A Unified Generative Retriever for Knowledge-Intensive Language Tasks via Prompt Learning
Abstract
- Knowledge-intensive language tasks (KILTs) 는 검색을 통해서 관련있는 정보를 가져옴을 통해 성능 향상을 보였다.
- KILTs에서 검색해야 하는 대상은 semantic granularity 면에서 다른 level을 가지고 있다. - Document retriever, passage retriever, sentence retriever, entity retriever
- 각각을 따로 학습하게 되면 성능의 Generalization 이 문제가 되었다.
- unified generative retriever (UGR) : different retrieval tasks를 다 풀 수 있도록 한다.
- 1) n-gram based identifier로 context를 반영한 Identifier를 설계한다.
- 2) prompt learning strategy : 서로 다른 task를 구별할 수 있게, 프롬프트 엔지니어링 방식을 통해서 통합할 수 있게 한다.
→ 이를 통해서 단순히 knowledge를 share하는 것 뿐만 아니라 여러 Task를 구분하여 문제를 풀며, SOTA를 뛰어넘는 성능을 보였다.
1. Introduction
- 기존의 KILTs에서의 retrieval 방식
-
1) one simply employs a single document retriever (level이 달라지게 되면 성능이 떨어짐)
-
2) specific retrievers for different retrieval tasks to support KILTs (각각에 대한 retriever를 따로 학습시켜야 한다는 단점이 있음)
→ Research Question: generalization이 잘 되면서도, 각 Task에 효과적인 성능을 낼 수는 없을까?
-
- A unified generative retriever
- a single generative model to perform a variety of information retrieval (IR) tasks
- share common knowledge + task-specific retrievers
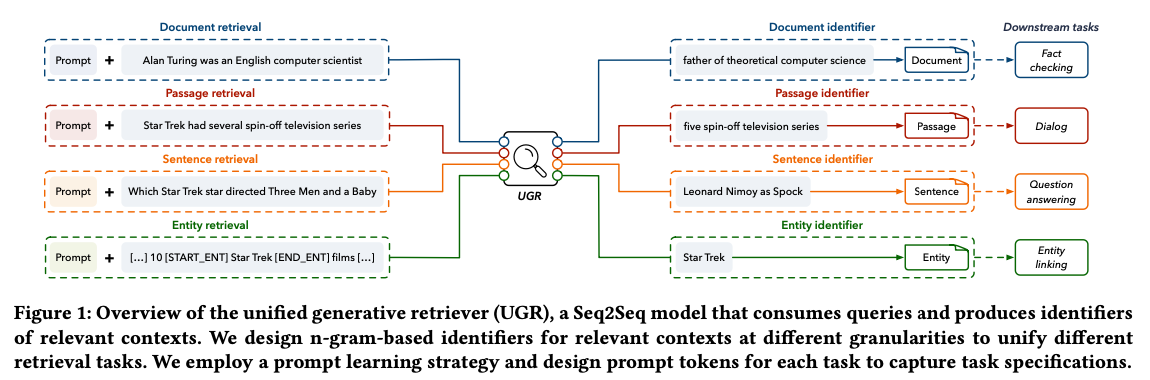
-
Unified generative retriever (UGR)
- 1) 다양한 retrieval task를 합치기 위하여 → n-gram-based identifier를 사용 (seq2seq의 output단)
- 2) 다양한 retrieval task를 구별하기 위하여 → prompt learning 방식을 사용함
-
Empirical findings
- UGR 은 in-domain, out-of-domain, unseen tasks에 대해서 높은 성능을 보임
- 기존 retirever + reader 모델에 비하여 UGR + reader 모델일 때 성능이 더 좋아진다는 것을 보임
2. Related Work
-
Knowledge-intensive language tasks
- tasks : fact checking, open domain question answering, slot filling, entity linking, dialogue
- retriever - reader component를 가지고 문제를 풀었음
-
Information retrieval for KILT
- 1) query가 주어졌을 때 Relevant document만 찾는 방식
- 주로 그냥 Wikipeida 문단 가져오게 하는 것으로 시작함
- (이 방식의 경우에는 reader가 필요로 하는 granularity를 무시한다는 단점이 있음)
- 2) task-specific models
- 각각에 대해서 training 을 하기 때문에 generalization이 어려움
- 3) generative retrieval
- NLP tasks를 Unify해서 푸는 방식의 성공적인 모습에 motivated (e.g. T0, T5, FLAN)
- seq2seq model을 사용해서, query가 들어왔을 때, identifier를 생성함으로써 retrieval을 진행한다.
- a single generative model can encode the global information (end-to-end optimization)
- (**) DPR의 경우 Batch accuracy로 optimization 되기 떄문에, (왜냐면 현실적으로 전체 배치에서 유사도를 구하게끔 back prop이 불가능. 따라서 End-to-end로 optimization할 수 있는 건 Generative method라고 소개하는것)
- embedding space의 병목 현상 (비슷한 embedding들이 다 그 주위에 몰려있기 때문에, 비슷한 정보가 너무 많을 때에는 성능이 좋지 못할 수 있다.) 과 large corpora index (dense vector index를 다 모아서 정리해놔야 했기 때문에 inference 단에서 드는 메모리가 많이 생긴다.)
- 이와 관련된 선행 연구들이 있었고, 어떻게 identifier를 구성할지에 대한 논의가 주를 이뤘다. UGR은 이 선행연구들의 논의를 따라가면서도, 다양한 granularity를 통합하는 Identifier를 제시한다.
- 1) query가 주어졌을 때 Relevant document만 찾는 방식
-
prompt learning
- NLP task에서 PLM을 가져다 쓰게 되면서, prompt engineering 분야도 중요해지기 시작했다.
- pre-training 과 Fine-tuning의 discrepancy를 줄이기 위해서 Prompt learning을 하기도 하였고
- generative model의 경우 prompt를 어떻게 넣어서 학습하느냐에 따라서 모델의 성능이 크게 달라지기도 하였다.
- discrete prompt, continuous prompt, hybrid prompt 등의 방식이 존재한다.
3. Our Approach
3.1 Retrieval task description
- KILT benchmark를 사용 : 모든 태스크들은 wikipeida 에서 문서를 가져와서 올바른 정답을 생성할 수 있게끔 해야 한다.
- generative IR 을 KILT에 practical하게 적용하기 위하여, 우리는 2가지의 retrieval task (Document, passage, sentence, entity) 를 unified seq2seq problem으로 디자인한다.
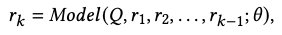
- Input query Q가 주어졌을 때, relevant context identifier r을 생성하게 하는 Seq2seq 문제라고 볼 수 있다.
3.2 Overview of the approach
(i) how to unify different retrieval tasks into a single generative form (section3.3)
→ context를 반영한 n-gram identifier
(ii) how to properly specialize for different retrieval tasks (section 3.4)
→ prompt-engineering으로 서로 다른 Task들을 구분해준다.
3.3 N-gram-based identifiers
-
좋은 identifier가 가져야 하는 조건
- 1) document content의 semantic information을 담을 수 있어야 한다.
- 2) cost-efficient 하게 생성될 수 있어야 한다. (identifier를 위해 human이 직접 labeling 하거나 하면 너무 비용이 많이 드니까…)
- 3) unique 해야 한다. (당연히! 여러 Document의 identifier가 다 같으면 안된다.)
-
proposed method : n-gram-based identifiers (위의 조건을 만족시키는,,,)
- key idea : 문서의 context에서 등장하는 중요한 n-gram 들을 Identifier로 사용하자. 그러면 search space나 structure를 힘들게 구성할 필요가 없다!
- 생성하는 방법 : BERT를 사용해서 [CLS] 토큰의 attention을 이용하여 가장 중요한 N-gram을 뽑아낸다. (아래 3단계로 이루어짐)
-
1) N-gram importance
- query Q와 relevant context C를 concatenate :
[CLS] Q [SEP] C [SEP] - [CLS] 토큰의 768 dimension hidden vector를 얻는다.
- i 번째 토큰에 대한, h번째의 어텐션 헤드에서 나온 [CLS]의 어텐션 값은 다음과 같다.
- query Q와 relevant context C를 concatenate :
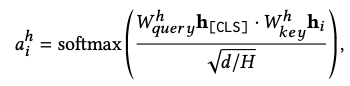
- scaled-dot attention 공식이라고 이해하면 쉽다! query가 CLS 인 것이고, content를 key 라고 보면 된다.
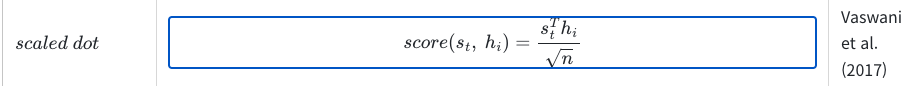
- 최종적인 token 별 importance는 H개의 attention head의 Importance를 평균내서 구한다.
- 2) N-gram distribution
- 하나의 토큰 ( 혹은 n-gram) 은 context 내에서 여러번 등장할 수 있기 때문에, 같은 토큰의 importance는 다 합산해준다.
- 최종적으로 distinct n-gram importance를 산출한다. (M_j는 n-gram)
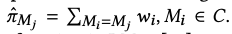
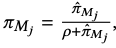
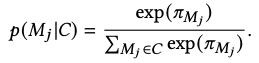
→ context에 있는 모든 n-gram에 대하여 softmax 분포를 구해서 n-gram 의 distribution을 산출한다.
- 3) Important n-gram sampling
- 0.04%의 문서만이 똑같은 n-gram identifier를 가졌다.
- we ignore the negligible identifier repetition problem
3.4 Prompt engineering
- 여러가지 retrieval task를 해결하다보면, 다른 task를 “blur out” 해버릴 수 있기 때문에, Task-specific prompt를 model 학습 시 query에 넣어줘서 specific task에 대한 구분이 가능하게 만들었다.
1) Discrete prompts
- manually 하게 cloze templates를 짜서 각 Retireval task 앞에 붙여줬다.

2) Continuous prompt
- trainable dense vector를 붙여줘서 학습하게 만든다.
- 여기서는 bi-LSTM 을 prompt encoder로 사용해서 학습하였다.
3) Hybrid prompt
- 모델이 실제적으로 작동하는 과정에서 good continuous prompt를 아무런 사전 정보 없이 학습하는 것은 어렵다.
- 따라서 anchor text (e.g. document) 등을 prompt encoder 앞에 붙여준 다음에 그 뒤에 continuous vector들이 학습되도록 하였다.
→ Task-specific prompts stimulate the model capacity in distinguish different retrieval tasks and achieving good generalization
3.5 Training and inference
- Multi-task training
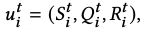
- t : retrieval task (document retrieval, passage retrieval, sentence retrieval, entity retrieval)
- S : prompt
- Q : query
- R : identifier
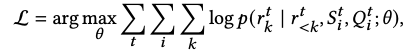
-
built on a transformer-based seq2seq model (BART)
-
seq2seq objective로 학습 : output identifier의 Likelihood를 Maximizing 하게 학습, with teacher forcing, 모델의 파라미터는 cross entropy loss로 end-to-end로 학습된다.
-
inference process
-
Wikipedia의 FM-index를 구성
-
FM-index 란?
- FM-index는 BWT에서 나온 string L (맨 마지막줄), 그리고 run을 돌리면서 계속 추가되는 F로 구성되고
- relative rank of F와 L은 항상 동일하기 때문에 constrained beam search에서 가능한 token 배열의 리스트를 구분하는 데에 사용한다.
-
Constrained-beam-search
Guiding Text Generation with Constrained Beam Search in 🤗 Transformers
The power of constrained language models.
custom_beam_search_with_GPT2.ipynb자세한 것은 선행 연구를 확인해보면 알 수 있다! (SEAL)
-
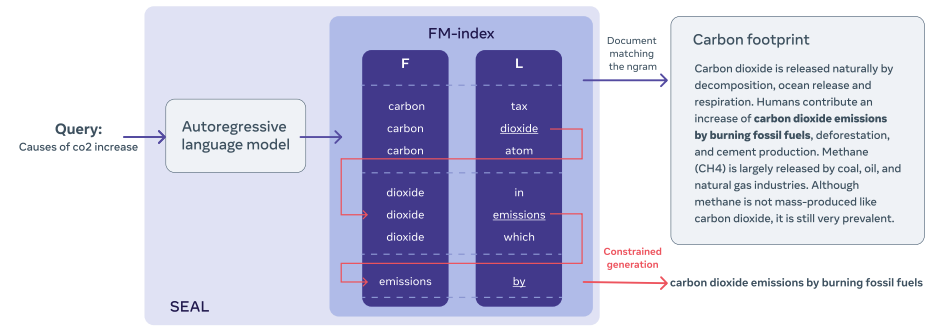
- FM-index space requirements are linear in the size of the corpus, and, with small vocabularies such as those used by modern subwordbased language models, is thus usually significantly smaller than the uncompressed corpus.
- The FMindex can be used to count the frequency of any sequence of tokens n in O(|n|log|V |)
-
FM-index 를 활용해서 output으로 나온 n-gram을 포함하는 document/passage/sentence/entity를 찾아오게 된다.
- https://github.com/foxish/2-BWT→ 1:1로 매칭해서 바로 문서를 가져오는 기존의 generative retrieval 방식과는 달리, n-gram을 생성하게 되고, 그것을 포함하는 문서를 다 가져와야 한다.
→ 따라서 그 n-gram을 포함하는 문서를 다 가져오는 과정이 느려지면 안되고, 속도가 빨라야 하는데,
→ 그 문제를 해결하기 위해서 BWT를 이용한 FM-index 알고리즘을 사용한다고 보면 되겠다.
-
shortcoming with n-gram-based identifiers : 다른 context들이 똑같은 n-gram을 포함하면 다 가져올 수 있다.
-
그래서 그 문서들 중 가장 유용한 것을 re-rank하는 함수를 정의하여 사용한다.
-
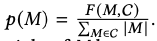
- unconditional ngram probabilities → to promote distinctive ngrams
- 코퍼스 C 전체 중에서 M이 몇번 등장하느냐
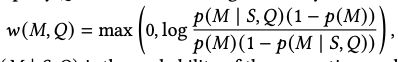
- TF-IDF와 BM25에서 아이디어를 얻어서 weight를 계산
- 현재의 프롬프트와 커리 기반으로 M이 나올 확률이 더 높으면 값이 높아지고, 여러 군데에 많이 등장하면 낮아지고
- 𝑝(𝑀 | 𝑆,𝑄) is the probability of the generative model decod- ing 𝑀 conditioned on the query 𝑄 and its prompt 𝑆
- 그러니까, LM과 FM-index를 다 활용해서 scoring 하는 방식
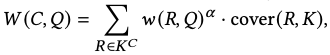
- The document-level score, then, is the weighted sum of all ngrams in K^C
- R이 n-gram 여러개 (여기서는 10개의 10-gram) 마다 weighted sum을 한다.
- K는 Q에서 생성된 모든 n-gram identifier들
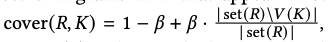
- a function of how many ngram tokens are not included in the coverage set C
- The purpose of the coverage weight is to avoid the overscoring of very repetitive documents, where many similar ngrams are matched.
- set(R)은 R에 나온 토큰들 set 연산 한 거 (토큰 개수)
- V(K)는 K(Q에서 생성된 모든 n-gram identifier들) 중 top-g개의 높은 점수를 가진 토큰이 (토큰 개수) → query에서 K 전체 중 가장 높은 탑 5가 몇개 들어갔는지 → 낮을 수록 좋은 것
- 반복적인 생성을 피하는 것이 목적. 즉, K에서 Q로부터 가장 연관있는 top-g개 중에서, 그걸 set 연산했을 때 얼마나 다양하게 생성이 되었는지를 확인. 그런 것을 갖고 문서를 뽑는다.
4. Experimental Setup
4.1 Datasets
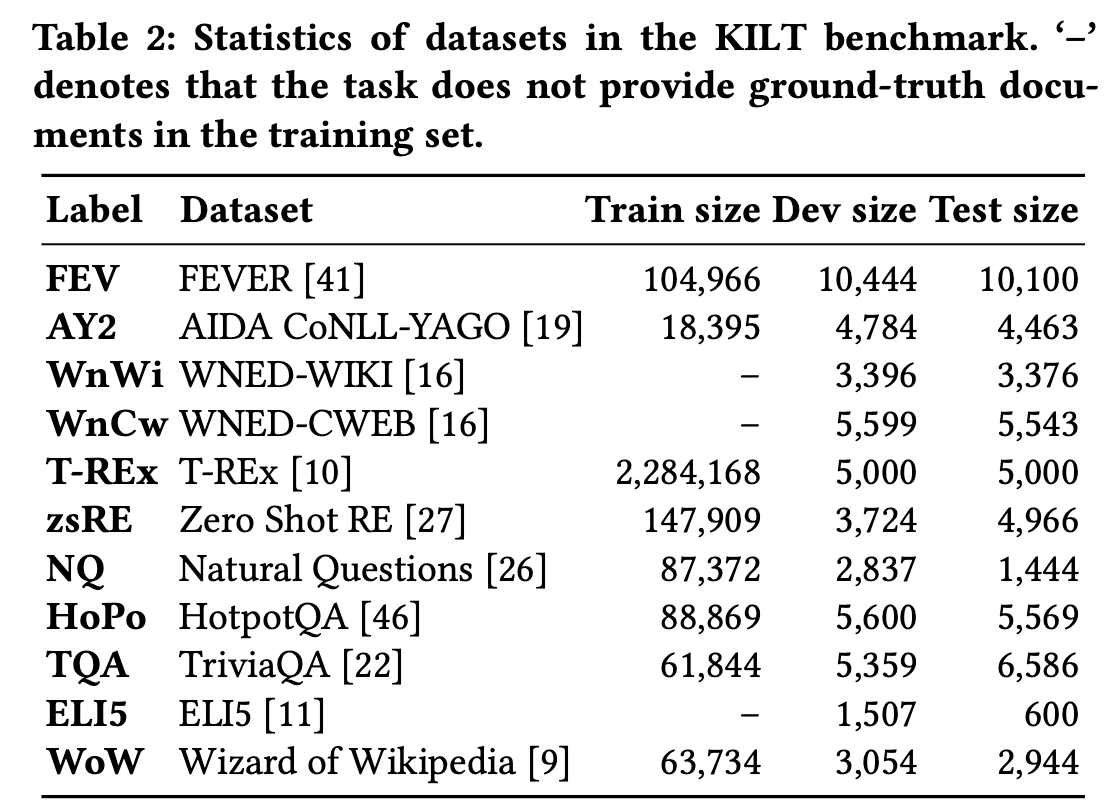
- KILT benchmark : DR, PR, SR, ER
- in-domain
- out-of-domain
- unseen task 로 구성
4.2 Baselines
- BART^sp : basic BART large model을 query를 넣으면 semantic id를 생성하도록 하는 것
- BART^sp_hp : hybrid prompt를 넣어준 것
- BART^mt : 위의 두 개는 각각의 task에 대하여 학습한 것이지만, 프롬프팅 없이 멀티태스크로 하는 것
- BM25
- GENRE : Document Retrieval
- SEAL : Passage Retrieval
- MT-DPR : sentence retrieval을 위해서 DPR model을 jointly 학습한 것
- BLINK : Entity Retrieval
4.3 Evaluation metrics
- R-precision
- downstream task에 대하여는 accuracy, exact match, Rouge, f1을 사용함
4.4 Implementation details
- Model architecture
- seq2seq transformer
- hidden size 1024
- feed-forward layer 4-96
- layer 12
- attention head 14
- bart large 로 초기화되었고, 크기는 406M
- Identifier construction
- BERT base를 사용
- n-gram의 n : 10
- the number of n-grams v : 10 (DR, PR), SR(5)
- ER은 바로 entity name을 Identifier로 설정
- Prompt Engineering
- LSTM hidden dimension 1024
- anchor text는 각각 document, passage, sentence, entity
- Training hyperparameters
- prompt encoder를 먼저 하습을 시키고,
- fix된 prompt encoder를 가지고 generative model을 학습 시켰다.
- Inference hyperparameters
- FM-index : sdsl-lite의 C++ implementation 을 사용
- Wikipedia의 영어 코퍼스 사용
- constrained beam search : 10 timesteps and 15 beams
- 알파는 2.0, 베타는 0.8, g는 5
5. Experimental Results
5.1 Evaluation on in-domain and out-of-domian datasets
(RQ1) How does UGR perform compared to strong retrieval baselines on both in-domain and out-of domain datasets?
in-domain results
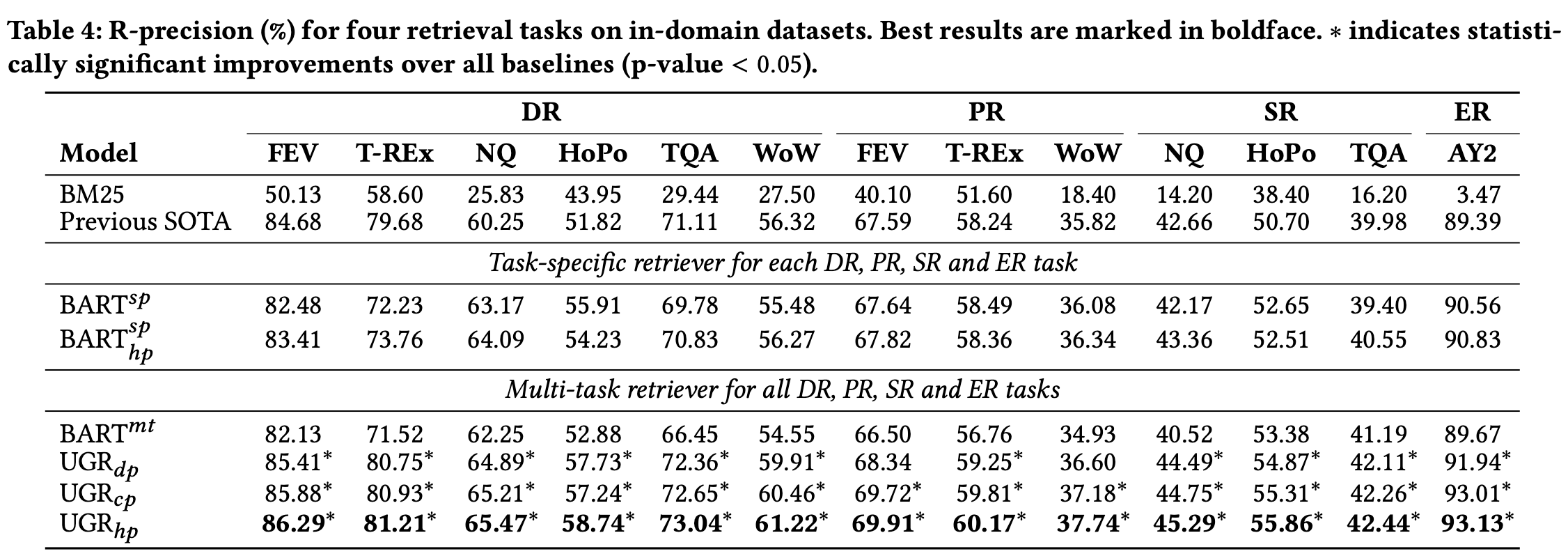
-
in-domain에서 task speicific한 방법론에 비해서 sota를 달성한 것을 확인할 수 있음
-
out-of-domain에서도 (그나마) SOTA를 달성한 것을 확인할 수 있음
-
BART^sp가 BART^mt보다 성능이 좋은 것을 보아, mixied dataset을 학습할 때 task-specific characteristics를 무시하면 안된다는 것을 알 수 있음
-
BART^sp_hp가 BART^sp보다 성능이 좋은 것을 보아, hybrid prompt engineering이 도움이 된다는 것을 알 수 있다. (각각의 task에 적용할 지라도 성능이 좋은 것을 확인할 수 있음!)
-
UGR_hp가 BART^mt보다 성능이 좋은 것을 통해서 prompt learning 방법론이 의미 있다는 것을 볼 수 있음
-
3가지의 프롬프트 방식 중에서는 hybrid prompt engineering이 가장 좋았던 것을 확인할 수 있음
→ 특히, 기존 SOTA를 모두 넘어서는 것을 확인해볼 때, generative IR 방법론들에 대한 연구가 더 탐구될 영역이 남았다는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
out-of-domain results
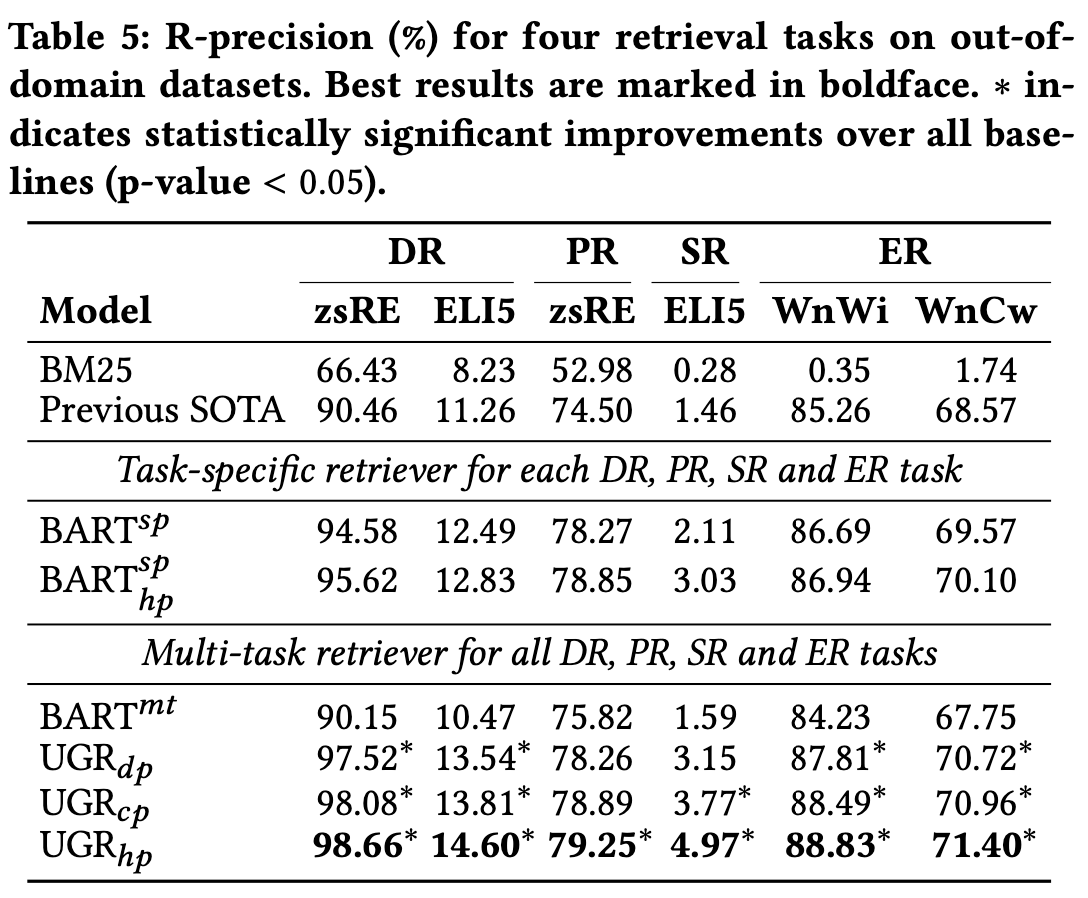
- 기존의 방법론들보다는 generalization이 되었다고 볼 수 있음
5.2 Adaptability to unseen tasks
(RQ2) How is the adaptability of UGR to unseen tasks?
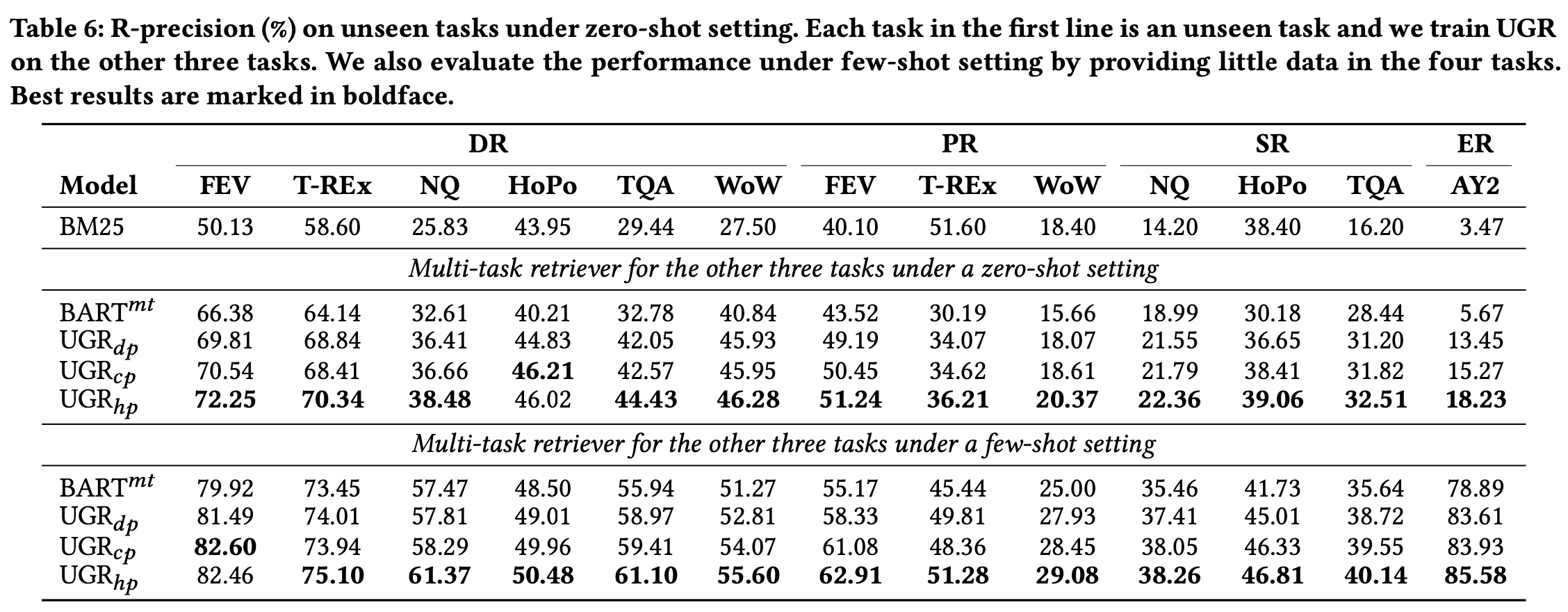
- zero-shot과 few-shot learning의 성능을 확인하고자 하였다.
- 실험 방식 (DR, PR, SR, ER 중) 나머지 3개로 학습한 다음에 나머지 1개로 성능을 평가했다.
- few-shot은 unseen task에 대하여 1000개를 random으로 픽해서 학습을 돌린 것이다.
- unseen task에 대해서도 성능이 꽤나 높게 나오는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. ㅏ
5.3 Analysis of n-gram-based identifiers
(RQ3) How does the n-gram-based identifier affect retrieval performance?
Impact of important n-gram sampling strategy
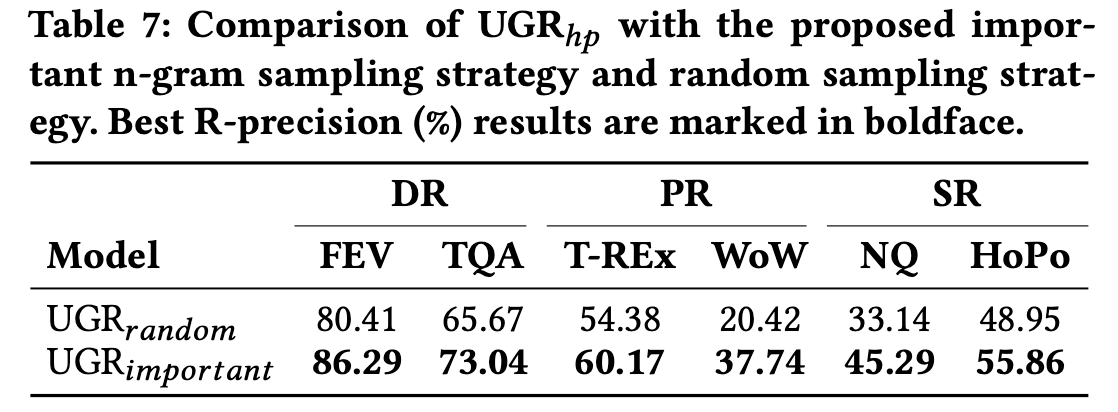
- 현재는 sementaic으로 의미 있는 것을 n-gram-based identifier로 제시하였는데, 랜덤으로 픽업하여보았다.
- random으로 identifier를 설정하였을 때 성능이 더 낮아지는 것을 볼 수 있었고, 이를 통해서 identifier를 구성함에 있어 random보다는 semantic으로 의미있는 것을 뽑는 것이 의미있다는 것을 알 수 있었다.
Impact of the length and number of n-grams
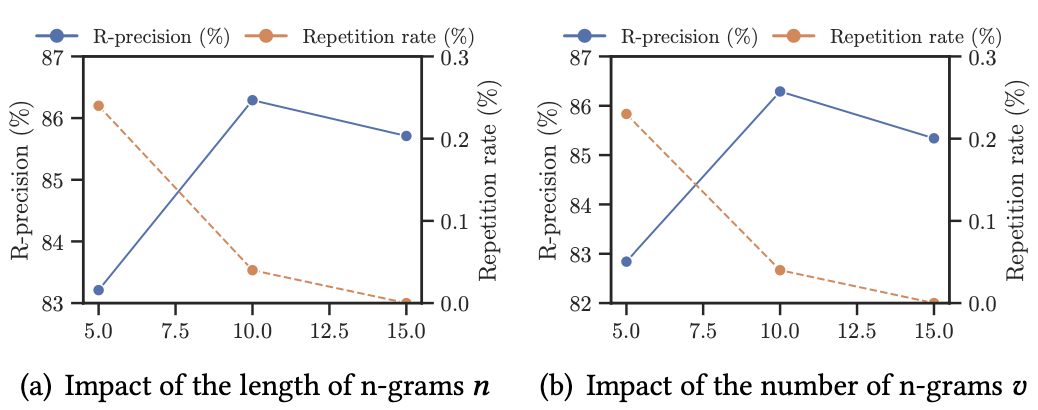
- n이랑 v를 10로 하는 것이 성능이 가장 좋아서 선택했다는 것을 보여준다.
5.4 Downstream performance
(RQ4) Can relevant contexts retrieved by UGR improve the performance of downstream tasks in KILT?
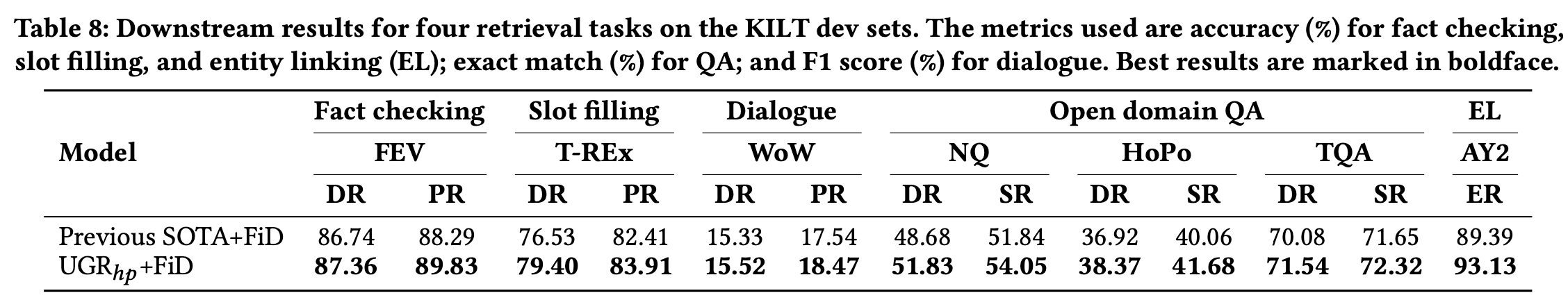
- 기존 SOTA보다 성능이 좋았기 떄문에, 당연히 downstream performance에서도 성능이 좋아지는 것을 확인할 수 있었음
5.5 Memory and inference efficiency
(RQ5) How does UGR perform com- pared to traditional retrieval methods and generative methods in terms of computational cost?
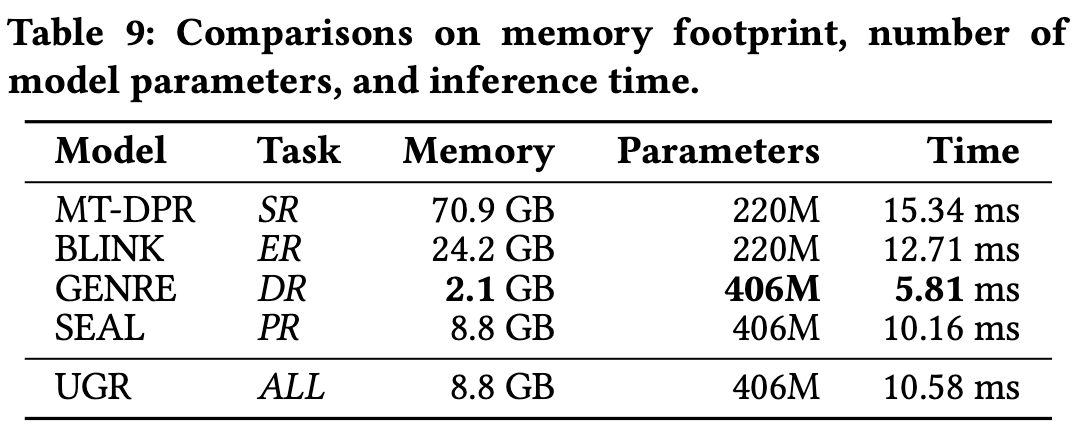
- traditional retrieval models (MT-DPR and BLINK) → dual encoder
- advanced generative retrieval models (GENRE and SEAL)
→ 기존 방식들과 메모리와 인퍼런스 속도 측면에서 비교를 진행
- traditional 방법과 비교해서, generative retrieval model이 더 많은 모델 파라미터를 가지지만, 메모리 foot print (the disk space required by each model)은 더 적고, 속도 또한 빠른 것을 확인할 수 있다. 왜냐하면 dense representation을 많이 보관해야 하기 떄문이다.
- prefix tree 방식으로 디코딩을 하는 GENRE와 다르게, SEAL과 UGR은 FM-index 방식의 디코딩을 진행하기 때문에 메모리와 inference 타임이 더 많이 드는 것을 확인할 수 있었다. (여기서 GENRE와 SEAL은 각 task 별로 따로 학습시켜야 하는 반면, UGR는 모든 task에서 unified 하게 사용될 수 있다는 점이 다르다.)
6. Conclusion
- UGR, Unified Generative Retriever, knowledge-intensive language tasks에 쓰이는 방식을 제시한다.
- retrieval problem을 conditional generation problem으로 변환한다.
- n-gram-based identifier를 사용하고
- prompt learning 방식을 사용한다.
- limitation : complex scoring function을 사용해서 identifier를 문서로 변환하는 단점을 가지고 있다. 따라서 efficient semantic identifier for generative retrieval을 찾는 것이 필요할 것이다.
Take-away point
- 여기서 Task가 다르다는 것이 검색해와야 하는 DB의 덩어리 크기가 다른 것이지, 아예 다른 DB에서 가져오는 혼란은 없다.
- generative retriver를 적용한 논문이 SIGIR 2023에 있었는데, 우리는 더 나아가서 다양한 task에 대한 Retriever를 unified할 수 있는 방식으로 expansion해볼 수 있을 것이라고 생각된다.
- generative, prompt engineering이 나왔으므로, instruction tuning 등 generative method를 적용하여 성능을 높이는 방식을 연구해볼 수 있을 것이다. 그러나 instruction tuning 자체가 다양한 task를 겨냥하는 것인데, 이걸 검색기에다가 적용하는 것이 무슨 의미가 있을지? 뭔가 해볼 수 있을 거 같은데, 생각은 잘 안나는 어려운 마음이다.
