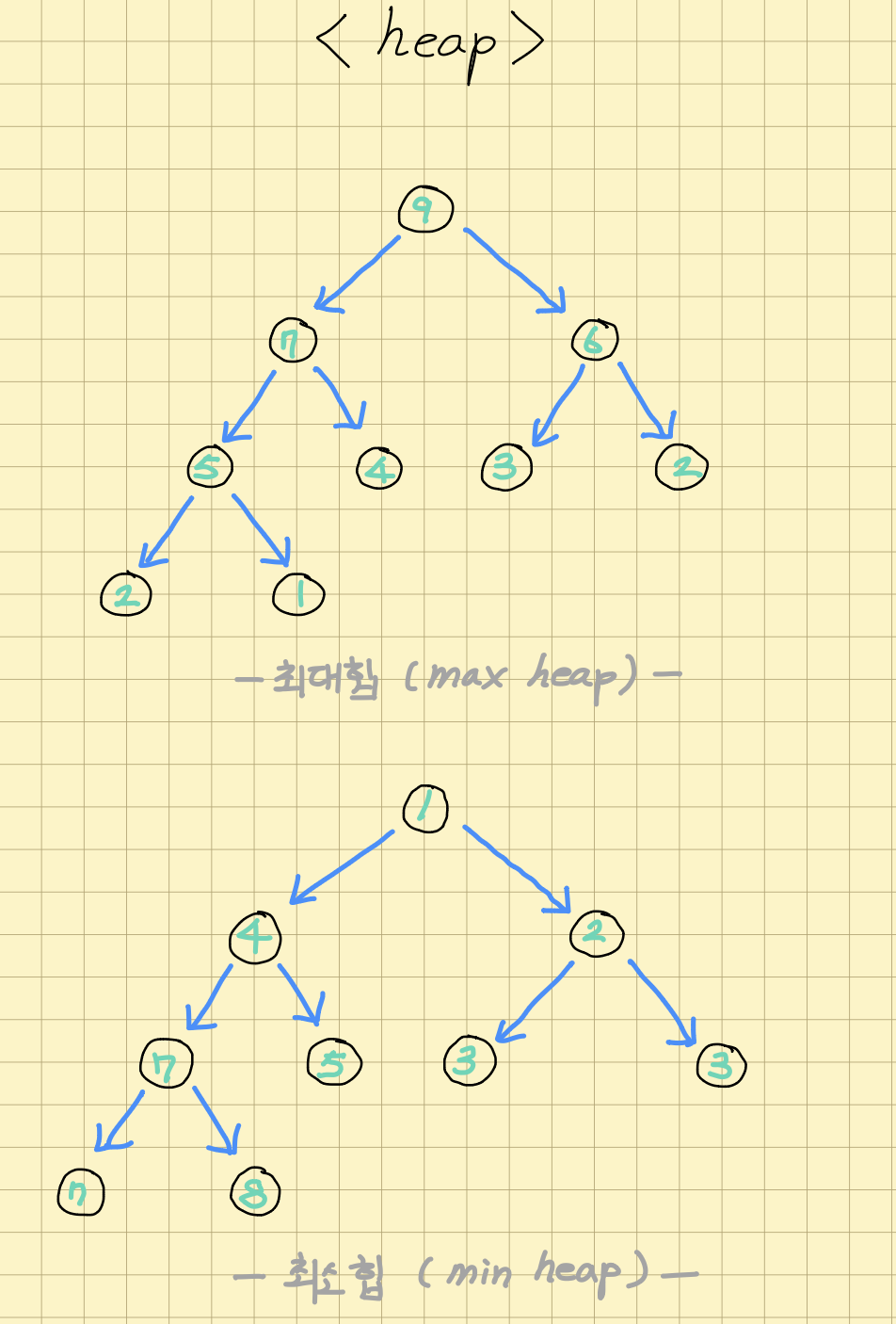
Heap 이란?
완전 이진 트리의 형태를 가지며, 부모 노드의 값이 자식 노드의 값보다 크거나 작은 규칙을 따르는 자료 구조이다. 주로 우선순위 큐(priority queue)를 구현하는 데 사용되며, 최대 힙(Max Heap)과 최소 힙(Min Heap)으로 나뉜다.
Heap의 특징
-
루트 노드의 값이 항상 최대(Max Heap) 또는 최소(Min Heap)이다.
-
완전 이진 트리의 형태를 유지한다.
-
배열로 효율적으로 구현이 가능하다.
Heap의 장점
- 우선순위 큐의 구현에 용이하며, 최댓값 또는 최솟값을 빠르게 찾을 수 있다.
시간 복잡도
-
삽입 및 삭제: O(log n) - 힙의 높이에 비례
-
힙 생성(Build Heap): O(n) - 선형 시간에 구성 가능
Heap 사용 예시
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class HeapExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 최소 힙(Min Heap) 생성
PriorityQueue<Integer> minHeap = new PriorityQueue<>();
// 최대 힙(Max Heap) 생성
PriorityQueue<Integer> maxHeap = new PriorityQueue<>((a, b) -> b - a);
// 요소 추가
minHeap.add(3);
minHeap.add(1);
minHeap.add(4);
maxHeap.add(3);
maxHeap.add(1);
maxHeap.add(4);
System.out.println("Min Heap: " + minHeap); // 출력: Min Heap: [1, 3, 4]
System.out.println("Max Heap: " + maxHeap); // 출력: Max Heap: [4, 3, 1]
// 최소값 또는 최대값 얻기 (삭제하지 않고)
int minElement = minHeap.peek();
int maxElement = maxHeap.peek();
System.out.println("Min Element: " + minElement); // 출력: Min Element: 1
System.out.println("Max Element: " + maxElement); // 출력: Max Element: 4
// 최소값 또는 최대값 삭제
minHeap.poll();
maxHeap.poll();
System.out.println("Min Heap after poll: " + minHeap); // 출력: Min Heap after poll: [3, 4]
System.out.println("Max Heap after poll: " + maxHeap); // 출력: Max Heap after poll: [3, 1]
}
}