Data
- 어떤 처리가 이루어지지 않은 상태의 문자(character)나, 수치(number), 그림(image) 등으로 단순히 측정하고 수집된 것
- 일종의 단순한 사실의 나열
Information
- 어떠한 목적이나 의도에 맞게 data를 가공 처리한 것
- 어떤 목적에 유용하게 사용할 수 있는 것
- 일종의 의미있는 Data
- 여기서 정량적인 부분을 도입한
amount of information개념을 사용하여 설명할 수도 있음. - 정보량은 학습의 결과로 인한
degree of surprise(놀람의 양)로 해석할 수 있음- 빈번하게 일어날 것 같지 않은 event가 발생하는 경우 빈번하게 일어나는 event가 일어나는 경우보다 더 많은 information 획득.
- 항상 발생하는 event가 발생할 경우, 얻는 information은 0
- 위의 개념을 받아들인다면 특정 event가 발생할 경우 얻어지는 정보량 이 해당 event의 발생확률 에 의해 결정된다고 볼 수 있음.
정보량 : Bit
- 어떤 Discrete random variable(이산 확률 변수) 에서 해당 값을 알게되는 경우 얻게되는 정보량을 Shannon이 제안한 방식으로 정량화하면 다음과 같은 수식이 됨.
- cf) 흔히 의 base는 2를 사용하며 이 경우 정보량의 단위가 바로
bit(binary digit)가 된다.- : 확률변수가 값을 가질 때의 정보량
- : 확률변수가 값을 가질 확률
- 다양한 경우의 수를 가지는 경우보다 확률변수가 0 또는 1을 가지는 경우로 한정하는 것이 가장 기본적임.
- 이는 information을 다루는 컴퓨터가 기본적으로 이진수를 사용하는 것과도 연관이 있음.
- 자연로그 를 사용하는 경우 단위는
Nat(about 1.443bit)
Entropy : 평균 정보량
- 가 0,1,2,...,n의 값을 가지는 random variable일 때, 에 대한 평균 정보량이
Entropy. - 해당 확률변수에서 기대되는 정보량(평균 정보량)이라고 할 수 있음.
- 확률변수가 절대 될 수 없는 값이 있을 경우, 해당 값의 발생확률
이 되므로 이는 entropy에 기여 없음.- 확률변수가 특정 상수로 고정될 경우, 이기 때문에
이 되므로 entropy가 0이 됨.
- 위의 경우는 discrete(불연속인)한 경우이며, continuous random variable의 경우는 다음과 같음.
- Noiseless coding theorem(Shannon)에서 Entropy가 평균정보량으로 제안되었고, 특정 데이터를 처리하는데 필요한 bit 수의 lower bound를 계산하는데 사용.
- Entrophy는 random variable의 상태를 전송하는데 필요한 bit 수의
Lower Bound라고 볼 수 있음.
Example) entrophy가 3.4라면, 4bit 이상이 필요하다.
- Entrophy는 random variable의 상태를 전송하는데 필요한 bit 수의
Entropy가 극대화 되는 경우
- Discrete random variable이 가질 수 있는 값들의 발생확률이 모두 같은 경우 즉, 해당 확률변수가 uniform probability distribution(균등 확률 분포)인 경우 Entrophy가 최대.
- Gaussian probability distribution을 따르는 Continuous random variable의 경우, 해당 분포의 Variance(분산), 가 클수록 entrophy가 증가.
- Gaussian probability distribution에서 variance가 무한대일 경우 entrophy는 최대.
- Variance가 무한대인 경우가 uniform probability distribution
Gaussian Distribution(Normal Distribution)
- = varience
- = standard deviation(표준편차)
- = mean(평균)
The Evolution of Information
- data를 처리하여 information으로 만들고, 해당 information으로 decision masking이나 task 수행.
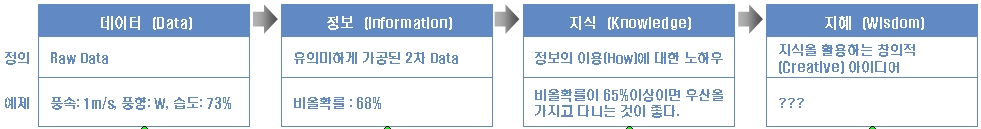
- 대부분의 경우 data와 information은 구분하지 않고 사용함.
- 보통 input으로 사용되는 측정 등으로 획득된 data를 raw data라고 부르며, 이후엔 거의 data라고 부름.
Computer and Data
- Computer의 또다른 정의는
외부로부터 입력된 값을 받아들여 처리한 결과를 출력시키거나 장래에 사용하기 위해 보관하는 장치임. - 이를 요약하면, Data를 처리하여 Information을 얻는 장치라고 할 수 있음.
Computer의 다른 이름인
Electronic Data Processing System(EDPS),Automatic Data Processing System(ADPS)들이 data processing에 초점을 둔 경우
Computer가 다루는 information
-
Data
1. Numerical data : number
2. Non-numerical data : Letter -
Data Structure
1. Linear Lists
2. Trees
3. Rings
4. etc... -
Program(Instruction set)
Data Representation
- 내부에서 사용되는 표현은 주로 계산을 위한 경우로 이진수를 기반으로 하는 numerical data 중심.
- 외부와의 information change를 위해 사용되는 code 등을 기반으로 한 표현은 non-numerical 중심.
- data 종류 및 용도에 따라 Internal Representation과 External Representation으로 바뀌어 컴퓨터에서 사용됨.
Numbers(for computing)
- 대부분의
numbers는 computer 안에 저장되어 있다가calculations로 바뀌게 됨. - Internal Representation for calculation efficiency.
- Final results need to be converted to as External Representation for presentability.
Alphabets, Symbols, and some Numbers
- 이러한 종류들의 information들은 processing 중에 바뀌지 않음.
- No needs for Internal Representation since they are not used for calculations.
- External Representation for processing and presentability.
Operations
- Computer가 data를 처리하는 연산으로 computer가 수행하는 작업을 가르키는 instruction과 비슷하게 사용.
- operation은 주로 숫자 또는 논리 연산 의미
- instruction은 자료의 로딩, 복사 등의 컴퓨터가 수행하는 작업들이 기본 단위를 의미하는 경우로 사용
Operation의 구분 : Operand에 따라 구분됨.
- Unary
- 1개의 operand(or input) and 1개의 output
shift,move,not
- Binary
- 2개의 operand(or input) and 1개의 output
and,or, 사칙연산
Operand의 type에 따라 다음과 같이 나뉘기도 함.
- Numerical Operator
- Logic Operator
Reference:
1) http://egloos.zum.com/yjhyjh/v/39721
2) https://dsaint31.me/mkdocs_site/CE
3) http://norman3.github.io/prml/docs/chapter02/3_1.html