<수업 내용>
boxplot
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def box_plot_test():
n_student = 100
math_scores = np.random.normal(loc=50, scale=10, size=(100,))
fig, axes = plt.subplots(nrows=3, ncols=4, figsize=(20, 15))
# axes = axes.flatten()
axes[0, 0].boxplot(math_scores)
axes[0, 0].set_title('basic')
axes[0, 1].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True)
axes[0, 2].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, whis=2)
axes[0, 3].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, whis=1, sym='bx')
axes[1, 0].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, showfliers=False)
axes[1, 1].boxplot(math_scores, notch=True, showfliers=False, vert=False)
median_props = {'linewidth': 2, 'color': 'k'}
axes[1, 2].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props)
box_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'k', 'alpha': 0.7}
axes[1, 3].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props, boxprops=box_props)
whisker_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue', 'alpha': 0.8}
axes[2, 0].boxplot(math_scores, medianprops=median_props, boxprops=box_props,
whiskerprops=whisker_props, capprops=whisker_props)
box_plot_test()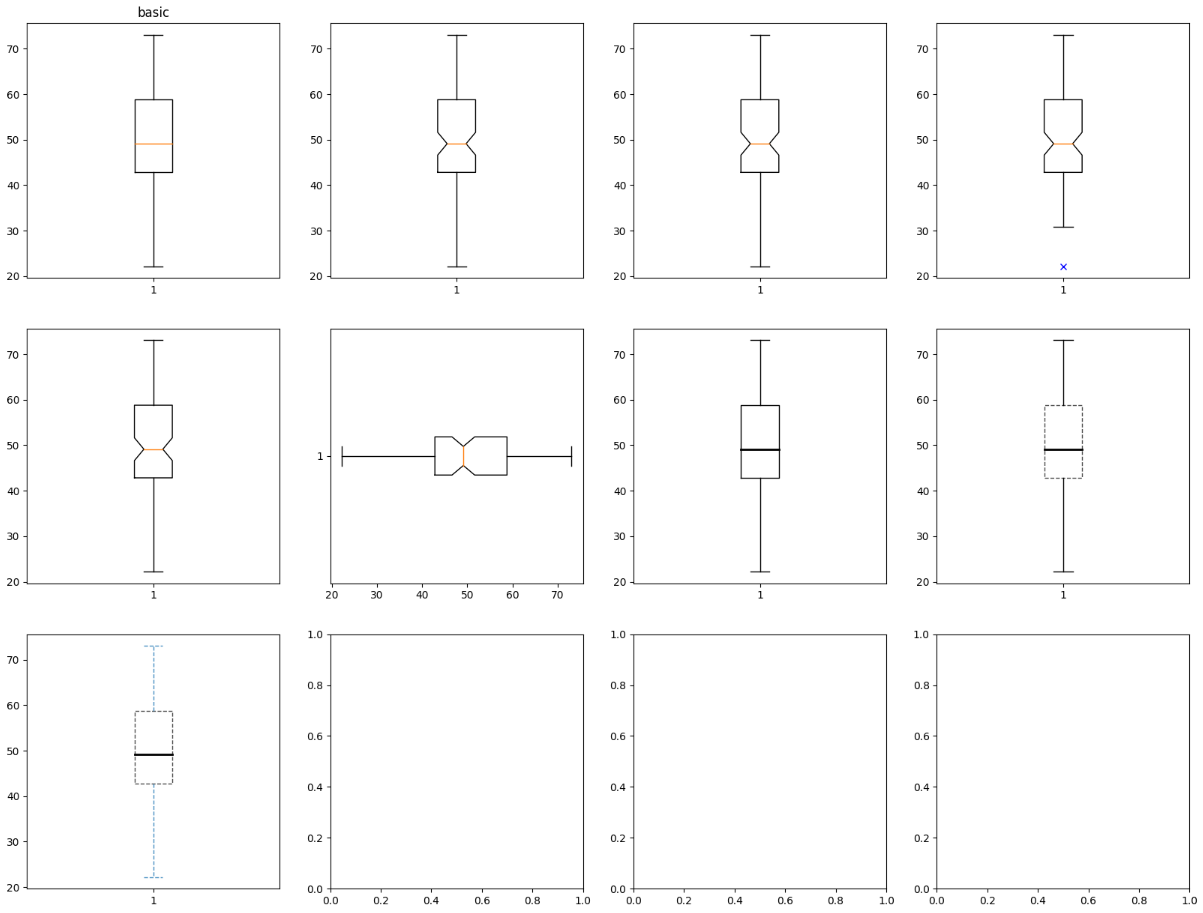
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
n_student=100
math_score=np.random.normal(loc=50,scale=15, size=(100,1))
chem_score=np.random.normal(loc=70,scale=10,size=(n_student,1))
phy_score=np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(n_student,1))
pro_score=np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(n_student,1))
data=np.hstack((math_score,chem_score,phy_score,pro_score))
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7))
ax.set_ylim([0,100])
ax.boxplot(data)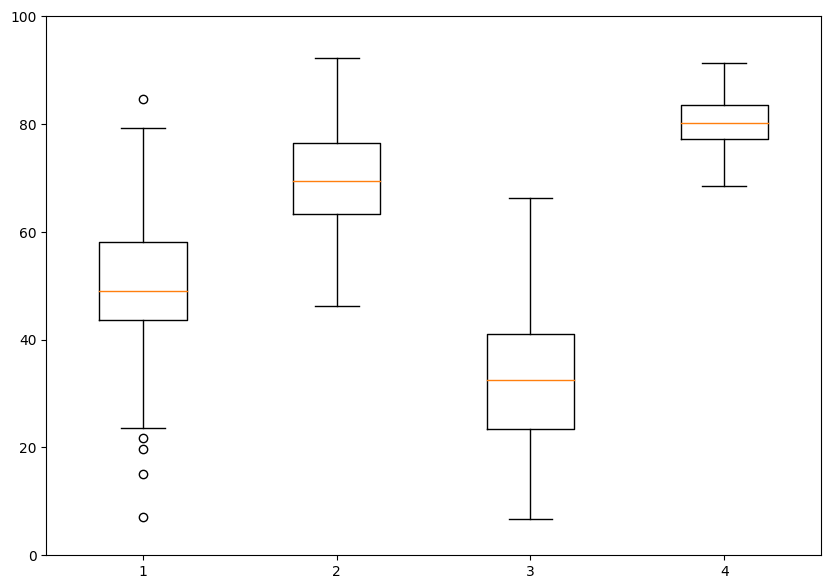
실습
n_student=100
math_score=np.random.normal(loc=50,scale=15, size=(100,1))
chem_score=np.random.normal(loc=70,scale=10,size=(n_student,1))
phy_score=np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(n_student,1))
pro_score=np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(n_student,1))
data=np.hstack((math_score,chem_score,phy_score,pro_score))
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7))
ax.set_ylim([0,100])
whisker_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue', 'alpha': 0.8}
ax.boxplot(data,notch=True, whis=1, whiskerprops=whisker_props, capprops=whisker_props)
ax.set_xticklabels(['Math', 'English','Pysics','Programming'], rotation=30, fontsize=15)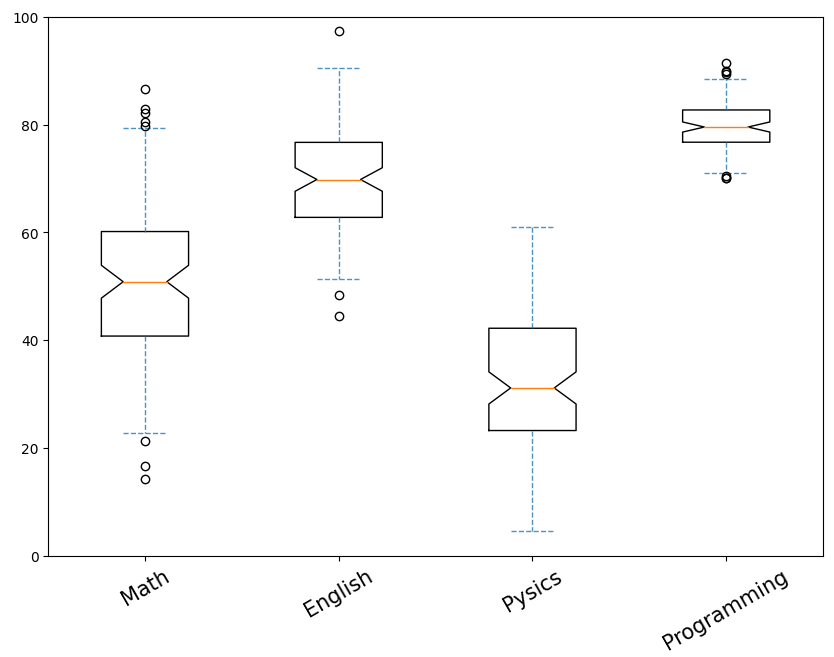
실습 정답
plt.style.use('seaborn')
n_student=100
math_score=np.random.normal(loc=50,scale=15, size=(100,1))
chem_score=np.random.normal(loc=70,scale=10,size=(n_student,1))
phy_score=np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(n_student,1))
pro_score=np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(n_student,1))
data=np.hstack((math_score,chem_score,phy_score,pro_score))
medianprops={'linewidth':1.5,'color':'tab:red'}
boxprops={'linewidth':1.5,'color':'k','alpha':0.7}
whisker_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue', 'alpha': 0.8}
fig,ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,7))
ax.set_ylim([0,100])
ax.boxplot(data,notch=True, whis=1,medianprops=medianprops,boxprops=boxprops, whiskerprops=whisker_props, capprops=whisker_props)
ax.set_xticklabels(['Math', 'English','Pysics','Programming'], rotation=30, fontsize=15)
major_yticks=np.arange(0,101,20)
minor_yticks=np.arange(0,101,5)
ax.set_yticks(major_yticks)
ax.set_yticks(minor_yticks, minor=True)
ax.tick_params(labelsize=20)
ax.tick_params(axis='x',labelrotation=10)
ax.grid(axis='y',linewidth=2)
ax.grid(axis='y',which='minor',linewidth=2,linestyle=':')
ax.grid(axis='x',linewidth=0)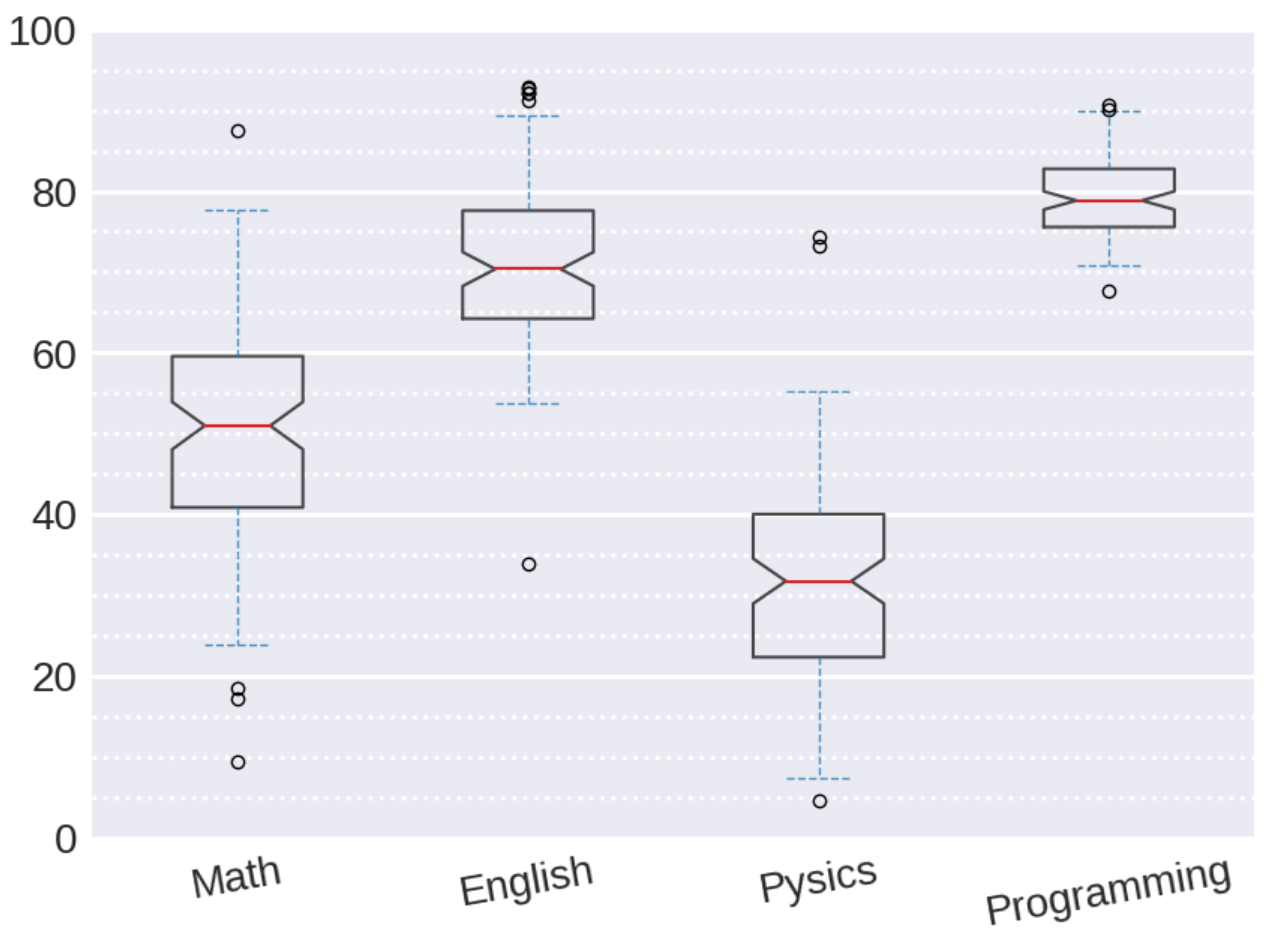
plt.style.use('seaborn')
n_student=100
math_score=np.random.normal(loc=50,scale=15, size=(100,1))
chem_score=np.random.normal(loc=70,scale=10,size=(n_student,1))
phy_score=np.random.normal(loc=30, scale=12, size=(n_student,1))
pro_score=np.random.normal(loc=80, scale=5, size=(n_student,1))
data=np.hstack((math_score,chem_score,phy_score,pro_score))
medianprops={'linewidth':1.5,'color':'tab:red'}
boxprops={'linewidth':1.5,'color':'k','alpha':0.7}
whisker_props = {'linestyle': '--', 'color': 'tab:blue', 'alpha': 0.8}
fig,ax=plt.subplots(2,1,figsize=(10,7))
ax[0].boxplot(data)
ax[1].violinplot(data)
ax[0].set_ylim([0,100])
ax[1].set_ylim([0,100])
ax[0].tick_params(labelsize=20,bottom=False,labelbottom=False)
ax[1].tick_params(labelsize=20)
## fig.subplots_adjust(hspace=0.1)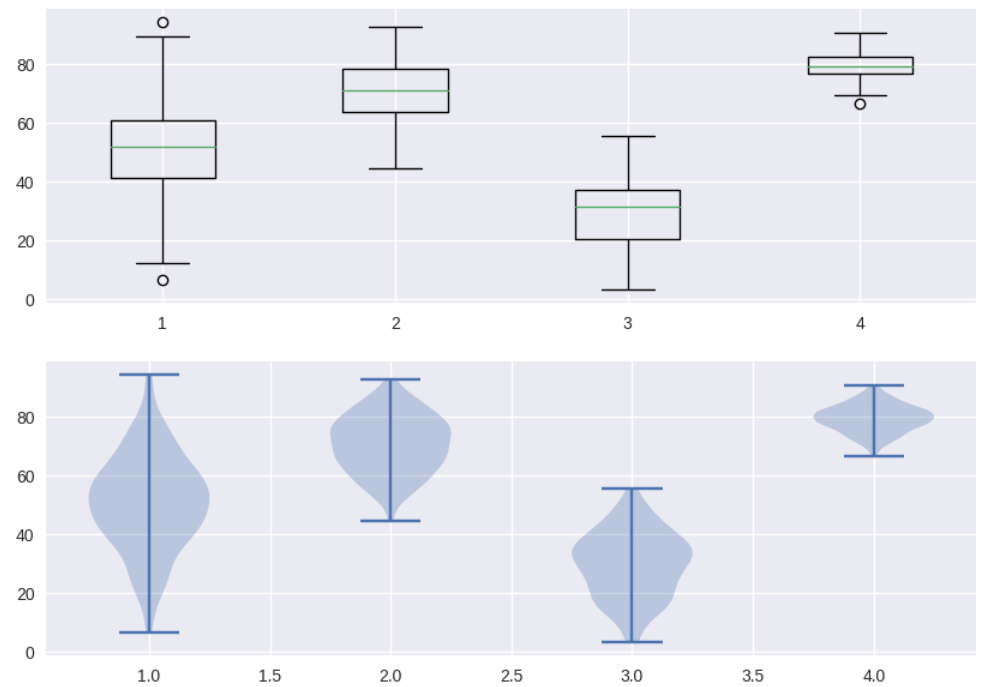
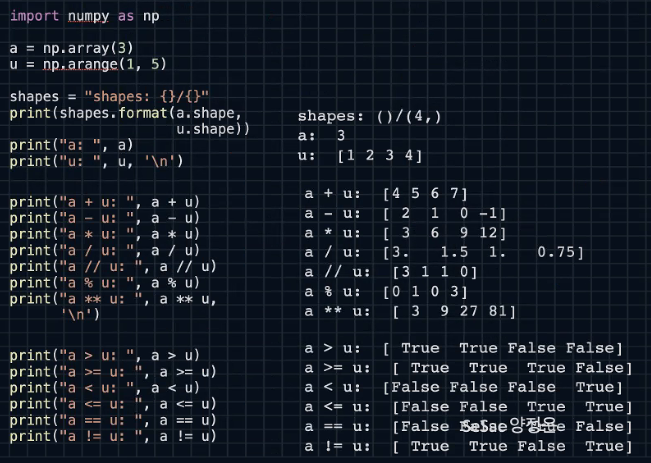
Numpy
- 파이썬 메소드 dir
a=[1,2,3]
for arr in dir(a):
print(arr)- 파이썬 리스트와 numpy array 차이
#파이썬으로 리스트의 원소들 더하기
u=[1,2,3]
v=[4,5,6]
W=u+v
W
>>[1,2,3,4,5,6]
w=[0]*len(u)
for data_idx in range(len(u)):
w[data_idx]=u[data_idx]+v[data_idx]
print(w)
>>[5,6,7]#넘파이로 array의 원소들 더하기
u=np.array([1,2,3])
v=np.array([4,5,6])
w=u+v
w
>>array([5, 7, 9])- numpy array의 shape확인 하기
#numpy array의 shape확인 하기
scalar_np=np.array(3.14)
vec_np=np.array([1,2,3])
mat_np=np.array([[1,2],[3,4]])
tensor_np=np.array([[[1,2,3],[4,5,6]],[[11,12,13],[14,15,16]]])
print(scalar_np.shape)
print(vec_np.shape)
print(mat_np.shape)
print(tensor_np.shape)
>>
()
(3,)
(2, 2)
(2, 2, 3)numpy array 생성하기
np.zeros((2,3))
>>
array([[0., 0., 0.],
[0., 0., 0.]])
np.ones((2,3))
>>
array([[1., 1., 1.],
[1., 1., 1.]])
np.full((2,3),3.14)
>>
array([[3.14, 3.14, 3.14],
[3.14, 3.14, 3.14]])
np.arange(2,5)
>>
array([2, 3, 4])
np.arange(2,10,2) #마지막 2는 원소의 간격
>>
array([2, 4, 6, 8])
np.linspace(0,1,5) # 마지막 5는 출력할 원소의 개수
>>
array([0. , 0.25, 0.5 , 0.75, 1. ])난수 생성
fig, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
random_value=np.random.randn(300) # 표준정규분포를 따르는 난수 300개 생성
ax.hist(random_value, bins=20)
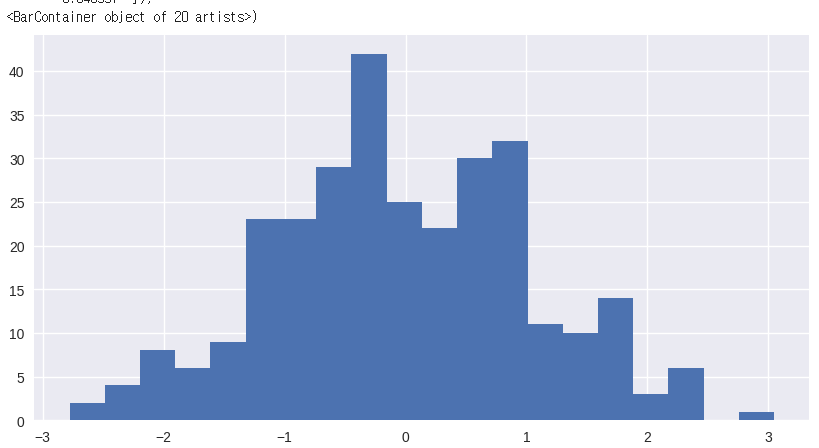
# 200X3 matrix의 정규분포를 따르는 난수 생성(3개의 열의 평균이 각각 -2,0,3이고 표준편차가 1,2,3
normal=np.random.normal(loc=[-2,0,3], scale=[1,2,3], size=(200,3))
normal
# 3개의 열이 모두 평균이 -2 표준편차가 1
normal=np.random.normal(loc=-2, scale=1, size=(200,3))
normalfrom numpy.random import uniform
plt.style.use('seaborn')
fig, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
uniform=np.random.rand(1000)#0,1 사이에서 1000개의 숫자를 임의로 뽑는다
ax.hist(uniform, bins=20)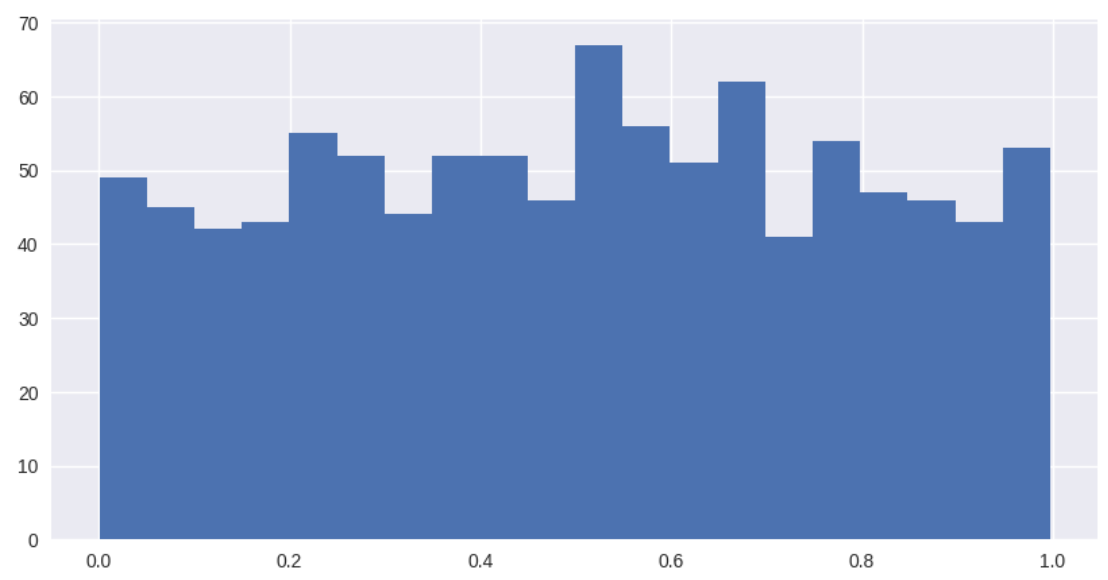
from numpy.random import uniform
plt.style.use('seaborn')
fig, ax=plt.subplots(figsize=(10,5))
#구간내에서 size만큼의 숫자를 임의로 생성
uniform=np.random.uniform(low=-10,high=10,size=10000)
ax.hist(uniform,bins=20)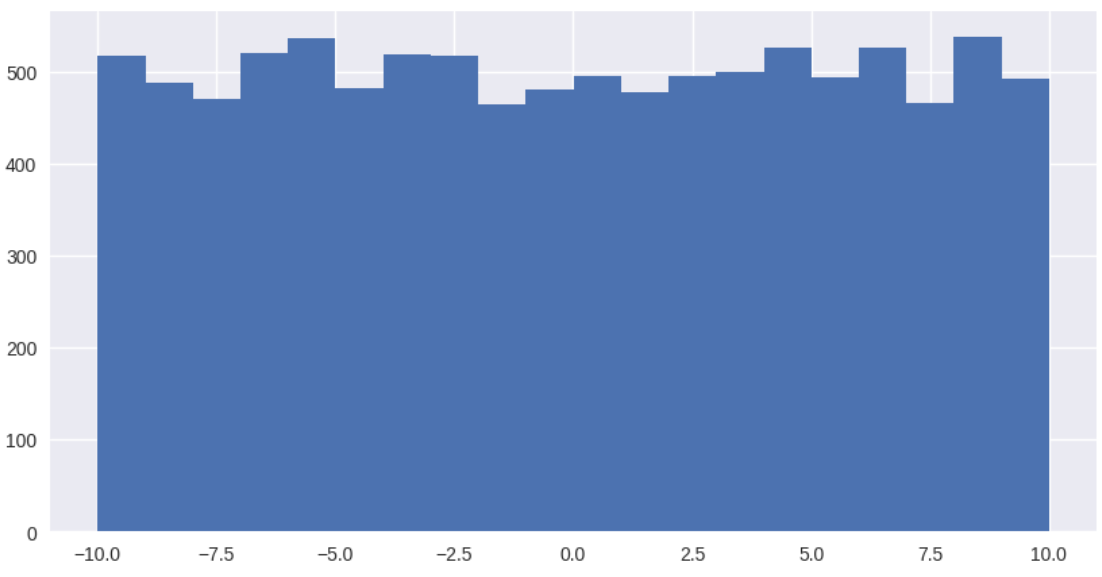
ranint=np.random.randint(low=0,high=7,size=20) #정수만 임의로 생성
ranint
>>
array([1, 2, 6, 3, 3, 3, 3, 4, 5, 0, 5, 0, 1, 5, 3, 6, 5, 2, 2, 4])array의 shape
A=np.ones(shape=(10,))
B=np.ones(shape=(3,4))
C=np.ones(shape=(3,4,5))
D=np.ones(shape=(2,3,4,5,6))
print(A.size)
print(B.size)
print(C.size)
print(D.size)
>>
10
12
60
720#reshape
a=np.arange(6)
b=np.reshape(a,(2,3))
print(a)
print(b)
>>
[0 1 2 3 4 5]
g
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]]
a=np.arange(24)
b=np.reshape(a,(2,3,4))
print(a)
print(b)
>>
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23]
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]
a=np.arange(12)
b=a.reshape((2,-1))
c=a.reshape((3,-1))
d=a.reshape((4,-1))
e=a.reshape((6,-1))
print(b.shape, c.shape, d.shape, e.shape)
>>
(2, 6) (3, 4) (4, 3) (6, 2)#size에 shape까지 설정할 수 있다
a=np.random.randint(0,10,size=(2,2))
a
>>
array([[8, 9],
[1, 5]])
# flatten의 기능
M=np.arange(9)
N=M.reshape((3,3))
O=N.flatten()
print(M)
print(N)
print(O)
>>
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]]
[0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8]
M=np.arange(27)
N=M.reshape((3,3,3))
O=N.flatten()
print(M)
print(N)
print(O)
>>
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26]
[[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8]]
[[ 9 10 11]
[12 13 14]
[15 16 17]]
[[18 19 20]
[21 22 23]
[24 25 26]]]
[ 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26]BroadCasting
-
shape이 서로 다른 두 matrix의 산술연산을 가능하게 한다
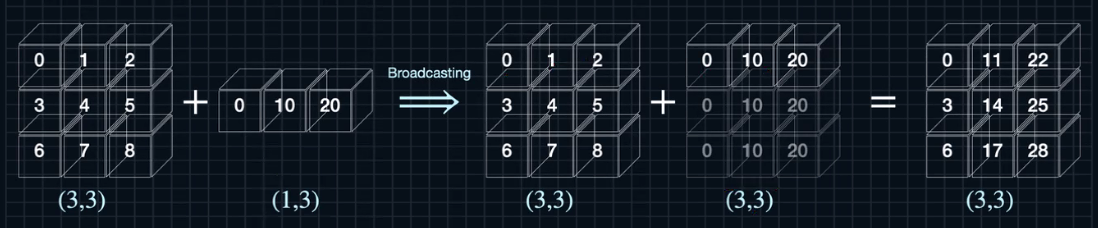
-
차원이 같은 shape이 다른 텐서
A=np.arange(9).reshape(3,3) #2차 텐서
B=10*np.arange(3).reshape(-1,3) #2차 텐서
print(A)
print(B)
>>
[[0 1 2]
[3 4 5]
[6 7 8]]
[[ 0 10 20]]
C=A+B
print(C)
>>
[[ 0 11 22]
[ 3 14 25]
[ 6 17 28]]
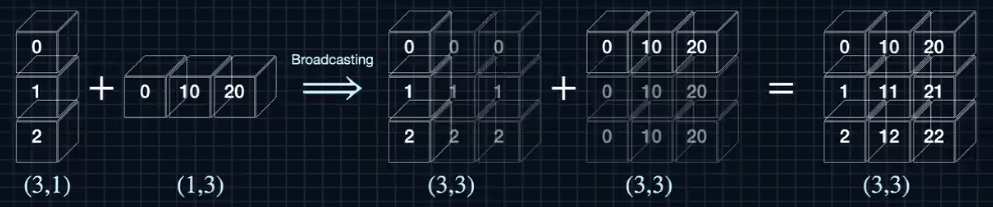
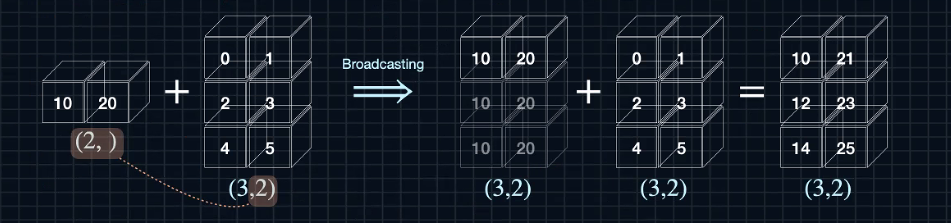
A=np.arange(3).reshape(3,-1)
B=10*np.arange(3).reshape(-1,3)
print(A)
print(B)
>>
[[0]
[1]
[2]]
[[ 0 10 20]]
C=A+B
print(C)
>>
[[ 0 10 20]
[ 1 11 21]
[ 2 12 22]]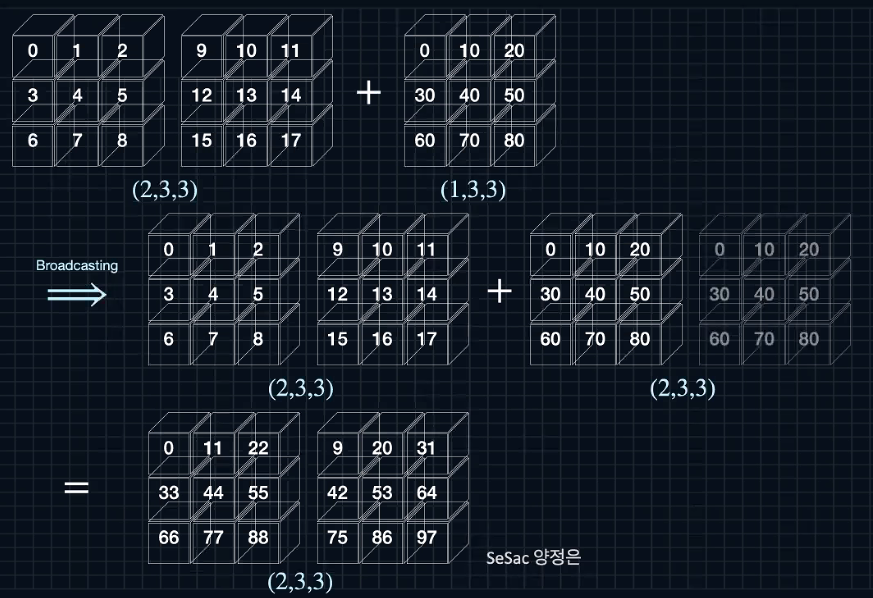
A=np.arange(18).reshape(2,3,3)
B=10*np.arange(9).reshape(1,3,3)
print(A)
print(B)
>>
[[[ 0 1 2]
[ 3 4 5]
[ 6 7 8]]
[[ 9 10 11]
[12 13 14]
[15 16 17]]]
[[[ 0 10 20]
[30 40 50]
[60 70 80]]]
C=A+B
print(C)
>>
[[[ 0 11 22]
[33 44 55]
[66 77 88]]
[[ 9 20 31]
[42 53 64]
[75 86 97]]]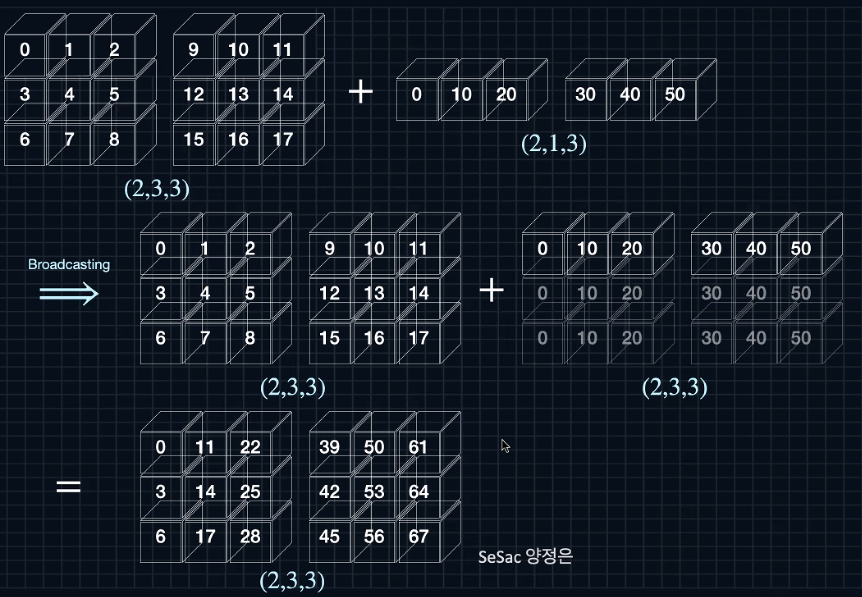
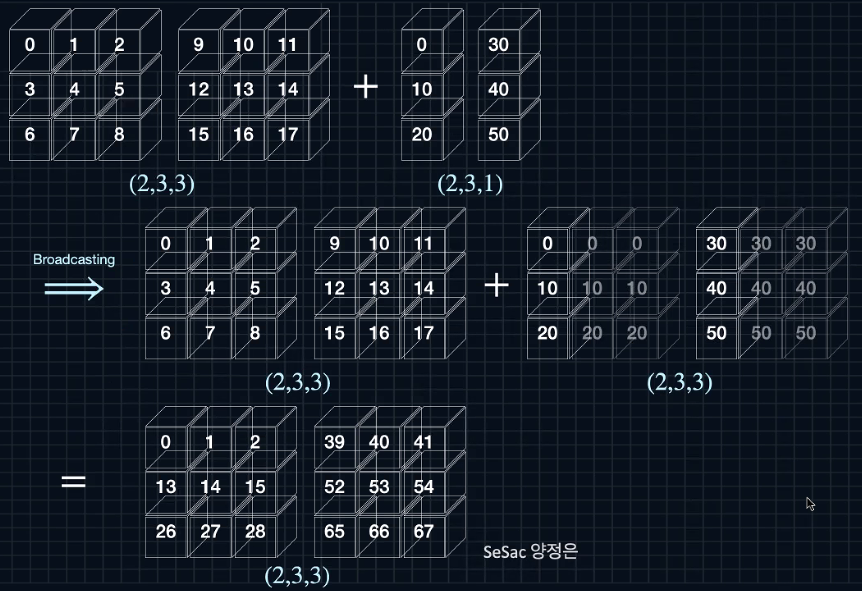
- 차원이 다른 텐서
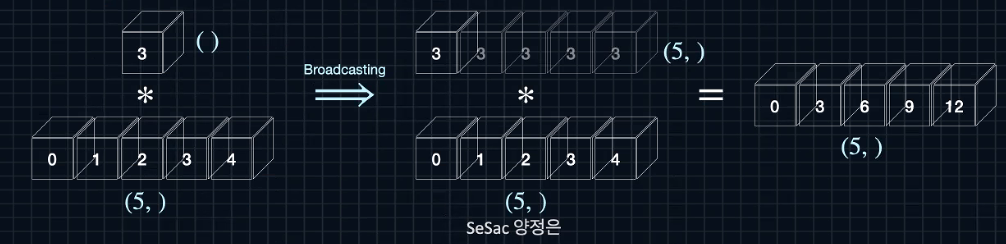
a=np.array(3) #스칼라
u=np.arange(5) #벡터
print(a)
print(u)
print(a*u)
>>
3
[0 1 2 3 4]
[ 0 3 6 9 12]
- 안쪽 수치가 동일해야 한다
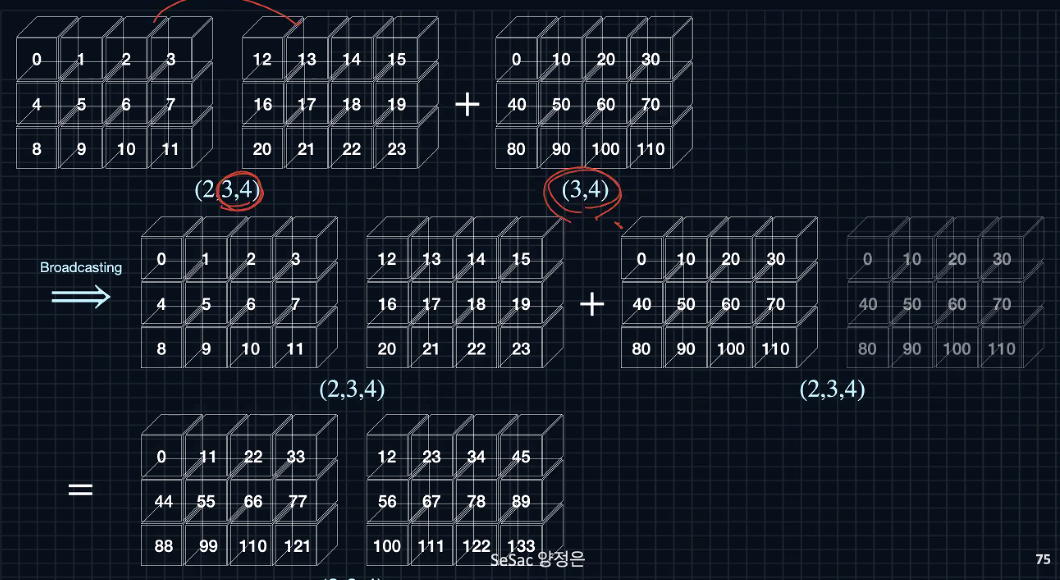
**(2,3,4)와 연산이 가능한 텐서는 (2,3,4), (3,4), (4,) (3,1)이다
a=np.arange(24).reshape(2,3,4)
u=np.arange(0,120,10).reshape(3,4)
print(a)
print(u)
print(a+u)
>>
[[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[[12 13 14 15]
[16 17 18 19]
[20 21 22 23]]]
[[ 0 10 20 30]
[ 40 50 60 70]
[ 80 90 100 110]]
[[[ 0 11 22 33]
[ 44 55 66 77]
[ 88 99 110 121]]
[[ 12 23 34 45]
[ 56 67 78 89]
[100 111 122 133]]]
array의 indexing & slicing
a=np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
a[2] # 3행 출력
>>
array([ 8, 9, 10, 11])
a=np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
a[0,1]
>>
1
a=np.arange(12).reshape(3,4)
print(a)
print(a[1:3,2])
>>
[[ 0 1 2 3]
[ 4 5 6 7]
[ 8 9 10 11]]
[ 6 10]