 이전 시간에 만든 fetch API 써보기 상품 목록과 상품 옵션을 불러오는 컴포넌트를 이용해 SPA를 만들어볼 것이다. SPA 시 주의할 점은
이전 시간에 만든 fetch API 써보기 상품 목록과 상품 옵션을 불러오는 컴포넌트를 이용해 SPA를 만들어볼 것이다. SPA 시 주의할 점은 index.html에서 스크립트를 불러올 때 절대 경로를 써야한다는 것이다.
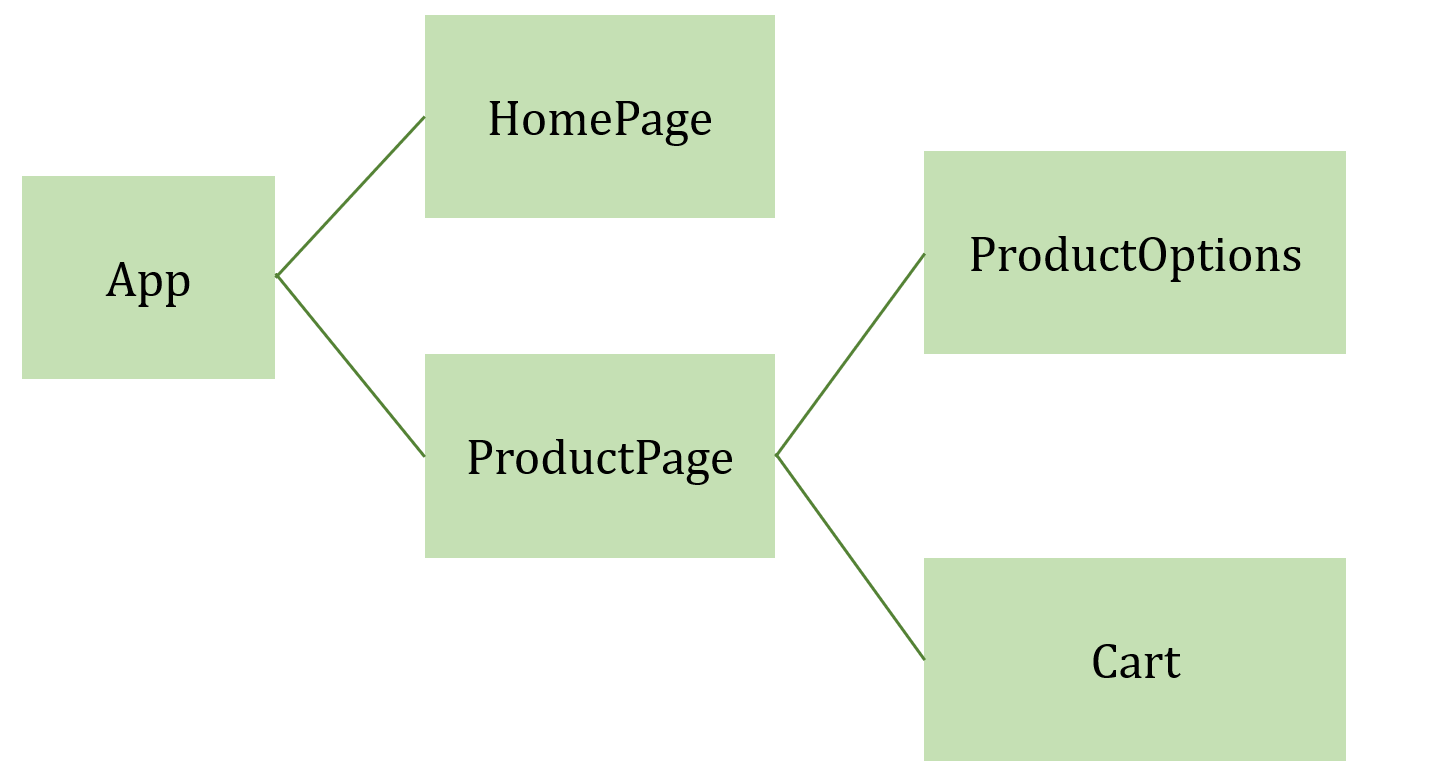
URL routing 처리하기
- URL path (
location.pathname) 별 각 화면을 페이지 컴포넌트로 정의location.pathname으로 현재 path를 얻어, 어떤 페이지 컴포넌트를 렌더링할지 라우팅하는 route 함수를 정의한다.- url이 변경되는 경우 route 함수가 호출되야 한다.
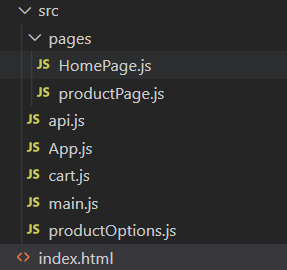
파일 구조는 다음과 같다.
index.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="ko">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
</head>
<body>
<main id="App"></main>
<script src="./src/main.js" type="module"></script>
<!-- 상대경로가 아닌 절대경로로 불러오기 -->
</body>
</html>main.js
import App from "./App.js"
const $target = document.querySelector("#App")
new App({ $target })App.js
페이지 컴포넌트를 생성하고, route( )를 이용해 어떤 컴포넌트를 렌더링할지 결정한다.
App 컴포넌트가 생성되자마자 this.init 함수를 통해 라우트를 호출하도록 한다. 그래야 처음 진입 시 현재 url에 맞는 페이지가 렌더링된다.
import HomePage from './pages/HomePage.js'
export default function App({ $target }){
const homePage = new HomePage({$target})
// 여기서 patnName에 따라 페이지 컴포넌트 렌더링 처리
this.route = () => {
const {pathname} = location
$target.innerHTML = '' // 라우트 전에 기존에 렌더링되었던걸 지우는 작업
if(pathname === '/'){
// 루트 경로일 경우 homrPage 그리기
homePage.render()
} else if(pathname.indexOf('/products/') > -1){
// productPage 그리기
} else{
// 404처리
$target.innerHTML = `<h1>404 Not Found</h1>`
}
}
this.init = () => {
this.route()
}
window.addEventListener('click', e => {
if(e.target.className === 'link'){
e.preventDefault()
// a 태그를 눌러도 href 링크로 이동하지 않게함
// a태그의 기본 기능을 꺼주고 pushstate 호출로 바꿔주기 위함
const {href} = e.target
e.preventDefault();
const path = href.replace(window.location.origin, '')
// location 중 origin 제거
history.pushState(null, null, path) // url 바꾸기
this.route() // 이벤트 발생 시 url 처리
}
})
/* 뒤로가기 or 앞으로가기는 click이 아니기 때문에 route()가 출력되지 않는다.
따라서 popstate 이벤트에 route() 함수 걸어주기 */
window.addEventListener('popstate', () => this.route())
this.init()HomePage.js
import {request} from '../api.js'
export default function Hompage({$target}){
const $home = document.createElement('div')
// 기존에는 컴포넌트를 만들자마자 $target에 appendChild를 했는데 여기선 하지 않을 것이다.
// route 함수에서 어떤 페이지 컴포넌트를 렌더링할지 정하기 때문이다.
this.render = () => {
request('products')
.then(products => {
$home.innerHTML = `
<h1>Home Page</h1>
<ul>
${products.map(product =>`
<li>
<a class="link" href="/products/${product.id}">${product.name}</a>
</li>`
).join('')}
</ul>
`
$target.appendChild($home)
})
}
}productPage.js
/* state 구조
{
productID: 1, // 외부에서 받는 값
product: product,
optionData: [],
selectedOptions : []
}
*/
import {request} from "../api.js"
import ProductOptions from "../productOptions.js"
import Cart from "../cart.js"
export default function ProductPage({
$target,
initialState
}){
const $product = document.createElement('div')
this.state = initialState // initialState => { productID: 1 }
// productOptionsComponent 컴포넌트 생성
const productOptionsComponent = new ProductOptions({
$target : $product,
initialState : [],
onSelect : (option) => {
const nextState = {...this.state}
const {selectedOptions} = nextState
const selectedOptionIndex = selectedOptions.findIndex((selectedOption) =>
selectedOption.optionID === option.optionID)
if (selectedOptionIndex > -1){
nextState.selectedOptions[selectedOptionIndex].ea++
}else{
nextState.selectedOptions.push({
optionID: option.optionID,
optionName: option.optionName,
optionPrice: option.optionPrice,
ea : 1
})
}
this.setState(nextState)
}
})
// Cart 생성
const cart = new Cart({
$target: $product,
initialState:{
productName: '',
basePrice: 0,
selectedOptions: [ ]
},
onRemove : (selectedOptionIndex) => {
const nextState = {...this.state}
nextState.selectedOptions.splice(selectedOptionIndex,1)
this.setState(nextState)
}
})
this.setState = (nextState) =>{
/* nextState.productId와 현재 this.state.productId가 맞지 않는 경우는
fetchOptionData에 nextState.productId를 넘겨준다. */
if(nextState.productID !== this.state.productID){
fetchOptionData(nextState.productID)
return
}
this.state = nextState
const {products,selectedOptions,optionData} = this.state
productOptionsComponent.setState(optionData)
// optionData가 fetch로 새로 들어오면 productOptionsComponent 상태도 같이 업데이트
cart.setState({
productName: products.name,
basePrice: products.basePrice,
selectedOptions: selectedOptions
})
this.render()
}
this.render = () => {
$target.appendChild($product)
}
// fetch 작업
const fetchOptionData = (productID) => {
return request(`products?id=${productID}`)
.then(product => {
const products = product[0]
console.log(product)
this.setState({
...this.state,
products,
optionData : [],
selectedOptions : []
})
// this.state : { productID: 1 } => { productID: 1, products, optionData : [] }
// 여기서 products 값이 채워짐
return request(`product-options?product.id=${products.id}`)
})
.then(productsOptions => {
return Promise.all([
Promise.resolve(productsOptions),
Promise.all(
productsOptions.map(productsOption => productsOption.id).map(id => {
return request(`product-option-stocks?productOption.id=${id}`)
})
)
])
})
.then(data => {
const [options, stocks] = data // Stocks [][][]
const optionData = options.map((options,i) =>{
const stock = stocks[i][0].stock
return {
optionID : options.id,
optionName : options.optionName,
optionPrice : options.optionPrice,
stock : stock
}
})
this.setState({
...this.state,
optionData
// this.state의 optionData에 값을 넣어주는 작업
// 초기 id만 있던 상태에서 products, optinData를 모두 가진 this.state 완성!
})
})
}
}productOptions.js
export default function ProductOptions({$target,initialState,onSelect}){
const $select = document.createElement('select')
$target.appendChild($select)
// 상품옵션 이름 렌더링 시 [상품명 + 옵션명 + 재고 : n개] 이런 형식으로 보여줘야 함
// 재고가 0인 상품의 경우 옵션을 선택하지 못하게 함
this.state = initialState
this.setState = (nextState) =>{
this.state = nextState
this.render()
}
const createOptionFullName = ({optionName, optionPrice, stock}) => {
return `${optionName}
${optionPrice > 0 ? `(옵션가 : ${optionPrice}` : '(옵션가 : 0'} |
${stock > 0 ? `재고 : ${stock})` :'(재고 없음)'}
`
}
$select.addEventListener('change',(e)=>{
const optionId = parseInt(e.target.value)
const option = this.state.find(option => option.optionID === optionId)
onSelect(option)
})
// 기본적으로 render 함수는 파라미터가 없어야 한다. 순수하게 state만을 보고 렌더링되어야 한다.
this.render = () => {
if(this.state && Array.isArray(this.state)){
// this.state가 제대로 들어있는지, 배열인지 아닌지 판별
$select.innerHTML = `
<option value='' disabled selected>선택하세요</option>
${this.state.map((option)=>
// <option disabled>
`<option value="${option.optionID}" ${option.stock === 0 ? 'disabled' : ''}>
${createOptionFullName(option)}</option>"`).join('')}
`
}
}
this.render()
}cart.js
/* state 구조
{
productName: 상품 이름,
basePrice: 기본 가격,
selectedOption: [option]
}
*/
export default function Cart({$target, initialState, onRemove}){
const $cart = document.createElement('div')
$target.appendChild($cart)
this.state = initialState
this.setState = (nextState) => {
this.state = nextState
this.render()
}
const calculateTotalPrice = () => {
const {basePrice, selectedOptions} = this.state
return selectedOptions.reduce((acc, option) =>
acc + (basePrice + option.optionPrice) * option.ea, 0)
}
this.render = () => {
const {productName, basePrice, selectedOptions} = this.state
$cart.innerHTML = `
<ul>
${Array.isArray(selectedOptions) && selectedOptions.map((option,i) =>
`<li data-index="${i}" class='cartItem'>${productName} - ${option.optionName} |
${basePrice + option.optionPrice}, ${option.ea}개
<button class='remove'> x </button>
</li>`).join('') }
</ul>
<div>${calculateTotalPrice()}</div>`
$cart.querySelectorAll('.remove').forEach($button=>{
$button.addEventListener('click',(e)=>{
const $li = e.target.closest('li') // 버튼에서 가장 인접한 li 찾기
const { index } = $li.dataset
onRemove(parseInt(index))
})
})
}
this.render()
}api.js
/* 서버를 여러개쓰면 서버 앞단의 공통된 도메인을 따로 뽑아 상수로 관리하는 것이 좋다. */
const API_END_POINT = "https://misc.edu-api.programmers.co.kr/"
export const request = (url) => {
return fetch(`${API_END_POINT}${url}`)
.then(res => {
if(res.ok){
return res.json()
}
throw new Error(`${res.state} Error`)
})
.catch(e => alert(e.message))
}
history API를 이용하면 화면 전환 없이 브라우저의 url을 바꿀 수 있다.history API로 url 변경 후 새로고침을 하면 변경된 url의 실제 파일을 찾으려 하기 때문에 404 에러가 난다.
