DAY19 - JAVA#6 배열
1. 배열
- 배열은 같은 타입의 데이터를 연속된 공간에 나열하고, 각 데이터에 인덱스(index)를 부여해놓은 자료구조입니다.
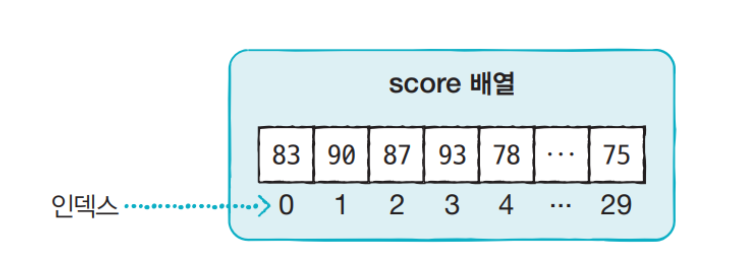
score 배열의 각 인덱스는 각 항목의 데이터를 읽거나 저장하는데 사용되며 다음과 같이 배열 이름 옆에 대괄호 [ ]에 기입됩니다. 인덱스는 0부터 시작합니다.
score[0]=83;
score[1]=90;
score[2]=87;
.
.
(1) 배열 선언
- 배열 변수 선언은 다음과 같이 두 가지 형식으로 작성할 수 있습니다.
1.타입[ ] 변수;
2.타입 변수[ ];
타입에는 데이터 자료형이 들어감.(String,double,int...)
(2) 배열 생성
-
배열 객체를 생성하려면 값 목록을 이용하거나 new 연산자를 이용하는 방법이 있습니다.
타입 변수[ ] = { 값0, 값1, 값2, 값3, … };
-
new 연산자로 배열 생성
값의 목록을 가지고 있지 않지만, 향후 값들을 저장할 배열을 미리 만들고 싶다면 new 연산자로 다음과 같이 배열 객체를 생성할 수 있습니다.
타입 변수[ ] = new 타입[길이];
예를 들어 배열 scores의 0, 1, 2 인덱스에 각각 83, 90, 75를 저장하는 코드는 다음과 같습니다.int[] scores = new int[3]; scores[0] = 83; scores[1] = 90; scores[2] = 75;
출처:링크텍스트
2. 배열 예제 연습
- 배열에 53,6,85,3,5를 넣은 다음 배열의 내용을 화면에 출력해 보자.
package com.human.ex;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]= {53,6,85,3,5}; // 배열 a 생성
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(a)); // 배열 a의 내용 출력
}
}- 배열 a[]={12,1,53,6,85,3}를 만든 다음에 배열의 모든 내용을 더한 값을 sum에 저장하여 출력하는 코드를 만들어 보자.
package com.human.ex;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]= {12,1,53,6,85,3};
int sum=0;
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++) {
sum=sum+a[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}- 배열 a에 1,2,3 을 넣은 후 배열 내의 모든 값에 2를 더한 값인 3,4,5로 변경한 다음에 배열의 내용을 화면에 인덱스 순서대로 출력해 보고 인덱스 역순으로 출력해보자.
package com.human.ex;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]= {1,2,3};
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++) {
a[i]=a[i]+2;
}
System.out.println(java.util.Arrays.toString(a));
for(int i=a.length-1; i>=0; i--) {
System.out.print(a[i]);
}
}
}
- 배열에 들어있는 값중 짝수만 화면에 출력하시오.
package com.human.ex;
import java.util.Arrays;
public class Array {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int a[]= {1,2,3,4,5,6};
for(int i=0; i < a.length; i++) {
if(a[i]%2==0) {
System.out.println(a[i]);
}
}
}
}