[BOJ. 2448] 별 찍기 - 11
1. 링크 백준 2448 별 찍기 - 11
2. 풀이
이 문제에서는 재귀가 큰 삼각형 안에서 작은 삼각형이 반복되는 형식으로 되어있습니다.
그러므로 이 문제는 재귀를 하면서 곧 바로 콘솔에 출력하는 형식으로는 해결할 수 없는 문제입니다.
그렇기 때문에 이 문제는 공간에 메모리를 할당한 후에 별을 찍는 과정을 재귀로 구현해야 풀 수 있는 문제입니다.
1. 할당
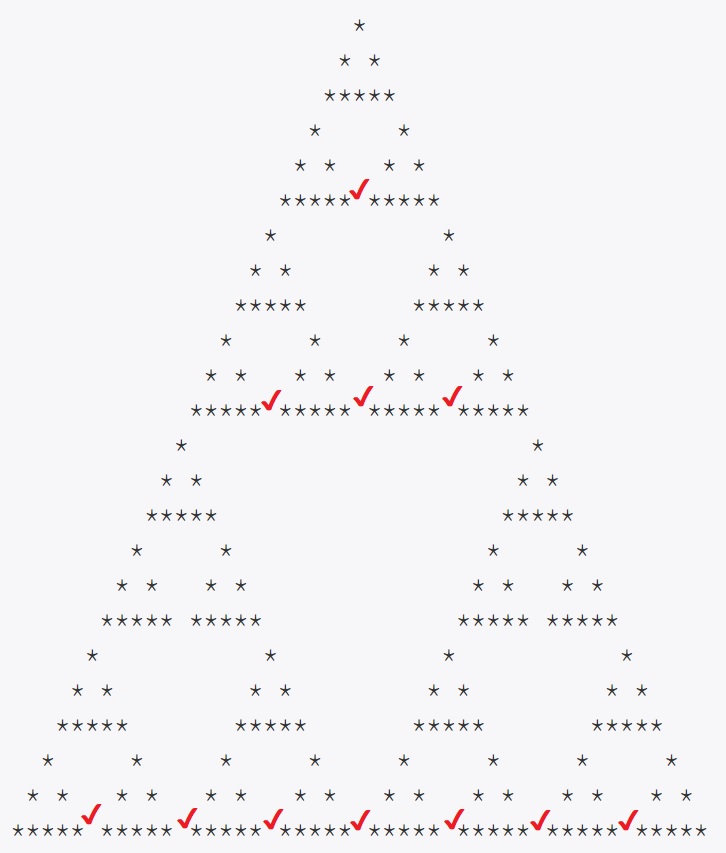
에서
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는
이를 일반화하면,
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는 (등비 수열의 합)
그러므로
일 때, 바닥면의 길이는 이 된다.
그러므로 할당은 세로의 길이는 N, 가로의 길이는 2 * N - 1만큼 해주면 된다.
2. 재귀
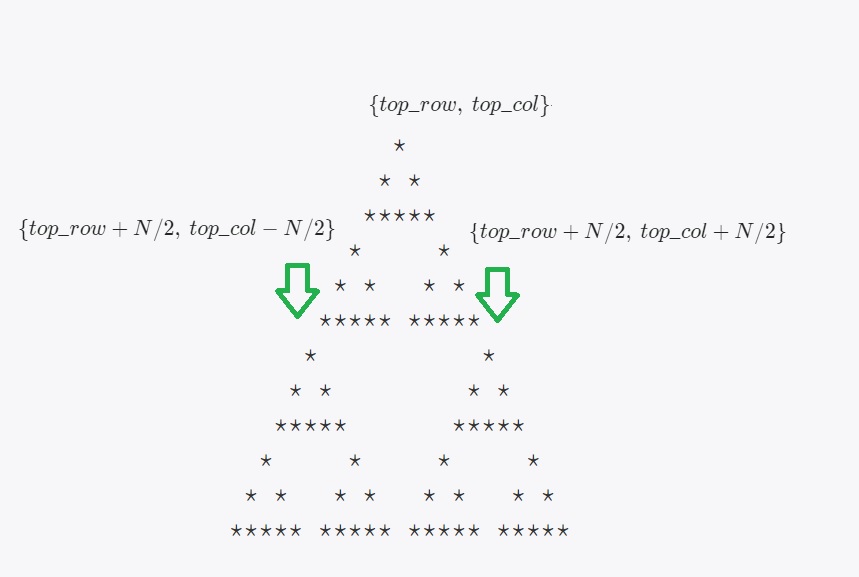
높이가 인 삼각형 안에서 맨 위의 꼭지점 부터 꼭지점을 찍는다고 하면,
왼쪽 삼각형의 꼭지점은 ,
오른쪽 삼각형의 꼭지점은이 된다.
N = 3일 때 삼각형을 찍고 그게 아니라면, 재귀를 반복하는 것을 Pseudo code로 짜면
imprint(top_row, top_col, N)
if(3 == N)
imprint_triangle(top_row, top_col)
imprint(top_row, top_col, N / 2)
imprint(top_row + N / 2, top_col - N / 2, N / 2)
imprint(top_row + N / 2, top_col + N / 2, N / 2) 이 된다.
3. 코드
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void imprint_original_triangle(vector<string>& stuff, int row_top, int col_top)
{
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
for (int j = -i; j <= i; j++)
{
stuff[row_top + i][col_top + j] = '*';
}
}
stuff[row_top + 1][col_top] = ' ';
}
void imprint_reculsive(vector<string>& stuff, int row_top, int col_top, int N)
{
if (3 == N)
imprint_original_triangle(stuff, row_top, col_top);
else
{
imprint_reculsive(stuff, row_top, col_top, N / 2);
imprint_reculsive(stuff, row_top + N / 2, col_top - N / 2, N / 2);
imprint_reculsive(stuff, row_top + N / 2, col_top + N / 2, N / 2);
}
}
void draw_triangles(int N)
{
vector<string> stuff(N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
stuff[i].assign(2 * N - 1, ' ');
}
imprint_reculsive(stuff, 0, N - 1, N);
for (int i = 0; i < N; i++)
{
cout << stuff[i] << '\n';
}
}
int main(void)
{
int N;
cin >> N;
draw_triangles(N);
}