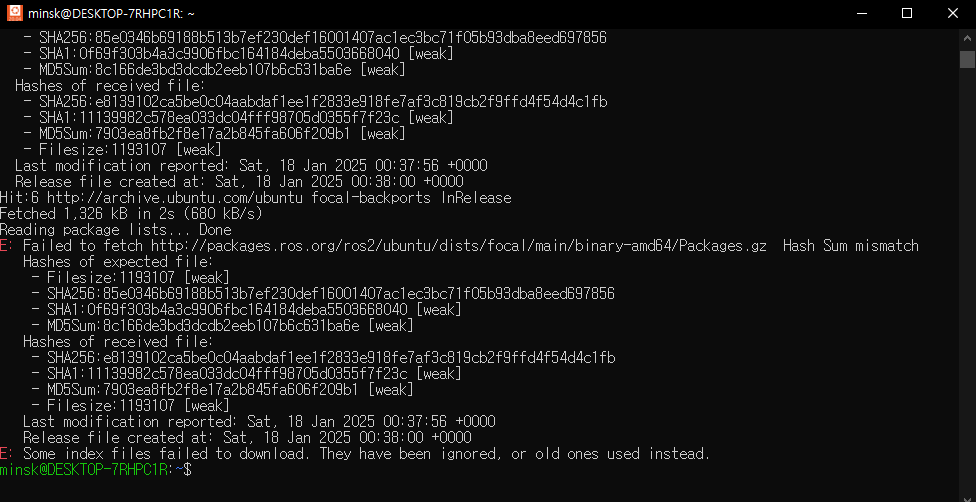
"Hash Sum mismatch" error usually indicates that APT’s local cache files are out of sync or corrupted compared to what the repository provides.
It can also happen if the system clock is incorrect or if network caching proxies are interfering.
Below are several steps you can try to resolve the error:
1. Check and correct your system date and time
An incorrect system clock can confuse APT’s validation of repository files.
Verify your system clock:
date
It seems that time is not the cause
but, if your date and time don't match, you have to try this.
sudo apt install ntp sudo systemctl enable ntp sudo systemctl start ntpMake sure the date/time isn't correct before proceeding.
2. Clean APT cache and remove old lists(I use this)
This forces APT to discard any corrupted or outdated files, then re-download everything fresh.
sudo apt clean
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/* # if necessary..
sudo apt update
- sudo apt clean removes cached .deb files in /var/cache/apt/archives/.
- Removing /var/lib/apt/lists/* forces APT to fetch fresh index files from repositories.
- sudo apt update then redownloads the package list from all configured repositories.
3. Deletes all cached package list files && Updates the local package list, prioritizing gzip-compressed metadata files
(25.04.02 edit)
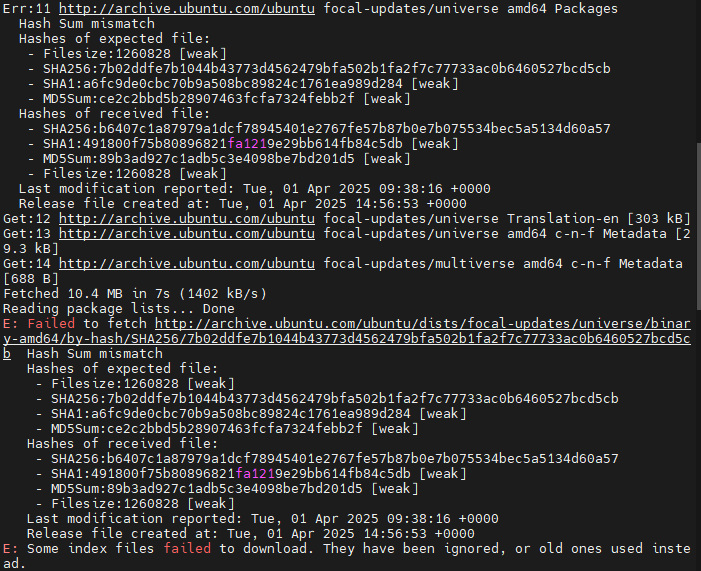
sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
sudo apt-get update -o Acquire::CompressionTypes::Order::=gz
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade1. sudo rm -rf /var/lib/apt/lists/*
Purpose: Deletes all cached package list files stored in /var/lib/apt/lists/.
This directory contains metadata about available packages (e.g., names, versions, and dependencies) fetched from repositories.
Why use it?: If the cached package lists are corrupted or outdated, removing them ensures APT fetches fresh data during the next update.
Breakdown:
sudo: Runs the command with administrative privileges.
rm: Deletes files or directories.
-r: Deletes directories and their contents recursively.
-f: Forces deletion without confirmation.
2. sudo apt-get update -o Acquire::CompressionTypes::Order::=gz
Purpose: Updates the local package list, prioritizing gzip-compressed metadata files.
Normally, APT fetches metadata in various compression formats (e.g., LZMA, Bzip2). This command forces it to use gzip (gz) to avoid issues with other formats.
Why use it?: To resolve issues like "Hash Sum mismatch," which can occur due to corrupted or incompatible compressed metadata files.
Breakdown:
sudo: Runs the command as an administrator.
apt-get update: Downloads updated package information from repositories listed in /etc/apt/sources.list.
-o Acquire::CompressionTypes::Order::=gz: Specifies that gzip should be used for downloading metadata.
3. sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
This is a combination of two commands executed sequentially using &&.
a. sudo apt update
Purpose: Refreshes the local package list by downloading updated metadata from repositories.
What it does: Contacts the repositories defined in /etc/apt/sources.list. Compares the versions of packages in the repository with those installed on your system. Updates the local cache with this information but does not install any updates yet.
b. sudo apt upgrade
Purpose: Upgrades all installed packages to their latest versions based on the updated package list.
What it does:Identifies outdated packages using the metadata fetched by apt update.Downloads and installs newer versions of these packages while preserving existing configurations.
Why use them together?
Running these commands together ensures:
The local package list is up-to-date (apt update).
Installed packages are upgraded to their latest versions (apt upgrade).
Summary of Workflow
Clear old or corrupted package lists (rm command).
Fetch fresh metadata using gzip compression (apt-get update with options).
Update your system by refreshing package lists and upgrading installed software (apt update && apt upgrade).

감사합니다. 덕분에 해결했어요~