모두 import java.util.*; 해줘야 함!
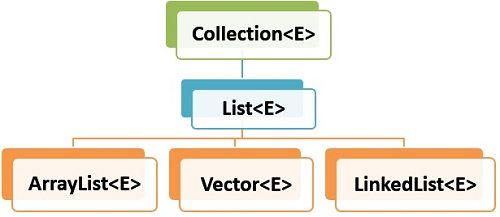
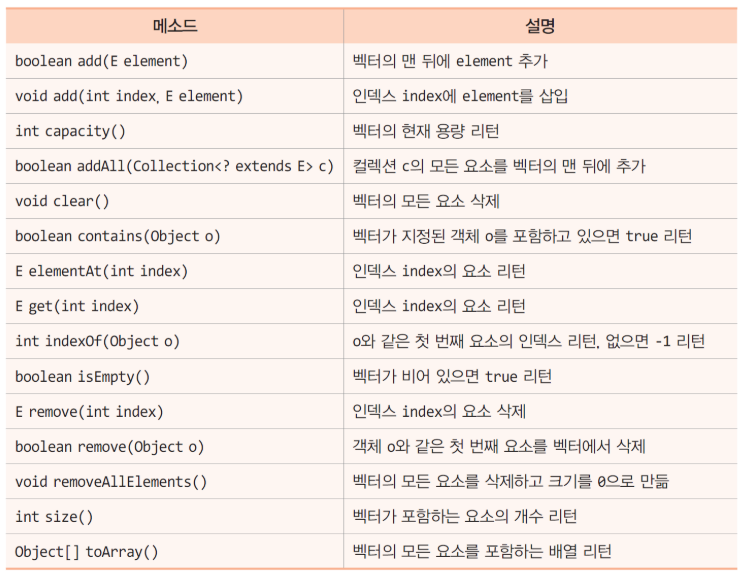
1. Vector<E> 클래스
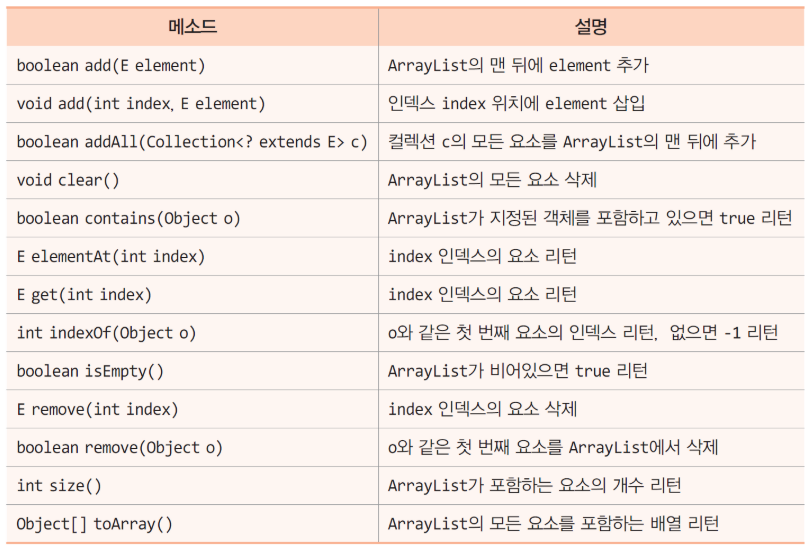
2. ArrayList<E> 클래스
3. Iterator<E> 인터페이스
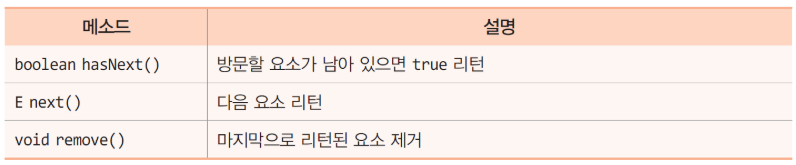
[사용법]
Vector<Integer> v = new Vector<Integer>();
Iterator<Integer> it = v.iterator();
while(it.hasNext()) { // 모든 요소 방문
int n = it.next(); // 다음 요소 리턴 ...}4. HashMap<K,V> 클래스
- HashMap은 Key와 Value의 쌍으로 구성되어있고 put()하는 값이 순서대로 저장되지 않기 때문에 출력 역시 입력한 순서대로 되지 않는다.
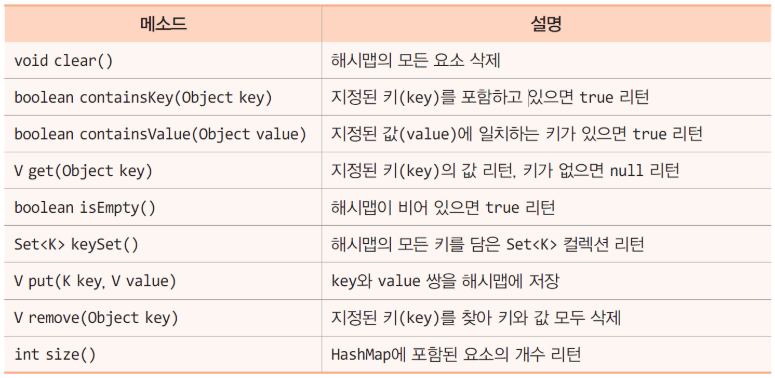
5. LinkedList<E> 클래스
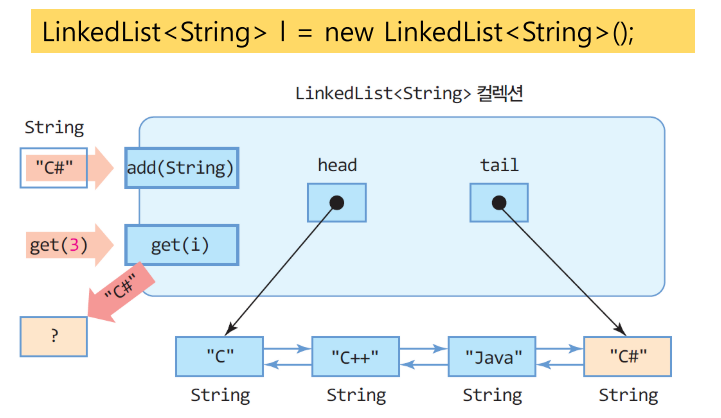
6. Collection 클래스
: 모든메소드는 static 타입이므로 Collection 객체를 생성할 필요가 없다.
- sort() : 요소를 오름차순으로 정렬
- reverse() : 요소를 내림차순으로 정렬
- max(), min() : 요소들의 최댓값과 최솟값 찾아내기
- binarySearch() : 이진 검색
[사용예시]
Collections.sort(myList);
int index = Collections.binarySearch(myList, "A");[참고]
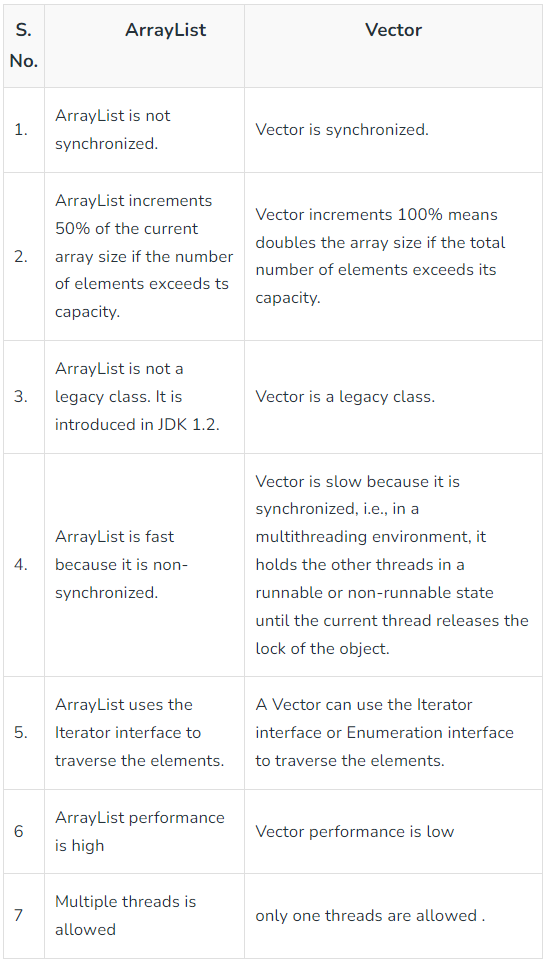
Vector와 ArrayList는 거의 동일한 컬랙션 클래스지만,
- ArrayList의 단점: 스레드 간에 동기화를 지원하지 않기 때문에, 다수의 스레드가 동시에 ArrayList에 요소를 삽입하거나 삭제할 때 ArrayList의 데이터가 훼손될 우려가 있음.
- ArrayList의 장점: 멀티스레드 동기화를 위한 시간 소모가 없기 때문에, Vector보다 속도가 빨라 단일 스레드 응용에는 더 효과적임.
출처: 명품 JAVA
출처: GeeksForGeeks