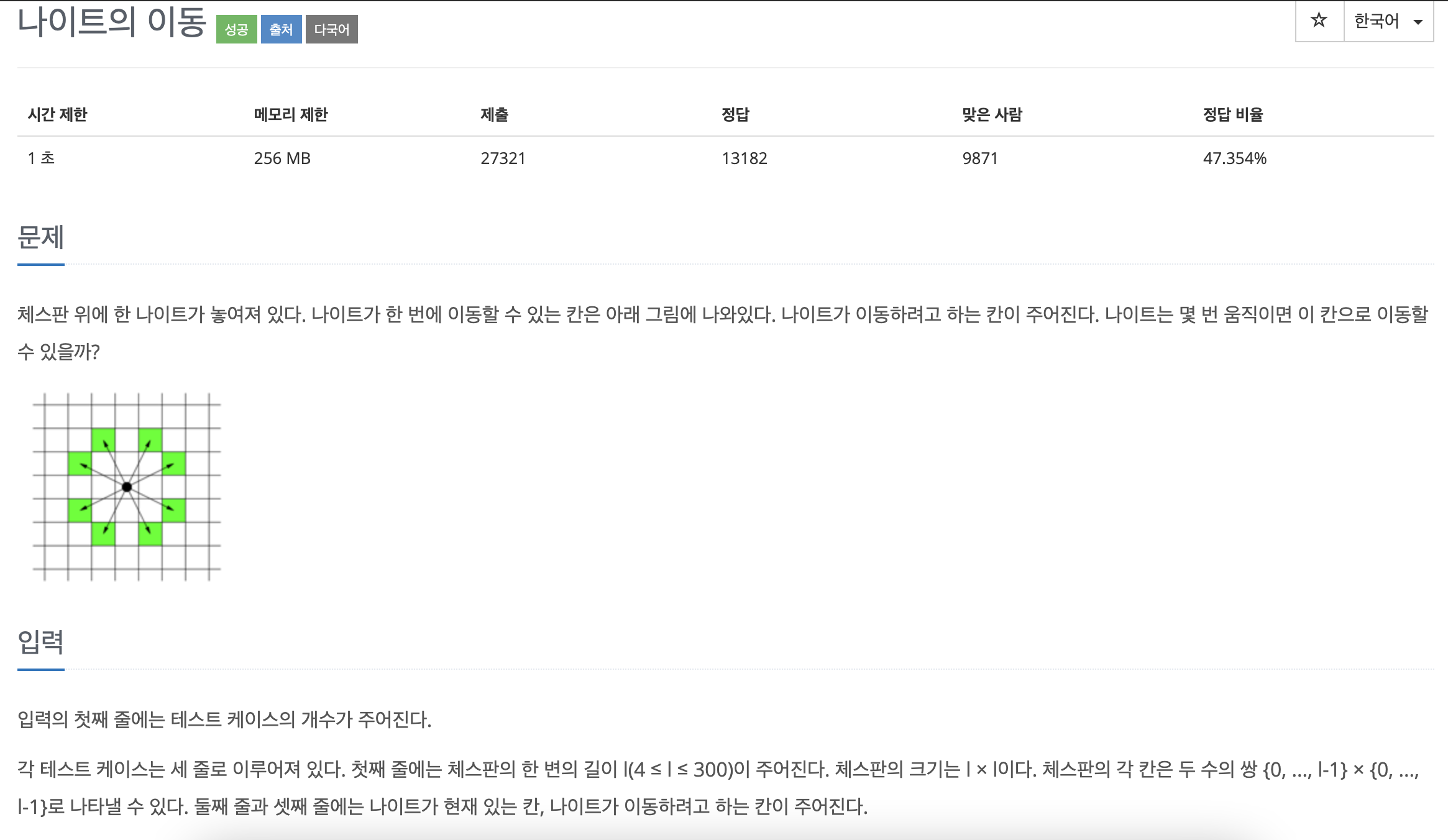
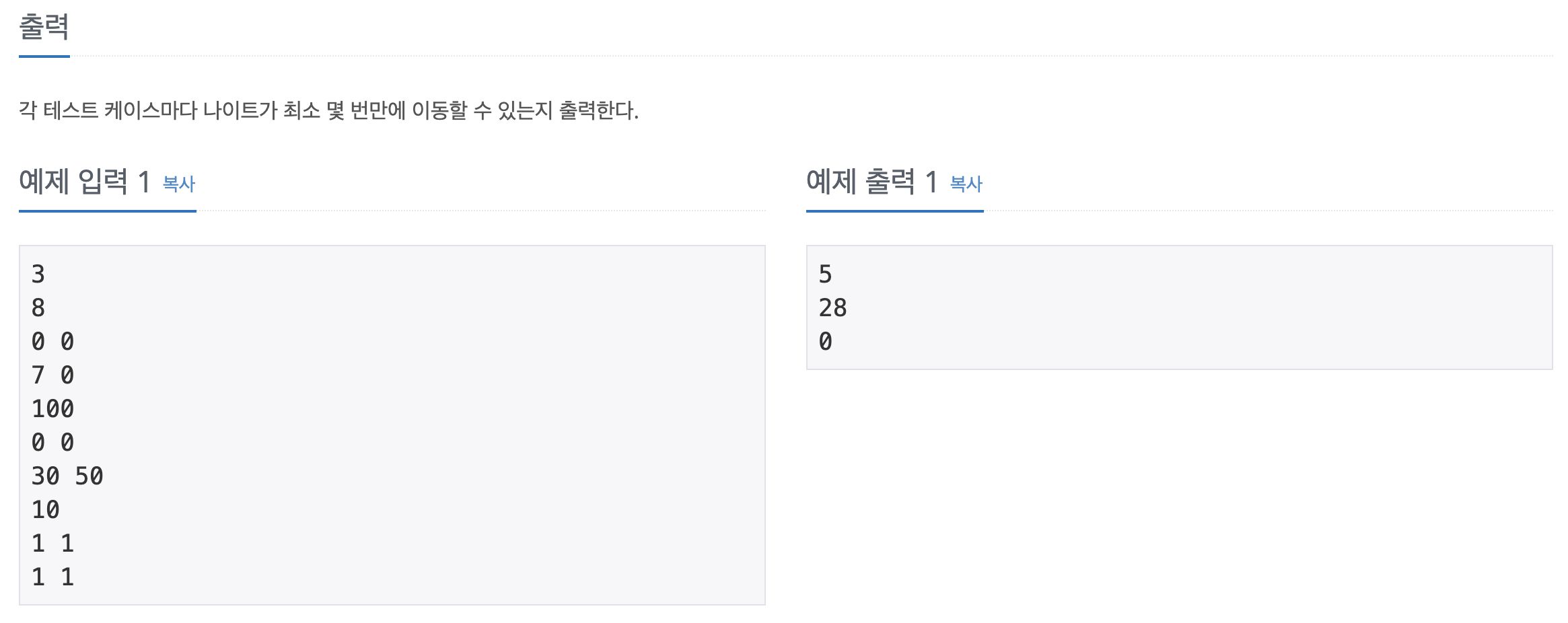
-- 문제를 더 정확하게 읽는다면 더 빨리 풀 수 있다고 생각! 꼼꼼하게 하자!
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <queue>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
int cnt, t, cs, xx, yy;
int dx[8] ={1, 2, 2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1};
int dy[8] ={2, 1, -1, -2, -2, -1, 1, 2};
queue<pair<int, int>> Q;
int chk[301][301];
void BFS() {
int x, y;
while (!Q.empty()) {
x = Q.front().first;
y = Q.front().second;
Q.pop();
for (int i = 0; i < 8; i++) {
// 문제조건 잘 읽자...
if (x + dx[i] < 0 || x + dx[i] >= cs || y + dy[i] < 0 || y + dy[i] >= cs) continue;
if (x + dx[i] == xx && y + dy[i] == yy) {
cout << chk[x][y] << endl;
return;
}
if (chk[x + dx[i]][y + dy[i]] == 0) {
Q.push(make_pair(x + dx[i], y + dy[i]));
chk[x + dx[i]][y + dy[i]] = chk[x][y] + 1;
}
}
}
}
int main(){
int x, y;
cin >> t;
for(int i=0; i<t; i++){
cin >> cs;
cin >> x >> y;
cin >> xx >> yy;
if (x == xx && y== yy){
cout << 0<< endl;
continue;
}
chk[x][y] = 1;
Q.push(make_pair(x, y));
BFS();
// 체크배열과 queue 초기화
memset(chk, 0, sizeof(chk));
Q = queue<pair<int,int>>();
}
}
- 배열 초기화
#include <cstring>
// 함수의 원형
void* memset(void* ptr, int value, size_t num);
memset(초기화할 배열 시작점, 초기화 값, 메모리의 길이);