1. 벨만포드 알고리즘
벨만-포드 알고리즘(Bellman-Ford Alrogithm)이란 한 노드에서 다른 노드까지의 최단 경로를 구하는 알고리즘이다. 다익스트라 알고리즘은 모든 가중치가 양수인 경우에만 사용할 수 있지만 벨만-포드 알고리즘은 가중치가 음수인 경우에도 사용할 수 있다. 다만 속도 측면에서는 다익스트라 알고리즘이 벨만-포드 알고리즘에 비해 빠른 속도를 갖는다.
벨만-포드 알고리즘은 각 정점들을 돌아 가면서 정점의 간선들을 탐색한다. 맨 처음은 시작점부터 탐색하며, 간선의 가중치와 시작점에서 정점까지의 거리의 합이 도달하고자 하는 정점의 기존 거리보다 작으면 값을 갱신한다.
d[T] <= d[S] + w(S,T)
T: 해당 간선이 도달하고자 하는 정점
S: 해당 간선의 시작점
d: 시작점에서 해당 정점의 거리
w: 해당 간선의 가중치_
그림을 통해서 벨만-포드 알고리즘이 어떻게 동작하는지 알아보겠다.
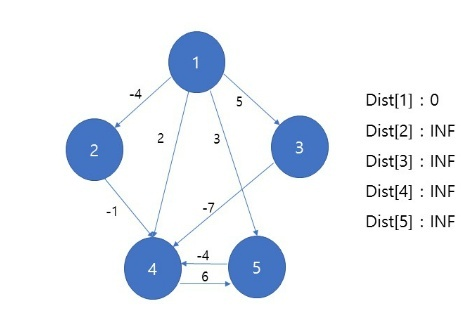
시작점을 1로 설정한다. 정점들의 거리를 저장하는 배열인 Dist를 정의한다. 시작점의 거리는 0으로 설정하고 다른 정점들을 탐색하지 않았기 때문에 무한대의 INF를 정의한다.
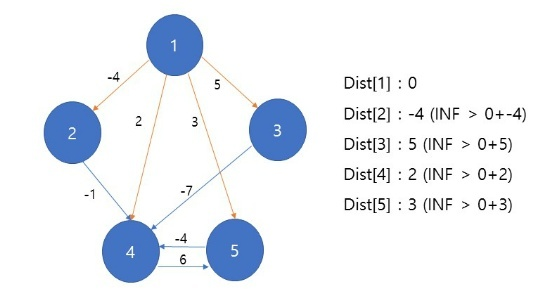
시작점부터 나갈 수 있는 간선들을 탐색하면서 갱신되는 값이 정점의 dist 값보다 작으면 값을 업데이트한다. Dist[2]부터 Dist[5]값들이 INF값보다 작기 때문에 정점들이 모두 업데이트 된다.
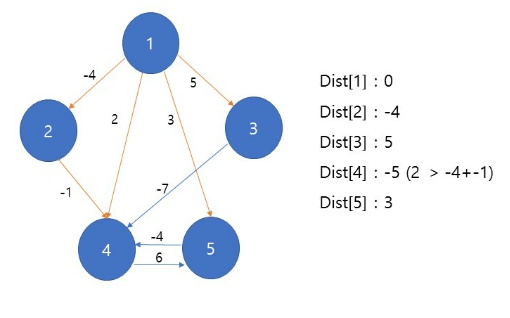
1번 정점이 끝났기 때문에 2번 정점으로 넘어간다. 2번 정점에 해당되는 간선들을 탐색할 때 4번 노드까지 가는 Dist[4]의 값이 업데이트 된다.
3~5번의 값도 이와 같은 방법으로 탐색한다.
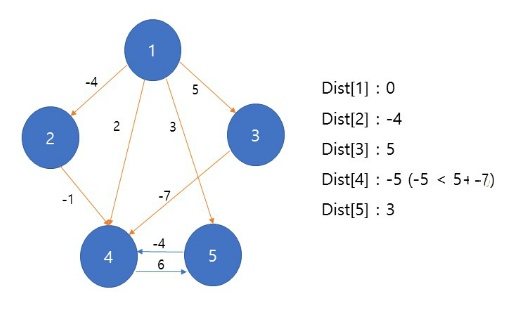
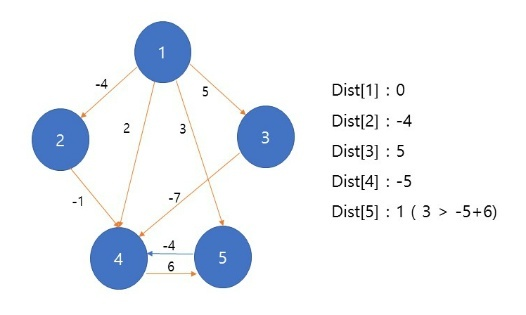
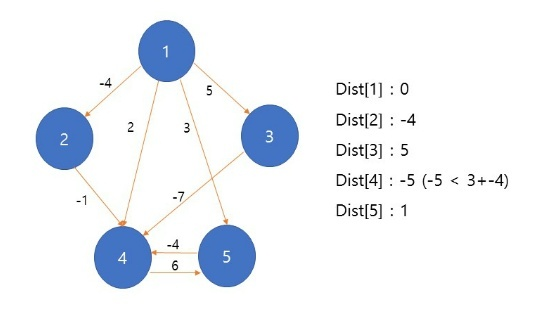
최종적으로 {0,-4,5,-5,1}의 값이 결과로 도출된다.
_
벨만-포드의 알고리즘은 음의 사이클이 존재한다는 특징이 있다. 음의 사이클은 그래프의 존재하는 사이클의 가중치 값이 음수인 경우를 뜻한다. 음수 사이클을 찾으려면 V까지의 반복을 하지 않고 한 번 더 해당 과정을 반복하는 것이 답이 된다. 이 과정을 거치면 음수 사이클이 존재하여 Dist의 특정값에 - 가중치를 더해주는 경우가 생긴다. V+1번재 탐색을 수행한 뒤 업데이트 되는 값이 존재하는지의 여부를 발견할 때 음수 사이클이 존재한다는 것을 알 수 있다.
_
벨만-포드 알고리즘을 구현한 소스 코드이다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <limits.h>
// 간선 구조체
// src = 시작점, dest = 도착점, weight = 가중치
struct Edge
{
int src, dest, weight;
};
// 그래프 구조체
// V :: 정점의 수 E :: 간선의 수
// edge :: 포인터 형식으로 서로 다른 정점을 연결하기 위해 존재
struct Graph
{
int V, E;
struct Edge* edge;
};
// V와 E를 통해 정점과 간선의 수를 가진 그래프를 생성한다.
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E)
{
struct Graph* graph = (struct Graph*) malloc(sizeof(struct Graph));
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = (struct Edge*) malloc(graph->E * sizeof(struct Edge));
return graph;
}
// 결과를 출력하기 위한 함수
void printArr(int dist[], int n)
{
printf("Vertex Distance from Source\n");
for (int i = 0; i < n; ++i)
dist[i] == INT_MAX ? printf("%d \t\tINF\n", i) : printf("%d \t\t %d\n", i, dist[i]);
}
// src에서 모든 다른 정점까지의 최단 거리를 찾아주는 BellmanFord 함수이다.
// 음의 가중치 까지 적용이 가능하다.
void BellmanFord(struct Graph* graph, int src)
{
int V = graph->V;
int E = graph->E;
int *dist = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*V); // int dist[V+1]과 같다.
// 모든 최단 거리를 무한대로 지정해주고,
// 시작점(src)만 0으로 초기화 한다.
for (int i = 0; i < V; i++)
dist[i] = INT_MAX;
dist[src] = 0;
// 벨만 포드 알고리즘
for (int i = 1; i <= V - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < E; j++)
{
int u = graph->edge[j].src;
int v = graph->edge[j].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[j].weight;
// 정점u가(시작점이) 무한대가 아니고,
// 시작점까지의 최단 거리 + 가중치가 도착점의 가중치
// 보다 작을 때 업데이트 해준다.
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
dist[v] = dist[u] + weight;
}
}
// 음의 가중치 때문에 무한히 최단 경로가 작아지는 것이 있다면
// 탐색하여 알려준다.
for (int i = 0; i < E; i++)
{
int u = graph->edge[i].src;
int v = graph->edge[i].dest;
int weight = graph->edge[i].weight;
// if문에서 현재위치 최단거리 + 가중치가 계속해서 더 작아질 경우
// 음의 사이클이 있다고 판단한다.
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[u] + weight < dist[v])
printf("Graph contains negative weight cycle\n");
}
printArr(dist, V);
return;
}
int main()
{
int V = 5; // 정점의 수
int E = 9; // 간선의 수
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// 그래프 정보를 입력해준다.
graph->edge[0].src = 0; // 0에서
graph->edge[0].dest = 2; // 2로 가는 간선의
graph->edge[0].weight = 1; // 가중치는 1로 정한다.
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 3;
graph->edge[1].weight = 5;
graph->edge[2].src = 1;
graph->edge[2].dest = 2;
graph->edge[2].weight = -2;
graph->edge[3].src = 2;
graph->edge[3].dest = 1;
graph->edge[3].weight = 4;
graph->edge[4].src = 2;
graph->edge[4].dest = 3;
graph->edge[4].weight = 4;
graph->edge[5].src = 3;
graph->edge[5].dest = 0;
graph->edge[5].weight = -1;
graph->edge[6].src = 3;
graph->edge[6].dest = 1;
graph->edge[6].weight = 3;
graph->edge[7].src = 4;
graph->edge[7].dest = 0;
graph->edge[7].weight = 1;
graph->edge[8].src = 4;
graph->edge[8].dest = 2;
graph->edge[8].weight = -1;
BellmanFord(graph, 0);
return 0;
}
출처: 벨만 포드 알고리즘 소스 코드 - Crocus[실행 결과]
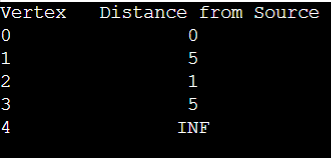
_
2. Leet code : 743. Network Delay Time

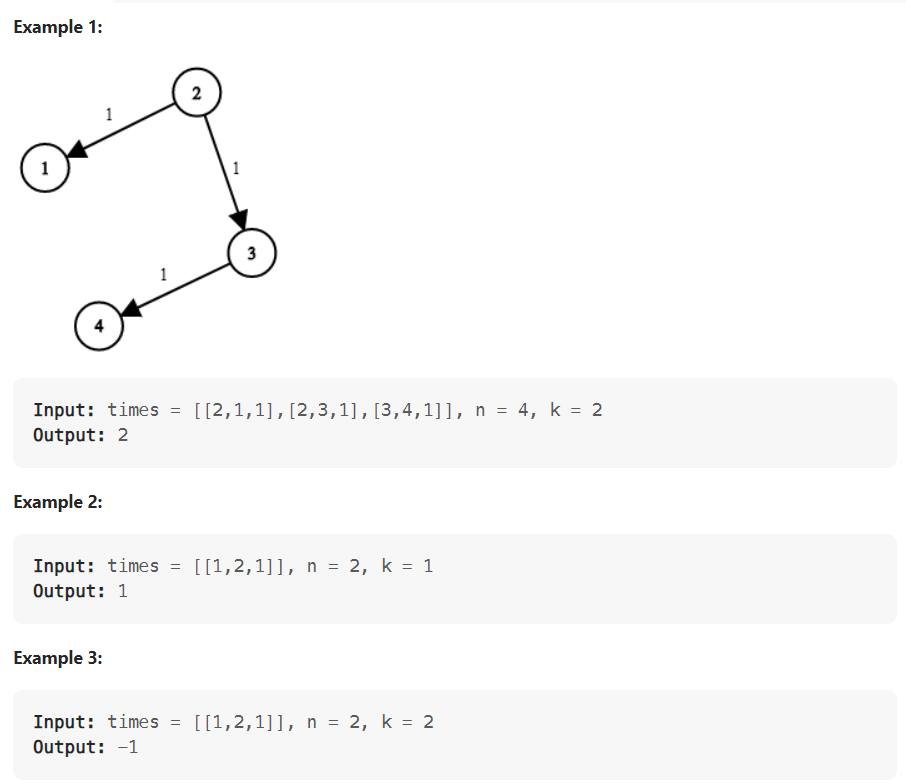
2.1. 다익스트라를 이용한 풀이
class Solution {
public:
// 인접 목록, 최대 노드 수에 따라 정의된다.
// 그러나 입력 크기로도 정의할 수 있다.
vector<pair<int, int>> adj[101];
void dijkstra(vector<int>& signalReceivedAt, int source, int n) {
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>,
greater<pair<int, int>>> pq;
pq.push({0, source});
// 시작 노드의 시간은 0이다.
signalReceivedAt[source] = 0;
while (!pq.empty()) {
int currNodeTime = pq.top().first;
int currNode = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (currNodeTime > signalReceivedAt[currNode]) {
continue;
}
// 신호를 인접 노드로 브로드캐스트한다.
for (pair<int, int> edge : adj[currNode]) {
int time = edge.first;
int neighborNode = edge.second;
// 이웃 노드에 대한 가장 빠른 시간
// signalReceivedAt[currNode] + time :
// 신호가 이웃 노드에 도달하는 시간
if (signalReceivedAt[neighborNode] > currNodeTime + time) {
signalReceivedAt[neighborNode] = currNodeTime + time;
pq.push({signalReceivedAt[neighborNode], neighborNode});
}
}
}
}2.2. 벨만포드를 이용한 풀이
class Solution {
public:
int networkDelayTime(vector<vector<int>>& times, int N, int K) {
int res = 0;
vector<int> dist(N + 1, INT_MAX);
dist[K] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < N; ++i) {
for (auto e : times) {
int u = e[0], v = e[1], w = e[2];
if (dist[u] != INT_MAX && dist[v] > dist[u] + w) {
dist[v] = dist[u] + w;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= N; ++i) {
res = max(res, dist[i]);
}
return res == INT_MAX ? -1 : res;
}
};_
3. 백준 문제 : 1916번 (옵션)
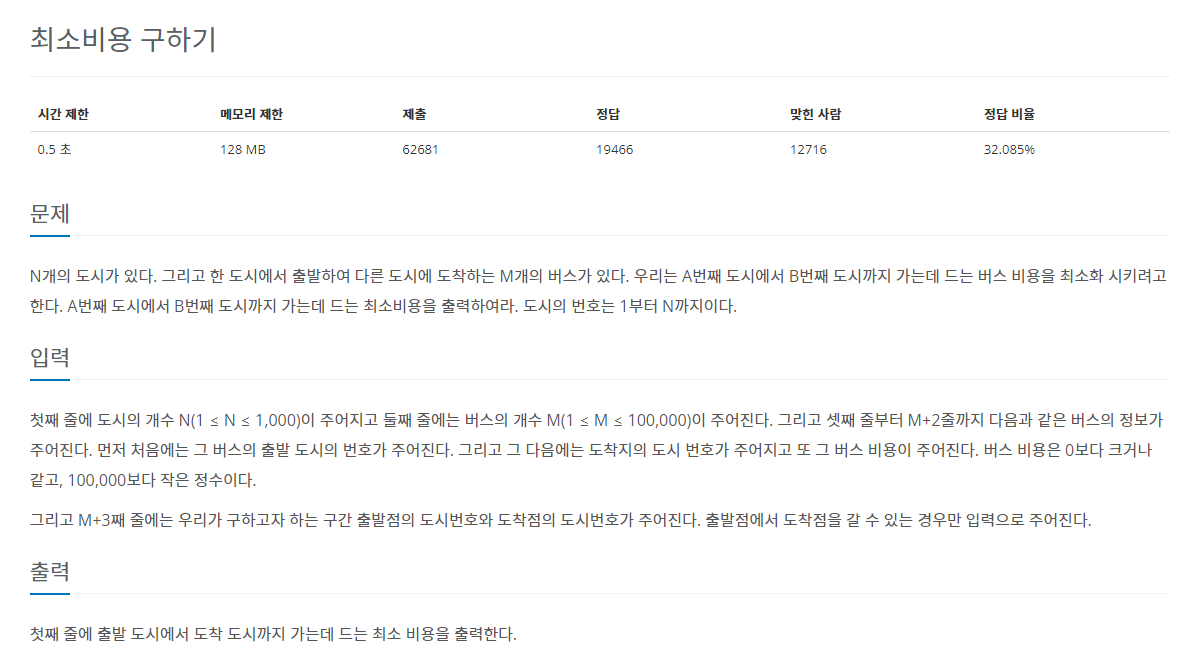
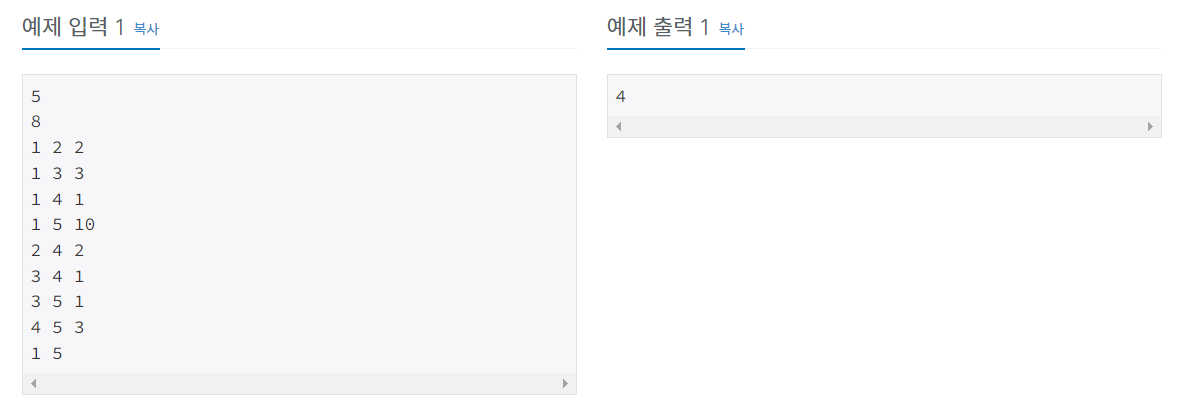
3.1. 다익스트라를 이용한 풀이
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
#define INF 987654321
using pii= pair<int, int>;
vector<pii> vec[1001];
vector<int> dist(1001, INF);
void dijkstra(int dept){
dist[dept] =0;
priority_queue<pii> pq;
pq.push({dist[dept], dept}); // 시작 weight, vertex
while(!pq.empty()){
int cur = pq.top().second;
int distance = pq.top().first * -1;
pq.pop();
if(dist[cur]<distance) continue;
for(int i=0; i<vec[cur].size(); i++){
int nxt=vec[cur][i].first;
int nxtdist = vec[cur][i].second + distance;
if(nxtdist<dist[nxt]){
dist[nxt]= nxtdist;
pq.push({nxtdist*-1, nxt});
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int N, M; cin>>N>>M; //도시의 개수, 버스의 개수
while(M--){
int s, e, w; cin>>s>>e>>w;
vec[s].push_back({e, w});
}
int dept, dest;
cin>>dept>>dest;
dijkstra(dept);
cout<<dist[dest];
return 0;
}3.2. 벨만포드를 이용한 풀이
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#define INF 987654321
using namespace std;
int V,M;
vector<pair<int, int> > v[1001];
int upper[1001];
int bellmanFord(int src) {
//시작점 제외 모든 정점까지의 최단거리 INF로 초기화
fill_n(upper, 1001, INF);
upper[src] = 0;
bool updated;
for(int i = 0; i < V; i++) {
updated = false;
for(int j = 1; j <= V; j++)
for(int k = 0; k < v[j].size(); k++) {
int there = v[j][k].first;
int cost = v[j][k].second;
if(upper[there] > upper[j] + cost) { // 완화 성공
upper[there] = upper[j] + cost;
updated = true;
}
}
if(!updated) break; //모든 간선에 대해 완화가 실패할경우 break;
}
if(updated) return 1; //음수 사이클이 존재
return 0;
}
int main(void) {
//ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false); cin.tie(NULL);
cin >> V >> M;
for(int i = 0; i < M; i++) {
int a,b,c;
cin >> a >> b >> c;
v[a].push_back(make_pair(b, c));
}
int start, arrive; cin >> start >> arrive;
if(!bellmanFord(start))
cout<<upper[arrive];
return 0;
}
출처: 코딩하기 좋은 날 