문제
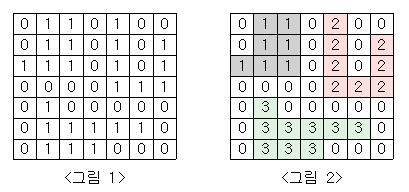
<그림 1>과 같이 정사각형 모양의 지도가 있다. 1은 집이 있는 곳을, 0은 집이 없는 곳을 나타낸다. 철수는 이 지도를 가지고 연결된 집의 모임인 단지를 정의하고, 단지에 번호를 붙이려 한다. 여기서 연결되었다는 것은 어떤 집이 좌우, 혹은 아래위로 다른 집이 있는 경우를 말한다. 대각선상에 집이 있는 경우는 연결된 것이 아니다. <그림 2>는 <그림 1>을 단지별로 번호를 붙인 것이다. 지도를 입력하여 단지수를 출력하고, 각 단지에 속하는 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오.
입력
첫 번째 줄에는 지도의 크기 N(정사각형이므로 가로와 세로의 크기는 같으며 5≤N≤25)이 입력되고, 그 다음 N줄에는 각각 N개의 자료(0혹은 1)가 입력된다.
출력
첫 번째 줄에는 총 단지수를 출력하시오. 그리고 각 단지내 집의 수를 오름차순으로 정렬하여 한 줄에 하나씩 출력하시오.
풀이
해당 문제는 bfs를 이용해서 풀 수 있다. 입력을 graph 배열에 넣어주고 같은 크기의 arr 배열을 생성했는데, 그 이유가 몇번째의 집인지 기억하기 위함이다. 따라서 graph에서 1이고 arr이 0일때는 bfs를 아직 하지 않은 곳이기 때문에 bfs를 수행한다. bfs를 수행하면서 arr의 해당 위치의 값을 count 값으로 변경하여 진행하면 된다.
최종적으로 count가 정해지면 그 값의 길이만큼 새롭게 배열을 만들어서 같은 번호의 집의 개수를 세어 넣어준 뒤 정렬하여 출력하면 된다.
소스
import java.util.*;
class Node {
private int x;
private int y;
public Node(int x, int y) {
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
}
public class Main {
public static int n;
public static int[][] graph, arr;
public static int[] dx = { -1, 1, 0, 0 };
public static int[] dy = { 0, 0, -1, 1 };
public static void bfs(int x, int y, int count) {
Queue<Node> q = new LinkedList<Node>();
q.offer(new Node(x, y));
arr[x][y] = count;
while (!q.isEmpty()) {
Node node = q.poll();
x = node.getX();
y = node.getY();
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
int nx = x + dx[i];
int ny = y + dy[i];
if (0 <= nx && nx < n && 0 <= ny && ny < n) {
if (graph[nx][ny] == 1 && arr[nx][ny] == 0) {
q.offer(new Node(nx, ny));
arr[nx][ny] = count;
}
}
}
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine();
graph = new int[n][n];
arr = new int[n][n];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
String str = sc.nextLine();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
graph[i][j] = str.charAt(j) - '0';
}
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (graph[i][j] == 1 && arr[i][j] == 0) {
bfs(i, j, ++count);
}
}
}
int[] ans = new int[count];
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
if (arr[i][j] != 0) {
ans[arr[i][j] - 1] += 1;
}
}
}
Arrays.sort(ans);
System.out.println(count);
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
System.out.println(ans[i]);
}
}
}