SpoonOS Graph System은 상태 기반 다단계 AI 에이전트 워크플로우를 구축하기 위한 라이브러리입니다. 애플리케이션을 방향성 그래프로 모델링하며, 노드는 액션(LLM 호출, 도구 실행, 데이터 처리)을 나타내고 엣지는 조건부 분기, 병렬 팬아웃, 반복적 추론을 위한 사이클을 포함하여 제어 흐름을 정의합니다.
왜 Graph System이 필요한가?
전통적인 LLM 애플리케이션은 종종 간단한 체인입니다: 프롬프트 → 응답 → 완료. 하지만 실제 AI 에이전트는 더 많은 것이 필요합니다:
- 상태 지속성 — 여러 단계와 상호작용에 걸쳐 컨텍스트 기억
- 조건부 로직 — LLM 출력이나 외부 데이터를 기반으로 다른 경로 선택
- 병렬 실행 — 여러 작업을 동시에 실행하고 결과 결합
- 인간 개입 루프 — 사용자 입력, 승인, 또는 수정을 위해 일시 중지
- 에러 복구 — 진행 상황을 잃지 않고 우아하게 실패 처리
Graph System은 이러한 패턴을 사후 고려가 아닌 일급 시민으로 만듭니다.
핵심 개념
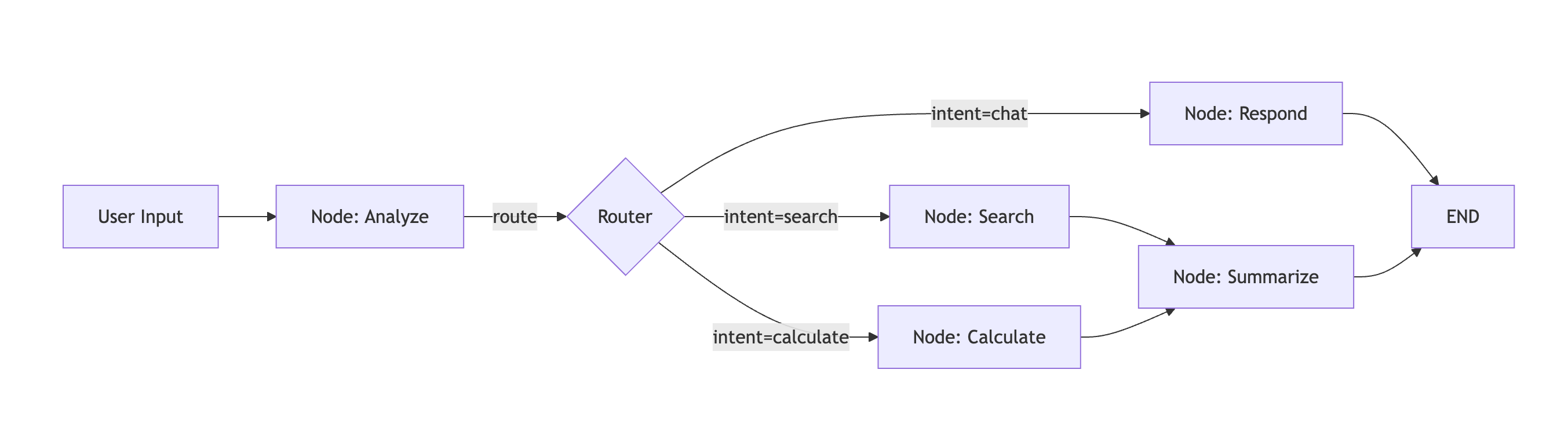
| 개념 | 설명 |
|---|---|
| State | 모든 노드에서 공유되는 타입이 지정된 딕셔너리(TypedDict). 각 노드는 상태를 읽고, 작업을 수행하며, 병합할 업데이트를 반환합니다. |
| Node | 상태를 받아 부분 업데이트를 반환하는 비동기 함수. 노드는 워크플로우의 "액션"입니다. |
| Edge | 노드 간 연결. 정적(항상 A→B로 이동), 조건부(상태 기반으로 A→B 또는 A→C로 이동), 또는 LLM 기반일 수 있습니다. |
| Checkpoint | 각 노드 전에 상태의 자동 스냅샷. 복구, 디버깅, 인간 개입 루프 중단을 가능하게 합니다. |
무엇을 만들 수 있을까?
| 사용 사례 | Graph System이 도움이 되는 방법 |
|---|---|
| 자율 에이전트 | 도구 호출, 관찰 루프, 적응형 계획을 가진 다단계 추론 |
| RAG 파이프라인 | 관련성 기반 조건부 라우팅을 가진 Retrieve → Grade → Regenerate 사이클 |
| 다중 에이전트 시스템 | 공유 상태와 핸드오프를 통해 협력하는 여러 전문 에이전트 |
| 승인 워크플로우 | 인간 검토를 위해 실행 일시 중지, 그 다음 체크포인트에서 재개 |
| 병렬 분석 | 여러 데이터 소스로 팬아웃, 구성 가능한 전략으로 결과 결합 |
Graph System vs LangGraph
SpoonOS Graph System은 LangGraph에서 영감을 받았으며 유사한 개념을 공유합니다. 주요 차이점:
| 기능 | SpoonOS Graph | LangGraph |
|---|---|---|
| Parallel Groups | 쿼럼 조인, 타임아웃, 서킷 브레이커를 가진 네이티브 add_parallel_group() | 수동 asyncio 또는 분기 |
| Routing Stack | 우선순위 기반: 명시적 → 규칙 → 지능형 → LLM → 폴백 | 조건부 엣지만 |
| Declarative Definition | 직렬화 가능하고 구성 가능한 그래프를 위한 GraphTemplate / NodeSpec / EdgeSpec | 명령형 빌더만 |
| Resource Control | 내장 속도 제한, 최대 동시성, 서킷 브레이커 | 외부 구현 |
| Web3/Crypto | SpoonOS 툴킷(CEX, DEX, 온체인)과의 네이티브 통합 | 서드파티 도구를 통해서만 |
프로덕션 수준의 병렬 실행, 다층 라우팅, 또는 암호화폐/Web3 통합이 필요할 때 SpoonOS Graph를 선택하세요.
빠른 시작
pip install spoon-aiimport asyncio
from typing import TypedDict
from spoon_ai.graph import StateGraph, END
class MyState(TypedDict):
query: str
result: str
async def process(state: MyState) -> dict:
return {"result": f"Processed: {state['query']}"}
graph = StateGraph(MyState)
graph.add_node("process", process)
graph.add_edge("__start__", "process")
graph.add_edge("process", END)
app = graph.compile()
async def main():
result = await app.invoke({"query": "Hello", "result": ""})
print(result["result"]) # Processed: Hello
asyncio.run(main())아키텍처
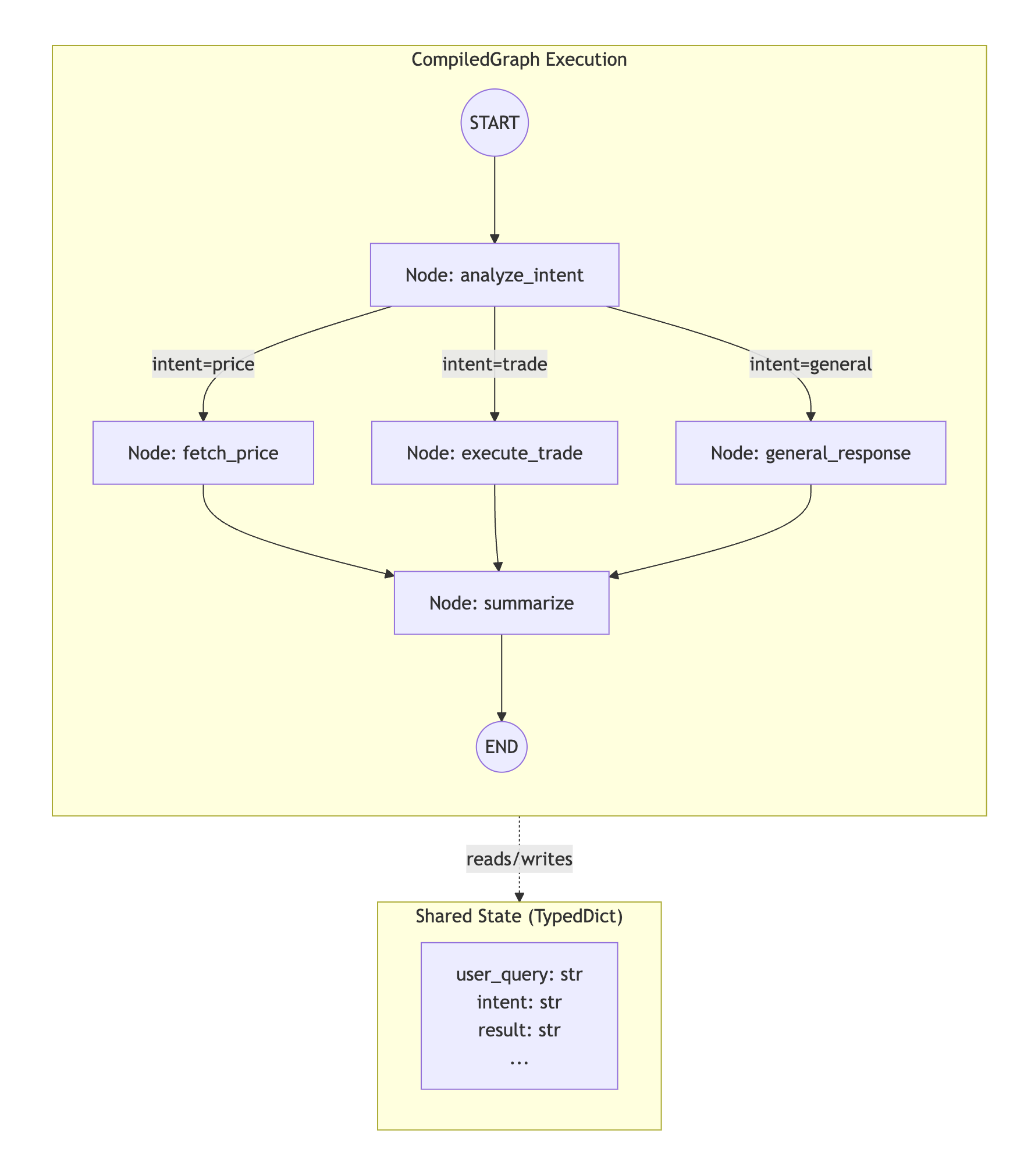
그래프 시스템은 세 가지 주요 구성 요소로 구성됩니다:
| 구성 요소 | 책임 |
|---|---|
StateGraph | 워크플로우 토폴로지 정의를 위한 빌더 클래스—노드, 엣지, 라우팅 규칙, 병렬 그룹 |
CompiledGraph | 상태 전환, 체크포인팅, 메트릭 수집을 관리하는 실행 가능한 런타임 |
GraphAgent | 그래프 실행을 SpoonOS 에이전트 생명주기 및 메모리와 통합하는 선택적 래퍼 |
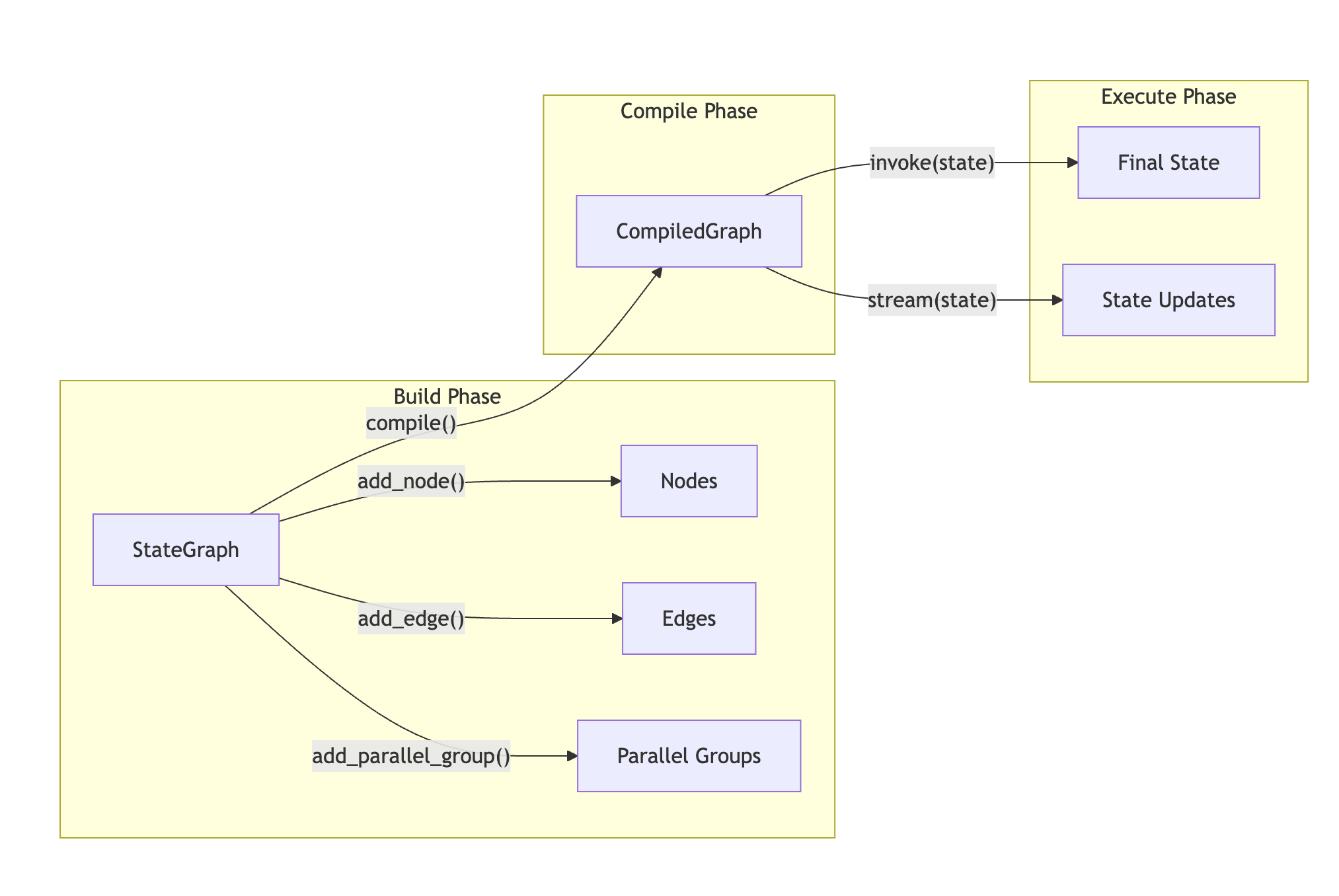
핵심 개념
Nodes
노드는 현재 워크플로우 상태를 받아 상태로 병합할 업데이트 딕셔너리를 반환하는 비동기 함수입니다.
from typing import TypedDict, Dict, Any
class AnalysisState(TypedDict):
user_query: str
symbol: str
price_data: Dict[str, Any]
analysis: str
async def fetch_price_node(state: AnalysisState) -> dict:
"""
Node that fetches price data for a trading symbol.
Receives: Full state dictionary
Returns: Dictionary of fields to update (merged into state)
"""
symbol = state.get("symbol", "BTC")
# Actual API call to data source
from toolkit.crypto_power_data import CryptoPowerData
client = CryptoPowerData()
ohlcv = await client.get_ohlcv(symbol=f"{symbol}USDT", interval="1h", limit=24)
return {
"price_data": {
"symbol": symbol,
"current_price": ohlcv[-1]["close"],
"high_24h": max(c["high"] for c in ohlcv),
"low_24h": min(c["low"] for c in ohlcv),
"volume_24h": sum(c["volume"] for c in ohlcv),
}
}노드 계약:
- Input: 현재 상태의 불변 뷰를 받음
- Output: 업데이트할 필드의
dict반환(부분 업데이트, 전체 교체 아님) - Async:
async def여야 함(동기 함수는 자동 래핑되지만 덜 효율적) - Idempotent: 동일한 상태가 주어지면 동일한 결과를 생성해야 함(재시도 안전을 위해)
Edges
엣지는 노드 간 전환을 정의합니다. 세 가지 타입이 지원됩니다:
from spoon_ai.graph import StateGraph, END
graph = StateGraph(AnalysisState)
# 1. Static edge: Always transitions to target
graph.add_edge("fetch_price", "analyze")
graph.add_edge("analyze", END)
# 2. Conditional edge: Routes based on state inspection
def route_by_intent(state: AnalysisState) -> str:
"""Return key from path_map based on detected intent."""
intent = state.get("intent", "unknown")
if intent == "price_query":
return "price"
elif intent == "technical_analysis":
return "technical"
return "general"
graph.add_conditional_edges(
source="classify_intent",
condition=route_by_intent,
path_map={
"price": "fetch_price",
"technical": "compute_indicators",
"general": "general_response",
}
)
# 3. Routing rule: Pattern-based with priorities
graph.add_routing_rule(
source_node="entry",
condition=lambda state, query: "bitcoin" in query.lower(),
target_node="btc_specialist",
priority=10 # Higher priority = checked first
)State
상태는 그래프를 통해 흐르는 공유 TypedDict입니다. 각 노드는 상태에서 읽고 병합할 업데이트를 반환합니다.
from typing import TypedDict, List, Dict, Any, Optional, Annotated
class CryptoAnalysisState(TypedDict):
# Input fields
user_query: str
user_id: str
# Intermediate fields
intent: str
symbol: str
timeframes: List[str]
# Data fields
price_data: Dict[str, Any]
technical_indicators: Dict[str, float]
news_sentiment: Dict[str, Any]
# Output fields
analysis: str
recommendations: List[str]
confidence: float
# System fields
messages: Annotated[List[dict], "Conversation history - appended via reducer"]
execution_log: List[str]상태 병합 동작:
| 필드 타입 | 병합 전략 |
|---|---|
dict | 깊은 병합(중첩된 딕셔너리가 재귀적으로 병합됨) |
list | 추가(무한 성장을 방지하기 위해 100개 항목으로 제한) |
messages 필드 | add_messages 리듀서 사용(중복 제거와 함께 추가) |
| 기타 타입 | 교체 |
Checkpointing
그래프 시스템은 각 노드 실행 전에 자동으로 상태를 체크포인트하여 다음을 가능하게 합니다:
- Recovery: 실패 후 마지막 성공한 노드에서 재개
- Debugging: 실행 기록의 어느 시점에서든 상태 검사
- Human-in-the-loop: 실행 일시 중지, 입력 수집, 재개
from spoon_ai.graph import InMemoryCheckpointer, StateGraph
# Configure checkpointer
checkpointer = InMemoryCheckpointer(max_checkpoints_per_thread=100)
graph = StateGraph(AnalysisState, checkpointer=checkpointer)
# After compilation, access state history
compiled = graph.compile()
result = await compiled.invoke(
{"user_query": "Analyze BTC"},
config={"configurable": {"thread_id": "session_123"}}
)
# Retrieve checkpoint history
config = {"configurable": {"thread_id": "session_123"}}
history = list(graph.get_state_history(config))
for checkpoint in history:
print(f"Node: {checkpoint.metadata.get('node')}")
print(f"Iteration: {checkpoint.metadata.get('iteration')}")
print(f"State keys: {list(checkpoint.values.keys())}")그래프 구축하기
Imperative API
간단한 워크플로우의 경우, 명령형 빌더 메서드를 직접 사용하세요:
from spoon_ai.graph import StateGraph, END
graph = StateGraph(AnalysisState)
# Add nodes
graph.add_node("classify", classify_intent_node)
graph.add_node("fetch_price", fetch_price_node)
graph.add_node("analyze", analyze_node)
graph.add_node("respond", generate_response_node)
# Add edges
graph.add_edge("classify", "fetch_price")
graph.add_edge("fetch_price", "analyze")
graph.add_edge("analyze", "respond")
graph.add_edge("respond", END)
# Set entry point
graph.set_entry_point("classify")
# Compile and execute
compiled = graph.compile()
result = await compiled.invoke({"user_query": "What is BTC price?"})Declarative API
더 큰 워크플로우의 경우, 유지보수성을 위해 GraphTemplate을 사용하세요:
from spoon_ai.graph import StateGraph, END
from spoon_ai.graph.builder import (
DeclarativeGraphBuilder,
GraphTemplate,
NodeSpec,
EdgeSpec,
ParallelGroupSpec,
)
from spoon_ai.graph.config import GraphConfig, ParallelGroupConfig
# Define node specifications
nodes = [
NodeSpec("classify", classify_intent_node),
NodeSpec("fetch_price", fetch_price_node, parallel_group="data_fetch"),
NodeSpec("fetch_news", fetch_news_node, parallel_group="data_fetch"),
NodeSpec("fetch_sentiment", fetch_sentiment_node, parallel_group="data_fetch"),
NodeSpec("analyze", analyze_node),
NodeSpec("respond", generate_response_node),
]
# Define edge specifications
edges = [
EdgeSpec("classify", "fetch_price"), # Entry to parallel group
EdgeSpec("fetch_price", "analyze"), # All parallel nodes -> analyze
EdgeSpec("fetch_news", "analyze"),
EdgeSpec("fetch_sentiment", "analyze"),
EdgeSpec("analyze", "respond"),
EdgeSpec("respond", END),
]
# Define parallel groups
parallel_groups = [
ParallelGroupSpec(
name="data_fetch",
nodes=["fetch_price", "fetch_news", "fetch_sentiment"],
config=ParallelGroupConfig(
join_strategy="all",
timeout=30.0,
error_strategy="collect_errors",
)
)
]
# Create template
template = GraphTemplate(
entry_point="classify",
nodes=nodes,
edges=edges,
parallel_groups=parallel_groups,
config=GraphConfig(max_iterations=50),
)
# Build graph
builder = DeclarativeGraphBuilder(AnalysisState)
graph = builder.build(template)라우팅 전략
그래프 시스템은 우선순위 순서로 라우팅을 평가합니다:
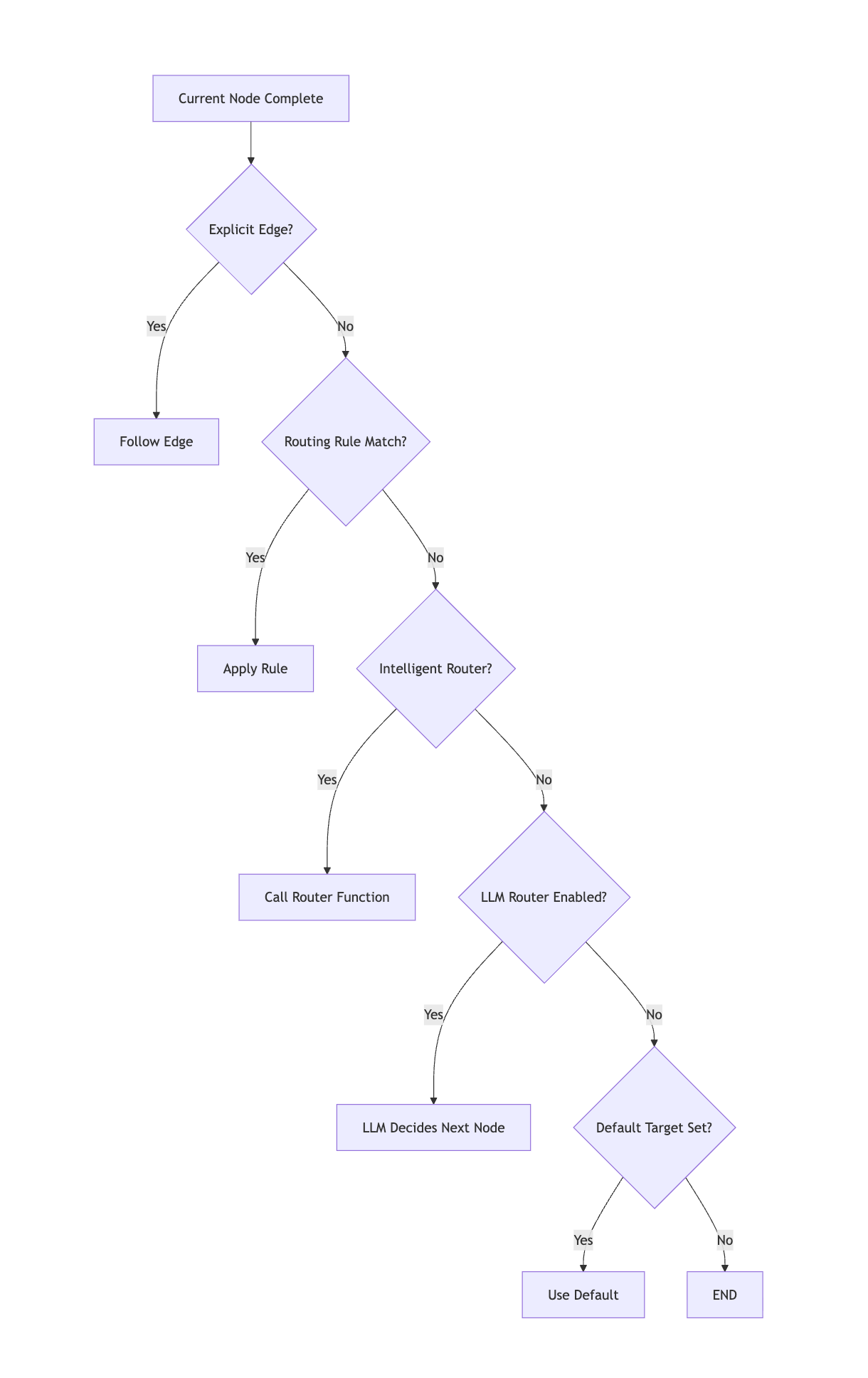
Conditional Edges
상태 검사를 기반으로 라우팅:
def route_by_confidence(state: AnalysisState) -> str:
"""Route based on analysis confidence level."""
confidence = state.get("confidence", 0.0)
if confidence >= 0.8:
return "high_confidence"
elif confidence >= 0.5:
return "medium_confidence"
return "low_confidence"
graph.add_conditional_edges(
"analyze",
route_by_confidence,
{
"high_confidence": "generate_recommendation",
"medium_confidence": "request_clarification",
"low_confidence": "escalate_to_human",
}
)LLM-Powered Routing
패턴이 복잡할 때 자연어 라우팅 활성화:
from spoon_ai.graph.config import GraphConfig, RouterConfig
config = GraphConfig(
router=RouterConfig(
allow_llm=True,
llm_timeout=8.0,
default_target="fallback_handler",
allowed_targets=["price_handler", "trade_handler", "analysis_handler"],
)
)
graph = StateGraph(AnalysisState)
graph.config = config
# Or enable after graph creation
graph.enable_llm_routing(config={
"model": "gpt-4",
"temperature": 0.1,
"max_tokens": 50,
})병렬 실행
구성 가능한 조인 및 에러 전략으로 여러 노드를 동시에 실행:
from spoon_ai.graph.config import ParallelGroupConfig, ParallelRetryPolicy
# Define parallel data collection
graph.add_parallel_group(
"market_data_collection",
nodes=["fetch_binance", "fetch_coinbase", "fetch_kraken"],
config=ParallelGroupConfig(
# Join strategy
join_strategy="quorum", # "all", "any", "quorum"
quorum=0.66, # 66% must complete (2 of 3)
# Timing
timeout=15.0, # Max wait time in seconds
# Error handling
error_strategy="collect_errors", # "fail_fast", "collect_errors", "ignore_errors"
# Retry policy for individual nodes
retry_policy=ParallelRetryPolicy(
max_retries=2,
backoff_initial=0.5,
backoff_multiplier=2.0,
backoff_max=5.0,
),
# Resource controls
max_in_flight=10, # Max concurrent tasks
circuit_breaker_threshold=5, # Disable group after N failures
circuit_breaker_cooldown=30.0, # Re-enable after cooldown
)
)조인 전략:
| 전략 | 동작 | 사용 사례 |
|---|---|---|
"all" | 모든 노드 대기 | 모든 소스에서 완전한 데이터 필요 |
"any" | 첫 번째 성공 시 반환 | 중복 소스, 가장 빠른 것 원함 |
"quorum" | 다수 대기 | 장애 허용 합의 |
에러 전략:
| 전략 | 동작 | 사용 사례 |
|---|---|---|
"fail_fast" | 모두 취소, 예외 발생 | 중요한 경로, 반드시 성공해야 |
"collect_errors" | 계속 진행, __errors__에 에러 저장 | 최선 노력, 문제 보고 |
"ignore_errors" | 계속 진행, 실패 버림 | 비중요한 보강 |
Human-in-the-Loop
사용자 입력을 수집하기 위해 실행 중단:
from spoon_ai.graph import interrupt, Command
async def confirm_trade_node(state: AnalysisState) -> dict:
"""Node that requires user confirmation before proceeding."""
trade_details = state.get("trade_details", {})
if not state.get("user_confirmed"):
# Interrupt execution
interrupt({
"type": "confirmation_required",
"question": f"Execute {trade_details['action']} {trade_details['amount']} {trade_details['symbol']}?",
"trade_details": trade_details,
})
# This code runs after resume with confirmation
return {"trade_executed": True, "execution_time": "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z"}
# Handling the interrupt
compiled = graph.compile()
# Initial execution - will interrupt
result = await compiled.invoke(
{"user_query": "Buy 0.1 BTC"},
config={"configurable": {"thread_id": "trade_session"}}
)
if "__interrupt__" in result:
interrupt_info = result["__interrupt__"][0]
print(f"Question: {interrupt_info['value']['question']}")
# Get user confirmation (from UI, API, etc.)
user_confirmed = await get_user_confirmation()
# Resume execution with confirmation
result = await compiled.invoke(
Command(resume={"user_confirmed": user_confirmed}),
config={"configurable": {"thread_id": "trade_session"}}
)GraphAgent 통합
GraphAgent는 그래프 실행을 SpoonOS 에이전트 생명주기 및 지속적인 메모리로 래핑합니다:
from spoon_ai.graph import StateGraph, GraphAgent, Memory
# Build graph
graph = build_analysis_graph()
# Create agent with memory
agent = GraphAgent(
name="crypto_analyzer",
graph=graph,
memory_path="./agent_memory",
session_id="user_123_session",
preserve_state=True, # Preserve state between runs
)
# Execute
result = await agent.run("Analyze BTC price trends")
print(result)
# Access execution metadata
metadata = agent.get_execution_metadata()
print(f"Successful: {metadata.get('execution_successful')}")
# Memory operations
agent.set_memory_metadata("last_analysis_time", "2024-01-15T10:30:00Z")
stats = agent.get_memory_statistics()
print(f"Total messages: {stats['total_messages']}")
# Search memory
matches = agent.search_memory("bitcoin", limit=5)
# Switch sessions
agent.load_session("user_456_session")모니터링 및 디버깅
Execution Metrics
# Enable monitoring
graph.enable_monitoring([
"execution_time",
"success_rate",
"routing_performance",
])
compiled = graph.compile()
result = await compiled.invoke(initial_state)
# Retrieve metrics
metrics = compiled.get_execution_metrics()
print(f"""
Execution Summary:
Total executions: {metrics['total_executions']}
Success rate: {metrics['success_rate']:.1%}
Avg execution time: {metrics['avg_execution_time']:.3f}s
Per-Node Statistics:
""")
for node, stats in metrics['node_stats'].items():
print(f" {node}:")
print(f" Calls: {stats['count']}")
print(f" Avg time: {stats['avg_time']:.3f}s")
print(f" Error rate: {stats['error_rate']:.1%}")Execution History
# Get detailed execution history
history = compiled.get_execution_history()
for step in history:
print(f"""
Step: {step['node']}
Iteration: {step['iteration']}
Success: {step['success']}
Execution time: {step['execution_time']:.3f}s
Timestamp: {step['timestamp']}
""")구성 참조
GraphConfig
from spoon_ai.graph.config import GraphConfig, RouterConfig
config = GraphConfig(
# Execution limits
max_iterations=100, # Maximum node transitions per invoke()
# Router configuration
router=RouterConfig(
allow_llm=False, # Enable LLM-based routing
allowed_targets=None, # Restrict valid routing targets (None = all)
default_target=None, # Fallback target when no route matches
llm_timeout=8.0, # Timeout for LLM router calls
enable_fallback_to_default=True, # Use default_target on routing failure
),
# Validation
state_validators=[], # List of (state) -> None functions
# Pre-configured parallel groups
parallel_groups={}, # name -> ParallelGroupConfig
)ParallelGroupConfig
from spoon_ai.graph.config import ParallelGroupConfig, ParallelRetryPolicy
config = ParallelGroupConfig(
# Join behavior
join_strategy="all", # "all", "any", "quorum"
quorum=None, # For quorum: 0.0-1.0 (ratio) or int (count)
join_condition=None, # Optional: async (state, completed_nodes) -> bool
# Timing
timeout=None, # Max wait time in seconds (None = unlimited)
# Error handling
error_strategy="fail_fast", # "fail_fast", "collect_errors", "ignore_errors"
retry_policy=ParallelRetryPolicy(
max_retries=0, # Retries per node
backoff_initial=0.5, # Initial backoff delay
backoff_multiplier=2.0, # Backoff multiplier
backoff_max=10.0, # Maximum backoff delay
),
# Resource controls
max_in_flight=None, # Max concurrent tasks (None = unlimited)
rate_limit_per_second=None, # Rate limit (None = unlimited)
# Circuit breaker
circuit_breaker_threshold=None, # Disable after N failures
circuit_breaker_cooldown=30.0, # Re-enable after cooldown seconds
)모범 사례
Node Design
-
단일 책임: 각 노드는 한 가지 일을 해야 합니다. 복잡한 로직을 여러 노드로 분할하세요.
-
멱등성: 노드는 동일한 상태가 주어지면 동일한 결과를 생성해야 합니다(안전한 재시도 가능).
-
최소 상태 업데이트: 변경된 필드만 반환하세요. 시스템이 병합을 처리합니다.
# Good: Returns only updated fields
async def good_node(state):
return {"result": "computed value"}
# Avoid: Returns entire state copy
async def avoid_node(state):
new_state = state.copy()
new_state["result"] = "computed value"
return new_stateState Management
-
상태 타입 지정: IDE 지원 및 문서화를 위해
TypedDict를 사용하세요. -
리스트 성장 제한: 무한 리스트를 방지하기 위해 리듀서 또는 명시적 트리밍을 사용하세요.
-
큰 객체 피하기: 상태는 자주 체크포인트됩니다. JSON 직렬화 가능하고 합리적인 크기로 유지하세요.
Error Handling
-
적절한 에러 전략 사용: 중요한 경로에는
fail_fast, 최선 노력에는collect_errors. -
검증 추가: 초기에 잘못된 상태를 잡기 위해
state_validators를 사용하세요. -
노드에서 로깅: 디버깅을 위해 에러 메시지에 컨텍스트를 포함하세요.
async def robust_node(state):
try:
result = await external_api_call(state["symbol"])
return {"data": result}
except ExternalAPIError as e:
logger.error(f"API call failed for {state['symbol']}: {e}")
return {"error": str(e), "data": None}예제
-
Intent Graph Demo — 병렬 실행을 가진 지능형 라우팅
(소스) -
Graph Crypto Analysis — 실시간 시장 분석 파이프라인
(소스)
관련 문서
- Agents —
GraphAgentvsReActAgent사용 시기 - Tools Integration — 그래프 노드에 도구 추가
- MCP Protocol — 워크플로우에서 동적 도구 발견
