linked list
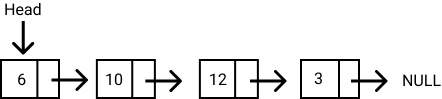
각 노드는 데이터와 다음노드를 가리키는 링크와 데이터를 갖고있다.
배열과 linked list의 차이
Array
- 정해진 크기
- 입력과 삭제가 비효율적
- 무작위 접근 가능 (ex:
array[4]이런식으로) - 메모리 낭비가 심할 수 있음
- 순차 접근이 더 빠름
- 이유: 각 요소의 메모리 위치가 순차적으로 있음
Linked list
- 크기가 동적임
- 입력과 삭제가 효율적
- 전체 데이터 구조를 재구성하지 않고, 노드를 링크된 목록에서 쉽게 제거하거나 추가할 수 있음.
- 무작위 접근 안됨
- 메모리 낭비 없음
- 순차 접근은 느림
- 이유: 각 요소의 메모리 위치가 순차적으로 있지 않음
- 단점
- 연결된 목록에서 검색 작업이 느림. 배열과 달리 데이터 요소의 임의 액세스는 허용되지 않음. 노드는 첫 번째 노드부터 순차적으로 액세스.
- 포인터의 저장 때문에 어레이보다 더 많은 메모리를 사용함.
linked lists의 종류
- singly linked lists
- 각 노드에는 다음 노드에 대한 포인터가 하나만 있음.
- doubly linked lists
- 각 노드는 두개의 포인터가 있으며, 포인터는 다음 노드와 이전의 노드에 대한 것.
- circular linked lists(순환 링크 목록)
- linked list의 변형. 마지막 노드가 첫번째 노드 또는 그 이전의 다른 노드를 가르키며 loop을 만듦.
JS으로 구현하기
list node
class ListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}위와 같이 하나의 노드는 다음노드를 가리키는 포인터와 데이터를 갖고있음
linked list
head가 통과되지 않으면, head는 null로 초기화됨.
class LinkedList {
constructor(head = null) {
this.head = head;
this.size = 0;
}
}연결하기
let node1 = new ListNode(2);
let node2 = new ListNode(5);
node1.next = node2; // node1의 포인터가 node2를 가리킴그리고 아래와같이 linkedList로 연결해준다.
let list = new LinkedList(node1);콘솔로 확인하면 아래와 같이 나타난다.
LinkedList {
head: ListNode { data: 2, next: ListNode { data: 5, next: null } }
}
LinkedList의 methods
위와같이 일일이 연결해주지 않아도, 추가하는 기능이 있는 method를 생성하면 손쉽게 생성, 연결할 수 있다.
class ListNode {
constructor(data) {
this.data = data;
this.next = null;
}
}
class LinkedList {
constructor(head = null) {
this.head = head;
this.size = 0;
}
getSize() {
return this.size;
}
clear() {
this.head = null;
}
add(data) {
let node = new ListNode(data);
let current;
if (this.head == null) {
this.head = node;
} else {
current = this.head;
// 마지막 node로 이동
while (current.next) {
current = current.next;
}
// add node
current.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}
getLast() {
let lastNode = this.head;
while (lastNode.next) {
lastNode = lastNode.next;
}
return lastNode;
}
getfirst() {
return this.head;
}
remove(element) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let prevNode;
if (currentNode.data === element) {
this.head = currentNode.next;
} else {
while (currentNode.data !== element) {
prevNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
prevNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
}
indexOf(element) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let index = -1;
while (currentNode) {
index++;
if (currentNode.data === element) {
return index;
}
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return -1;
}
elementAt(index) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let count = 0;
while (count < index) {
count++;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
return currentNode.data;
}
addAt(index, element) {
let node = new ListNode(element);
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode;
let currentIndex = 0;
if (index > this.size) {
return false;
}
if (index === 0) {
node.next = currentNode;
this.head = node;
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
node.next = currentNode;
previousNode.next = node;
}
this.size++;
}
removeAt(index) {
let currentNode = this.head;
let previousNode;
let currentIndex = 0;
if (index < 0 || index >= this.size) {
return null;
}
if (index === 0) {
head = currentNode.next;
} else {
while (currentIndex < index) {
currentIndex++;
previousNode = currentNode;
currentNode = currentNode.next;
}
// currentIndex === 삭제할 index 일 때:
previousNode.next = currentNode.next;
}
this.size--;
// 삭제한 데이터
return currentNode.data;
}
}
let list = new LinkedList();
list.add(7);
list.add(8);
list.add(13);
list.remove(8);
list.add(14);
list.add(18);
list.addAt(0, 1);
console.log(list);
console.log(list.removeAt(1));
console.log(list);
