4장 CLASSES AND INTERFACES
4.1 Recap
class를 사용할 때 typescript와 javascript의 차이점
- protected, public, private 사용
- this 안써줘도 됨
- constructor 만들 때 접근제어자, 이름, 타입 써주기
- 추상 클래스
- 추상 클래스 상속받으면 추상 클래스에서 구현한 함수 사용 가능
- 추상 메소드
- 구현이 되어있지 않고 call signature만 가지고 있음
- 추상 클래스를 상속받는 클래스에서 구현을 해야함
Hash Map
사전에 새 단어 추가, 단어 찾기, 단어 삭제 메소드
type Words = {
[key:string]: string
}
class Dict {
private words: Words
}object의 Type을 선언해야할 때 씀
이 object는 제한된 양의 property만을 가질 수 있다
property의 이름은 모르지만 타입을 알 때 사용
type Words = {
[key:string]: string
}
class Dict {
private words: Words
constructor(){ // constructor에서 수동으로 초기화
this.words = {}
}
add(word:Word){
if(this.words[word.term] === undefined){ // 사전에 단어가 존재하지 않으면
this.words[word.term] = word.def
}
}
def(term:string){
return this.words[term]
}
}
class Word {
constructor(
public term:string,
public def: string
){}
}
const kimchi = new Word("kimchi","배추김치")
const dict = new Dict()
dict.add(kimchi)
dict.def("kimchi")
[key: string]: string키, 값 쌍private words: Words constructor(){property가 constructor로부터 바로 초기화되지 않는 부분add(word:Word)class를 type처럼 사용할 수 있다.
4.2 Interfaces
public이면서 맘대로 변경할수는 없도록 하려면 property를 readonly로
class Word {
constructor(
public readonly term:string,
public readonly def: string
){}
}readonly는 js에서 보이지않음
static
static은 js에도 있는거
Interfaces
type 지정
type Nickname = string // 이렇게 alias로 사용 가능
type Health = number
type Friends = Array<string> // stirng[]
type Player = {
nickname: Nickname,
healthBar: Health
}type을 지정된 옵션으로만 제한 가능
type Team = "red" | "blue" | "yellow"
type Health = 1 | 5 | 10
type Player = {
nickname:string,
team: Team,
health: Health
}
const mk: Player = {
nickname:"mk",
team: "blue",
health: 10
}오브젝트의 모양을 설명하는 다른 방법인 인터페이스
인터페이스는 오직 한가지 용도만을 가지고 있음
- 오브젝트의 모양을 특정,설명해주는 것
type Team = "red" | "blue" | "yellow"
type Health = 1 | 5 | 10
interface Player {
nickname:string,
team: Team,
health: Health
}
const mk: Player = {
nickname:"mk",
team: "blue",
health: 10
}type 키워드는 interface보다 더 다양한 목적으로 활용 가능
- 오브젝트 모양 정의
- 특정 값으로 제한
- alias 만들기
interface User {
name: string
}
interface Player extends User {
}
const mk: Player = {
name: "mk"
}인터페이스는 클래스와 닮았음
객체지향프로그래밍 방식 유사
type User = {
name: string
}
type Player = User & {
}
const mk: Player = {
name: "mk"
}같은 코드를 type 방식으로 작성한 코드
interface 방식이 더 편리하고 직관적임
interface는 property를 축적시킬 수 있음
interface User {
name: string
}
interface User {
lastname: string
}
interface User {
health: number
}
const mk: User ={
name:'mk',
lastname:'cyb',
health:10
}type으로는 이렇게 여러번 만드는거 할 수 없음

interface는 같은 인터페이스에 다른 이름을 가진 property들을 쌓을 수 있음
4.3 Interfaces part Two
abstract class를 사용하는 이유
다른 클래스들이 표준화된 property와 메소드를 갖도록 해주는 청사진을 만들기 위해 추상클래스를 사용
abstract class를 컴파일하면 그냥 class가 됨
interface 를 컴파일하면 사라짐 >> interface는 가벼움
abstract class를 interface로 바꾸기
인터페이스는 오브젝트나 클래스의 모양을 묘사하도록 해줌
인터페이스를 클래스가 쓸 때는 extends 대신 implements 를 써줘야함
implements는 js에 없는 문법
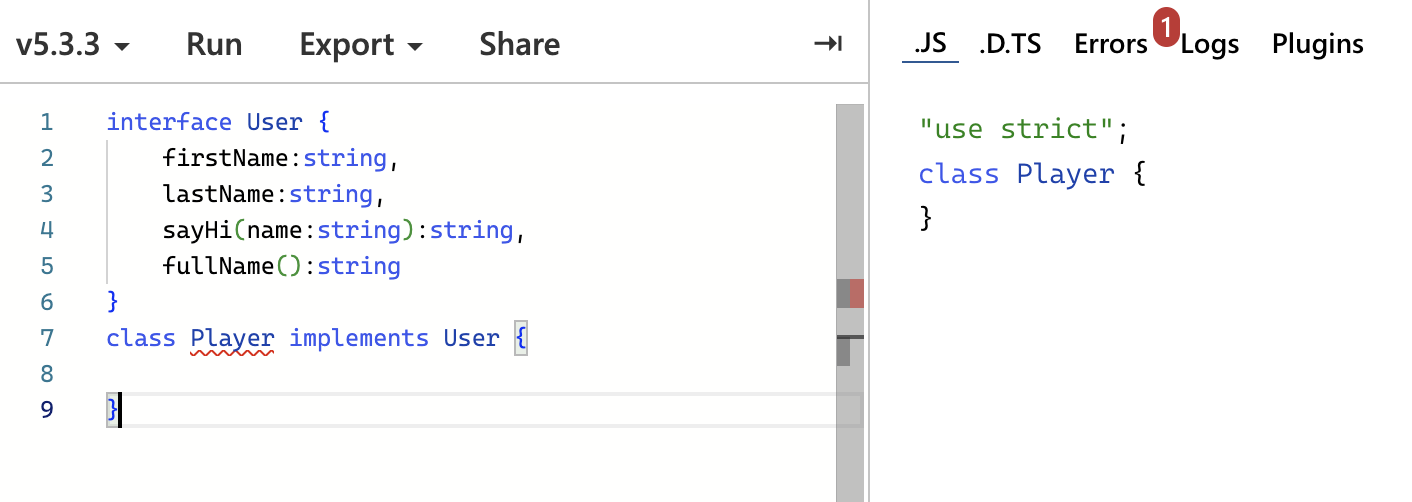
컴파일되면 인터페이스는 사라지므로 코드가 엄청 가벼워짐

인터페이스 사용해서 클래스가 원하는대로 행동하고 원하는 property를 가지도록 강제할수 있게됨
interface User {
firstName:string,
lastName:string,
sayHi(name:string):string,
fullName():string
}
class Player implements User {
constructor(
public firstName:string,
public lastName:string,
){}
fullName(){
return `${this.firstName} ${this.lastName}`
}
sayHi(name:string){
return `Hello ${name}. My name is ${this.fullName()}`
}
}interface를 상속할 때는 property가 private, protected가 될 수 없음 무조건 public만 가능
파일 사이즈 줄이고 싶으면 인터페이스 사용
interface에서는 constructor 사용할 수 없음
interface Human{
health: number
}
...
class Player implements User,Human {
constructor(
public firstName:string,
public lastName:string,
public health:number
){}
...
}여러 개의 interface 상속 가능
interface 타입 지정 가능
function makeUser(user: User): User{
return {
firstName:"aa",
lastName:"bb",
fullName: () => "xx",
sayHi: (name: string) => "yy"
}
}
makeUser({
firstName:"aa",
lastName:"bb",
fullName: () => "xx",
sayHi: (name: string) => "yy"
})interface를 argument type으로 지정하거나 return type으로 지정할 수 있음
return 할 땐 new 안쓰고 그냥 objec로 return 해주면 됨
