영상처리
1. 직접 데이터 접근 (C++) -> 자바, C#
2. 있는 라이브러리 활용(딥러닝 세계)
둘 다 고전적 영상처리
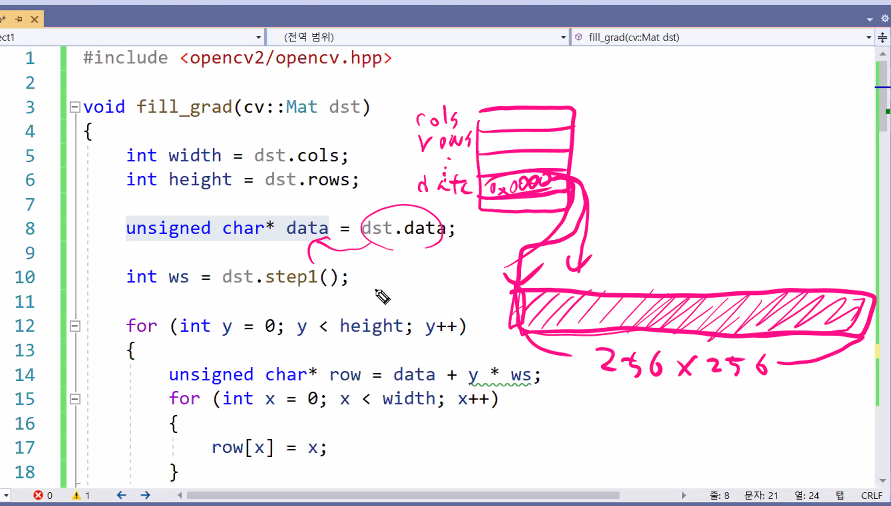
실제 메모리의 크기는 9byte
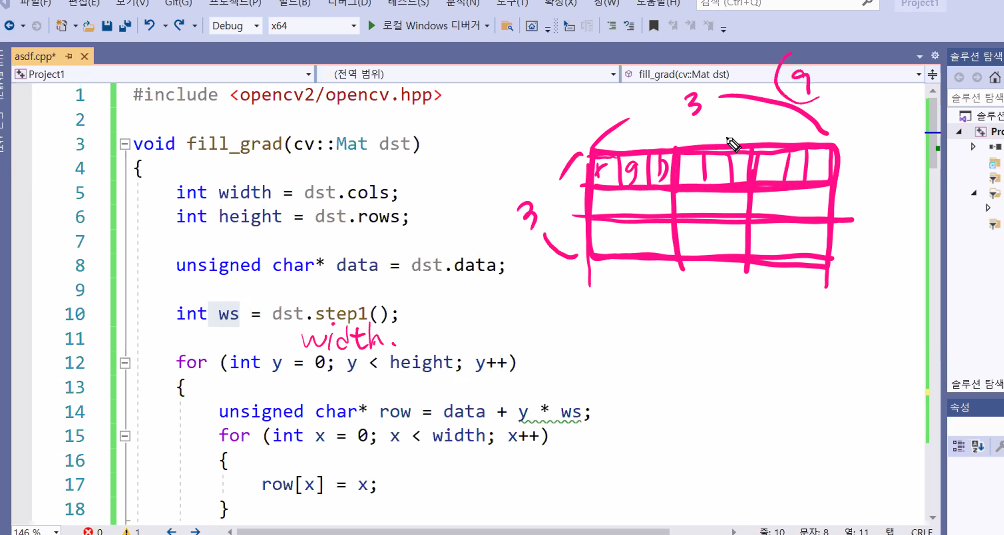
접근할 수 있는 포인터를 가져오고

포인터 값을 획득하는 것
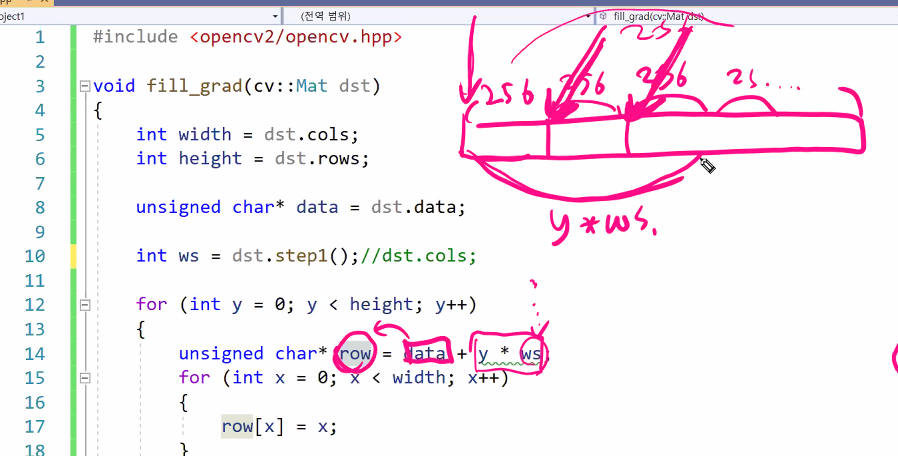
row[x] = x; 대신 data[y * ws +x]=x;도 가능
근데 row포인터를 새로 만드는게 빠르긴 함
row에 값을 집어 넣을 때 최적화를 위해 y와 x값을 살려줘야함
여기서 for문 한 번만 쓰는 것도 가능
x에 본인이 원하는 영상처리를 집어 넣으면 됨
8bit는 0~255까지 저장할 수 있는데
256 이상부터 저장하면 overflow가 일어남
overflow를 컴공으로 풀어보면
256 -> 0 x 0100
257 -> 0 x 0101
#include <opencv2/opencv.hpp>
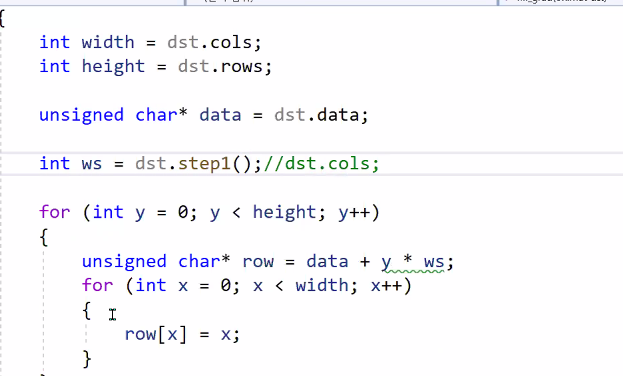
void fill_grad(cv::Mat dst)
{
int width = dst.cols;
int height = dst.rows;
unsigned char* data = dst.data;
// data 행렬에 대한 포인터 값을 받아올 수 있음
int ws = dst.step1();
// step은 width와 똑같은 값 가짐
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
unsigned char* row = data + y * ws;
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
row[x] = x;
}
}
}
void alpha_mix(cv::Mat src, cv::Mat dst, double alpha = 0.5)
{
int width = dst.cols;
int height = dst.rows;
// src와 dst가 같아야함
if(src.cols != dst || src.rows != dst.rows)
{
}
unsigned char* srcData = src.data;
unsigned char* dstData = dst.data;
int ws = dst.step1();
for (int y = 0; y < height; y++)
{
for (int x = 0; x < width; x++)
{
dstData[y * ws + x] =
(1 - alpha) * dstData[y * ws + x]
+ alpha * srcData[y * ws + x];
}
}
}
void add(cv::Mat src, cv::Mat dst)
{
int width = dst.cols;
int height = dst.rows;
unsigned char* srcData = src.data;
unsigned char* dstData = dst.data;
int ws = dst.step1();
int size = width * height;
/*for (int i = 0; i < size; i++)
{
dstData[i] += srcData[i];
}*/
unsigned char* srcDataEnd = srcData + size;
for (; srcData < srcDataEnd; srcData++, dstData++)
{
*dstData += *srcData;
}
}
//threshold???
//(python)import numby as np
//= (c)np::zeros
//(python) class Mat:
def _init_(self, rows, cols, type):
//=(c)def -init-(int self, int rows, int cols):
pass
//=(c)def -init-(float self, float rows, float cols):
pass
// int받는 거, float 만든 거 따로 해줘야함
int main()
{
cv::Mat mat(256, 256, CV_8UC1);
//fill_grad(mat);
cv::imshow("fill_grad", mat);
//imshow와 waitKey는 항상 같이 써야함, show만 하면 퍼포먼스가 할당이 안 됨
cv::waitKey(0); //시간 입력, 0은 무한히 기다리는 거, 화면에 띄워줄 수 있는 시간을 벌어줌
cv::Mat mat2 = cv::Mat::zeros(256, 256, CV_8UC1);
alpha_mix(mat, mat2);
cv::imshow("alpha_mix", mat2);
cv::waitKey(0);
cv::Mat mat3 = cv::Mat::ones(256, 256, CV_8UC1) * 10;
//mat3 += mat;
add(mat, mat3);
cv::imshow("add", mat3);
cv::waitKey(0);
}이전 프로그램이 썼던 데이터가 남아있는 경우가 쓰레기 값 보통 컴퓨터를 킬 때 랜덤 쓰레기 값이 적어져 있음
zeros : 다 0으로 초기화 시켜주자
