[ 파일 비동기 채널 ]
FileChannel의 read()와 write() 메소드는 파일 입출력 작업 동안 블로킹된다. 만약 UI 및 이벤트를 처리하는 스레드에서 이 메소드들을 호출하면 블로킹되는 동안에 UI 갱신이나 이벤트 처리를 할 수 없다. 따라서 별도의 작업 스레드를 생성해서 이 메소드들을 호출해야 한다. 만약 동시에 처리해야 할 파일 수가 많다면 스레드의 수도 증가하기 때문에 문제가 될 수 있다.
그래서 자바 NIO는 불특정 다수의 파일 및 대용량 파일의 입출력 작업을 위해서
비동기 파일 채널(AsynchronousFileChannel)을 별도로 제공하고 있다.
AsynchronousFileChannel은 파일의 데이터 입출력을 위해 read()와 write() 메소드를 호출하면 스레드풀에게 작업 처리를 요청하고 이 메소드들을 즉시 리턴시킨다. 실질적인 입출력 작업 처리는 스레드풀의 작업 스레드가 담당한다. 작업 스레드가 파일 입출력을 완료하게 되면 콜백(callback) 메소드가 자동 호출되기 때문에 작업 완료 후 실행해야 할 코드가 있다면 콜백 메소드에 작성하면 된다.
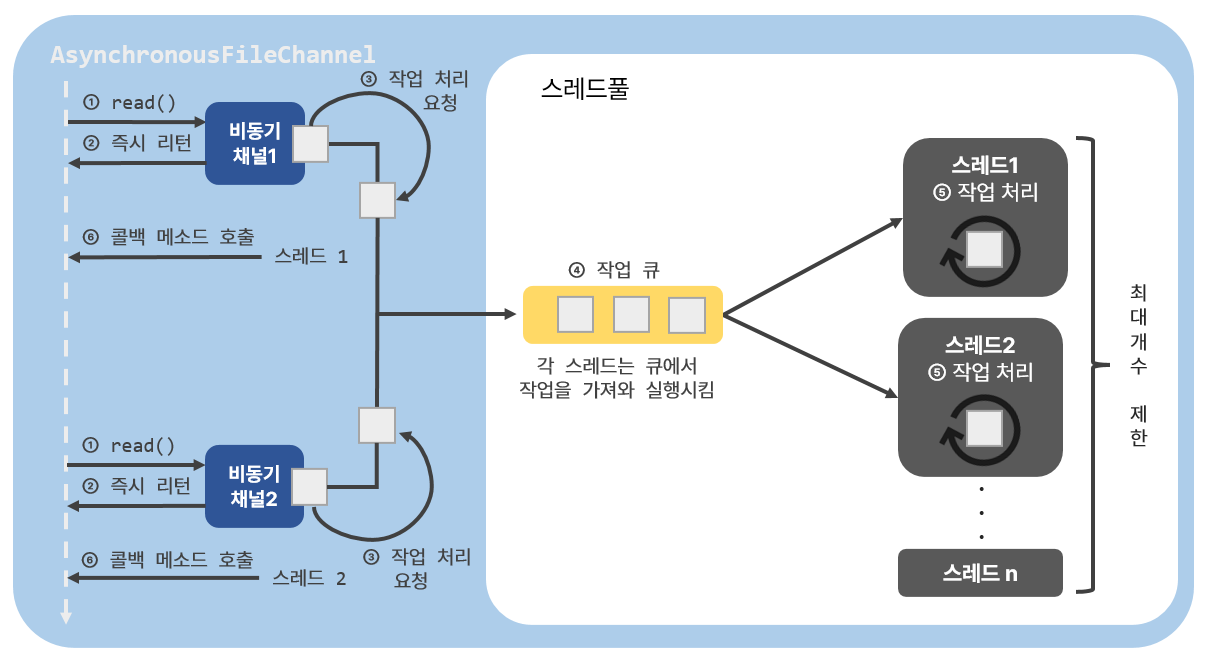
AsynchronousFileChannel 생성과 닫기
AsynchronousFileChannel은 두 가지 정적 메소드인open()을 호출해서 얻을 수 있다.
- 첫 번째
open()메소드는 다음과 같이 파일의Path객체와 열기 옵션 값을 매개값으로 받는다.
AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Path file,
OpenOption... options
);- 이렇게 생성된
AsynchronousFileChannel은 내부적으로 생성되는 기본 스레드풀을 이용해서 스레드를 관리한다. 기본 스레드풀의 최대 스레드 개수는 개발자가 지정할 수 없기 때문에 다음과 같이 두 번째open()메소드로AsynchronousFileChannel을 만들 수도 있다.
AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Path file,
Set<? extends OpenOption> options,
ExecutorService executor,
FileAttribute<?>... attrs
);file매개값은 파일의Path객체이고,options매개값은 열기 옵션 값들이 저장된Set객체이다.executor매개값은 스레드풀인ExecutorService객체이다.attrs매개값은 파일 생성 시 파일 속성값이 될FileAttribute를 나열하면 된다.
예를 들어 "C:\Temp\file.txt" 파일에 대한 AsynchronousFileChannel은 다음과 같이 생성할 수 있다.
ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(
Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()
);
AsynchronousFileChannel fileChannel = AsynchronousFileChannel.open(
Paths.get("C:/Temp/file.txt"),
EnumSet.of(StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.WRITE),
executorService
);Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors()는 CPU의 코어 수를 리턴한다.- 쿼드 코어 CPU일 경우는 4를 리턴, 하이퍼 스레딩일 경우는 8을 리턴한다.
EnumSet.of()메소드는 매개값으로 나열된 열거 상수를 Set 객체에 담아 리턴한다.AsynchronousFileChannel을 더 이상 사용하지 않을 경우에는 다음과 같이close()메소드를 호출해서 닫아준다.
fileChannel.close();파일 읽기와 쓰기
AsynchronousFileChannel이 생성되었다면read(),write()메소드를 이용해서 입출력할 수 있다.read(ByteBuffer dst, long position, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer, A> handler); write(ByteBuffer src, long position, A attachment, CompletionHandler<Integer, A> handler);
- 이 메소드들을 호출하면 즉시 리턴되고, 스레드풀의 스레드가 입출력 작업을 진행한다.
dst와src매개값은 읽거나 쓰기 위한ByteBuffer이고,position매개값은 파일에서 읽을 위치이거나 쓸 위치이다.- 파일의 첫 번째 바이트부터 읽거나 첫 번째 위치에 바이트를 쓰고 싶다면
position을0으로 주면 된다.
- 파일의 첫 번째 바이트부터 읽거나 첫 번째 위치에 바이트를 쓰고 싶다면
attachment매개값은 콜백 메소드로 전달할 첨부 객체이다.- 첨부 객체는 콜백 메소드에서 결과값 외에 추가적인 정보를 얻고자 할 때 사용되는 객체를 말한다.
- 만약 첨부 객체가 필요없다면
null을 대입해도 된다.
handler매개값은Completion<Integer, A>구현 객체를 지정한다.Integer는 입출력 작업의 결과 타입으로,read()와write()가 읽거나 쓴 바이트 수이다.A는 첨부 객체 타입으로 개발자가CompletionHandler구현 객체를 작성할 때 임의로 지정이 가능하다.- 만약 첨부 객체가 필요 없다면
A는Void가 된다.
- 만약 첨부 객체가 필요 없다면
✅ CompletionHandler<Integer, A> 구현 객체는 다음 두 가지 메소드를 가져야 한다.
- 비동기 작업이 정상적으로 완료된 경우와 예외 발생으로 실패된 경우에 자동 콜백되는 다음 두 가지 메소드를 가지고 있어야 한다.
| 리턴 타입 | 메소드명(매개 변수) | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| void | completion(Integer result, A attachment) | 작업이 정상적으로 완료된 경우 콜백 |
| void | failed(Throwable exc, A attachment) | 예외 때문에 작업이 실패된 경우 콜백 |
completed()메소드의result매개값은 작업 결과가 대입되는데,read()와write()작업 결과는 읽거나 쓴 바이트 수이다.attachment매개값은read()와write()호출 시 제공된 첨부 객체이다.
failed()메소드의exc매개값은 작업 처리 도중 발생한 예외이다.- 콜백 메소드를 실행하는 스레드는
read()와write()를 호출한 스레드가 아니고 스레드풀의 작업 스레드이다. 그렇기 때문에JavaFX애플리케이션일 경우 UI 생성 및 변경 작업을 이 메소드에서 직접할 수 없고Platform.runLater()를 이용해야 한다.
- 콜백 메소드를 실행하는 스레드는
CompletionHandler구현 클래스는 다음과 같이 작성하면 된다.
new CompletionHander<Integer, A>() {
@Override
public void completed(Integer result, A attachment) { ... }
@Override
public void failed(Throwable etx, A attachment) { ... }
}[ TCP 블로킹 채널 ]
NIO를 이용해서 TCP 서버/클라이언트 애플리케이션을 개발하려면 블로킹, 넌블로킹, 비동기 구현 방식 중에서 하나를 결정해야 한다. 이 결정에 따라 구현이 완전히 달라지기 때문이다.
다소 복잡해지기도 했지만 네트워크 입출력의 성능과 효율성 면에서 선택의 폭이 넓어졌기 때문에 최적의 네트워크 애플리케이션을 개발할 수 있게 되었다.
서버소켓 채널과 소켓 채널의 용도
NIO에서 TCP 네트워크 통신을 위해 사용하는 채널은
java.nio.channels.ServerSocketChannel과java.nio.channels.SocketChannel이다.
이 두 채널은 IO의 ServerSocket과 Socket에 대응되는 클래스로, IO가 버퍼를 사용하지 않고 블로킹 입출력 방식만 지원한다면 ServerSocketChannel, SocketChannel은 버퍼를 이용하고 블로킹과 넌블로킹 방식을 모두 지원한다.
사용 방법은 IO와 큰 차이점이 없는데, ServerSocketChannel은 클라이언트 SocketChannel의 연결 요청을 수락하고 통신용 SocketChannel을 생성한다.
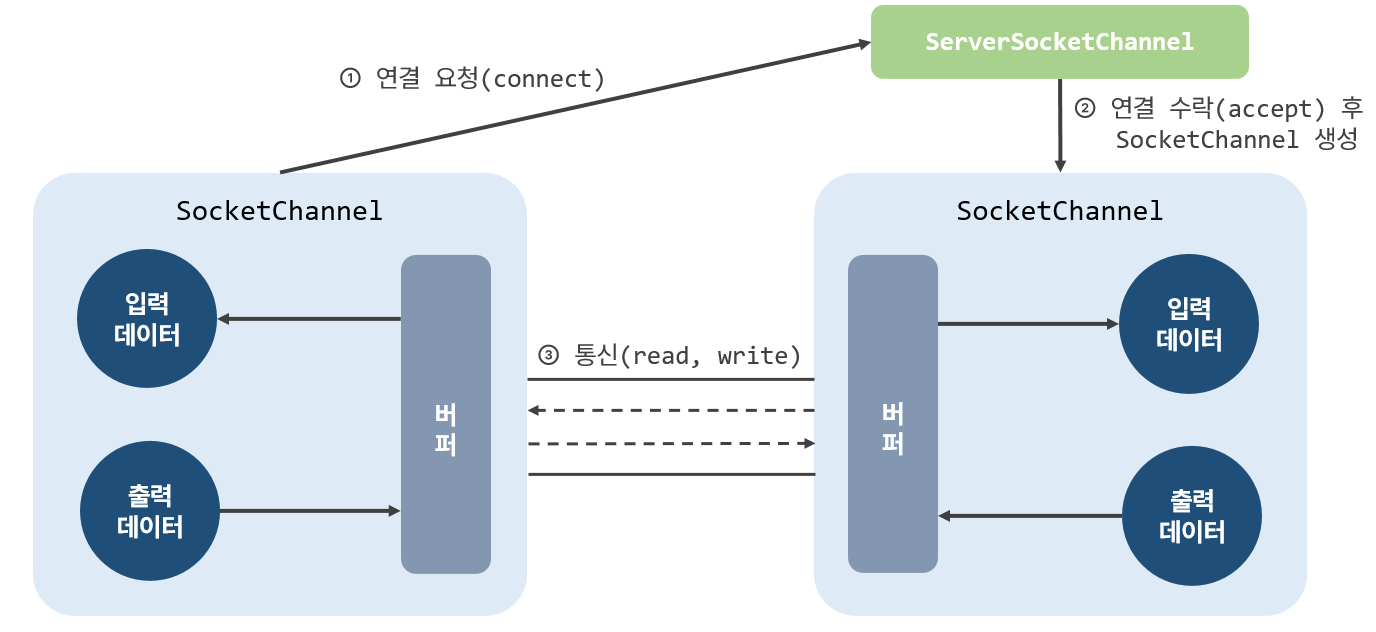
서버소켓 채널 생성과 연결 수락
1. 서버를 개발하려면 우선 ServerSocketChannel 객체를 얻어야 한다.
ServerSocketChannel은 정적 메소드인open()으로 생성하고, 블로킹 방식으로 동작시키기 위해configureBlocking(true)메소드를 호출한다.- 기본적으로 블로킹 방식으로 동작하지만, 명시적으로 설정하는 이유는 넌블로킹과 구분하기 위해서이다.
- 포트에 바인딩하기 위해서 포트 정보를 가진
InetSocketAddress객체를 매개값으로bind()메소드가 호출하면 된다.
ServerSocketChannel serverSocketChannel = ServerSocketChannel.open();
serverSocketChannel.configureBlocking(true);
serverSocketChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(5001));2. 포트 바인딩까지 끝났다면 ServerSocketChannel은 클라이언트 연결 수락을 위해 accept() 메소드를 실행해야 한다.
accept()메소드는 클라이언트가 연결 요청을 하기 전까지 블로킹되기 때문에 UI 및 이벤트를 처리하는 스레드에서accept()메소드를 호출하지 않도록 한다.- 클라이언트가 연결 요청을 하면
accept()는 클라이언트와 통신할SocketChannel을 만들고 리턴한다.
SocketChannel socketChannel = serverSocketChannel.accept();3. 연결된 클라이언트의 IP와 포트 정보를 알고 싶다면 SocketChannel의 getRemoteAddress() 메소드를 호출해서 SocketAddress를 얻으면 된다.
- 실제 리턴되는 것은
InetSocketAddress인스턴스이므로 다음과 같이 타입 변환할 수 있다.
InetSocketAddress socketAddress = (InetSocketAddress) socketChannel.getRemoteAddress();InetSocketAddress에는 다음과 같이 IP와 포트 정보를 리턴하는 메소드들이 있다.
| 리턴 타입 | 메소드명(매개 변수) | 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| String | getHostName() | 클라이언트 API 리턴 |
| int | getPort() | 클라이언트 포트 번호 리턴 |
| String | toString() | "IP:포트번호" 형태의 문자열 리턴 |
4. 더 이상 클라이언트를 위해 연결 수락이 필요 없다면 ServerSocketChannel의 close() 메소드를 호출해서 포트를 언바인딩시켜야 한다.
- 그래야 다른 프로그램에서 해당 포트를 재사용할 수 있다.
serverSocketChannel.close();[ 참고자료 ]
이것이 자바다 책

