
[Tree] Height of a Binary Tree
난이도: ★★☆☆☆ • solved on: 2025-12-05
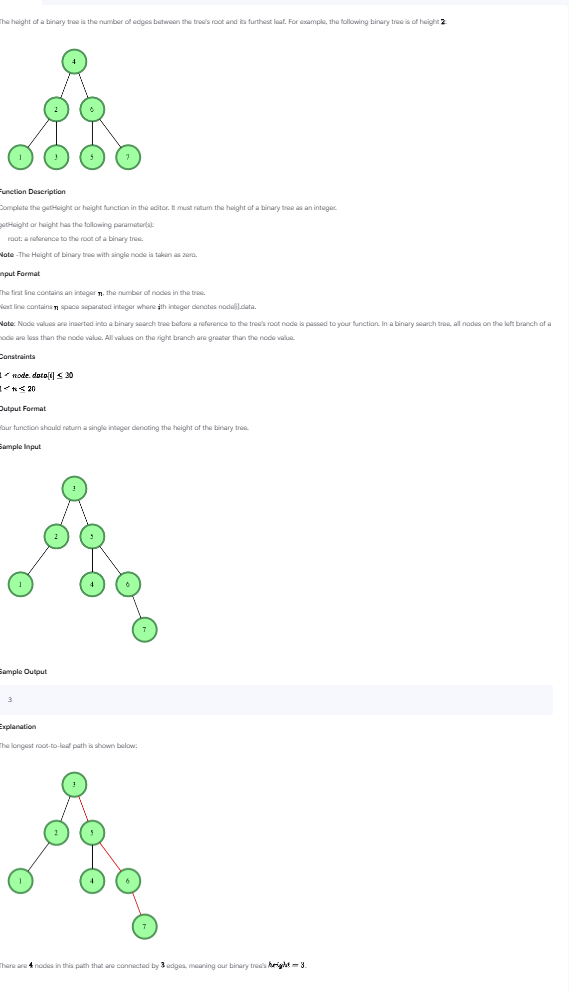
문제 요약
- 문제 유형: 트리(Tree), DFS
- 요구사항: 이진 트리의 height(높이) 를 계산해야 한다. height는 root에서 leaf까지의 edge 수로 정의된다.
사용 개념
-
자료구조
- Binary Tree(Node 구조)
-
알고리즘/기법
- DFS(재귀)
- 분할 정복(divide and conquer)
-
핵심 키워드
- height 계산
- leaf 처리
- edge count 기반 정의
풀이 아이디어 및 코드
방법 1 : child 존재 여부 기반 height 증가 방식
- 문제 분해
- height 증가 시점을 명확하게 잡기 어렵다고 판단하여,
“child가 있으면 +1, 없으면 0으로 전환”하는 방식을 채택했다.- 기본값을 1로 두고, 자식이 없는 경우 height를 0으로 조정한다.
- 핵심 로직 흐름
if root == null → 0 tmpLeft = 1, tmpRight = 1 왼쪽 자식이 있으면 height(left) 더하기 없으면 tmpLeft = 0 오른쪽 동일 처리 return max(tmpLeft, tmpRight)
예외 처리
- 자식이 없는 leaf 노드는 height = 0
- null root height = 0
public static int height(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int tmpLeft = 1;
int tmpRight = 1;
int tmpRoot = 0;
if (root.left != null) {
tmpLeft += height(root.left);
} else {
tmpLeft = 0;
}
if (root.right != null) {
tmpRight += height(root.right);
} else {
tmpRight = 0;
}
return tmpRoot + Math.max(tmpLeft, tmpRight);
}방법 2 : 개선된 정석 DFS 풀이 (max(left, right) + 1)
- 문제 분해
- 트리 height = “두 서브트리의 height 중 큰 값 + 1”
- leaf 노드의 height는 0
- null 노드는 height = 0 으로 처리하면 HackerRank 기준과 일치한다.
- 핵심 로직 흐름
if root is null: return 0 left = height(root.left) right = height(root.right) return max(left, right) + 1
예외 처리
- root가 null → height = 0
- leaf 노드는 left=right=0 → height = 1?
HackerRank에서는 leaf height = 0이므로 위 수식을 기반으로 0을 유지한다.
public static int height(Node root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int left = height(root.left);
int right = height(root.right);
return Math.max(left, right) + 1;
}시간·공간 복잡도
방법 1
- 시간 복잡도: O(N)
- 공간 복잡도: O(H)
방법 2
- 시간 복잡도: O(N)
- 공간 복잡도: O(H)
두 방식 모두 DFS 기반이므로 동일한 복잡도를 가진다. 하지만 가독성 면에서 방법 2가 압도적으로 좋다
어려웠던 점
- 레벨 단위로 BFS를 먼저 떠올렸으나, height를 edge count로 세는 구조와 맞지 않아 DFS로 전환했다.
- height 증가 시점을 어디에 두어야 하는지 감이 잡히지 않아 여러 구조를 시도했다.
- leaf 여부를 조건으로 height 조정하는 방식(tmpLeft 기본값을 1로 두고 없으면 0으로 변경)이 그 당시 문제 해결에는 유용했지만, 이후 더 단순한 공식(max+1)이 존재함을 알게 되었다.
배운 점 및 팁
- DFS height 계산은 “max(left, right) + 1” 이라는 패턴을 기억하면 대부분의 트리 높이 문제에 적용된다.
- height 정의가 node count인지 edge count인지 문제마다 다르므로 반드시 확인해야 한다.
- BFS는 level 탐색에 적합하지만 height 계산에서는 DFS가 코드가 간결하다.
참고 및 링크
- 문제 링크: https://www.hackerrank.com/challenges/tree-height-of-a-binary-tree/problem
- 참고 블로그/깃허브: 없음
추가 연습 문제
-
비슷한 유형 (GPT 추천)
-
확장 문제 (GPT 추천)
