[Vue] 반응성, 템플릿, Ref, Dom, 생명주기
출처 : https://www.udemy.com/course/vue-router-composition-api/learn/lecture/33775462#overview
Vue: behind the scenes
- how vue works
- understanding virtual DOM & DOM Updating
vue의 내부에서 일어나는 일들
- vue의 data, methods 등은 모두 내부에서 전역으로 관리하는 하나의 반응형 객체로 합쳐진다
- js의 내장 기능인 proxy로 data property를 래핑해서 data에 새 값이 할당될 때마다 Vue에 알리는 작업을 한다
- proxy에게 변경사항이 있다는 것을 전해들으면 html 코드를 스캔하고 변경사항이 있는 프로퍼티를 확인해서 업데이트 한다
- this가 위의 전역 객체를 가리키도록 한다
proxy란?
자바스크립트는 반응형이 아니기 때문에 아래처럼 변경사항을 반영하지 않는다

this로 vue instance를 찍어보면 _renderProxy가 있을 걸 확인할 수 있다
안에 handler, target, isRevoked가 있는 걸 확인할 수 있다 (js 내장 함수 proxy와는 조금 다른 형태. 아마 render된 형태의 proxy 같다)
- handler
- target
- isRevoked
let message= "Hello!"
let longMessage = message + 'World!'
//Hello World
message = 'Hello!!!!'
longMessage //Hello! World!const data = {
message: 'Hello!'
}
const handler = {
set(target,key,value){
//프록시가 지원하는 트랩을 정의할 수 있다
//set함수를 정의하면 target, key, value를 받는다
console.log(target) //proxy의 첫번째 인자
console.log(key)//변경한 키
console.log(value)//변경한 값
}
}
const proxy = new Proxy(data, handler)//모던 자바스크립트 내장 함수
//래핑할 객체, 객체를 조작할 핸들러
//handler에 setter함수를 정의하는데 속성에 새로운 값이 설정될 때 변경된다
proxy.message = 'Hello!!!!'
//접근 가능모던 js의 내장 함수 proxy
vue는 proxy로 data와 handler를 받는다
data : 변경사항을 추적할 대상
handler : 받은 data의 값을 set함수의 첫 인자인 target으로 받고, 변경한 키와 값을 두번째, 세번째 인자인 key,value로 받는다
Ref
input 요소로부터 값을 가지고 오는 방법들
1. saveInput, currentUserInput
<section id="app">
<input type="text" @input="saveInput">
</section>- 모든 키 입력에 대해 saveInput가 실행 된다
- saveInput 메서드를 통해 currentUserInput에 event.target.value를 넣는다
- 이 프로퍼티를 이용해서 입력된 값을 message에 할당한다
2. v-model
<input v-model="currentUserInput">3. Ref
- DOM 요소를 필요할 때만 가져오고 싶을 때 사용할 수 있다
- 이벤트 리스터를 추가하는 게 아니라 ref 속성을 추가한다
- 기본 html 속성이 아니라서 브라우저는 이해 못하고 vue가 이해
- p, h, section, input, textarea 등 어떤 곳에든 정의할 수 있다
- vue가 지원하는 내장 프로퍼티는 $로 시작한다
<input type="text" ref="userText">methods: {
setText(){
this.message = this.$refs.userText.value
//위에 ref를 적은 엘리먼트를 받아온다
}
}vue가 DOM을 업데이트하는 방법
- vue의 원리와 핵심 기능
- Vue가 화면을 어떻게 업데이트하는지
내장 반응성
업데이트를 어떻게 감지하고 어디에 업데이트를 하는지는
성능최적화 방식으로 수행하는 일은 아직 안 배웠다
브라우저 개발자 도구에서 확인을 할 때 페이지에서 test를 입력하고 set text를 누르면
해당 테스트가 있는 문단이 우측에 나타나게 된다. 즉 화면 전체가 아닌 해당 문단만 업데이트한 것
virtual DOM을 통해 부분적으로만 업데이트한다
-
Vue Instance
: Vue 앱, Vue 인스턴스는 데이터와 연산 프로퍼티, 메서드 등을 저장한다 -
Browser DOM
: html 콘텐츠는 브라우저를 통해 렌더링 된다
: Vue가 제어하는 템플릿을 DOM에 렌더링한다
: Vue가 제어하는 렌더링 프로세스 중에 동적 부분과 플레이스홀더 보간 그리고 바인딩이 제거 되고 실제 값이 들어간다
ex. {{변수}}를 대신해서 실제 값이 들어간다
@click 등의 vue의 속성들이 사라지고 브라우저에만 있을 수 있는 값이 남는다
데이터와 연산 프로퍼티들이 변경될 때마다 변경된 부분만 리렌더링하고 나머지 부분들은 변경하지 않는다
<h2>title</h2>
<p>not the title</p>어떻게 일부만 변경하는 걸까?
Vue가 과거 DOM values와 새로운 것들을 비교해서 변경된 것들만 업데이트한다
Vue가 먼저 렌더링된 전체 DOM과 포함하는 콘텐츠를 인식하고 Vue 앱에 저장된 데이터 프로퍼티와 해당 콘텐츠를 비교한다
전체를 읽어들이는 것 또 전체 페이지를 렌더링하는 것만큼은 아니지만 그만큼이나
virtual dom을 사용한다
- js-based dom which exits only in memory
- js 객체의 집합으로 어떤 html 태그가 필요하며 해당 태그의 콘텐츠가 무엇인지를 기억한다
- 데이터에 업데이트가 발생하면
1) 새로운 가상 DOM을 생성 2) 기존 가상 DOM과 비교해서 3) 변경사항만 실제 DOM에 렌더링을 한다
1.값이 바뀌면 변경사항 감지
(vue : proxy가 래핑하고 있는 반응형 data 객체 내부 값,
proxy 함수의 handler로 변경된 값을 인식할 수 있다)
2.가상 DOM과 실제 DOM을 비교
3.달라진 부분만 실제 DOM 업데이트
생명주기
Rendering Mechanism
VDOM = real DOM (react)
Virtual DOM is more of a pattern than a specific technology, so there is no one canonical implementation
vnode
plain js obj
virtual node
contains all info that we need to create the actual element
-
mount : runtime renderer can walk a virtual DOM tree and construct a real DOM tree from it
-
patch (=diffing, reconciliation) : two copies of virtual DOM trees, the renderer can also walk and compare the two trees, figure out diffs, apply those changes to the acutal DOM
programmatically create, inspect, compose desired UI structures in a declarative way
while leaving direct DOM manipulation to the renderer
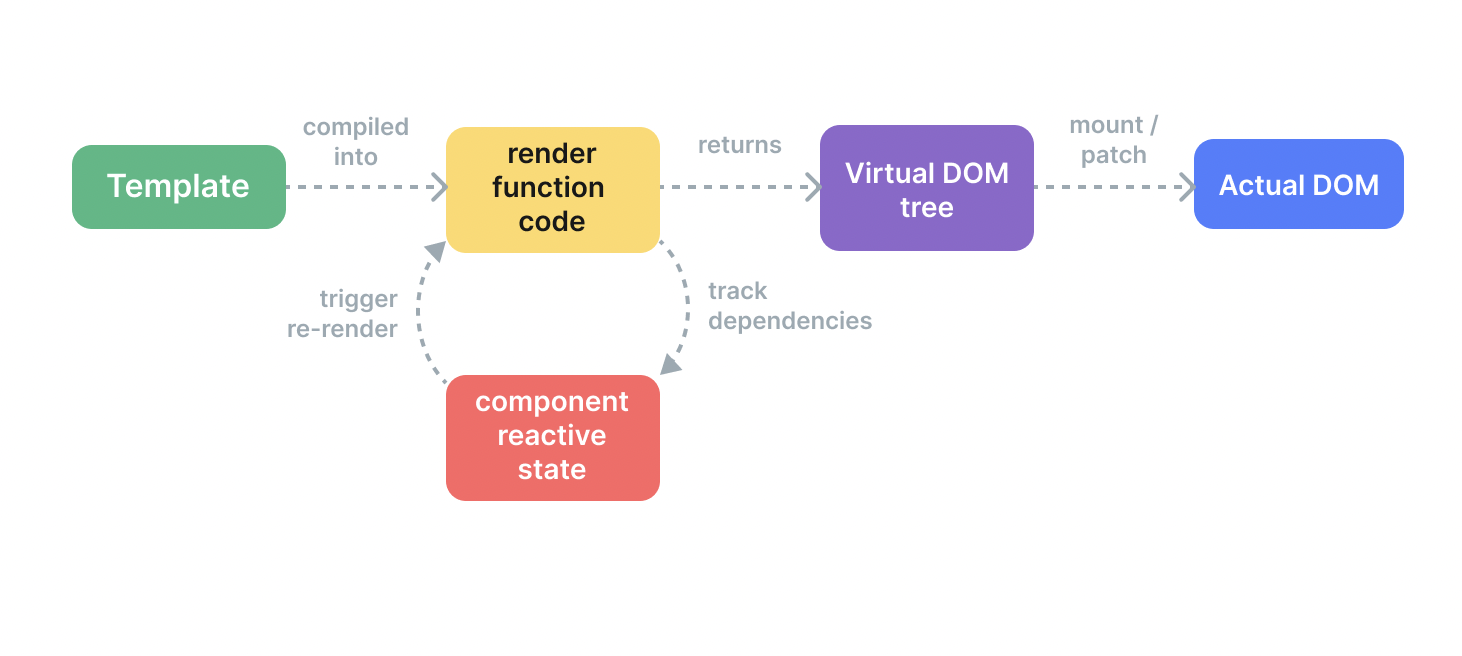
Render Pipeline
mount되면
1. Compile
- Vue templates are compiled into render functions (functions that return virtual DOM trees)
- 미리 build step 중 or 실행 중 runtime compiler 통해
2. Mount
the runtime renderer
- invokes render functions
- walks the returned virtual DOM tree
- creates actual DOM nodes based on it
- this step is performed as a reactive effect
: keeps track of all reactive dependencies that were used
3. Patch
-
mount 중 사용되었던 dependency가 변경되면 위에서 말한 reactive effect가 다시 돈다
-
새로운 업데이트된 Virtual DOM 트리가 생성된다
-
runtime renderer가 새로운 트리를 훑으면서 과거의 트리와 비교한다
-
필요한 업데이트들을 원래 DOM에 적용한다
Templates vs Render Functions
- Vue templates are compiled into virtual DOM render functions.
- Vue also provides APIs that allow us to skip the template compilation step and directly author render functions. Render functions are more flexible than templates when dealing with highly dynamic logic, because you can work with vnodes using the full power of JavaScript.
So why does Vue recommend templates by default? There are a number of reasons:
- Templates are closer to actual HTML.
This makes it easier to reuse existing HTML snippets, apply accessibility best practices, style with CSS, and for designers to understand and modify.
- Templates are easier to statically analyze due to their more deterministic syntax.
This allows Vue's template compiler to apply many compile-time optimizations to improve the performance of the virtual DOM (which we will discuss below).
In practice, templates are sufficient for most use cases in applications. Render functions are typically only used in reusable components that need to deal with highly dynamic rendering logic. Render function usage is discussed in more detail in Render Functions & JSX.
virtual Node는 실제 DOM 엘리먼트와 정확하게 일치하지는 않다
Virtual DOM은 컴포넌트로 만들어진 VNode 트리