저번 포스팅에 간단한 vue실습코드를 올렸다.
테스트 페이지 만들기
1. 파일 생성
Vue VSCode Snippets를 설치후 vbase를 누르면 생성 된다
/src/views/MyTest.vue
<template><div><div style="background-color: yellow">My Test Vue</div></div></template><script>
export default {};
</script><style lang="scss" scoped></style><template>안에는 하나의 태그
<template><div>test vue1</div><div>test vue2</div></template>2. 라우터 연결
URL을 통해 해당 페이지를 서비스 하기 위해서는 라우터에서 웹주소와 페이지를 연결 해야 한다.
생성한MyTest.vue 파일의 라우터를 연결
/src/router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import HomeView from '../views/HomeView.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'home',
component: HomeView
},
{
path: '/about',
name: 'about',
// route level code-splitting
// this generates a separate chunk (about.[hash].js) for this route
// which is lazy-loaded when the route is visited.
component: () => import(/* webpackChunkName: "about" */ '../views/AboutView.vue')
},
{
path: '/mytest',
name: 'MyTest',
component: () => import('../views/MyTest.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router
참고 앞으로의 라우터 연결에서 편의상 name은 사용하지 않도록 한다. (라우터 호출은 path를 통해서만 하도록 한다.)
3. 링크 연결
메인 화면에 링크를 걸어 준다. (<router-link to="/mytest">MyTest</router-link>)(vuejs의 링크는 <a href>를 사용하지 않고 라우터 링크 방식을 사용해야 한다. - SPA의 특징)
/src/App.vue
<template><div id="app"><h1>Hello My Vuejs</h1><nav><router-link to="/">Home</router-link> | <router-link to="/about">About</router-link> |
<router-link to="/mytest">MyTest</router-link></nav><router-view /></div></template>
...(생략)...
메인 화면에서 위 링크를 클릭해서 접속해 본다.직접 주소창으로 접속해도 된다http://localhost:8080/mytest
Life-cyle-Hooks
vue의 life-cyle은 다음과 같다.beforeCreated --> created --> beforeMount --> mounted (–> beforeUpdated --> updated) --> beforeDestroy --> destroyed
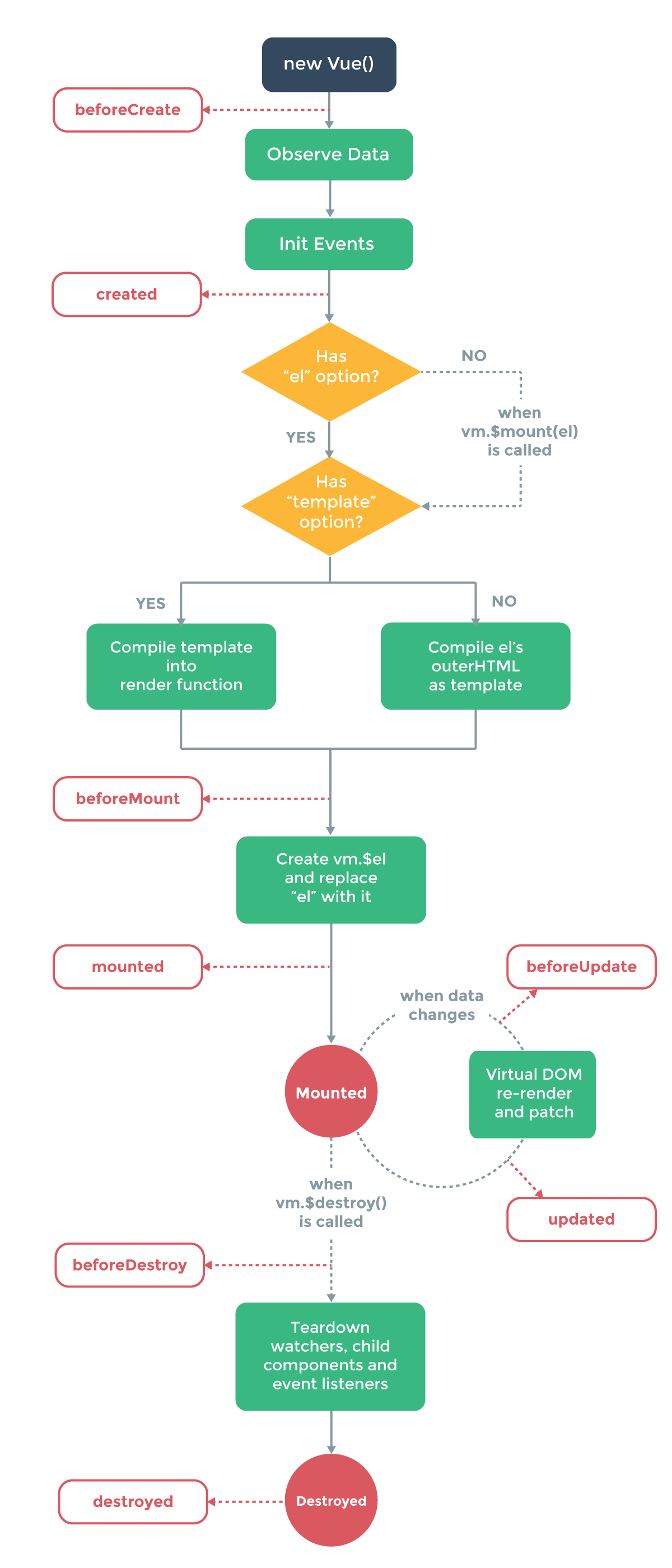
각 라이프사이클이 언제 동작 하는지 알아 본다.다음과 같이 MyTest.vue파일에 각 라이프 사이클을 출력해 본다.
/src/views/MyTest.vue
<template><div><div style="background-color: yellow">My Test Vue</div></div></template><script>
export default {
beforeCreate() {
console.log('beforeCreate')
},
created() {
console.log('created')
},
beforeMount() {
console.log('beforeMount')
},
mounted() {
console.log('mounted')
},
beforeUpdate() {
console.log('beforeUpdate')
},
updated() {
console.log('updated')
},
beforeDestroy() {
console.log('beforeDestroy')
},
destroyed() {
console.log('destroyed')
}
}
</script><style lang="scss" scoped></style>테스트 방법
- Home페이지로 접속 한다.
http://localhost:8080/- Reload(f5)를 한두번 눌러 클리어 해준다.
- 브라우저에서 개발자 도구(f12)를 꺼낸다.
- 개발자 도구의
Console탭을 클릭 한다.
- 개발자 도구의
- 테스트 페이지를 접속 한다.
http://localhost:8080/mytest - 개발자 도구의
Console탭을 관찰 한다.(출력 되는 문구의 차례를 살펴 본다.)- beforeCreate
- created
- beforeMount
- mounted
- 테스트 페이지에서
Home링크를 클릭 한다.http://localhost:8080/ - 개발자 도구의
Console탭을 관찰 한다. (출력 되는 문구를 살펴 본다.)- beforeDestroy
- destroyed
참고 추후 자식 컴포넌트와 부모 컴포넌트 사용 시 어떤 컴포넌트가 먼저 생성되는지 위 테스트 방법을 통해 확인할 수 있다.
Data binding
vue에서는 별도의 노력 없이 데이터를 실시간으로 바인딩 할 수 있다.다음의 파일을 생성하고 라우터를 등록 한다.
1. 입력 파일 생성
/src/views/InputTest.vue
<template><div><h1>binding test</h1><div><input v-model="message" /></div><div style="background-color: yellow">{{ message }}</div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
message: ''
}
}
}
</script><style lang="scss" scoped></style>2. 라우터 등록
/src/router/index.js
...(생략)...
const routes = [
...(생략)...
{
path: '/input-test',
component: () => import('../views/InputTest.vue')
}
]
...(생략)...
http://localhost:8080/input-test 주소로 접속할 수 있다.텍스트를 입력하면 실시간으로 출력되는 것을 알 수 있다.
주의 위 코드는 한글 타이핑시 문제가 발생 한다.한글 타이핑 해결은 다음과 같이 할 수 있다.
다음의 파일을 만들고 라우터를 등록해 준다. (라우터 path는 /input-test-kor로 한다)
/src/views/InputTestKor.vue
<template><div><h1>binding test</h1><div>영문: <input v-model="engText" /></div><div>한글: <input v-model="korText" @input="typingKor" /></div><div><h3>바인딩 영문: {{ engText }}</h3><h3>바인딩 한글: {{ korText }}</h3></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
engText: '',
korText: ''
}
},
methods: {
typingKor(e) {
this.korText = e.target.value
}
}
}
</script><style lang="scss" scoped></style>그렇다고 굳이 typingKor를 이용해서 실시간 처리를 해줄 필요는 없다.
event, method
이벤트를 발생시켜 method에서 처리할 수 있다.http://localhost:8080/test-event
/src/views/TestEvent.vue
<template><div><h1>Event test</h1><h3>1. 클릭/더블클릭 이벤트</h3><div><div><p>나의 나이는: {{ age }}</p><button @click="addAge(1)">1살 추가</button><button @click="deleteAge(1)">1살 삭제</button><button @dblclick="addAge(10)">10살씩 추가(더블클릭)</button><button @click.once="addAge(1)">1살 추가(한번만)</button></div><div style="margin-top: 20px"><input v-model="message" /><button @click="printMessage">콘솔 프린트</button></div></div><h3>3. 마우스 추적 이벤트</h3><div><div style="margin-top: 20px; height: 200px; width: 300px; border: 1px solid red" @mousemove="mouseTrack">
마우스 X: {{ mouseX }}, 마우스 Y: {{ mouseY }}
</div></div><h3>4. 키보드 이벤트</h3><div><div>이름: <input v-model="inputName" @keyup.enter="setMyName" />(Enter 이벤트)</div><div>아이디: <input v-model="inputId" @keyup.ctrl.enter="setMyId" />(Ctrl-Enter 이벤트)</div><p>나의 이름: {{ myName }}</p><p>나의 아이디: {{ myId }}</p></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
age: 20,
message: null,
mouseX: 0,
mouseY: 0,
inputName: null,
inputId: null,
myName: null,
myId: null
}
},
methods: {
addAge: function (year) {
this.age += year
},
deleteAge: function (year) {
this.age -= year
},
printMessage() {
console.log(this.message)
},
mouseTrack(event) {
// console.log(event)
this.mouseX = event.offsetX
this.mouseY = event.offsetY
},
setMyName() {
this.myName = this.inputName
},
setMyId() {
this.myId = this.inputId
}
}
}
</script>(v-on:click은 @click와 같다.)@click: 클릭 이벤트@dblclick: 더블클릭 이벤트@mousemove: 마우스 움직임 감지 이벤트@keyup: 키보드 감지 이벤트(keyup, keydown, keypress)
이벤트가 많기 때문에 필요할때마다 찾아서 사용하도록 한다.참고 브라우저 이벤트 정의 (https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/Events)참고 Html 이벤트 테스트 (https://www.w3schools.com/tags/ref_eventattributes.asp)참고 이벤트 핸들링 (https://kr.vuejs.org/v2/guide/events.html)
method vs computed
http://localhost:8080/test-computed
method와 computed의 차이점은 다음과 같다.
http://localhost:8080/test-computed
/src/views/TestComputed.vue
<template><div><h1>Computed Test</h1><button @click="a++">Add To A</button><button @click="b++">Add To B</button><p>A - {{ a }}</p><p>B - {{ b }}</p><p>Age + A = {{ addToA }}</p><p>Age + B = {{ addToB }}</p></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
a: 0,
b: 0,
age: 20
}
},
computed: {
addToA: function () {
console.log('addToA', this.a, this.age)
return this.a + this.age
},
addToB() {
console.log('addToB', this.b, this.age)
return this.b + this.age
}
}
}
</script>(addToA: function ( ) 과 addToB()는 작성 방법은 다르지만 동일하다. (후자가 더 많이 쓰임)computed는 이벤트가 발생하지 않아도 페이지 로딩 시 실행 된다.computed는 마치 변수처럼 사용 하는데 어떤 값이나 상태를 가공 한 후 리턴 받을 수 있다.
computed에서 전달인자(파라미터)를 받는 방법
computed에서는 기본적으로 파라미터를 받을 수 없지만 리턴 함수를 이용하면 받을 수 있다.
...
computed: {
someFuc () {
return (param1, param2) => {
const returnVal = param1 + param2
return returnVal
}
}
},
...
위와 같이 someFnc함수의 리턴 함수에 param1, param2를 파라미터로 받을 수 있다. (method처럼 동작 한다.)
v-if, v-show
http://localhost:8080/test-conditionv-if, v-showif문과 show문을 사용하여 특정 조건일 때 해당 노드를 제어할 수 있다.http://localhost:8080/test-condition
/src/views/TestCondition.vue
<template><div><h1>v-if, v-show Test</h1><button @click="error = !error">Toogle error</button><button @click="success = !success">Toggle success</button><div><h3>v-if</h3><div><p>현재 error 상태는?</p><p v-if="error" class="errBox">에러입니다.</p><p v-else>에러 상태가 아닙니다.</p></div><h3>v-show</h3><div><p>현재 success 상태는?</p><p v-show="success" class="sucBox">성공입니다.</p><p v-show="!success">성공 상태가 아닙니다.</p></div></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
error: false,
success: false
}
}
}
</script><style scoped>
.errBox {
background: red;
color: white;
}
.sucBox {
background: green;
color: white;
}
</style>v-if는 해당 노드 자체가 실제로 나타나거나 사라지는 반면v-show는 해당 노드의 style속성에서 display:none값으로 제어 한다.(브라우저의 개발자 모드에서 확인할 것수 있다.)
v-for
for문을 이용해 반복 처리를 할 수 있다.http://localhost:8080/test-loop
for문을 이용해 반복 처리를 할 수 있다.
/src/views/TestLoop.vue
<template><div><h1>v-for Test</h1><h2>원본 출력</h2><div><div>{{ fruits }}</div><div>{{ users }}</div></div><h2>다듬어서 출력</h2><div><h3>과일 리스트</h3><div style="margin-left: 40%; margin-right: 40%"><ul><li v-for="(fruit, index) in fruits" :key="`fruit-${index}`">{{ fruit }}</li></ul></div><h3>사용자 리스트</h3>
1) 그대로 출력
<div v-for="(user, index) in users" :key="`user-${index}`">
{{ user }}
</div>
2) 항목별 출력
<div v-for="(user, index) in users" :key="index"><span>{{ user.name }}: {{ user.age }}, {{ user.gender }}</span></div></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
fruits: ['apple', 'orange', 'banana', 'mango'],
users: [
{ name: '홍길동', age: 20, gender: 'male' },
{ name: '김길동', age: 23, gender: 'male' },
{ name: '고길순', age: 25, gender: 'female' }
]
}
}
}
</script>참고 :key 속성은 필수 이며 전체 노드로 부터 유일해야 한다. (이것이 지켜지지 않는 경우 [Vue warn]: Duplicate keys detected에러가 나타난다.)(:key는 v-bind:key(바인드 변수)를 의미 한다.)
mixin
http://localhost:8080/test-mixin
mixin을 활용하면 전역변수나 전역메소드 같은 효과를 줄 수 있다.다음과 같은 mixin파일을 생성한다. (위치나 이름은 자유롭게 설정할 수 있다.)
/src/components/mixin/commonMixin.js
export default {
data() {
return {
mixin: {
test: 'mixinTest'
}
}
},
methods: {
mixinTest() {
console.log('This is mixin method')
}
}
}
다음과 같은 테스트 파일을 생성한다.
/src/views/TestMixin.vue
<template><div><h1>Mixin Test</h1><p>{{ mixin.test }}</p></div></template><script>
import commonMx from '@/components/mixin/commonMixin'
export default {
mixins: [commonMx],
data() {
return {}
},
created() {
this.mixinTest()
}
}
</script>import 할때 @/components/mixin/commonMixin와 같이 @를 사용하면 현재 서버의 절대 경로를 사용하게 된다.
화면 출력(mixin Test)과 콘솔 출력(This is mixin method)을 확인 할 것.
Bootstrap-vue
http://localhost:8080/test-bootstrap
부트스트랩이란 트위터에서 사용하는 각종 레이아웃, 버튼, 입력창 등의 디자인을 css와 javascript로 만들어서 사용하기 쉽도록 제공하는 라이브러리이다. (부트스트랩을 이용한 상용 디자인 프레임워크도 많이 있다.)
vue에서 bootstrap를 사용해 보자.다음과 같이 bootstrap-vue를 설치 한다.
https://bootstrap-vue.org/docs공식 문서를 참고하여 어떤 버전을 설치해야 하는지 확인 한다.
> npm install bootstrap@4.6.1 bootstrap-vue@2.22.0 --save
main.js파일에 다음과 같이 설정 한다.
/src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
// bootstrap
import { BootstrapVue } from 'bootstrap-vue'
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css'
import 'bootstrap-vue/dist/bootstrap-vue.css'
Vue.use(BootstrapVue)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
부트스트랩 컴포넌트: https://bootstrap-vue.org/docs/components다음과 같이 몇가지 부트스트랩 컴포넌트를 확인 해 본다.
/src/views/TestBootstrap.vue
<template><div><h1>Botstrap Test</h1><b-row><b-col><h3>Left</h3></b-col><b-col style="text-align: left"><h3>Center</h3><div><h4>button</h4><b-button>Button</b-button><b-button variant="danger">Button</b-button><b-button variant="success">Button</b-button><b-button variant="outline-primary">Button</b-button></div><div><h4>input text</h4><b-form-input placeholder="Enter your name"></b-form-input></div><div><h4>checkbox</h4><b-form-checkbox id="checkbox-1" name="checkbox-1" value="accepted" unchecked-value="not_accepted">
I accept the terms and use
</b-form-checkbox></div><div><h4>radio</h4><b-form-group><b-form-radio name="some-radios" value="A">Option A</b-form-radio><b-form-radio name="some-radios" value="B">Option B</b-form-radio></b-form-group></div><div><h4>select</h4><b-form-select v-model="selected" :options="options"></b-form-select></div><div><h4>textarea</h4><b-form-textarea id="textarea" placeholder="Enter something..." rows="3" max-rows="6"></b-form-textarea></div><div><h4>input group</h4><b-input-group prepend="Username" class="mt-3"><b-form-input></b-form-input><b-input-group-append><b-button variant="outline-success">Button</b-button><b-button variant="info">Button</b-button></b-input-group-append></b-input-group></div><div><h4>table</h4><b-table striped hover :items="items"></b-table></div></b-col><b-col><h3>Right</h3></b-col></b-row></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
selected: null,
options: [
{ value: null, text: 'Please select an option' },
{ value: 'a', text: 'This is First option' },
{ value: 'b', text: 'Selected Option' },
{ value: { C: '3PO' }, text: 'This is an option with object value' },
{ value: 'd', text: 'This one is disabled', disabled: true }
],
items: [
{ age: 40, first_name: 'Dickerson', last_name: 'Macdonald' },
{ age: 21, first_name: 'Larsen', last_name: 'Shaw' },
{ age: 89, first_name: 'Geneva', last_name: 'Wilson' },
{ age: 38, first_name: 'Jami', last_name: 'Carney' }
]
}
}
}
</script><style scoped>
div h4 {
margin-top: 20px;
}
</style>component
http://localhost:8080/test-comp
header와 footer를 component로 구성해 본다.
1) Header component 만들기
/src/views/comp/Header.vue
<template><div><div style="background-color: yellow; height: 50px">This is header</div><hr /></div></template><script>
export default {}
</script>2) Footer component 만들기
/src/views/comp/Footer.vue
<template><div><hr /><span>COPYRIGHT COMPANY ALL RIGHTS RESERVED.</span></div></template><script>
export default {}
</script>3) component 호출하기
/src/views/comp/index.vue
<template><div><app-header /><h1>Component Test</h1>
여기는 body 영역
<app-footer /></div></template><script>
import Header from '@/views/comp/Header.vue'
import Footer from '@/views/comp/Footer.vue'
export default {
components: {
'app-header': Header,
'app-footer': Footer
}
}
</script>app-header라는 이름은 변경이 가능하다.(kebab-case로 가능)
4) router 세팅은 이렇게
/src/router/index.js
{
path: '/test-comp',
component: () => import('../views/comp') // 호출되는 파일이 index.vue인 경우에는 파일명을 생략할 수 있다.
}
만일 컴포넌트에서 호출하는 파일이 index.vue로 되어있으면 해당 파일명을 생략할 수 있다.(../views/comp/index.vue ⇒ ../views/comp)
URL을 호출했을때 Header와 Footer가 한 페이지 내에 함께 존재하는지 확인 한다.
Not Found
존재하지 않는 url을 호출해도 페이지에는 아무런 에러 메세지가 없다.(예: http://localhost:8080/abc123 --> 이런 페이지는 없지만 화면은 깨끗하게 잘 나온다.)
1) Not Found 페이지 만들기
다음과 같이 Not Found에서 사용할 페이지를 만든다. (위치는 크게 상관 없지만 보통 component들이 모여있는 곳에 작성 한다)
/src/components/NotFound.vue
<template><div><h1 class="text-60">404</h1><p class="text-36 subheading mb-3">Page not found!</p><p class="mb-5 text-muted text-18">Sorry! The page you were looking for doesn't exist.</p><a class="btn btn-lg btn-primary btn-rounded" href="/">Go back to home</a></div></template><script>
export default {}
</script>2) Router 설정
Not Found를 설정하기 위해서는 라우터의 설정이 중요하다.다음과 같은 설정은 반드시 라우터 설정의 맨 하단에 위치해야 한다.
/src/router/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import VueRouter from 'vue-router'
import Home from '../views/Home.vue'
Vue.use(VueRouter)
const routes = [
{
path: '/',
name: 'Home',
component: Home
},
...
{
path: '/test-comp',
component: () => import('../views/comp')
},
{
path: '*', // NotFound 설정을 위한 path('*')는 반드시 맨 하단에 위치 해야 한다.
component: () => import('../components/NotFound.vue')
}
]
const router = new VueRouter({
mode: 'history',
base: process.env.BASE_URL,
routes
})
export default router
path: '*'의 뜻는 모든 path를 잡아낸다는 뜻이다. 따라서 맨 하단에 위치해야 위에서 놓치는(존재 하지 않는)URL의 모든 것을 잡아낼 수 있다.(맨 상단에 있으면 어떤 일이 발생 할까??)
다음과 같이 존재하지 않는 url을 방문해 보자http://localhost:8080/abc123
props
http://localhost:8080/test-family/props
부모 컴포넌트에서 자식 컴포넌트로 값을 전달 할 수 있다.
1) 자식1(Alice) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/props/Child1.vue
<template><div><h3>Hi, I am Alice</h3><p>I have to {{ job }}</p><p>{{ user.name }} {{ user.who }}</p></div></template><script>
export default {
props: {
job: {
type: String,
required: false,
default: 'Nothing'
},
user: {
type: Object,
required: false,
default: null
}
}
}
</script>props로 선언된 부분을 통해 부모 컴포넌트에서 프로퍼티를 전달할 수 있다.
2) 자식2(Bob) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/props/Child2.vue
<template><div><h3>Greeting to you, I am Bob</h3><p>I have to {{ job }}</p></div></template><script>
export default {
props: {
job: {
type: String,
required: false,
default: 'Nothing'
}
}
}
</script>3) 부모(Parent) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/props/Parent.vue
<template><div><h1>Props Test</h1><h2>I am Parent</h2><p>I will make my children do something.</p><div style="border: 1px solid red"><alice job="homework" :user="myAlice" /></div><div style="border: 1px solid blue"><bob job="clean my room" /></div></div></template><script>
import Alice from './Child1.vue'
import Bob from './Child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
Alice,
Bob
},
data() {
return {
myAlice: {
name: 'Alice',
who: 'My daughter'
}
}
}
}
</script><alice job="something" />와 같이 job프로퍼티를 통해 자식 컴포넌트에 값을 전달할 수 있다.자세한 props사용에 대해서는 https://kr.vuejs.org/v2/guide/components-props.html 문서를 참조 할 것.
변수를 전달할때는 v-bind를 이용 해서 전달 한다.(v-bind:user는 :user와 같다.)
4) Router 세팅
/src/router/index.js
{
path: '/test-family/props',
component: () => import('../views/family/props/Parent.vue')
},
라우터 세팅 후 페이지를 확인해 볼 수 있다.전달하는 job의 값에 따라 자식 컴포넌트의 job값이 달라짐을 확인 할 것.
emit
http://localhost:8080/test-family/emit
자식 컴포넌트에서 발생한 사건을 부모 컴포넌트로 전달할 수 있다.
1) 자식1(Alice) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/emit/Child1.vue
<template><div><h3>Hi, I am Alice</h3><p>I want my parent to give me money.</p><b-button variant="primary" @click="updateTodo">Money</b-button></div></template><script>
export default {
methods: {
updateTodo: function () {
this.$emit('updateTodo', 'give to Alice money')
}
}
}
</script>this.$emit('updateTodo', 'give to Alice money') 와 같이 $emit을 통해 부모로 부터 프로퍼티로 할당 받은 updateTodo 를 호출할 수 있다.(여기에 기록된 updateTodo 메소드는 부모 메소드가 아니라 부모가 호출한 자식 컴포넌트의 속성명이다.)
2) 자식2(Bob) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/emit/Child2.vue
<template><div><h3>Greeting to you, I am Bob</h3><p>I want my parent to give me food.</p><b-button variant="success" @click="updateTodo">Food</b-button></div></template><script>
export default {
methods: {
updateTodo: function () {
this.$emit('updateTodo', 'feed Bob food')
}
}
}
</script>Bob은 Alice와는 다른 요구를 한다. (feed Bob food)
3) 부모 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/emit/Parent.vue
<template><div><h1>Emit Test</h1><h2>I am Parent</h2><p>I have to do something for my children.</p><p style="font-weight: bold">I will {{ todo }}</p><div style="border: 1px solid red"><alice @updateTodo="updateTodo($event)" /></div><div style="border: 1px solid blue"><bob @updateTodo="updateTodo($event)" /></div></div></template><script>
import Alice from './Child1.vue'
import Bob from './Child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
Alice,
Bob
},
data() {
return {
todo: 'do nothing'
}
},
methods: {
updateTodo: function (newTodo) {
this.todo = newTodo
}
}
}
</script>부모 컴포넌트는 자식 컴포넌트 호출 시 <alice @updateTodo="updateTodo($event)" />에서 $event를 통해 자식 컴포넌트에서 전달한 값을 받을 수 있다. (객체도 가능함)
4) Router 세팅
/src/router/index.js
{
path: '/test-family/emit',
component: () => import('../views/family/emit/Parent.vue')
},
중요 포인트 부모와 자식 컴포넌트에서 사용하는 updateTodo이름이 중복 되는데 누구를 호출하는지 구분할 수 있어야 한다.(호출 메소드와 응답 메소드를 짝지을 수 있어야 한다.)
event bus
http://localhost:8080/test-family/event-bus
자식 컴포넌트 끼리 event를 발생 시킬 수 있다. (하지만 권장하지는 않는다. Store를 사용하면 된다.)
1) EventBus 파일 생성
/src/views/family/eventBus/eventBus.js
import Vue from 'vue'
export const EventBus = new Vue()
2) 자식1(Alice) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/eventBus/Child1.vue
<template><div><h3>Hi, I am Alice</h3><p>
I said: Hey Bob. where's my stuff??
<b-button size="sm" variant="primary" @click="whatIsaid">send to Bob</b-button></p><p>Bob said:</p></div></template><script>
import { EventBus } from './eventBus'
export default {
data() {
return {
count: 0
}
},
methods: {
whatIsaid: function () {
this.count += 1
EventBus.$emit('aliceSaid', `Give me my stuff ! x ${this.count}`)
}
}
}
</script>EventBus.$emit('eventName', 'message') 를 통해서 이벤트를 전파할 수 있다.eventName: 전파하는 이벤트 이름message: 전파하는 메세지(객체도 가능함)
3) 자식2(Bob) 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/eventBus/Child2.vue
<template><div><h3>Greeting to you, I am Bob</h3><p>Alice said to me: {{ aliceMessage }}</p><p>
Bob said: I don't know. <b-button size="sm" variant="success">reply to Alice</b-button>(여기를 구현해 보도록
하자.)
</p></div></template><script>
import { EventBus } from './eventBus'
export default {
data() {
return {
aliceMessage: ''
}
},
created() {
EventBus.$on('aliceSaid', message => {
this.aliceMessage = message
})
}
}
</script>EventBus.$on('eventName', function (message) { ... })를 통해서 메세지를 받을 수 있다.
함수 function (message) { ... }는 message => { ... }와 같다. (화살표 함수)
4) 부모 컴포넌트 만들기
/src/views/family/eventBus/Parent.vue
<template><div><h1>Event Bus Test</h1><h2>I am Parent</h2><p>Let's listen to the children's conversation.</p><div style="border: 1px solid red"><alice /></div><div style="border: 1px solid blue"><bob /></div></div></template><script>
import Alice from './Child1.vue'
import Bob from './Child2.vue'
export default {
components: {
Alice,
Bob
},
data() {
return {}
}
}
</script>부모 컴포넌트에서는 그냥 두 자식컴포넌트를 호출했을 뿐이다.
자식1(Alice)컴포넌트의 [send to Bob]버튼을 통해 메세지 전달 테스트를 해보자.
자식2(Bob)컴포넌트에서 자식1(Alice)컴포넌트로 메세지를 보내 보자. ([reply to Alice]버튼 기능 구현)
Store (Vuex)
UserList: http://localhost:8080/test-user/listUserInfo: http://localhost:8080/test-user/info
Vuex란 state를 관리할 수 있도록 도와주는 상태 관리 라이브러리이다. 상세 설명은 (여기) 참고
보통 Store라고 명칭 한다.
가상의 User정보를 store를 통해 호출해 본다.
1) User Store 파일 생성(빈 파일 생성)
/src/store/models/user.js
export default {
state: {
// state에 사용할 모델이나 값을 선언 한다.
},
getters: {
// getters을 통해 state값을 호출 한다.
},
mutations: {
// mutations는 동기적이어야 함.(비동기 사용 불가)
},
actions: {
// action은 비동기적 사용이 가능하다. (action에서 mutation을 호출하는 방법을 권장함)
}
}
2) Store의 index파일에서 User Store파일 import 하기
/src/store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import Vuex from 'vuex'
import User from './models/user'
// Load Vuex
Vue.use(Vuex)
// Create Store
export default new Vuex.Store({
modules: {
User
}
})
3) User Store 파일 코딩
위와 같이 빈 파일을 만들었으면 이제는 다음과 같이 가상의 User정보를 조회하는 Store를 만들어 보자.
/src/store/models/user.js
export default {
state: {
// state에 사용할 모델이나 값을 선언 한다.
User: {
id: 0,
name: null,
username: null,
email: null
}, // User 상세 정보용 state
UserList: [] // User 리스트용 state
},
getters: {
// getters을 통해 state값을 호출 한다.
User: state => state.User,
UserList: state => state.UserList
},
mutations: {
// mutations는 동기적이어야 함.(비동기 사용 불가)
setUser(state, data) {
state.User = data
},
setUserList(state, data) {
state.UserList = data
}
},
actions: {
// action은 비동기적 사용이 가능하다. (action에서 mutation을 호출하는 방법을 권장함)
// 사용자 정보 출력
actUserInfo(context, payload) {
console.log('actUserInfo', payload) // payload를 통해 검색 조건을 받을 수 있다.
const testUserInfo = {
id: payload,
name: 'test',
username: 'testUser',
email: 'test@email.com'
} // 이 값을 RestAPI에서 받아오면 된다.
context.commit('setUser', testUserInfo) // mutation을 통해 User값을 세팅 한다.
},
// 사용자 리스트 조회
actUserList(context, payload) {
console.log('actUserList', payload) // payload를 통해 검색 조건을 받을 수 있다.
const testUserList = ['user1', 'user2', 'user3'] // 이 값을 RestAPI에서 받아오면 된다.
context.commit('setUserList', testUserList) // mutation을 통해 UserList값을 세팅 한다.
}
}
}
참고 actions에서 정의하는 메소드의 첫번째 파라미터context는 보통 { commit }만 받아서 처리하는 예제가 많다.하지만 context에는 { commit }외에도 유용하게 사용할 수 있는 여러 항목들이 많이 있기 때문에 context자체를 사용해서 익숙해 지는 것을 권장 한다.
4) User List 파일 생성
/src/views/user/UserList.vue
<template><div><h1>Store Test</h1><div><h3>User List</h3><b-button variant="primary" @click="searchUserList">Search</b-button><div style="border: 1px solid red">
{{ userList }}
</div></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
searchParams: null // 검색 조건을 넣을 수 있음
}
},
computed: {
userList() {
return this.$store.getters.UserList
}
},
methods: {
searchUserList() {
this.$store.dispatch('actUserList', this.searchParams) // 검색 조건을 넘겨 준다.
}
}
}
</script>- 검색:
this.$store.dispatch('actUserList', this.searchParams)를 통해 검색 실행을 시킬 수 있다. - 조회:
this.$store.getters.UserList를 통해 UserList정보를 가져올 수 있다.
5) User Info 파일 생성
/src/views/user/UserInfo.vue
<template><div><h1>Store Test</h1><div><h3>User Info</h3><b-container fluid><b-row><b-col style="text-align: right">User.id</b-col><b-col style="text-align: center"><b-form-input v-model="id" placeholder="User.id를 검색하세요.(1~10)" /></b-col><b-col style="text-align: left"><b-button variant="primary" @click="searchUserInfo">Get User Info</b-button></b-col></b-row></b-container><div style="border: 1px solid red">
{{ userInfo }}
</div></div></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
id: null // 검색할 User.id
}
},
computed: {
userInfo() {
return this.$store.getters.User
}
},
methods: {
searchUserInfo() {
this.$store.dispatch('actUserInfo', this.id)
}
}
}
</script>위와 같이 세팅된 Store의 정보는 다른 컴포넌트에서도 실시간으로 받아볼 수 있다.(this.$store.getters.User를 통해 동일한 User정보를 받을 수 있음)
Axios
UserList: http://localhost:8080/test-user/listUserInfo: http://localhost:8080/test-user/info
백엔드의 RestAPI를 호출하기 위해서 axios를 설치 한다.Axios란? https://github.com/axios/axios
1) Axios 설치
> npm install axios vue-axios --save
2) axios 함수 파일 생성
다음과 같이 axios를 처리하는 함수를 만들어서 사용하도록 한다.
/src/store/apiUtil.js
import axios from 'axios'
const api = axios.create()
export default api
향후 위 파일에서 api.interceptors.request와 api.interceptors.response를 사용하면 편리하다. (토큰 처리에 탁월 하다)
2) Store 파일 수정
jsonplaceholder.typicode.com는 RestAPI를 테스트를 하기위해 가상의 정보를 응답해 주는 서비스 이다.
이를 이용해 다음과 같은 테스트용 Rest API를 호출 한다. (Postman에서 아래 URL의 응답을 먼저 테스트 해 보자)사용자 리스트 GET https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users사용자 상세정보GET https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/<:id>
다음과 같이 User Store파일을 수정 한다.
/src/store/models/user.js
import api from '../apiUtil'
export default {
state: {
// state에 사용할 모델이나 값을 선언 한다.
User: {
id: 0,
name: null,
username: null,
email: null
}, // User 상세 정보용 state
UserList: [] // User 리스트용 state
},
getters: {
// getters을 통해 state값을 호출 한다.
User: state => state.User,
UserList: state => state.UserList
},
mutations: {
// mutations는 동기적이어야 함.(비동기 사용 불가)
setUser(state, data) {
state.User = data
},
setUserList(state, data) {
state.UserList = data
}
},
actions: {
// action은 비동기적 사용이 가능하다. (action에서 mutation을 호출하는 방법을 권장함)
// 사용자 정보 출력
actUserInfo(context, payload) {
console.log('actUserInfo', payload) // payload를 통해 검색 조건을 받을 수 있다.
/*
const testUserInfo = {
id: payload,
name: 'test',
username: 'testUser',
email: 'test@email.com'
} // 이 값을 RestAPI에서 받아오면 된다.
context.commit('setUser', testUserInfo) // mutation을 통해 User값을 세팅 한다.
*/
// RestAPI로부터 UserInfo를 가져온다.
api
.get(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users/${payload}`)
.then(response => {
console.log('response', response)
const userInfo = response && response.data // response중 userInfo만 추출 한다.
context.commit('setUser', userInfo) // mutation을 통해 User값을 세팅 한다.
})
.catch(err => {
const initUser = {
id: 0,
name: null,
username: null,
email: null
}
console.log('response error', err) // 어떤 에러값이 출력되는지 살펴 보자
context.commit('setUser', initUser) // 에러인 경우 사용자 정보를 초기화 한다.
})
},
// 사용자 리스트 조회
actUserList(context, payload) {
console.log('actUserList', payload) // payload를 통해 검색 조건을 받을 수 있다.
/*
const testUserList = ['user1', 'user2', 'user3'] // 이 값을 RestAPI에서 받아오면 된다.
context.commit('setUserList', testUserList) // mutation을 통해 UserList값을 세팅 한다.
*/
// RestAPI로부터 UserList를 가져온다.
api.get('https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/users').then(response => {
console.log('response', response)
const userList = response && response.data // response중 userList만 추출 한다.
context.commit('setUserList', userList) // mutation을 통해 User값을 세팅 한다.
})
}
}
}
User List 테스트
http://localhost:8080/test-user/list 에서 [Search]를 클릭하면 실제 네트워크를 통해 정보를 받아 온다.
User Info 테스트
http://localhost:8080/test-user/info 에서 User.id값에 따라 해당 사용자가 조회 된다. (범위는 1~10)
(해당 사용자 범위를 벗어나는 id를 입력해 보자. --> 서버에서 404에러가 리턴되는 것을 확인해 볼 것)
SocketIo를 이용한 간단한 채팅 구현
1) SocketIo 서버 생성(Node.js)
개발PC에서 C:\Workspace\Study\socketserver 폴더를 생성한다.해당 폴더에 다음과 같이 nodejs를 이용해서 SocketIo서버를 만든다.(vue 파일이 아니다.)
다음과 같이 해당 프로젝트 폴더로 이동 한다.
> cd C:\Workspace\Study\socketserver
1-1) npm init
다음과 같이 npm 초기화를 한다.
> npm init -y
생성된 package.json파일을 확인해 본다.
1-2) npm install
소켓 서버로 사용하기 위한 최소한의 라이브러리만 설치 한다.
> npm install http socket.io
1-3) index.js 생성
다음과 같이 웹소켓 서버를 생성 한다.
/index.js
const { createServer } = require("http");
const { Server } = require("socket.io");
const httpServer = createServer();
const io = require("socket.io")(httpServer, {
// CORS 처리
cors: {
origin: "http://localhost:8080",
methods: ["GET", "POST"]
}
});
// socket.io 연결
io.on("connection", (socket) => {
console.log('connected socket.io', socket.id);
socket.on('chat', msg => {
console.log('chat', msg);
io.emit('chat', msg);
});
});
// http서버 실행
const port = 3010;
httpServer.listen(port);
console.log(`socket.io listening: ${port}`);
nodejs를 통해 http서버를 동작 시킨다.
> node index.js
socket.io listening: 3010
connected socket.io hQHYkUvolpvRH0MOAAAB
2) SocketIo 클라이언트 생성(Vue.js)
http://localhost:8080/test-socket
vuetest 프로젝트에서 소켓 클라이언트를 만들어 보자.
2-1) socketIo-client 설치
> npm install socket.io-client --save
2-2) main.js에 socket 등록
다음과 같이 main.js파일에 socket.io를 등록하도록 한다.
/src/main.js
import Vue from 'vue'
import App from './App.vue'
import router from './router'
import store from './store'
// socket.io
import io from 'socket.io-client'
const socket = io('http://127.0.0.1:3010')
Vue.prototype.$socket = socket
// bootstrap
import { BootstrapVue } from 'bootstrap-vue'
import 'bootstrap/dist/css/bootstrap.css'
import 'bootstrap-vue/dist/bootstrap-vue.css'
Vue.use(BootstrapVue)
Vue.config.productionTip = false
new Vue({
router,
store,
render: h => h(App)
}).$mount('#app')
Vue.prototype.$socket = socket를 통해 vue인스턴스 변수로 등록하여 컴포넌트에서 this.$socket으로 호출할 수 있도록 했다.
2-2) socketIo-client 파일 생성
/src/views/TestSocket.vue
<template><div><h1>Socket Test</h1><b-container fluid><b-row><b-col style="text-align: right"></b-col><b-col style="text-align: center"><b-form-input v-model="message" placeholder="message" /><h5>Chat message</h5><b-form-textarea id="textarea" v-model="messageHistory" rows="7" max-rows="6"></b-form-textarea></b-col><b-col style="text-align: left"><b-button variant="primary" @click="sendMessage">Send</b-button></b-col></b-row></b-container></div></template><script>
export default {
data() {
return {
message: '',
messageHistory: ''
}
},
created() {
this.$socket.on('chat', data => {
this.messageHistory += data + '\n'
})
},
methods: {
sendMessage() {
this.$socket.emit('chat', this.message)
this.message = ''
}
}
}
</script>웹브라우저 두개를 띄워서 각각의 페이지에서 메세지를 입력해 보자. (종류가 다른 브라우저에서도 가능하다.)
i18n(다국어 처리)
i18n을 통해 다국어를 처리할 수 있다.
다국어 처리에 대해서는 참고만 하도록 한다.https://kazupon.github.io/vue-i18n/started.html#html 방지를 위해)