Insertion sort
1. Sorting problem
- input : a sequence of n numbers (keys) , , ,
- output : a permutation , , , of the input sequence such that
2. Pseudocode
- 분명하고 간결한 method로 given algorithm을 명시
- algorithm의 essence를 간결하게 전달하기 위해 대부분의 software engineering 관련 issues를 무시
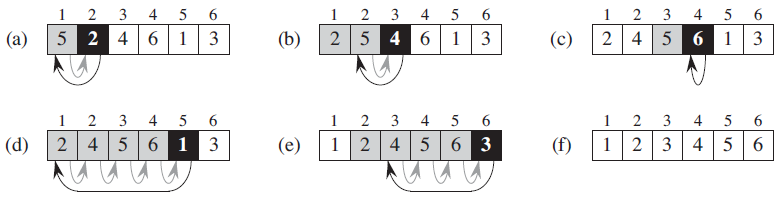
3. Procedure and operation
-
parameter로 array 을 받는 INSERTION-SORT의 procedure
-
array 일 때 INSERTION-SORT의 operation
Loop invariants and the correctness of insertion sort
1. Loop invariant
- algorithm의 loop에서 각 iteration 전 또는 후에 항상 true인 property
- INSERTION-SORT에서 lines 1-8의 를 만드는 loop의 loop invariants
1. 처음 parameter로 들어왔을 때 A[1 .. j - 1]의 elements로 구성돼 있다
2. 순서대로 정렬돼 있다- algorithm의 correctness를 이해하기 위해 사용한다
2. Initialization, Maintenance, Termination
- loop invariant를 보이기 위한 세 가지
- Initialization : 첫 번째 iteration전에 true
- Maintenance : iteration전에 true이면, 다음 iteration전에도 true
- Termination : loop가 종료됐을 때, invariant는 algorithm의 correctness를 보일 수 있는 유용한 property를 제공
3. The correctness of insertion sort
- Initialization
일 때, 은 이다. 의 element는 parameter로 처음 들어올 때 의 element와 같다. 그리고 은 정렬돼 있다. 따라서 첫 번째 iteration전의 loop invariant은 true이다. - Maintenance
lines 4-7에서 의 element는 proper position을 찾을 때 까지 , , , .. 로 이동한다. line 8에서 의 element를 삽입한다. 그러면 는 초기의 의 elements로 이루어져 있고 정렬된 상태가 된다. 따라서 의 increment가 이루어진 후 다음 iteration시작 전 은 loop invariant를 만족한다. loop variant의 true는 유지된다. - Termination
for loop의 종료 condition은 이고 iteration하면서 는 1씩 증가하기 때문에 언젠간 돼 반드시 종료된다. loop invariant의 를 로 치환해보면, 초기 의 elements로 정렬된 를 종료 후 얻게 된다. 이 때 은 전체 array의 elements를 정렬한 것이므로, insertion sort는 correct algorithm이다.