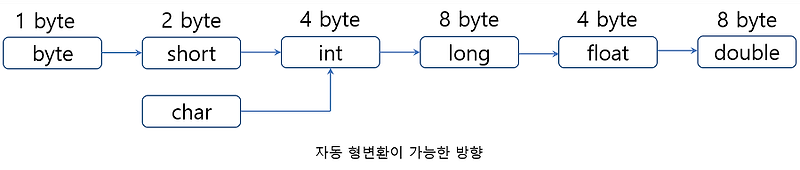
1️⃣ 프로모션 (= 자동 형 변환, 업캐스팅)
Range가 더 작은 타입을 더 큰 타입에 대입할 때, 자동으로 큰 타입으로 변환되는 현상
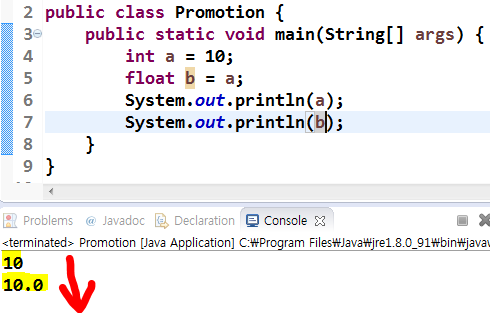
public class main{
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 10;
float b = a; // 오류없이 자동으로 변환
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
}
}
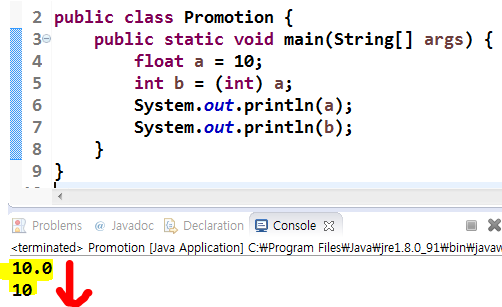
2️⃣ 캐스팅 (= 명시적 형 변환, 다운캐스팅)
크기가 더 큰 타입을 더 작은 타입에 대입할 때, 타입을 명시하여 강제로 형변환 시키는 것
→ 데이터 손실이나 변형이 발생할 수 있음
public class test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
float a = 10;
//int b = a; // 오류 발생
int b = (int) a; // 명시적으로 알려줘야함
}
}
3️⃣ 클래스 타입의 형 변환
프로모션과 캐스팅을 객체에서도 사용할 수 있음
class Person {
String name;
Person(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
class Student extends Person {
String check;
Student(String name) {
super(name);
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("홍길동");
Person p1 = s1; // 업캐스팅
p1.name = "이름이다.";
Person p2 = new Student("홍길동");
Student s2 = (Student)p2; // 다운캐스팅
s2.name = "김유신";
}
}
참고자료
https://m.blog.naver.com/haejoon90/220781157092
https://dad-rock.tistory.com/1060
https://sf2020.tistory.com/38
