문제
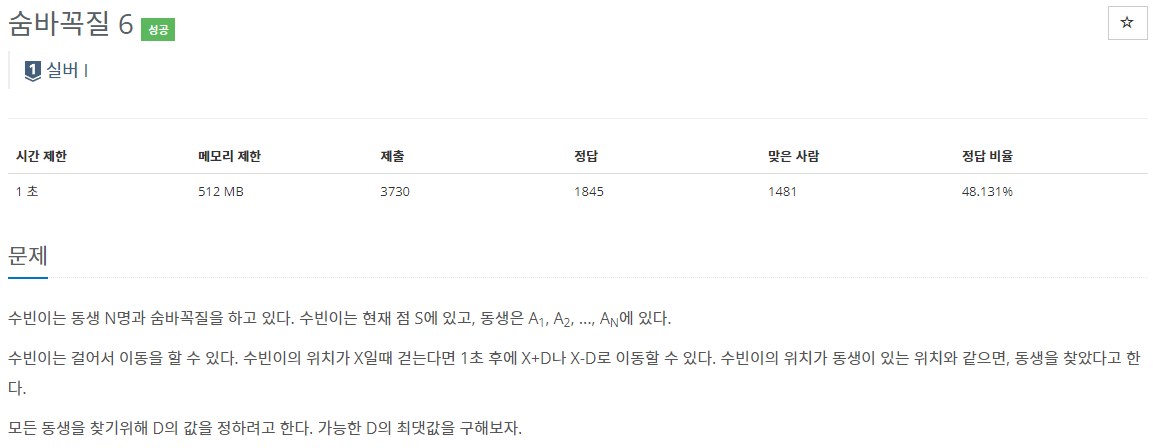
입력 및 출력
풀이
import java.io.*;
class Main {
public static int gcd(int A, int B) {
if (B == 0) {
return A;
} else {
return gcd(B, A % B);
}
}
public static void main(String args[]) throws Exception {
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String[] strArray = br.readLine().split(" ");
// N, S
int N = Integer.parseInt(strArray[0]);
int S = Integer.parseInt(strArray[1]);
// 동생들의 위치
String[] position = br.readLine().split(" ");
// 나와 동생들의 거리
int[] distance = new int[N];
for (int i = 0; i < position.length; i++) {
// 나의 거리에서 동생의 거리를 뺀 값을 num에 저장
int num = S - Integer.parseInt(position[i]);
// 음수를 양수로 전환
if (num < 0) {
num = num * -1;
}
distance[i] = num;
}
// 나와 동생들 거리의 최대공약수
int result = distance[0];
for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) {
result = gcd(result, distance[i]);
}
// 결과값 출력
System.out.println(result);
}
}결과 및 해결방법
[결과]

[정리]
해결방법
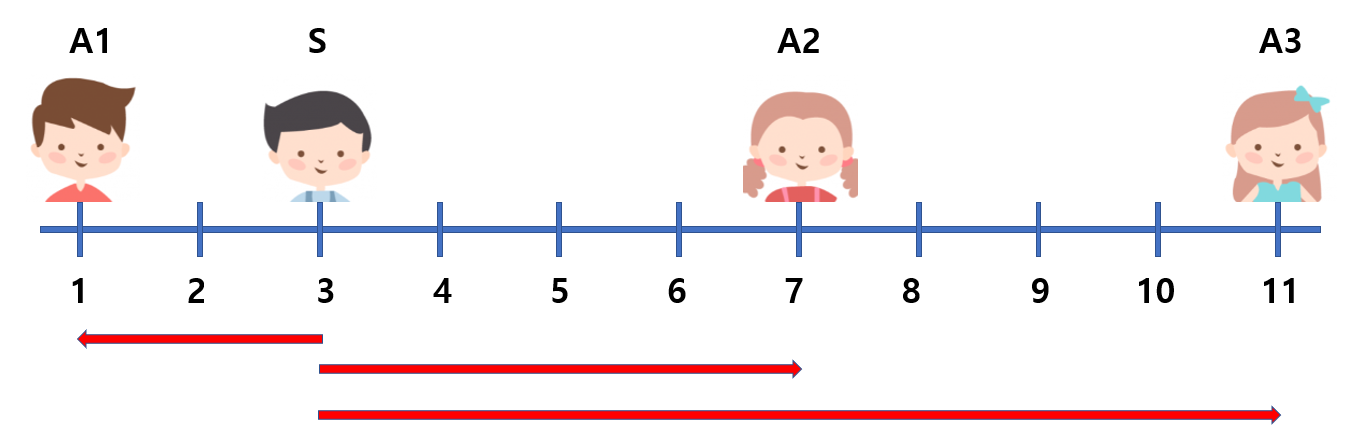
수빈이의 위치 S와 동생들의 수 N을 입력받는다. 동생들의 수 만큼 동생들의 위치를 입력받아 배열에 넣어준다.
위 그림을 참고하면 수빈이(S)를 기준으로 각 동생들의 거리를 뺸다. 만약 뺀 거리가 음수일 경우 -1을 곱하여 양수로 만들어준다. 그 후, 나와 동생들의 거리를 저장할 distance배열에 넣어준다.
모든 동생들을 찾기위한 D의 값을 구하고 있으므로 distance배열의 각 원소별 최대공약수를 구하면 D값을 찾을 수 있다.
