자료구조&알고리즘

자료구조
- 메모리를 효율적으로 사용하면서 빠르고 안정적인 데이터를 처리하는 것이 궁극적인 목표이다.
- Stack, Queue, Graph, Tree 등
알고리즘
- 특정 문제를 효율적으로 빠르게 해결하는 것이 궁극적인 목표로 정해진 일련의 절차나 방법을 공식화한 형태로 표현한 것이다.
- 이진 탐색, 최단 거리 탐색 등
개발자로서 꼭 갖춰야할 핵심 역량 ->
문제 해결 능력
논리적 사고, 전산화 능력, 엣지 케이스 탐색(버그 줄이기)
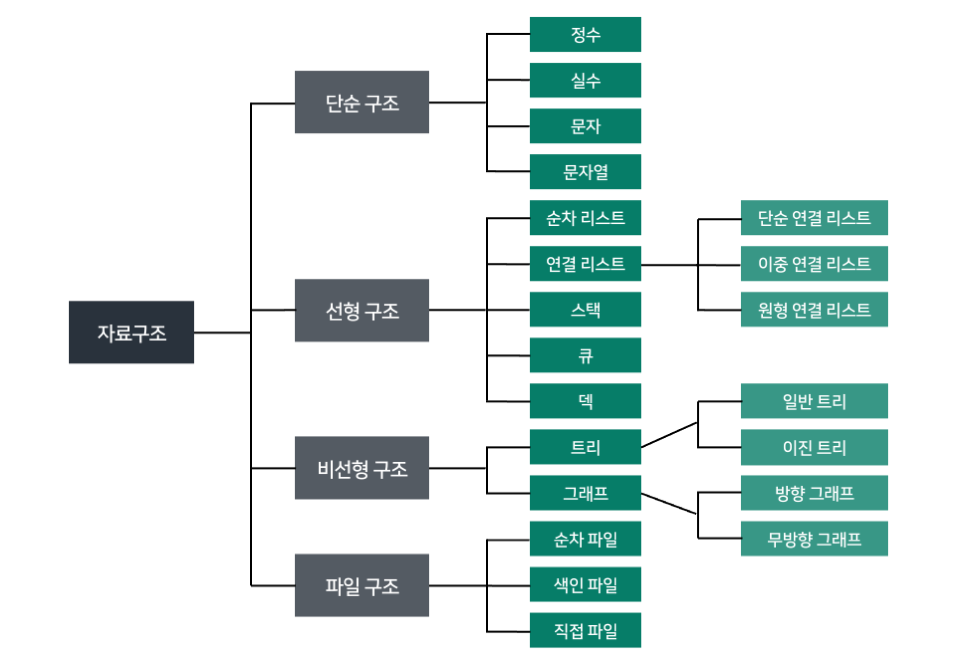
선형구조
- 자료들이 선형으로 나열되어 있는 구조. 한 원소 뒤에 하나의 원소 만이 존재하는 형태로 배열, 연결 리스트, 스택, 큐 등이 있다.
비선형구조
- 계층적 구조나 망형 구조를 표현하기에 적절하며 원소 간 다대다 관계를 가지는 구조로 트리, 그래프 등이 있다.
시간 복잡도
- 프로그램의 성능을 정확히 파악하는 것은 불가능...
- 컴퓨터 과학자들이 대략적으로 성능을 비교하기 위해 상대적인 표기법을 사용하기로 했다.
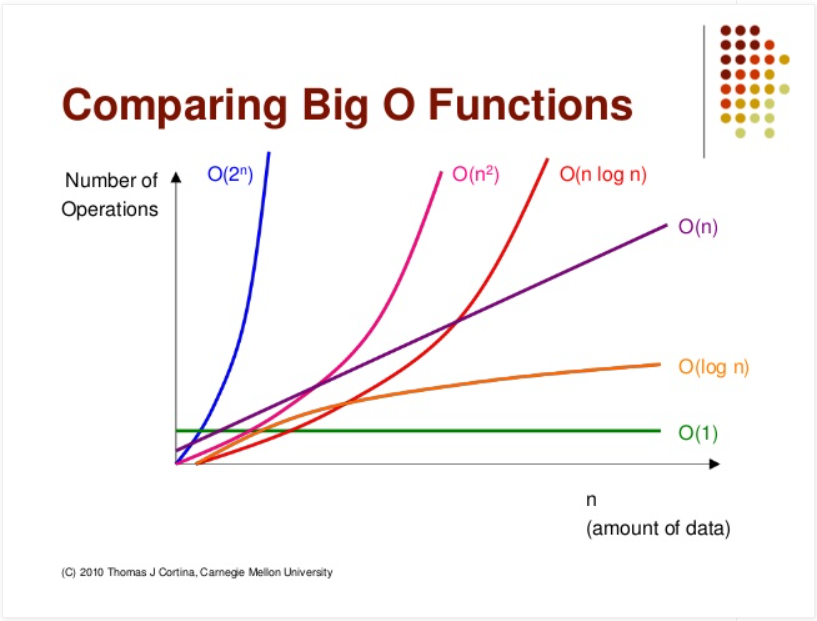
빅오 표기법
- 점근적 표기법을 따름(함수의 증강추세를 비교)
O(1) < O(log n) < O(n) < O(n log n) < O(n²) < O(2ⁿ) < O(n!)
for(let i=0; i<n; i++){
//선형시간 O(n)
}
for(let i=1; i<=n; i*=2){
//O(log n)
}
for(let i=0; i<n; i++){
for(let j=1; j<=n; j*=2){
//O(n log n)
}
}
for(let i=0; i<n; i++){
for(let j=0; j<n; j++){
// O(n²)
}
}가장 중요한 것!!!
- 상수항은 무시
- 가장 큰 항 외엔 무시
- 그럼 성능 측정법은?
// Date 객체를 이용
//시작 시간을 구함
const start = new Date().getTime();
//코드 구현
//끝 시간을 구함
const end = new Date().getTime();
console.log(end - start);배열
- 연관된 데이터를 연속적인 형태로 구성한 구조(순서대로 index를 가짐)
배열의 특징
- 고정된 크기를 가지며 일반적으로 동적으로 크기를 늘릴 수 없다.
- JS처럼 대부분 스크립트 언어는 동적으로 크기가 증감되도록 설정되어 있다.
- 원소의 index를 알고 있다면 O(1)로 원소를 찾을 수 있다.
- 원소를 삭제 시 해당 index에 빈자리가 생긴다.
- 삭제 후 순서를 맞춘다면 O(n)이 소요된다(index 재조정)
- 배열 중간에 요소를 추가한다면 O(n)이 소요된다.
😏추가와 삭제가 반복되는 로직이라면 배열 사용 권장X 탐색에 유리
배열 생성
//빈 Array 생성
let arr1 = [];
console.log(arr1);
//미리 초기화된 Array 생성
let arr2 = [1,2,3,4,5];
console.log(arr2);
//많은 값을 같은 값으로 초기화한 배열 생성 fill
let arr3 = Array(10).fill(1);
console.log(arr3);
//특정 로직을 사용해 초기화 할 경우 from
let arr4 = Array.from({length : 100}, (_,i) => i);
console.log(arr4);배열 요소 추가, 삭제
const arr = [1,2,3,4];
console.log(arr);
//끝에 5 추가
arr.push(5);
//여러 개 추가도 가능
arr.push(6,7);
//3번 인덱스에 100 추가
arr.splice(3,0,100); //O(n)
console.log(arr);
//3번 인덱스 값 제거
arr.splice(3,1); //O(n)
console.log(arr);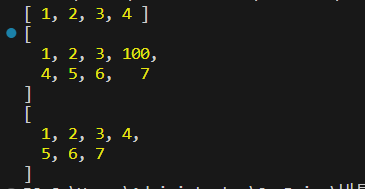
- index가 숫자가 아닌 문자열이나 논리값도 들어갈 수 있다.(근본적으로 객체 타입이기 때문)
- 인덱스가 무관한 값이면 길이에 영향을 미치지 않는다.
- 크기가 동적으로 변한다.
const arr = [1,1,2,3];
arr["string"] = 10;
arr[false] = 0;
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);
arr[4] = 15;
console.log(arr);
console.log(arr.length);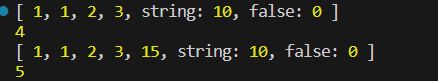
연결리스트
- 추가와 삭제가 반복되는 로직이라면 뭘 써야할까?
- 각 요소를
포인터로 연결하여 관리하는 선형 자료구조이다. 각 요소는노드라고 부르며 데이터 영역, 포인트 영역을 가지고 있다.
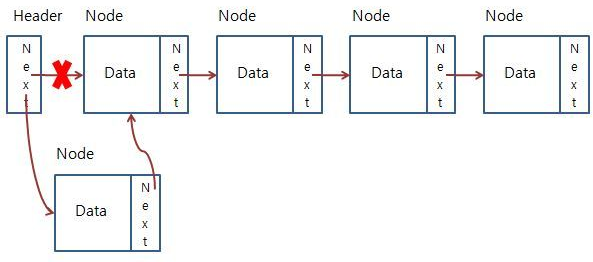
연결리스트의 특징
- 메모리가 허용하는 한 요소를 제한없이 추가할 수 있다.
- 탐색은 O(n)이 소요된다.
- 요소를 추가하거나 삭제할 때는 O(1)이 소요된다.🙄(추가, 제거에 용이)
- Singly Linked List, Doubly Linked List, Circular Linked List가 존재
배열과 연결리스트의 차이점
- 배열은 순차적인 데이터가 들어가기 때문에 메모리의 영역을 연속적으로 사용
- 연결리스트는 순차적이지 않기 때문에 데이터가 퍼져있다.(위치를 알기 위해 포인터를 사용)
- 배열 요소 추가와 삭제 -> O(n) 연결리스트는 ? O(1)
Singly Linked List
Head(시작)에서Tail(끝)까지 단방향으로 이어지는 연결 리스트
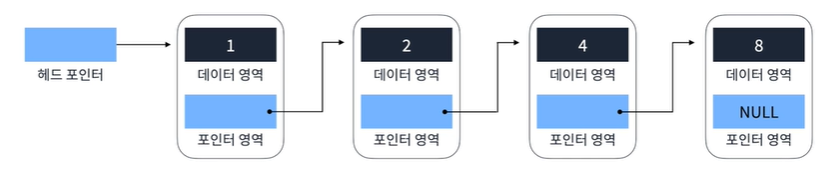
- 핵심 로직 > 요소 찾기
O(n), 요소 추가, 요소 삭제O(1)
Singly Linked List 알아보기
class Node{
constructor(value){
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class SinglyLinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0; // 길이 추가
}
find(value){ //요소 찾기
let curNode = this.head;
while(curNode.value !== value){
curNode = curNode.next;
}
return curNode;
}
append(newValue){ //요소 추가 > 끝 부분에
const newNode = new Node(newValue); //새로운 노드 생성
if(this.head === null){ //연결리스트에 아무런 값이 없을 시
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}else{
this.tail.next = newNode;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
insert(node,newValue){ //요소 추가 > 중간에
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
newNode.next = node.next; //새로운 노드의 다음이 입력받은 노드의 다음을 가르키도록 함
node.next = newNode; //입력받은 노드의 다음이 새로운 노드가 되도록 함
this.length++;
}
remove(value){ //요소 삭제 > 여기서는 값을 찾은 다음 삭제하도록 작성 O(n) 소요
// 상수 시간이 되고 싶으면 삭제할 노드의 이전 노드를 매개 변수로 작성해 주면 됨
let preNode = this.head;
while(preNode.next.value !== value){
preNode = preNode.next;
}
if(preNode.next !== null){
preNode.next = preNode.next.next;
// 다음의 다음노드를 가리키도록 설정하면 중간 노드가 아무런 노드와 연결되지 않기 때문에 자동으로 삭제된다.
// 가비지 컬렉션 통해 메모리 상에서도 자연스럽게 삭제됨
}
this.length--;
}
display(){
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = '[';
while(curNode !== null){
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString
.substr(0,displayString.length-2);
displayString += ']';
console.log(displayString);
}
}
const linkedlist = new SinglyLinkedList();Doubly Linked List
- 양방향으로 이어지는 연결 리스트, Singly Linked List보다 자료구조의 크기가 조금 더 크다.
- 포인터가 2개이다. (이전, 다음)
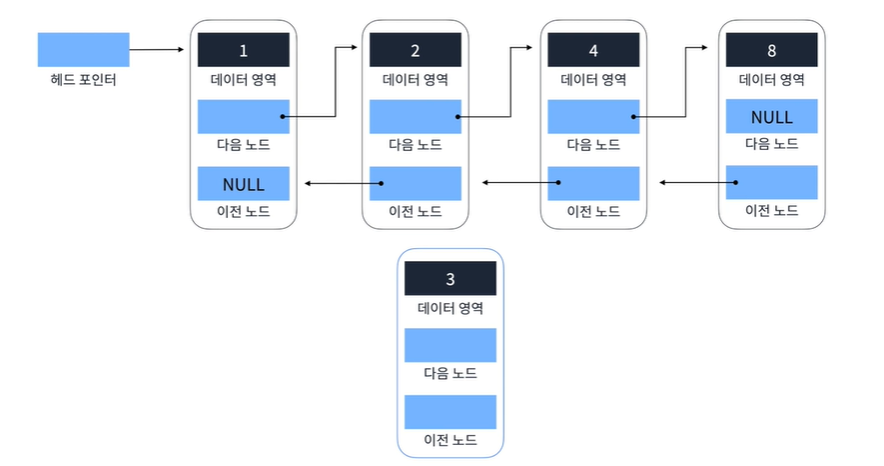
class Node{
constructor(value){
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
this.prev = null;
}
}
class DoublyLinkedList{
constructor(){
this.head = null;
this.tail = null;
this.length = 0;
}
find(value){
let curNode = this.head;
while(curNode.value !== value){
curNode = curNode.next
}
return curNode;
}
append(newValue){
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
if(this.head === null){
this.head = newNode;
this.tail = this.head;
}else{
this.tail.next = newNode;
newNode.prev = this.tail;
this.tail = newNode;
}
this.length++;
}
insert(node,newValue){
const newNode = new Node(newValue);
const next = node.next;
next.prev = newNode;
node.next = newNode;
newNode.next = next;
newNode.prev = node;
this.length++;
}
remove(preNode,value){
if(preNode.next !== null){
const next = preNode.next.next;
preNode.next = next;
next.prev = preNode;
}
this.length--;
}
display(){
let curNode = this.head;
let displayString = '[';
while(curNode !== null){
displayString += `${curNode.value}, `;
curNode = curNode.next;
}
displayString = displayString
.substr(0,displayString.length-2);
displayString += ']';
console.log(displayString);
}
}
const example = new DoublyLinkedList();Circular Linked List
- 단방향, 양방향 연결 리스트에서 Tail이 Head로 연결되는 연결 리스트
- 메모리를 아껴쓸 수 있고, 원형 큐 등을 만들 때도 사용된다.
- 중간에서 탐색하더라도 한바퀴를 돌아 탐색 가능
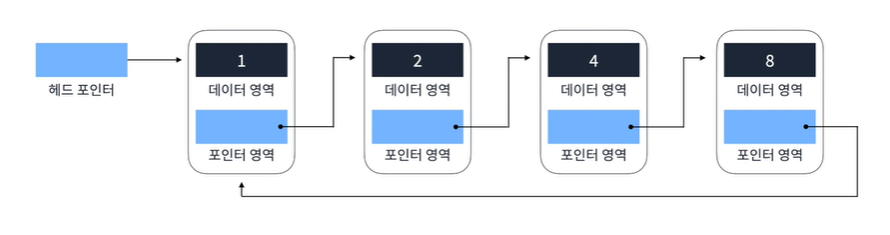
스택
- `Last Input First Out(LIFO) 개념을 가진 자료구조(pop, push)
- 맨 위의 요소는
top - Array로 stack 구현
const stack = [];
stack.push(1);
stack.push(2);
stack.push(3);
console.log(stack); //[ 1, 2, 3 ]
stack.pop();
console.log(stack); //[ 1, 2 ]- Linked List로 stack 구현
head가top> head를 추가하고 제거하는 방식
class Node{
constructor(value){
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Stack{
constructor(){
this.top = null;
this.size = null;
}
push(value){
const newNode = new Node(value);
newNode.next = this.top;
this.top = newNode;
this.size++;
}
pop(){
const value = this.top.value;
this.top = this.top.next;
this.size--;
return value;
}
size(){
return this.size;
}
}
const stack1 = new Stack();