<수업 내용>
연속형 data(feature)의 decision tree
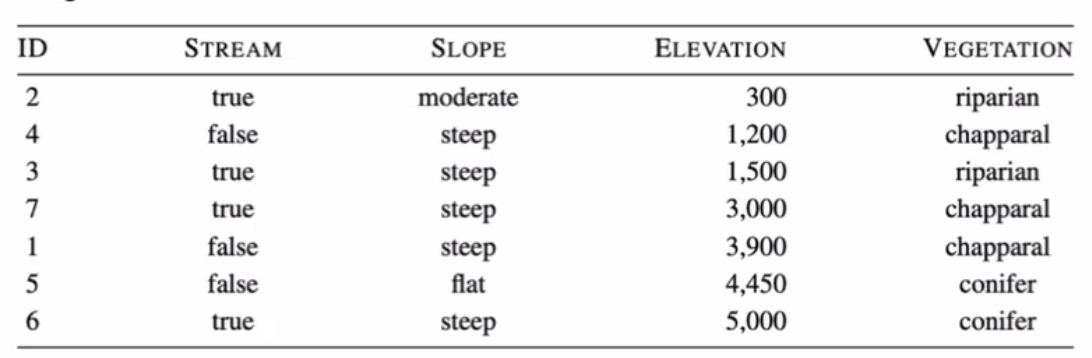
import numpy as np
total_entropy=-((2/7)*np.log2(2/7)+(3/7)*np.log2(3/7)+(2/7)*np.log2(2/7))
rem_stream=(4/7)*(-((2/4)*np.log2(2/4)+(1/2)*np.log2(1/4)))+(3/7)*(-((2/3)*np.log2(2/3)+(1/3)*np.log2(1/3)))
rem_slope=(5/7)*(-((3/5)*np.log2(3/5)+(2/5)*np.log2(1/5)))
IG_stream=total_entropy-rem_stream
IG_slope=total_entropy-rem_slope
rem_treshold_750=(6/7)*(-((3/6)*np.log2(3/6)+(1/6)*np.log2(1/6)+(2/6)*np.log2(2/6)))
rem_treshold_1350=(2/7)*(-((1/2)*np.log2(1/2)+(1/2)*np.log2(1/2)))+(5/7)*(-((1/5)*np.log2(1/5)+(2/5)*np.log2(2/5)+(2/5)*np.log2(2/5)))
rem_treshold_2250=(3/7)*(-((2/3)*np.log2(2/3)+(1/3)*np.log2(1/3)))+(4/7)*(-((2/4)*np.log2(2/4)+(2/4)*np.log2(2/4)))
rem_treshold_4175=(5/7)*(-((2/5)*np.log2(2/5)+(3/5)*np.log2(3/5)))
IG_treshold_750=total_entropy-rem_treshold_750
IG_treshold_1350=total_entropy-rem_treshold_1350
IG_treshold_2250=total_entropy-rem_treshold_2250
IG_treshold_4175=total_entropy-rem_treshold_4175
print(IG_stream,IG_slope,IG_treshold_750,IG_treshold_1350,IG_treshold_2250,IG_treshold_4175)
>>
0.30595849286804166 0.5774062828523452 0.3059584928680419 0.18385092540042125 0.5916727785823274 0.863120568566631- 첫 분기는 treshold_750가 기준이 된다
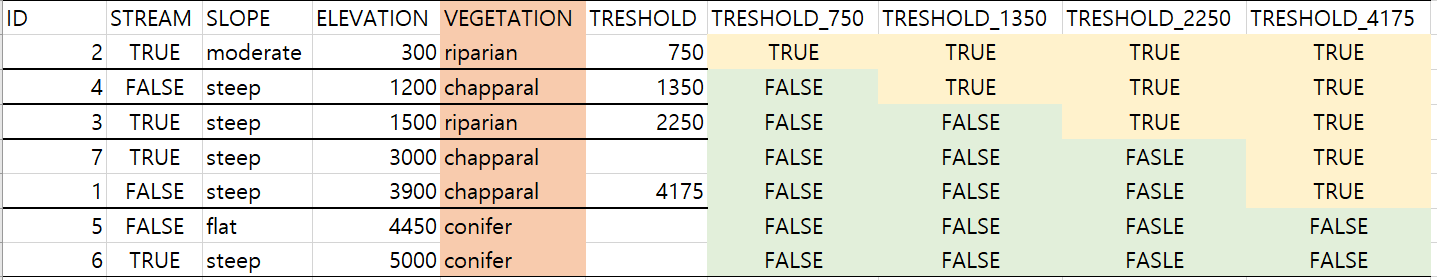
import numpy as np
total_entropy=-((2/5)*np.log2(2/5)+(3/5)*np.log2(3/5))
rem_stream=(3/5)*(-((2/3)*np.log2(2/3)+(1/3)*np.log2(1/3)))
rem_slope=(4/5)*(-((3/4)*np.log2(3/4)+(1/4)*np.log2(1/4)))
rem_treshold_750=(4/5)*(-((3/4)*np.log2(3/4)+(1/4)*np.log2(1/4)))
rem_treshold_1350=(2/5)*(-((1/2)*np.log2(1/2)+(1/2)*np.log2(1/2)))+(3/5)*(-((1/3)*np.log2(1/3)+(2/3)*np.log2(2/3)))
rem_treshold_2250=(3/5)*(-((2/3)*np.log2(2/3)+(1/3)*np.log2(1/3)))
IG_stream=total_entropy-rem_stream
IG_slope=total_entropy-rem_slope
IG_treshold_750=total_entropy-rem_treshold_750
IG_treshold_1350=total_entropy-rem_treshold_1350
IG_treshold_2250=total_entropy-rem_treshold_2250
print(IG_stream,IG_slope,IG_treshold_750,IG_treshold_1350,IG_treshold_2250)
>>
0.4199730940219749 0.3219280948873623 0.3219280948873623 0.01997309402197489 0.4199730940219749- 두 번째 분기는 treshold_2250 혹은 IG_stream로 잡으면 된다
- IG_stream로 해보자
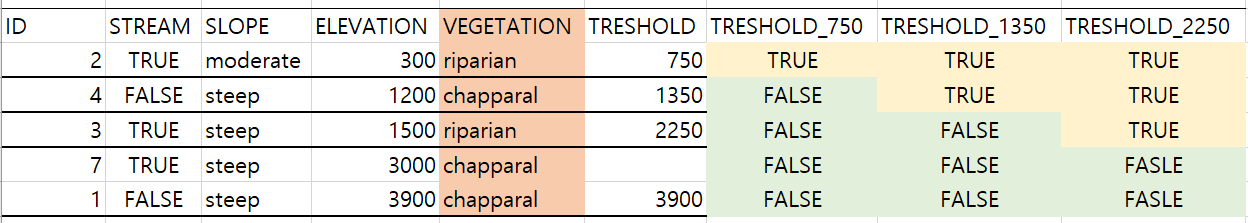
- 세 번째 분기가 treshold_2250된다
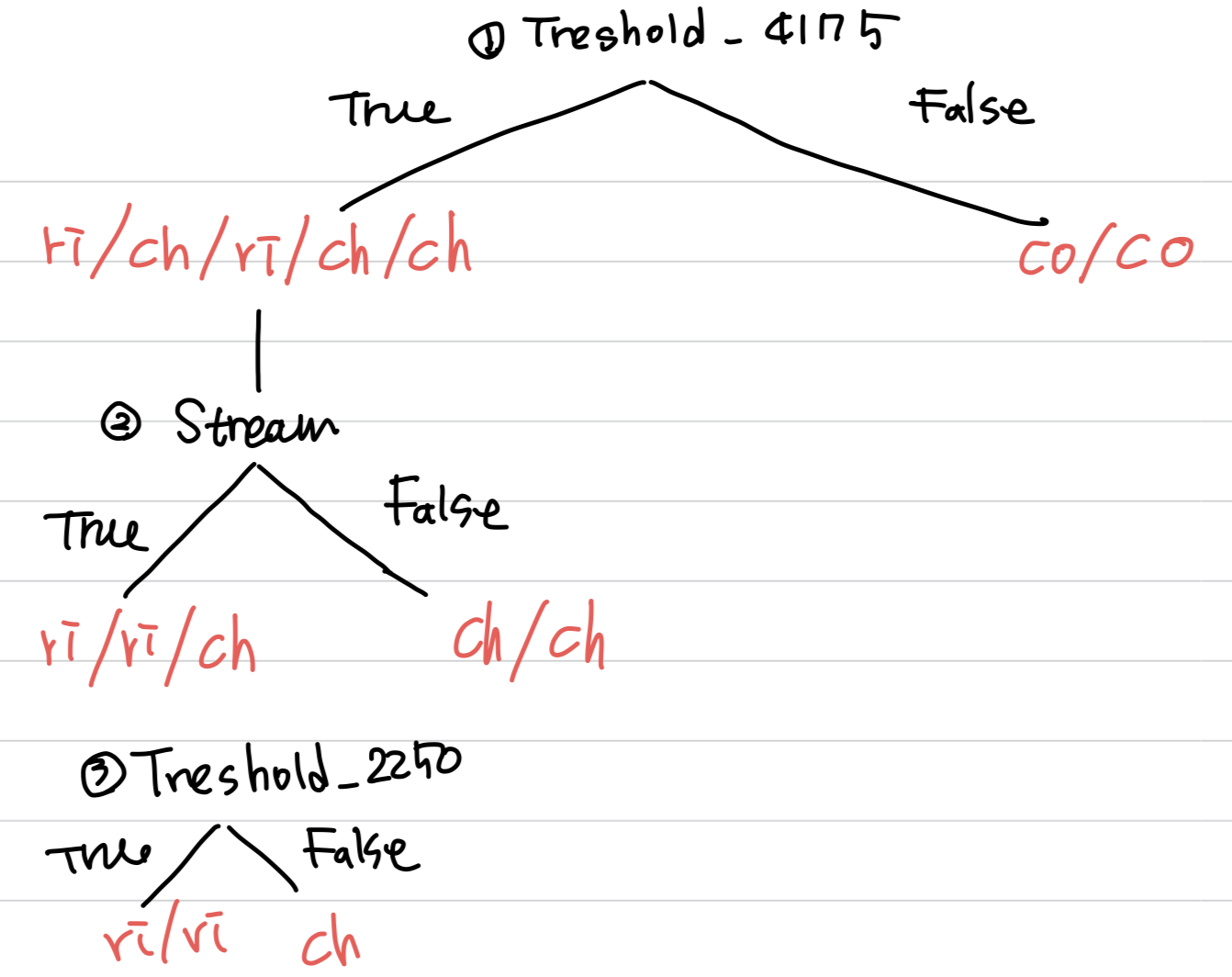
연속형 data(target)의 decision tree

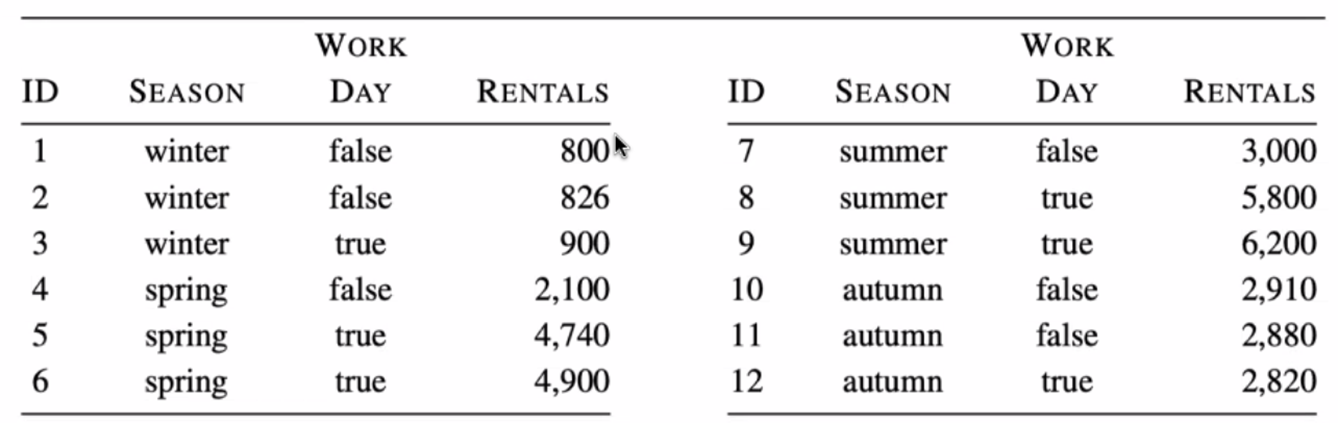
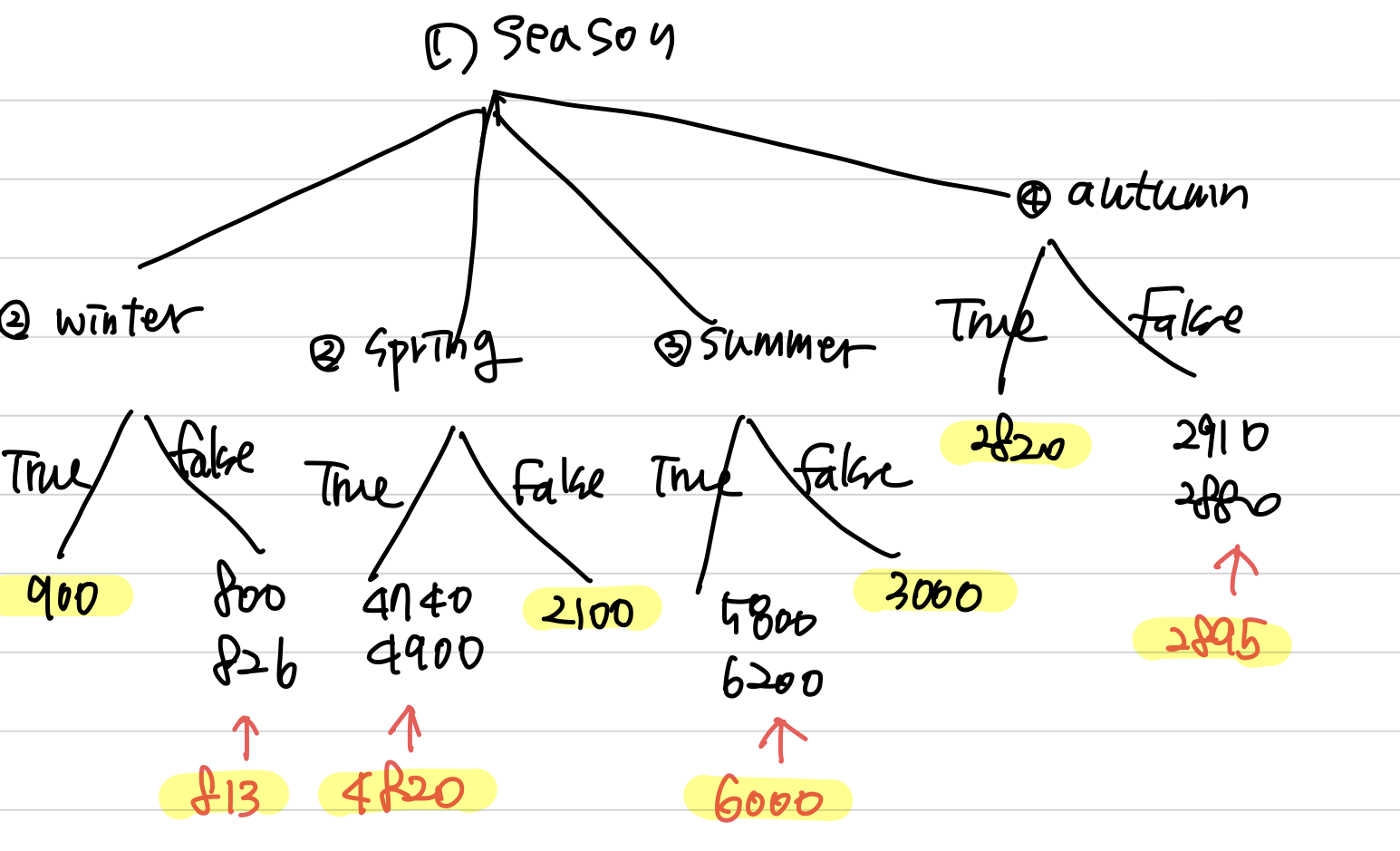
1. season의 winter, spring, summer, autumn에 대한 rentals의 분산을 각각 구하면
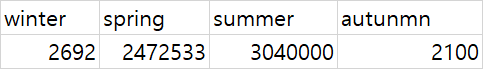
2. 위의 값에 각각 가중치 를 곱하여 더하면 이 된다.
3. work day의 true, false에 대한 rentals의 분산을 각각 구하면
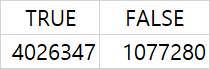
4. 위의 값에 각각 가중치 를 곱하여 더하면 이 된다
5. 분산이 작은 season을 첫 번째 분기의 기준으로 잡고, 두 번째 분기의 기준은 work day가 된다
6. leaf node의 평균을 계산하여 decision tree를 완성한다
sklearn 으로 decision tree 구현하기
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
iris=load_iris()
data, targets =iris.data, iris.target
print("data / target shape")
print(data.shape, targets.shape, '\n')
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(iris.data, iris.target, test_size=0.2, random_state=11)
print(f'{type(X_train)=}/{X_train.shape=}')
print(f'{type(X_test)=}/{X_test.shape=}')
print(f'{type(y_train)=}/{y_train.shape=}')
print(f'{type(y_test)=}/{y_test.shape=}')
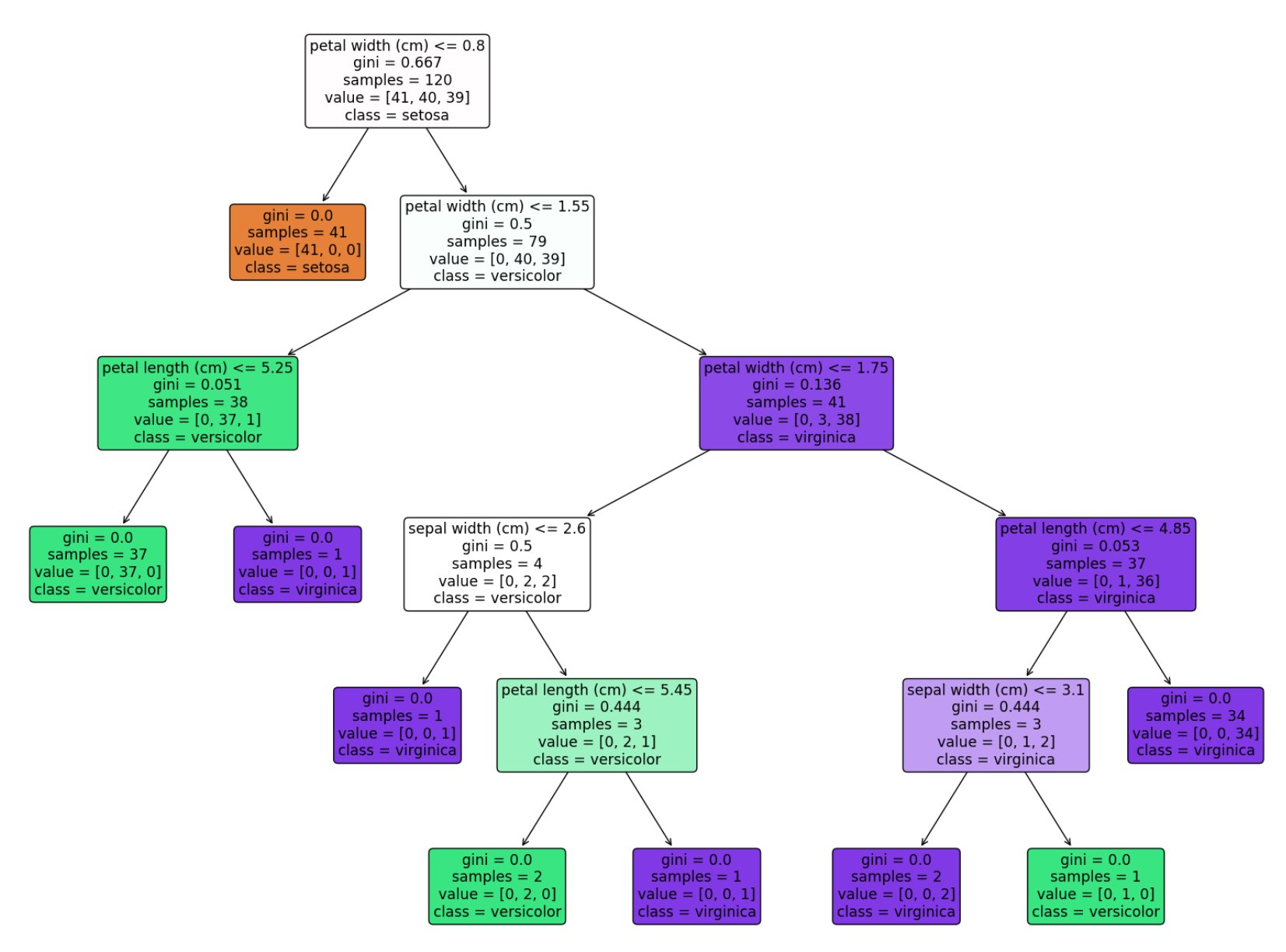
#gini계수로 disicion tree그리기
model=DecisionTreeClassifier()
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy=model.score(X_test,y_test)
print(f'{accuracy=:.4f}')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
plt.figure(figsize=(20,15))
tree.plot_tree(model,
class_names=iris.target_names,
feature_names=iris.feature_names,
impurity=True, filled=True,
rounded=True)
plt.show()
#entropy로 decision tree구하기
model=DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion='entropy')
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy=model.score(X_test,y_test)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
plt.figure(figsize=(20,15))
tree.plot_tree(model,
class_names=iris.target_names,
feature_names=iris.feature_names,
impurity=True, filled=True,
rounded=True)
plt.show()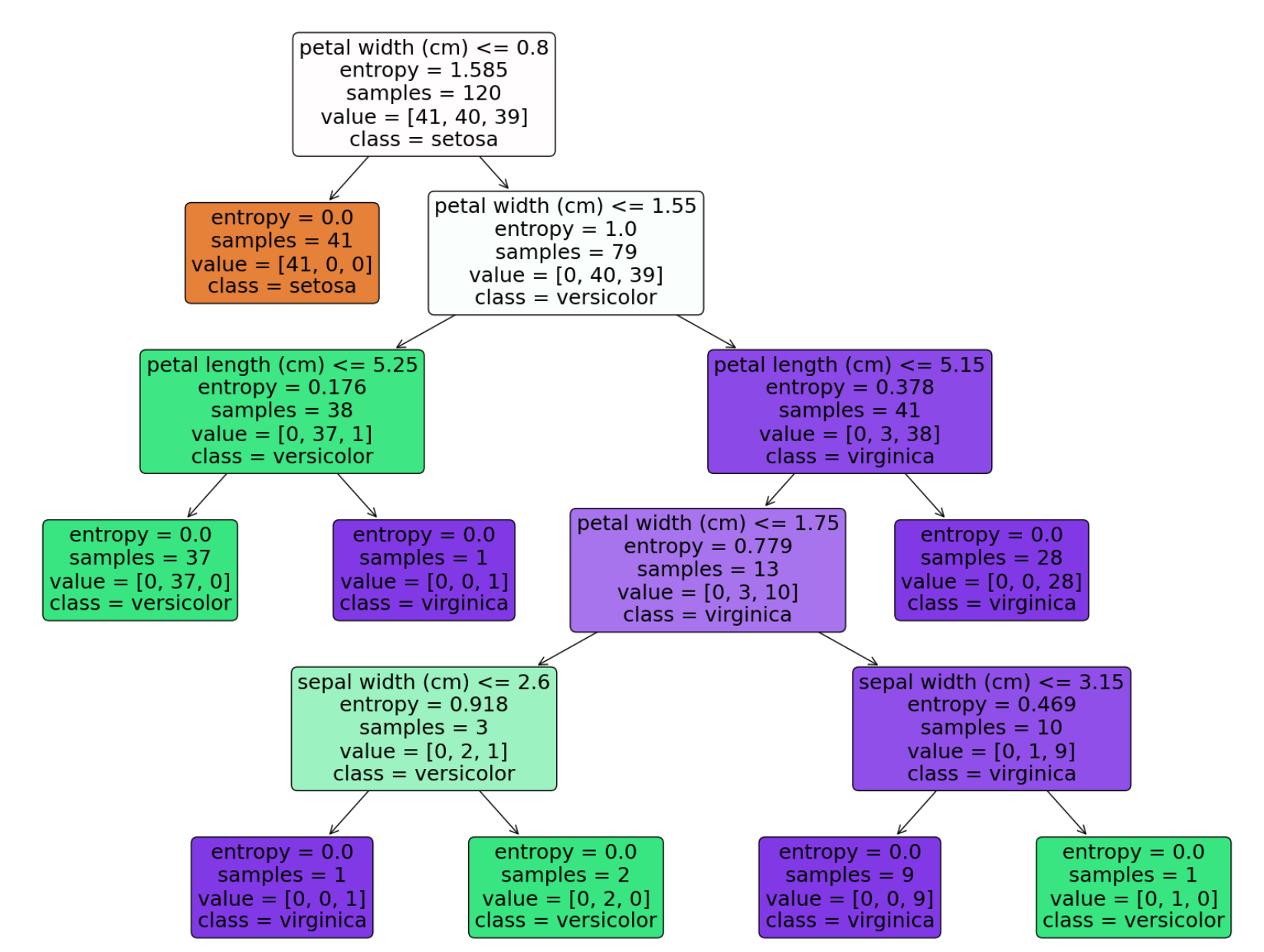
실습
from sklearn.datasets import load_diabetes
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
import numpy as np
diabetes=load_diabetes()
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(diabetes.data, diabetes.target, test_size=0.1, random_state=11)
model=DecisionTreeRegressor()
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy=model.score(X_test,y_test)
preds=model.predict(X_test)
>>
0.3027477160757822
[181. 47. 85. 128. 47. 258. 94. 272. 121. 172. 70. 272. 63. 118.
75. 59. 48. 85. 200. 61. 153. 144. 113. 59. 164. 202. 137. 131.
258. 88. 166. 293. 129. 118. 96. 69. 61. 110. 242. 262. 97. 91.
233. 173. 262.]
mean_target=diabetes.target.mean()
denominator=np.sum((y_test-mean_target)**2)
molecule=np.sum((y_test-preds)**2)
coefficient_=1-(molecule/denominator)
coefficient_
>>
0.30431151788125865
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./bike_sharing.csv")
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(df.iloc[:,2:-1], df['cnt'], test_size=0.2, random_state=11)
model=DecisionTreeRegressor(max_depth=3)
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy=model.score(X_test,y_test)
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
plt.figure(figsize=(20,15))
tree.plot_tree(model,
class_names="cnt",
feature_names=df.columns[:-1],
impurity=True, filled=True,
rounded=True)
plt.show()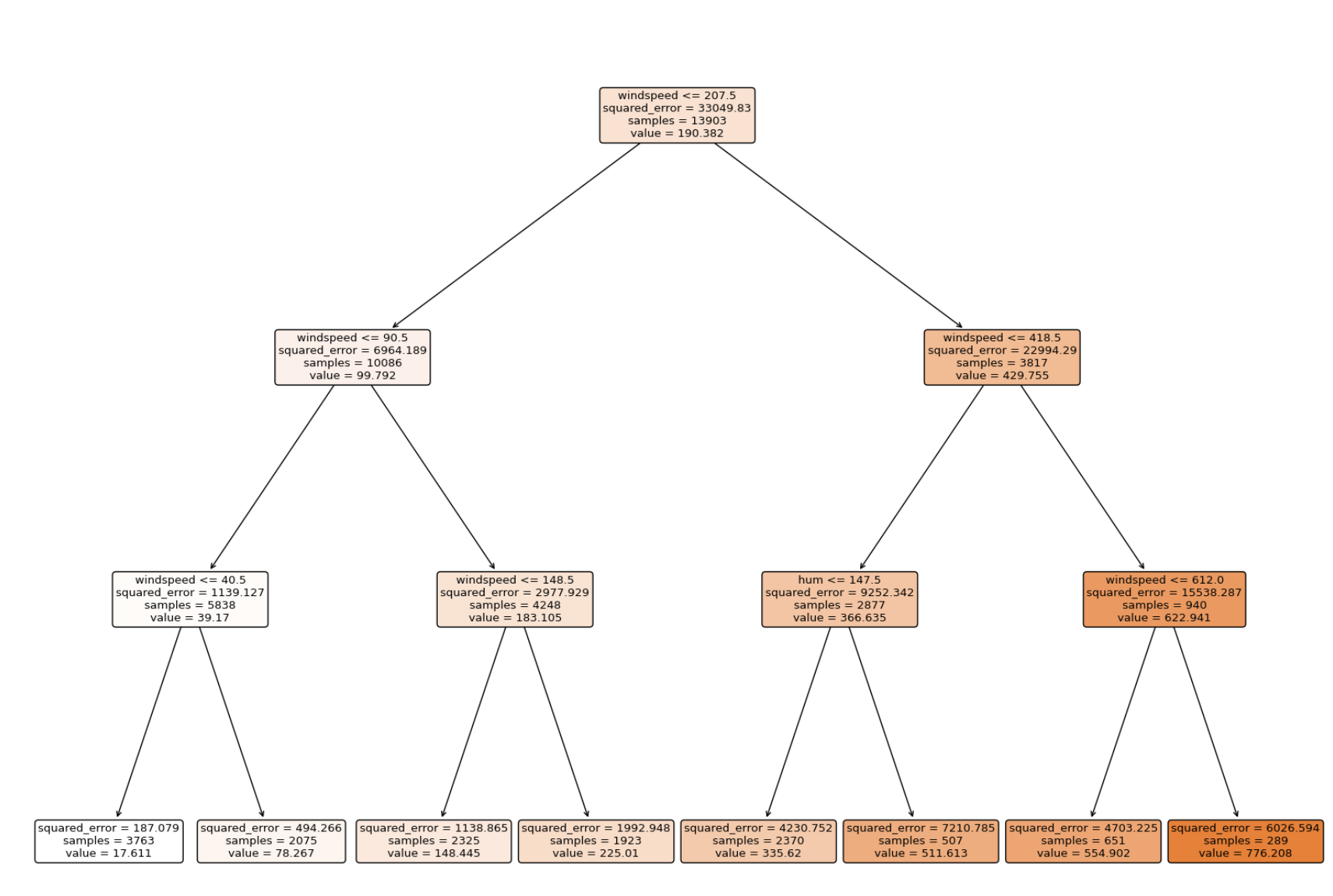
import pandas as pd
df=pd.read_csv("./register_golf_club.csv")
import numpy as np
def get_entropy(df):
prob_list=[]
for j in range(len(df.columns[1:-1])):
entry = df[f'{df.columns[1:-1][j]}'].unique()
prob = 0
for i in range(len(entry)):
target=df["register_golf_club"].unique()
for k in range(len(target)):
weight = df.groupby(f"{df.columns[1:-1][j]}")["register_golf_club"].get_group(f'{entry[i]}').count()
entropy=(df.groupby(f"{df.columns[1:-1][j]}")["register_golf_club"].get_group(f'{entry[i]}')==f'{target[k]}').sum()
if entropy ==0:
continue
prob += (weight/total)*(-(entropy/weight)*np.log2(entropy/weight))
prob_list.append(prob)
return print("features별 entropy:", prob_list, "가장 작은 entropy:", min(prob_list))
from sklearn.preprocessing import LabelEncoder
# LabelEncoder 객체 생성
label_encoder = LabelEncoder()
# 레이블 인코딩 수행
for i in range(len(df.columns)):
df[f'{df.columns[i]}'] = label_encoder.fit_transform(df.iloc[:,i])
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(df.iloc[:,1:-1], df.iloc[:,-1], test_size=0.2, random_state=11)
#gini계수로 disicion tree그리기
model=DecisionTreeClassifier(criterion="entropy")
model.fit(X_train,y_train)
accuracy=model.score(X_test,y_test)
print(f'{accuracy=:.4f}')
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn import tree
plt.figure(figsize=(20,15))
tree.plot_tree(model,
class_names=df.columns[1:-1],
feature_names=df.columns[-1],
impurity=True, filled=True,
rounded=True)
plt.show()
