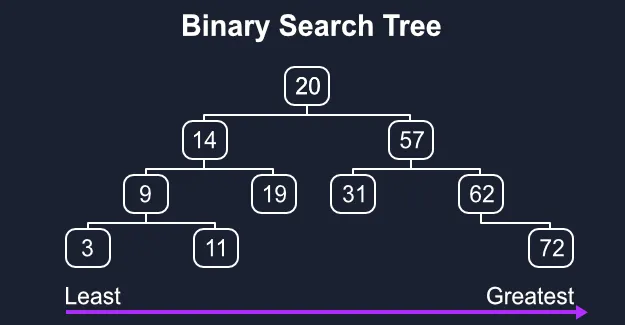
이진 탐색 트리란?
이진 탐색 트리는 각 노드가 최대 두 개의 자식 노드를 가지며, 각 노드의 왼쪽 서브 트리는 해당 노드보다 작은 값들로, 오른쪽 서브 트리는 해당 노드보다 큰 값들로 이루어진다. 이렇게 구성된 트리는 탐색 및 삽입 연산이 빠르게 수행된다.
이진 탐색 트리의 특징
-
각 노드는 최대 두 개의 자식 노드를 가진다. 각 노드의 왼쪽 서브 트리에는 해당 노드보다 작은 값들이 위치하며, 오른쪽 서브 트리에는 해당 노드보다 큰 값들이 위치한다. 이러한 특성으로 인해 탐색 연산이 빠르게 수행되며 특정 값을 찾을 때, 현재 노드의 값과 비교하여 탐색 방향을 결정할 수 있다.
-
중위 순회(In-order traversal)를 통해 이진 탐색 트리의 모든 노드를 정렬된 순서로 방문할 수 있다. 따라서 이진 탐색 트리는 정렬된 데이터를 유지하면서 삽입, 삭제, 검색이 가능한 자료구조로 사용된다.
-
이진 탐색 트리에서의 검색 연산의 시간 복잡도는 O(log n)이며, 이는 트리의 높이에 의해 결정된다. 따라서 큰 데이터셋에서도 효율적으로 탐색 및 정렬이 가능하다.
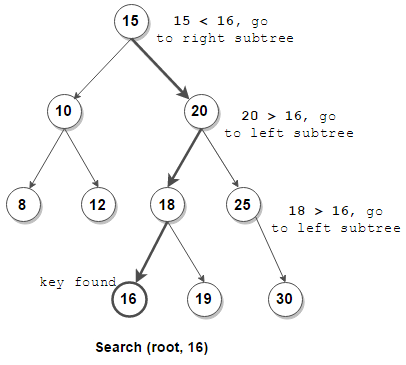
- 삽입 및 삭제 연산 또한 트리의 높이에 의존하며, 평균적으로 O(log n)의 시간 복잡도를 갖는다. 특정 케이스에서는 트리가 한쪽으로 치우쳐져 불균형한 형태를 갖게 되어 시간 복잡도가 O(n)이 될 수 있다. 따라서 균형을 유지하는 트리 구조(예: AVL 트리, 레드-블랙 트리)를 사용하기도 한다.
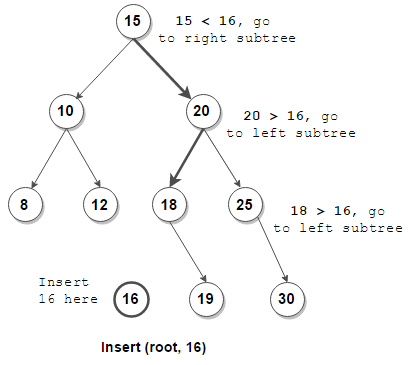
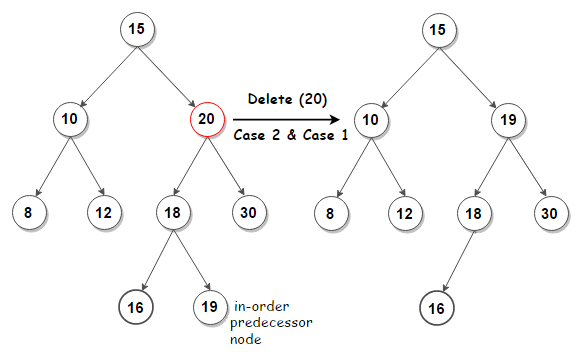
-
이진 탐색 트리에서 가장 왼쪽에 있는 노드는 전체 트리에서 가장 작은 값이고, 가장 오른쪽에 있는 노드는 가장 큰 값이다. 따라서 최소값 또는 최대값을 찾는 데에도 효율적이다.
-
이진 탐색 트리는 재귀적인 방식으로 구현이 가능하다. 각 노드는 키 값, 왼쪽 서브 트리, 오른쪽 서브 트리로 이루어져 있으며 삽입, 삭제, 검색 등의 연산을 구현하면서 트리의 균형을 유지하는 것이 중요하다.
이진 탐색 트리 구현
class Node {
int key;
Node left, right;
public Node(int item) {
key = item;
left = right = null;
}
}
public class BinarySearchTree {
private Node root;
public BinarySearchTree() {
root = null;
}
// 검색
public Node search(int key) {
return searchRec(root, key);
}
private Node searchRec(Node root, int key) {
if (root == null || root.key == key)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
return searchRec(root.left, key);
return searchRec(root.right, key);
}
// 삽입
public void insert(int key) {
root = insertRec(root, key);
}
private Node insertRec(Node root, int key) {
if (root == null) {
root = new Node(key);
return root;
}
if (key < root.key)
root.left = insertRec(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = insertRec(root.right, key);
return root;
}
// 삭제
public void delete(int key) {
root = deleteRec(root, key);
}
private Node deleteRec(Node root, int key) {
if (root == null)
return root;
if (key < root.key)
root.left = deleteRec(root.left, key);
else if (key > root.key)
root.right = deleteRec(root.right, key);
else {
// 노드가 한 개 또는 없는 경우
if (root.left == null)
return root.right;
else if (root.right == null)
return root.left;
// 노드가 두 개인 경우
root.key = minValue(root.right);
// 오른쪽 서브 트리에서 후계자 값을 삭제
root.right = deleteRec(root.right, root.key);
}
return root;
}
private int minValue(Node root) {
int minValue = root.key;
while (root.left != null) {
minValue = root.left.key;
root = root.left;
}
return minValue;
}
// 중위 순회
public void inOrder() {
inOrderRec(root);
}
private void inOrderRec(Node root) {
if (root != null) {
inOrderRec(root.left);
System.out.print(root.key + " ");
inOrderRec(root.right);
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BinarySearchTree tree = new BinarySearchTree();
tree.insert(50);
tree.insert(30);
tree.insert(20);
tree.insert(40);
tree.insert(70);
tree.insert(60);
tree.insert(80);
System.out.println("중위 순회 결과:");
tree.inOrder();
int keyToSearch = 40;
Node searchResult = tree.search(keyToSearch);
if (searchResult != null) {
System.out.println("\n검색 결과: " + keyToSearch + " 찾음");
} else {
System.out.println("\n검색 결과: " + keyToSearch + " 찾지 못함");
}
int keyToDelete = 30;
tree.delete(keyToDelete);
System.out.println("\n노드 " + keyToDelete + " 삭제 후 중위 순회 결과:");
tree.inOrder();
}
}