- base case
(1) If first > last, return false
끝까지 갔는데 찾지 못했으면 false 반환하고 종료
(2) if item==info[midPoint], return true
아이템의 위치를 찾으면 true 반환하고 종료- general case
(1) If item < info[midPoint] , search the first half
찾으려고 하는 값이 중간값보다 작으면 앞을 살핀다.
(2) If item > info[midPoint] , search the second half
찾으려고 하는 값이 중간값보다 크면 뒤를 살핀다.
// Recursive Implementation
template<class ItemType>
bool BinarySearch(ItmeType info[], ItemType item, int fromLoc, int toLoc) // 양쪽 끝을 param으로 받음
{
int mid;
if ( fromLoc > toLoc ) // base case-끝까지 갔는데 없는 경우. false 반환 후 종료.
return false;
else
{
mid=(fromLoc+toLoc)/2;
if(info[mid]==item) // base case-찾은 경우. true 반환 후 종료.
return true;
else if (item<info[mid]) // 작은 경우 앞부분
return BinarySearch(info, item, fromLoc, mid-1);
else // 큰 경우 뒷부분
return BinarySearch(info, item, mid+1, toLoc);
}
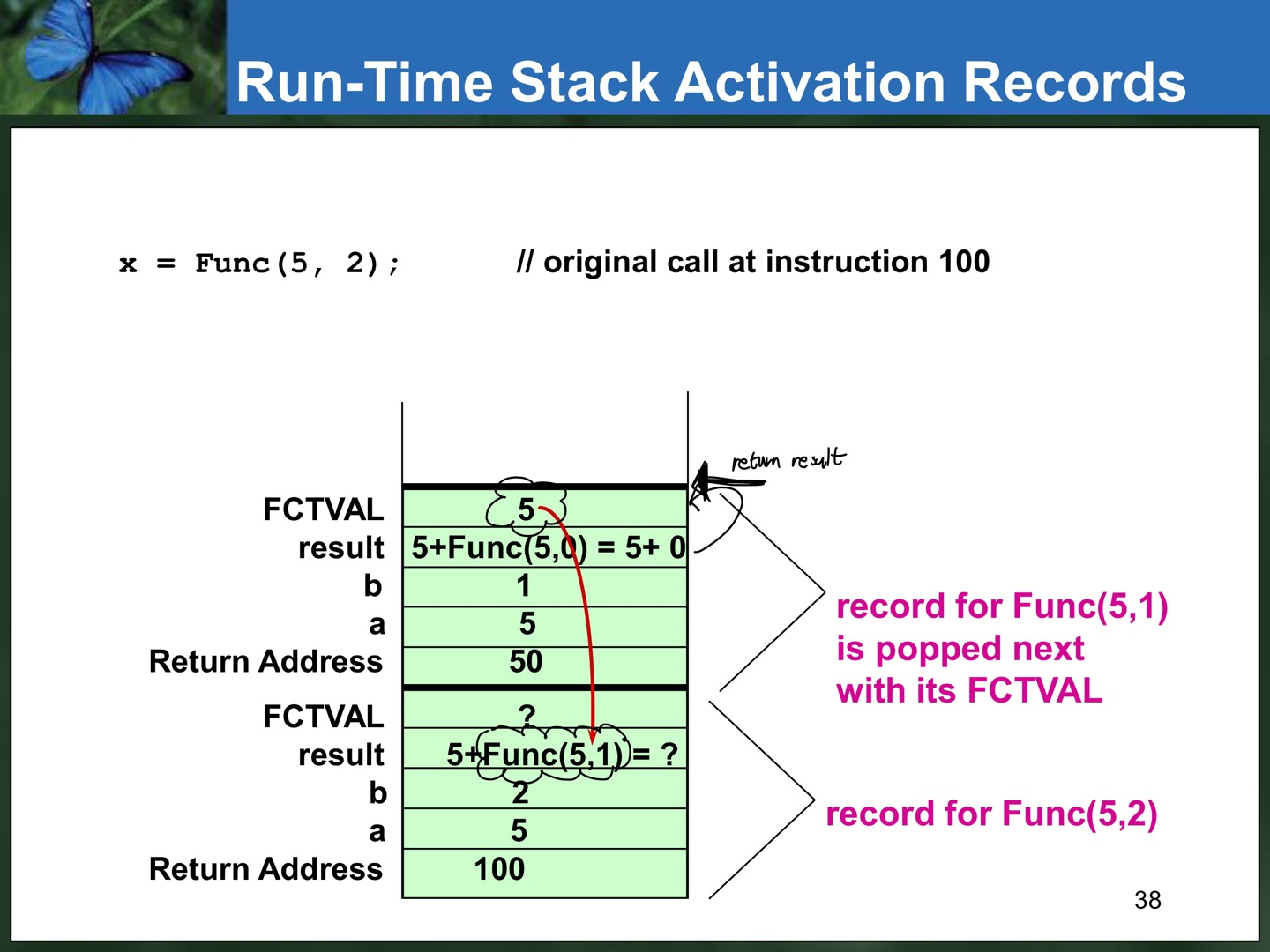
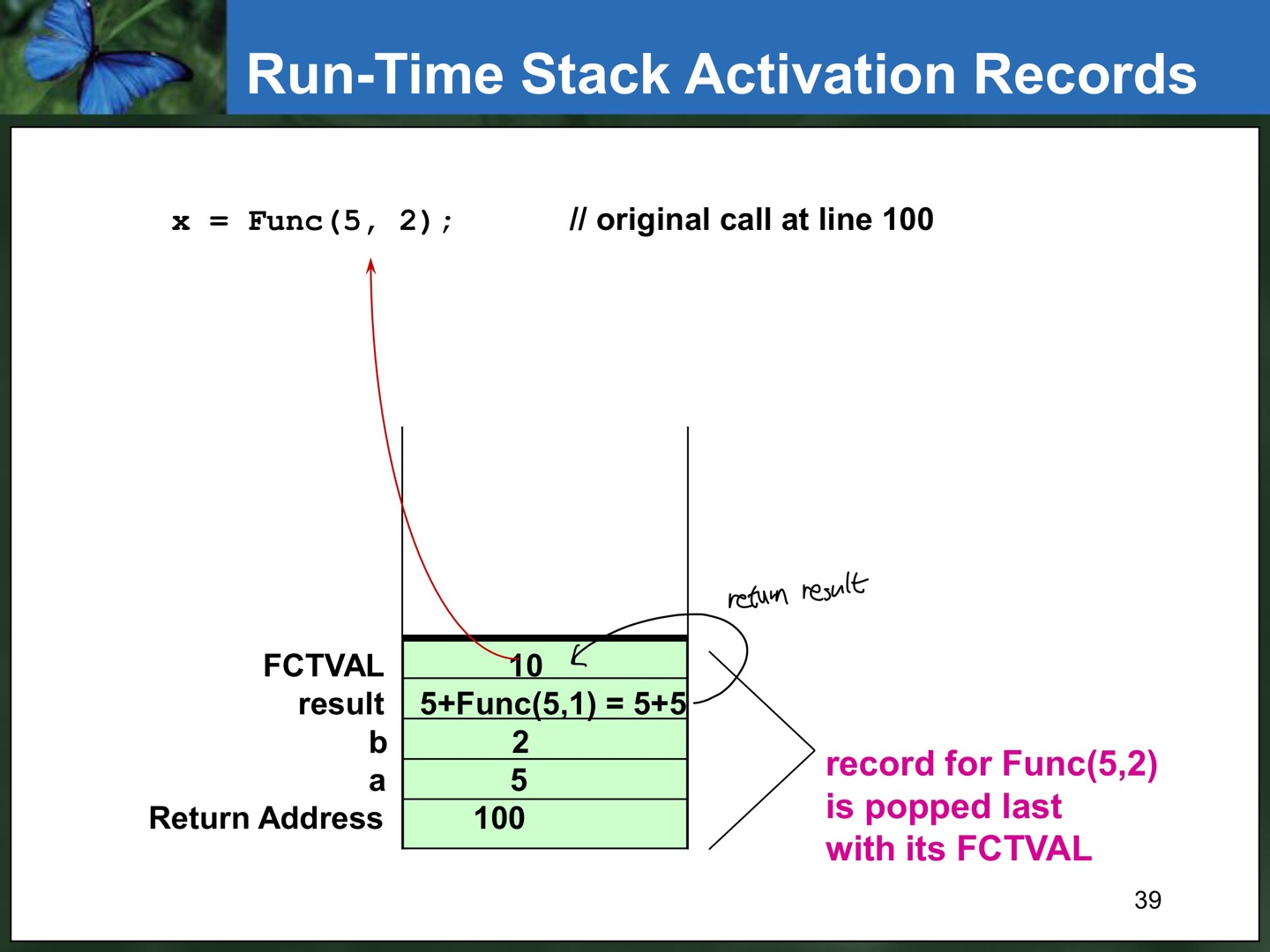
}9. 함수 호출될 떄 Runtime Stack
- 함수의 코드에서 블럭(block)을 호출하는 것으로부터 통제(control)의 전환(transfer)이 발생한다. 함수 코드가 실행된 이후에 호출하는 블럭에서 올바른 위치로 반환(return)하는 것이 필요하다. 이 올바른 위치를 반환 주소(return address)라 부른다
- 어떤 함수가 호출될 때 runtime stack이 사용된다. 함수 호출에서 activation record(stack frame)가 이 스택에 쌓인다.
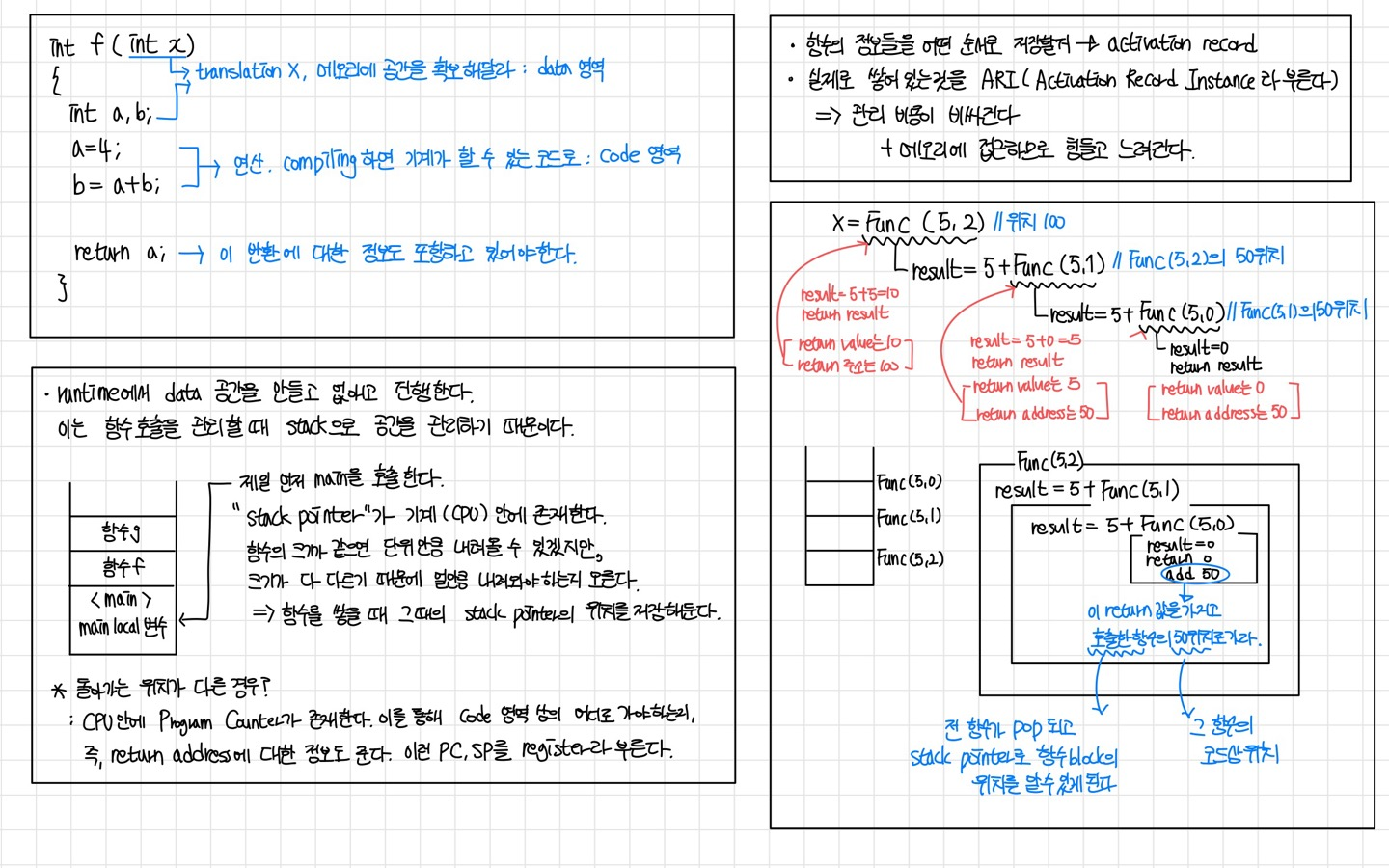
- activation record는 이 함수 호출에 대한 return address와 함께 입력 parameter, 지역 변수, (void 아닐 경우) 함수의 반환 값에 대해 저장한다.
- 함수 코드의 마지막 닫는 괄호에 도달하거나 함수 코드에서 return statement에 도달한 경우, 특정 함수 호출에 대한 activation record는 runtime stack에서 pop되어서 나간다.
- 이때 void가 아니라면 그 함수의 반환값은 거기에 쓰인 반환 주소 호출 블럭으로 가져와진다.
// Another recursive function
// instruction : 코드 상 위치를 명시
int Func(int a, int b) // instruction 100
{
int result;
if (b==0) // base case
result=0;
else if (b>0) // general case1
result=a+Func(a,b-1); // instruction 50
else //general case2
result=Func(-a,-b); // instruction 70
return result;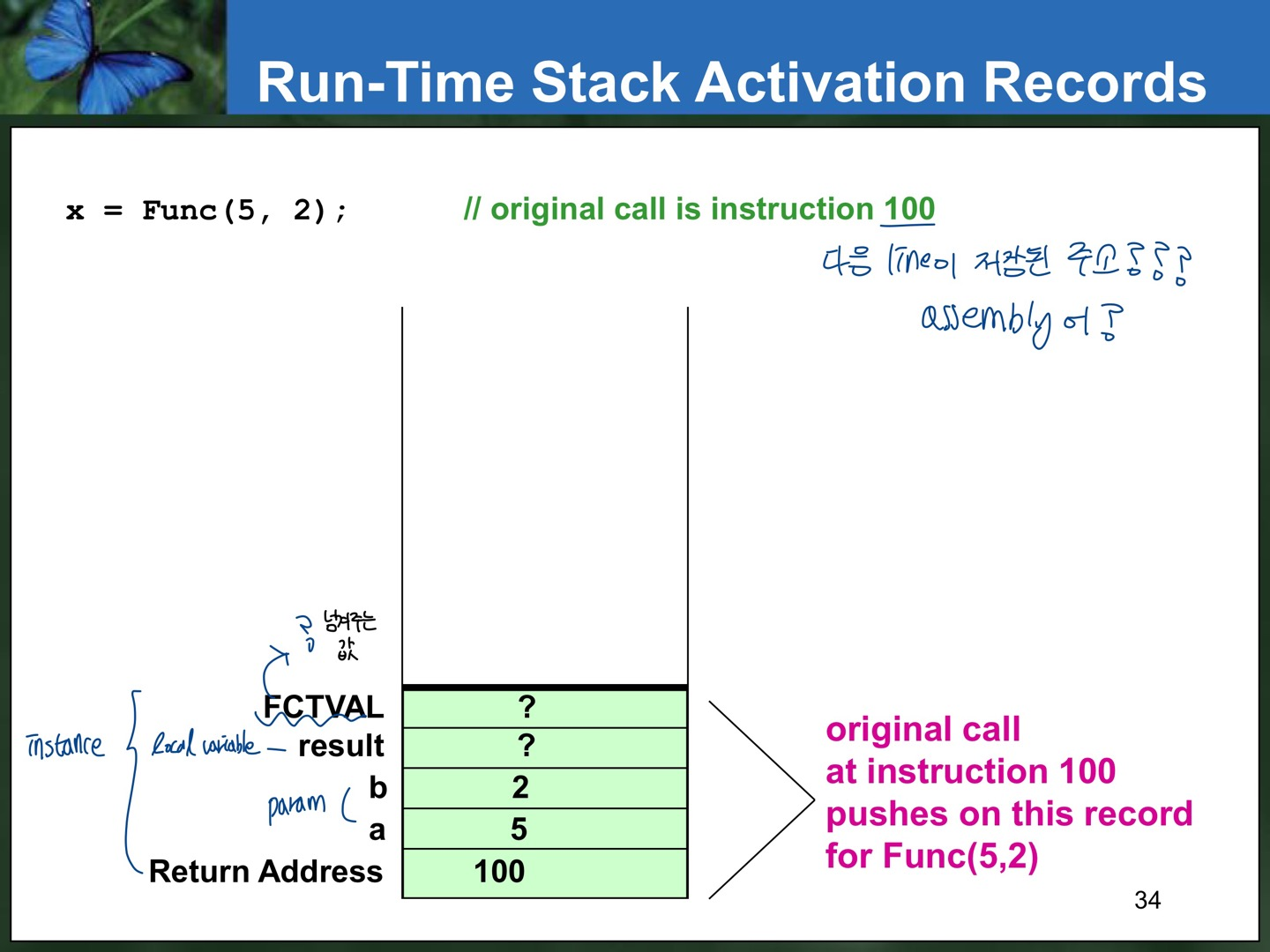
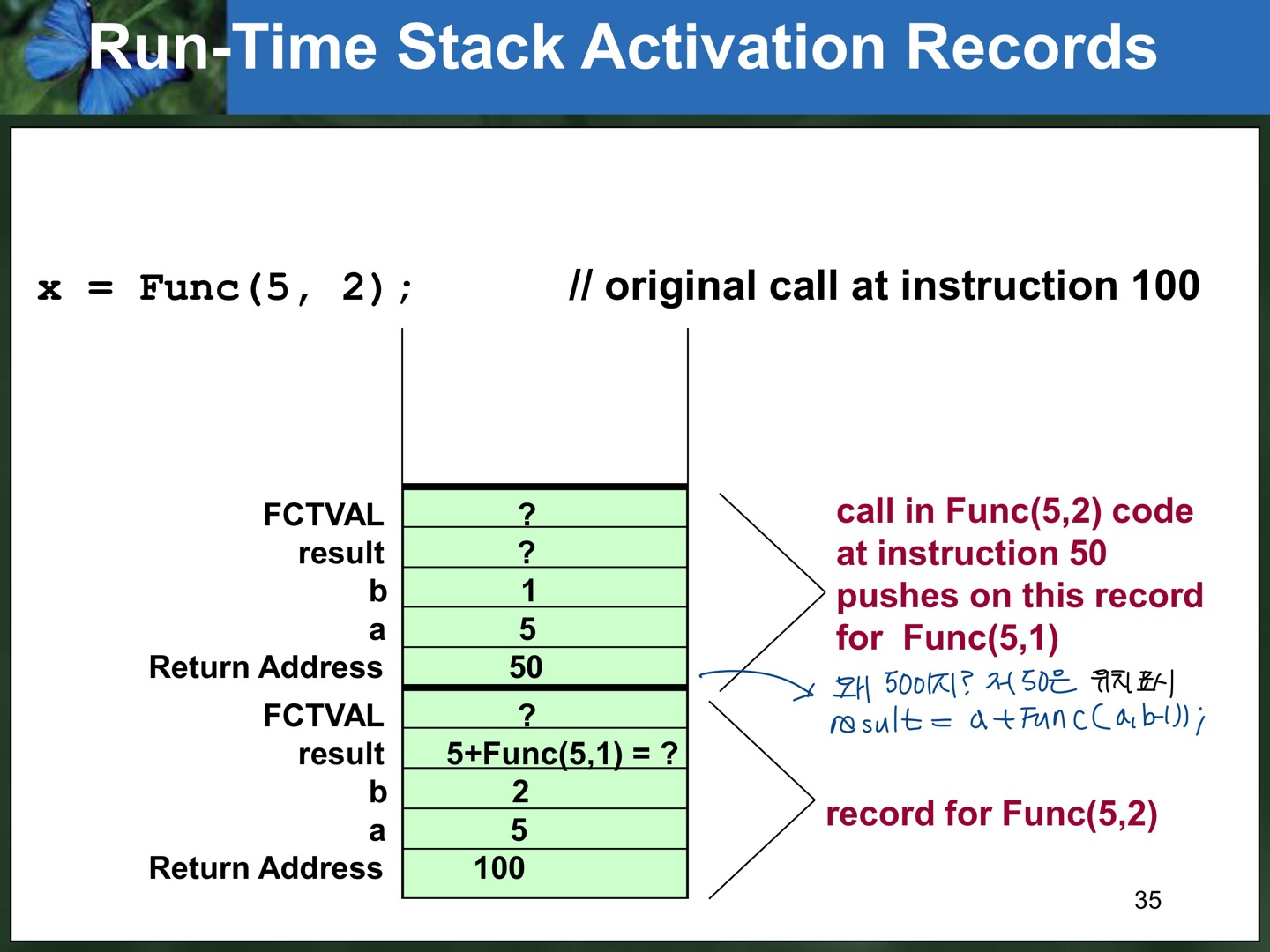
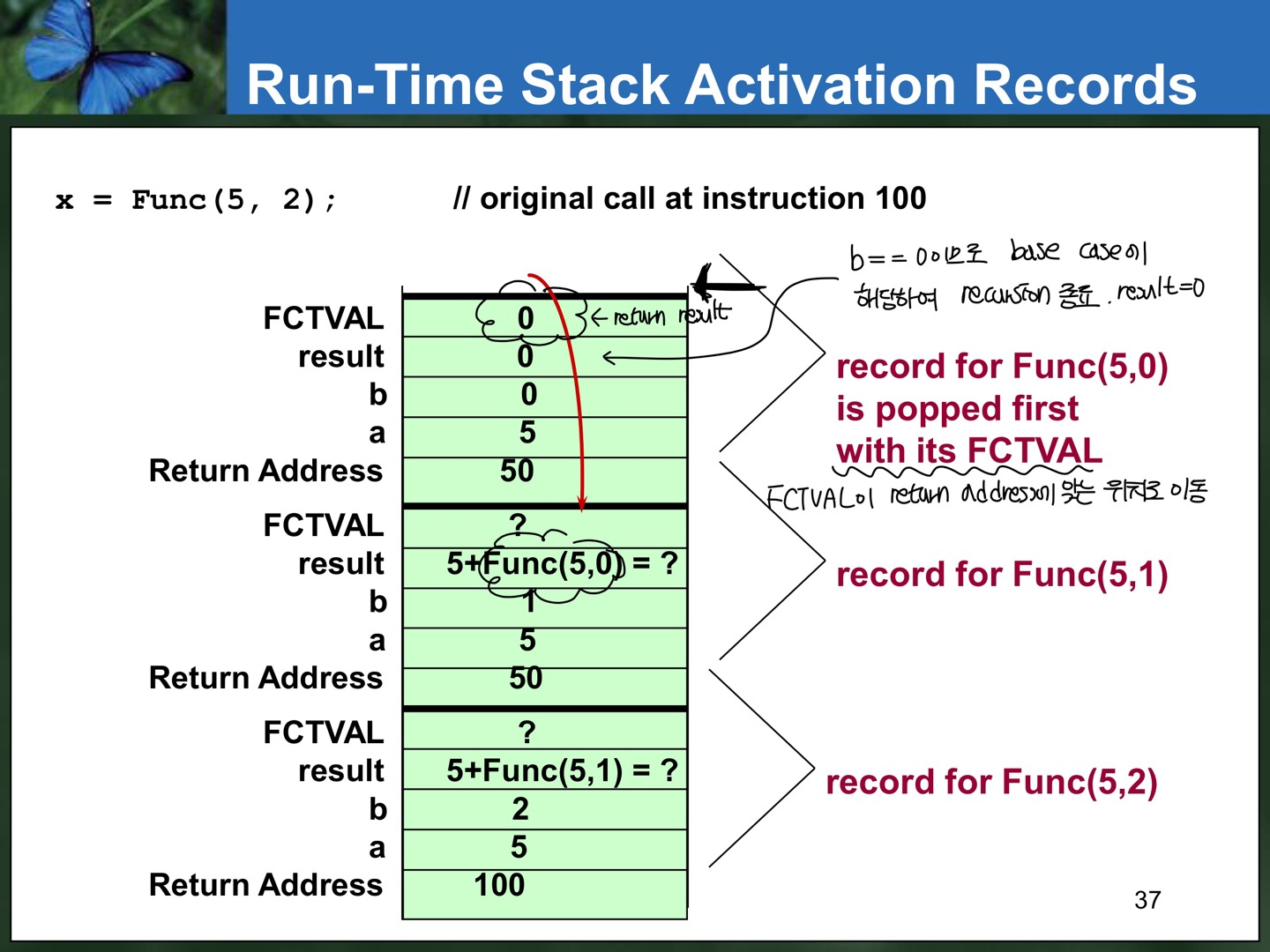
10. Sorted list의 InsertItem의 Recursive Implementation
- size factor : 현재 리스트에 있는 원소의 수
- base case
1 - 리스트가 비어있는 경우, 아이템을 빈 리스트에 넣는다.
2 - 맨 앞 아이템보다 작은 경우, 맨 앞에 넣는다. - general case : 다음 칸에서 재귀 호출을 한다.
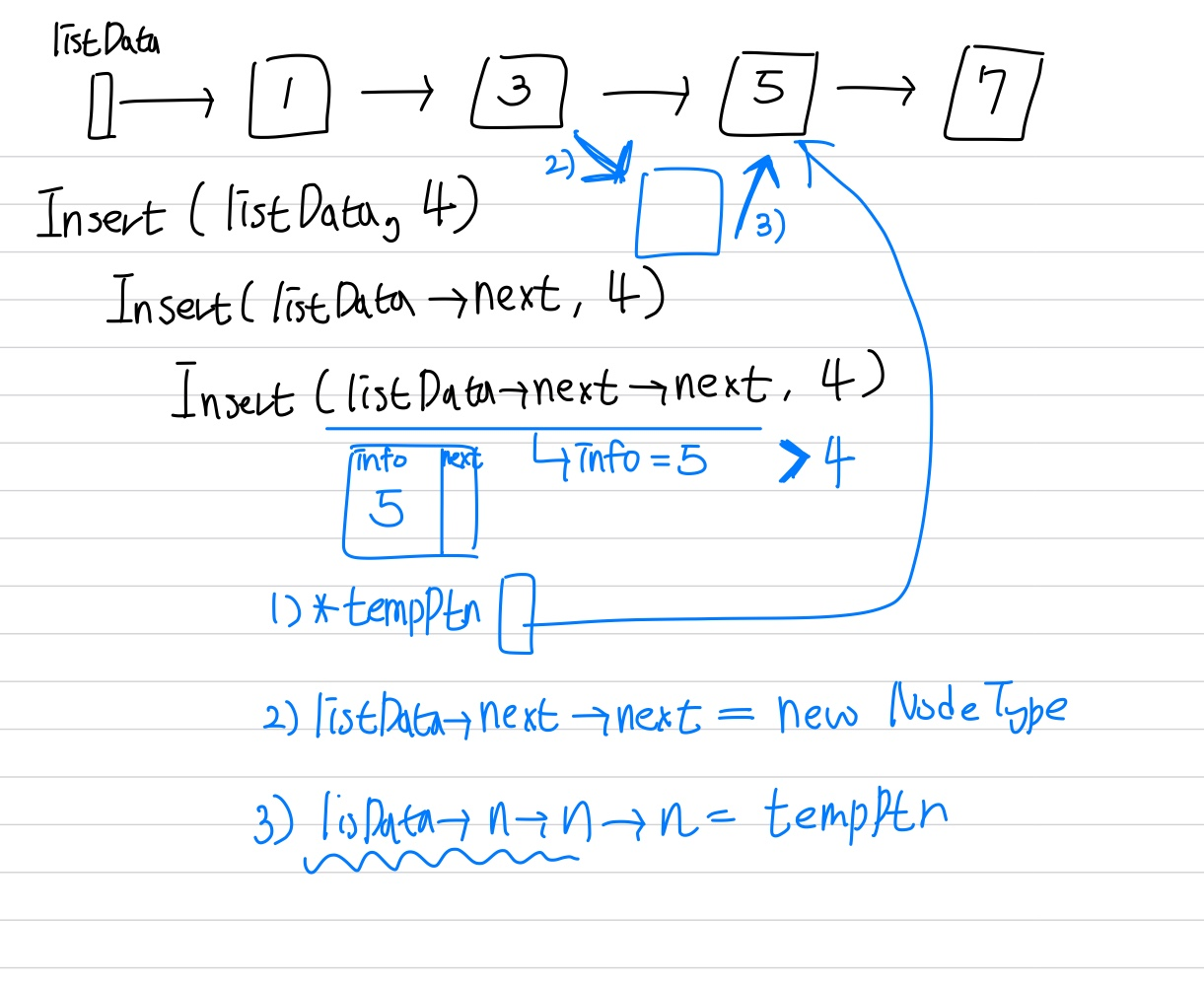
template <class ItemType>
void Insert(NodeType<ItemType> *&location, ItmeType item)
{
if( (location==NULL) || (item<location->info) // base case
// 비어있을 때 또는 맨 끝에 들어갈 때 OR 나보다 큰 값 찾았을 때 : STOP
{
NodeType<ItemType<* tempPtr=location;
location=new NodeType<ItemType>;
location->info=item;
location->next=tempPtr;
}
else
Insert(location->next, newItem); // general case
}
template <class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::InsertItem(ItemType newItem)
{
Insert(listData, newItem);
}여기서 가장 중요한 것은 reference 타입으로 받은 location의 포인터를 사용한다는 것이다.
* pointer : local variable 값을 주소로 갖는 일반 변수. 새 공간을 잡히고 location 변수에 영향을 주지 않는다.
*& : 파라미터가 location 공간과 동일한 공간을 의미하게 된다. 바뀌면 location도 바뀐다.
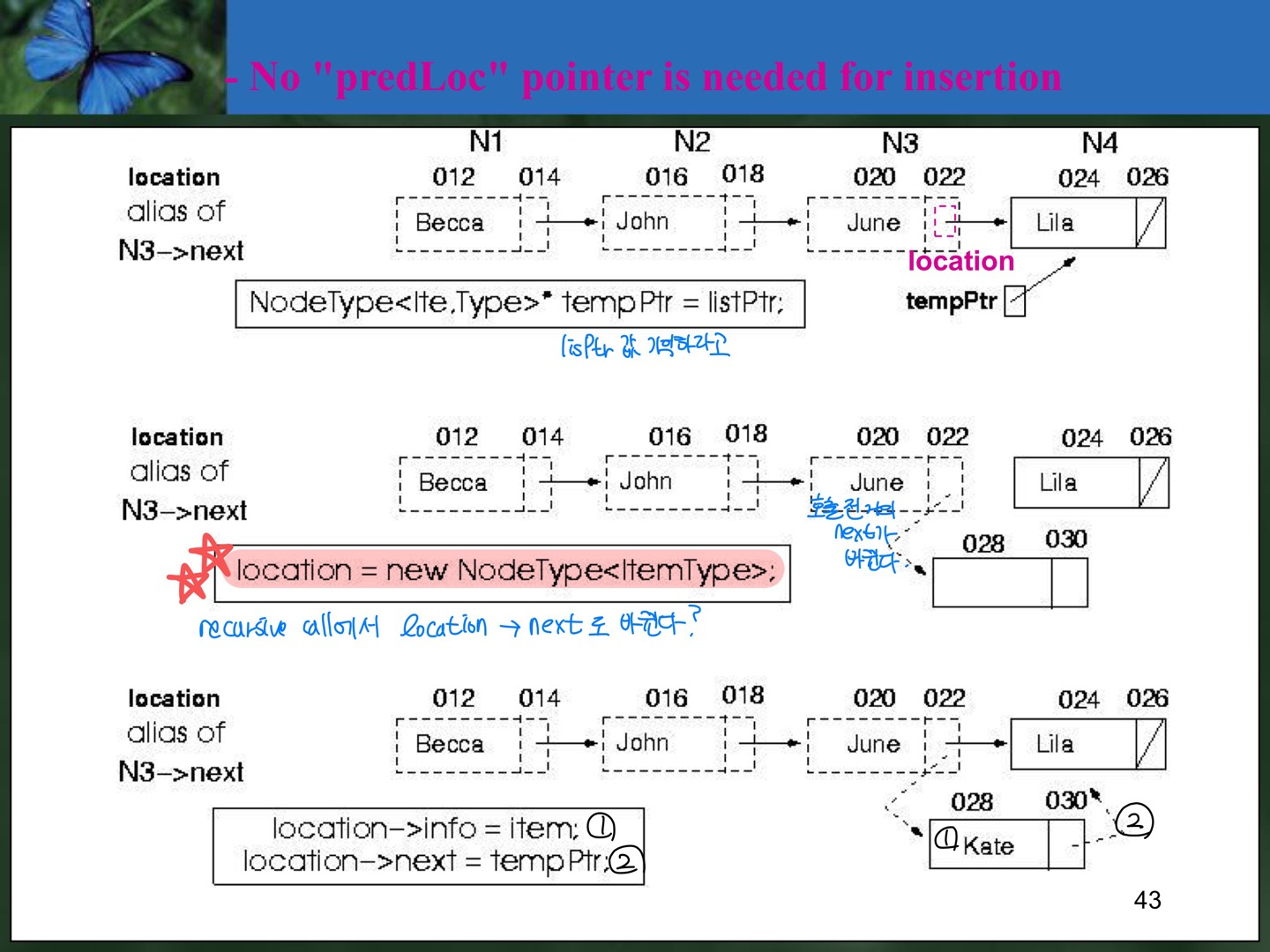
- 1) 현재 location 포인터가 가리키는 칸을 별도로 기억해둔다.
- 2) location 포인터가 새로 만든 칸을 가리키게 만든다. (location 자체가 새로운 값으로 바뀐다.)
- 3) 새로 만든 칸의 다음이 이전에 location이 가리키던 칸이 되도록 이어준다.
- non-recursive인 loop로 만들기 위해선 앞의 노드의 값에 대한 정보인 predLoc 포인터를 두어서 값을 비교했는데, 이 predLoc이 필요가 없어진다. (선배님 velog에서 가져옴)
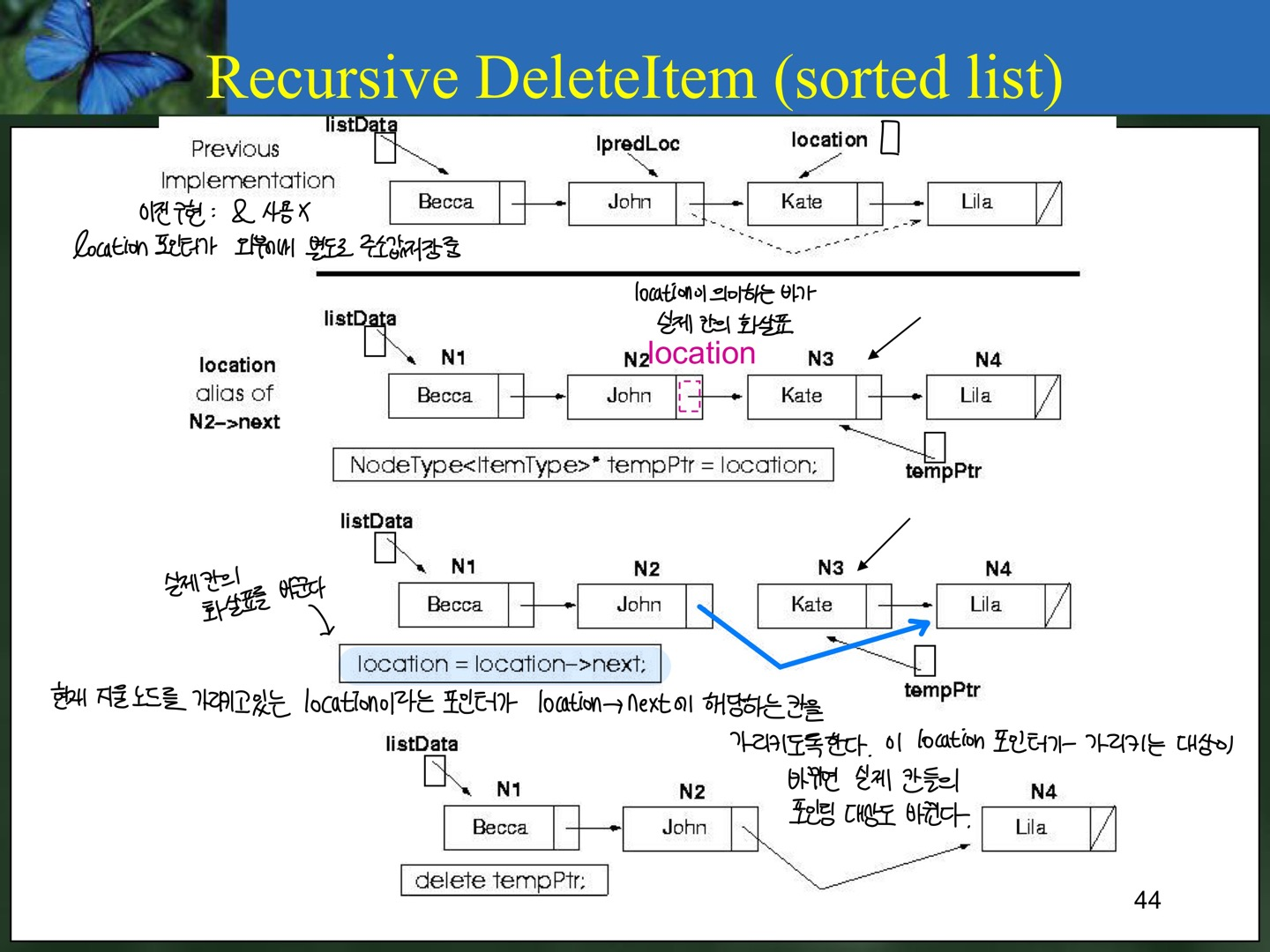
11. Sorted list의 DeleteItem의 Recursive Implementation
- size factor : 리스트 원소 수
- base case : location이 가리키는 칸의 info가 지울 아이템일 때 ( item == location->info) 지운다.
- general case : 다음 칸에서 재귀 호출. Delete(location->next, item)
templace <class ItemType>
void Delete(NodeType<ItemType>* &location, ItemType item)
// 포인팅(화살표) 변경을 반영하도록 reference 타입으로 받는다. 앞의 next가 내 다음을 pointing 하도록 만든다.
{
if (item==location->info)
{
NodeType<ItemType>* tempPtr=location;
location=location->next;
delete tempPtr;
}
else
Delete(location->next, item);
}
template <class ItemType>
void SortedType<ItemType>::DeleteItem(ItemType item)
{
Delete(listData, item);
}
12. Tail Recursion
- 함수의 가장 뒤에서 Recursion이 일어날 때를 Tail Recursion이라고 한다. Tail Recursion은 쉽게 Iteation 형태로 변경할 수가 있다. 함수의 파라미터와 지역 변수들을 저장할 필요가 없기 대문이다.
- Tail이 아닌 경우 Loop로 변경하는 방법이 없을까. 저장해야 하는 정보들을 stack으로 집어넣었다가 나오면서 Pop을 한다면 가능할 것이다.
//Non recursive version - stacks : RevPrint()
// pre. stack을 구현한다.
void ListType::RevPrint()
{
StackType<NodeType*> stack;
NodeType* listPtr;
listPtr=listData;
while(listPtr!=NULL) // Put pointers onto the stack
{
stack.Push(listPtr);
listPtr=listPtr->next;
}
while(!stack.IsEmpty()) // Retrieve pointers in reverse order and print elements
{
listPtr=stack.Top();
stack.Pop();
cout<<listPtr->info;
}
}13. Recursion vs Iteration
- branching structure
- 시간과 공간에 있어 덜 효율적이지만, 문제를 simplify하여 shorter source code가 되므로 쉽게 이해할 수 있다.
- SHALLOW DEPTH, LOW EFFICIENCY, HIGH CLARITY
