1. HA 란?
참조 : 위키백과 - 고가용성
"
고가용성(高可用性, 영어: high availability, HA)은 서버, 네트워크, 프로그램 등의 정보 시스템이 상당히 오랜 기간 동안 지속적으로 정상 운영이 가능한 성질을 말한다. 고(高)가용성이란 "가용성이 높다"는 뜻으로서, "절대 고장 나지 않음"을 의미한다. 고가용성은 흔히 가용한 시간의 비율을 99%, 99.9% 등과 같은 퍼센티지로 표현하는데, 1년에 계획된 것 제외 5분 15초 이하의 장애시간을 허용한다는 의미의 파이브 나인스(5 nines), 즉 99.999%는 매우 높은 수준으로 고품질의 데이터센터에서 목표로 한다고 알려져 있다. 하나의 정보 시스템에 고가용성이 요구된다면, 그 시스템의 모든 부품과 구성 요소들은 미리 잘 설계되어야 하며, 실제로 사용되기 전에 완전하게 시험되어야 한다.
고가용성 솔루션(HACMP)[1]을 이용하면, 각 시스템 간에 공유 디스크를 중심으로 집단화하여 클러스터로 엮어지게 만들 수 있다. 동시에 다수의 시스템을 클러스터로 연결할 수 있지만 주로 2개의 서버를 연결하는 방식을 많이 사용한다. 만약 클러스터로 묶인 2개의 서버 중 1대의 서버에서 장애가 발생할 경우, 다른 서버가 즉시 그 업무를 대신 수행하므로, 시스템 장애를 불과 몇 초만에 복구할 수 있다. 고가용성 저장 장치로 레이드(RAID) 방식과 샌(SAN) 방식이 많이 이용되고 있다.
"
2. Keepalived
로드 밸런싱은 실제 서버 클러스터에 IP 트래픽을 분산시켜 하나 이상의 고가용성 가상 서비스를 제공하는 방법입니다. 로드 밸런싱 토폴로지를 설계할 때 로드 밸런서 자체와 그 뒤에 있는 실제 서버의 가용성을 고려하는 것이 중요합니다.
Keepalived는 로드 밸런싱과 고가용성을 위한 프레임워크를 제공합니다. 로드 밸런싱 프레임워크는 계층 4 로드 밸런싱을 제공하는 잘 알려지고 널리 사용되는 IPVS(Linux Virtual Server) 커널 모듈을 사용합니다. Keepalived는 상태에 따라 로드 밸런싱된 서버 풀을 동적으로 적응적으로 유지 관리하는 상태 검사기 세트를 구현합니다. 고가용성은 VRRP(Virtual Redundancy Routing Protocol)를 통해 달성됩니다. VRRP는 라우터 장애 조치를 위한 기본 벽돌입니다. 또한 keepalived는 저수준 및 고속 프로토콜 상호 작용을 제공하는 VRRP 유한 상태 머신에 대한 후크 세트를 구현합니다. 각 Keepalived 프레임워크는 독립적으로 또는 함께 사용하여 탄력적인 인프라를 제공할 수 있습니다.
이러한 맥락에서 로드 밸런서는 디렉터 또는 LVS 라우터라고도 합니다.
IPVS(IP Virtual Server) 모드는 리눅스 커널에 있는 L4 로드밸런싱 기술입니다. 리눅스 커널 안 네트워크 관련 프레임워크인 넷필터(Netfilter) 에 포함되어 있습니다. 따라서 IPVS 커널 묘듈이 노드에 설치되어야 합니다.
출처: https://kimjingo.tistory.com/152 [김징어의 Devlog:티스토리]
VRRP(Virutal Router Redundancy Protocol) : IBM에서 개발한 게이트웨이 이중화 솔루션 입니다. Master , Backup 라우터로 선출은 우선순위를 기준으로 정합니다. ( 출처 : https://blog.naver.com/sik7854/221869000354)
2.1 Keepalived 소개
keepalived 는 C로 작성 됐습니다.
keepalived 는 실시간 네트워킹 설계를 제공하는 중앙 I/O 멀티플렉서를 중심으로 구성됩니다. 모든 요소 사이에 동일한 모듈 제공과 코드 중복을 제거하기 위해 해당 라이브러리가 만들어졌습니다. 목표는 안전하고 안전한 코드를 생성하여 생산 견고성과 안정성을 보장하는 것입니다.
견고성과 안정성을 보장하기 위해 데몬은 3개의 개별 프로세스로 분할됩니다.
분기된 하위 프로세스 모니터링을 담당하는 최소한의 상위 프로세스입니다.
두 개의 하위 프로세스가 있는데, 하나는 VRRP 프레임워크를 담당하고 다른 하나는 상태 확인을 담당합니다.
각 하위 프로세스에는 자체 스케줄링 I/O 멀티플렉서가 있습니다. VRRP 스케줄링은 상태 검사기보다 더 합리적이고 중요하므로 VRRP 스케줄링 지터가 최적화됩니다. 이 분할 설계는 외부 라이브러리의 사용 상태 확인을 최소화하고 자체적으로 발생하는 오작동을 방지하기 위해 메인 루프까지 자체 작업과 유휴 메인 루프를 최소화합니다.
상위 프로세스 모니터링 프레임워크를 watchdog이라고 하며 각 하위 프로세스가 Unix 도메인 소켓을 허용하도록 설계한 다음 데몬 부트스트랩 동안 상위 프로세스는 해당 Unix 도메인 소켓에 연결하고 하위 프로세스에 정기적(5초) hello 패킷을 보냅니다. 부모가 원격으로 연결된 Unix 도메인 소켓에 hello 패킷을 보낼 수 없으면 간단히 자식 프로세스를 다시 시작합니다.
이 설계는 두 가지 이점을 제공합니다. 첫째, 상위 프로세스에서 원격으로 연결된 하위 프로세스로 전송된 모든 hello 패킷은 I/O 멀티플렉서 스케줄러를 통해 하위 스케줄링 프레임워크에서 교착 루프를 감지할 수 있는 방식으로 수행됩니다. 두 번째 이점은 sysV 신호를 사용하여 죽은 어린이를 감지할 수 있다는 점입니다.
2.2 커널 구성
Keepalived 는 4개의 linux kernel 을 사용합니다.
- LVS Framework: getsockopt 및 setockopt 호출을 사용하여 소켓에 대한 옵션을 가져오고 설정합니다.
- Netfilter Framework: NAT 및 Masquerading 을 지원하는 IPVS 코드입니다.
- Netlink Interface: 네트워크 인터페이스에서 VRRP 가상 IP를 설정하고 제거합니다.
- Multicast: VRRP advertisements 는 예약된 VRRP MULTICAST 그룹(224.0.0.18)으로 전송됩니다.
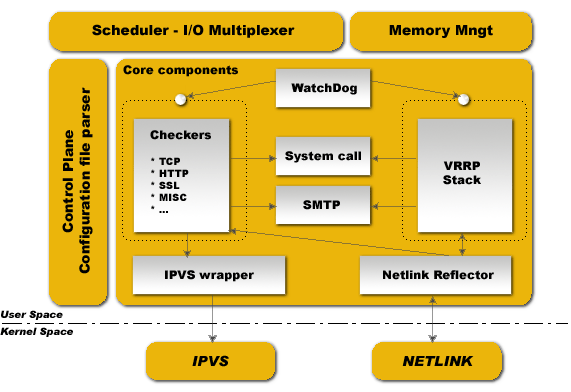
- Control Plane
Keepalived 구성은 keepalived.conf 파일을 통해 수행됩니다. 구문 분석에는 컴파일러 설계가 사용됩니다. 파서는 각 구성 키워드를 특정 처리기로 매핑하기 위해 키워드 트리 계층 구조와 함께 작동합니다. 중앙 다중 레벨 재귀 함수는 구성 파일을 읽고 키워드 트리를 탐색합니다. 구문 분석 중에 구성 파일은 내부 메모리 표현으로 변환됩니다.
- Scheduler - I/O Multiplexer
All the event are scheduled into the same process. Keepalived is a single process. Keepalived is a network routing software, it is so closed to I/O. The design used here is a central select(...) that is in charge of scheduling all internal task. POSIX thread libs are NOT used. This framework provide its own thread abstraction optimized for networking purpose.
- Memory Management
This framework provides acces to some generic memory managements functions like allocation, reallocation, release,... This framework can be used in two mode : normal_mode & debug_mode. When using debug_mode it provide a strong way to eradicate and track memory leaks. This low level env provide buffer under-run protection by tracking allocation memory and released. All the buffer used are length fixed to prevent against eventual buffer-overflow.
- Core Components
This framework define some common and global libraries that are used in all the code. Those libraries are : html parsing, link-list, timer, vector, string formating, buffer dump, networking utils, daemon management, pid handling, low level TCP layer4. The goal here is to factorize code to the max to limite as possible code duplication to increase modularity.
- WatchDog
This framework provide children processes monitoring (VRRP & Healthchecking). Each child accept connection to its own watchdog unix domain socket. Parent process send “hello” messages to this child unix domain socket. Hello messages are sent using I/O multiplexer on the parent side and accepted/processed using I/O multiplexer on children side. If parent detect broken pipe it test using sysV signal if child is still alive and restart it.
- Checkers
This is one of the main Keepalived functionality. Checkers are in charge of realserver healthchecking. A checker test if realserver is alive, this test end on a binary decision : remove or add realserver from/into the LVS topology. The internal checker design is realtime networking software, it use a fully multi-threaded FSM design (Finite State Machine). This checker stack provide LVS topology manipulation accoring to layer4 to layer5/7 test results. Its run in an independent process monitored by parent process.
- VRRP Stack
The other most important Keepalived functionality. VRRP (Virtual Router Redundancy Protocol : RFC2338) is focused on director takeover, it provide low-level design for router backup. It implements full IETF RFC2338 standard with some provisions and extensions for LVS and Firewall design. It implements the vrrp_sync_group extension that guarantee persistence routing path after protocol takeover. It implements IPSEC-AH using MD5-96bit crypto provision for securing protocol adverts exchange. For more informations on VRRP please read the RFC. Important things : VRRP code can be used without the LVS support, it has been designed for independant use.Its run in an independent process monitored by parent process.
- System Call
This framework offer the ability to launch extra system script. It is mainly used in the MISC checker. In VRRP framework it provides the ability to launch extra script during protocol state transition. The system call is done into a forked process to not pertube the global scheduling timer.
- Netlink Reflector
Same as IPVS wrapper. Keepalived work with its own network interface representation. IP address and interface flags are set and monitored through kernel Netlink channel. The Netlink messaging sub-system is used for setting VRRP VIPs. On the other hand, the Netlink kernel messaging broadcast capability is used to reflect into our userspace Keepalived internal data representation any events related to interfaces. So any other userspace (others program) netlink manipulation is reflected to our Keepalived data representation via Netlink Kernel broadcast (RTMGRP_LINK & RTMGRP_IPV4_IFADDR).
- SMTP
The SMTP protocol is used for administration notification. It implements the IETF RFC821 using a multi-threaded FSM design. Administration notifications are sent for healthcheckers activities and VRRP protocol state transition. SMTP is commonly used and can be interfaced with any other notification sub-system such as GSM-SMS, pagers, etc.
- IPVS Wrapper
This framework is used for sending rules to the Kernel IPVS code. It provides translation between Keepalived internal data representation and IPVS rule_user representation. It uses the IPVS libipvs to keep generic integration with IPVS code.
-
IPVS
The Linux Kernel code provided by Wensong from LinuxVirtualServer.org OpenSource Project. IPVS (IP Virtual Server) implements transport-layer load balancing inside the Linux kernel, also referred to as Layer-4 switching. -
NETLINK
The Linux Kernel code provided by Alexey Kuznetov with its very nice advanced routing framework and sub-system capabilities. Netlink is used to transfer information between kernel and user-space processes. It consists of a standard sockets-based interface for user space processes and an internal kernel API for kernel modules.
- Syslog
All keepalived daemon notification messages are logged using the syslog service.
2. Keeaplived 설치
- yum
yum install keepalived- Debian
apt-get install keepalived- RHEL/CentOS 의존성
yum install curl gcc openssl-devel libnl3-devel net-snmp-devel- Debian 의존성
apt-get install curl gcc libssl-dev libnl-3-dev libnl-genl-3-dev libsnmp-dev- Build and Install
curl --progress http://keepalived.org/software/keepalived-1.2.15.tar.gz | tar xz
cd keepalived-1.2.15
./configure
make
sudo make install3. Keepalived Config 작성법
- Global Definitions Synopsis
global_defs {
notification_email {
email
email
}
notification_email_from email
smtp_server host
smtp_connect_timeout num
lvs_id string
}| Keyword | Definition | Type |
|---|---|---|
| global_defs | identify the global def configuration block | |
| notification_email | email accounts that will receive the notification mail | List |
| notification_email_from | email to use when processing “MAIL FROM:” SMTP command | List |
| smtp_server remote SMTP | server to use for sending mail notifications | alphanum |
| smtp_connection_timeout | specify a timeout for SMTP stream processing | numerical |
| lvs_id | specify the name of the LVS director | alphanum |
- Virtual Server Definitions Synopsis
virtual_server (@IP PORT)|(fwmark num) {
delay_loop num
lb_algo rr|wrr|lc|wlc|sh|dh|lblc
lb_kind NAT|DR|TUN
(nat_mask @IP)
persistence_timeout num
persistence_granularity @IP
virtualhost string
protocol TCP|UDP
sorry_server @IP PORT
real_server @IP PORT {
weight num
TCP_CHECK {
connect_port num
connect_timeout num
}
}
real_server @IP PORT {
weight num
MISC_CHECK {
misc_path /path_to_script/script.sh
(or misc_path “ /path_to_script/script.sh <arg_list>”)
}
}
}
real_server @IP PORT {
weight num
HTTP_GET|SSL_GET {
url { # You can add multiple url block
path alphanum
digest alphanum
}
connect_port num
connect_timeout num
retry num
delay_before_retry num
}
}| Keyword | Definition | Type |
|---|---|---|
| virtual_server | identify a virtual server definition block | |
| fwmark | specify that virtual server is a FWMARK | |
| delay_loop | specify in seconds the interval between checks | numerical |
| lb_algo | select a specific scheduler (rr | wrr |
| lb_kind | select a specific forwarding method (NAT | DR |
| persistence_timeout | specify a timeout value for persistent connections | numerical |
| persistence_granularity | specify a granularity mask for persistent connections | |
| virtualhost | specify a HTTP virtualhost to use for HTTP | SSL_GET |
| protocol | specify the protocol kind (TCP | UDP) |
| sorry_server | server to be added to the pool if all real servers are down | |
| real_server | specify a real server member | |
| weight | specify the real server weight for load balancing decisions | numerical |
| TCP_CHECK | check real server availability using TCP connect | |
| MISC_CHECK | check real server availability using user defined script | |
| misc_path | identify the script to run with full path path | |
| HTTP_GET | check real server availability using HTTP GET request | |
| SSL_GET | check real server availability using SSL GET request | |
| url | identify a url definition block | |
| path | specify the url path | alphanum |
| digest | specify the digest for a specific url path | alphanum |
| connect_port | connect remote server on specified TCP port | numerical |
| connect_timeout | connect remote server using timeout | numerical |
| retry | maximum number of retries | numerical |
| delay_before_retry | delay between two successive retries | numerical |
- VRRP Instance Definitions Synopsis
vrrp_sync_group string {
group {
string
string
}
notify_master /path_to_script/script_master.sh
(or notify_master “ /path_to_script/script_master.sh <arg_list>”)
notify_backup /path_to_script/script_backup.sh
(or notify_backup “/path_to_script/script_backup.sh <arg_list>”)
notify_fault /path_to_script/script_fault.sh
(or notify_fault “ /path_to_script/script_fault.sh <arg_list>”)
}
vrrp_instance string {
state MASTER|BACKUP
interface string
mcast_src_ip @IP
lvs_sync_daemon_interface string
virtual_router_id num
priority num
advert_int num
smtp_alert
authentication {
auth_type PASS|AH
auth_pass string
}
virtual_ipaddress { # Block limited to 20 IP addresses
@IP
@IP
@IP
}
virtual_ipaddress_excluded { # Unlimited IP addresses
@IP
@IP
@IP
}
notify_master /path_to_script/script_master.sh
(or notify_master “ /path_to_script/script_master.sh <arg_list>”)
notify_backup /path_to_script/script_backup.sh
(or notify_backup “ /path_to_script/script_backup.sh <arg_list>”)
notify_fault /path_to_script/script_fault.sh
(or notify_fault “ /path_to_script/script_fault.sh <arg_list>”)
}| Keyword | Definition | Type |
|---|---|---|
| vrrp_instance | identify a VRRP instance definition block | |
| state | specify the instance state in standard use | |
| Interface | specify the network interface for the instance to run on | string |
| mcast_src_ip | specify the src IP address value for VRRP adverts IP header | |
| lvs_sync_daemon_inteface | specify the network interface for the LVS sync_daemon to run on | string |
| virtual_router_id | specify to which VRRP router id the instance belongs | numerical |
| priority | specify the instance priority in the VRRP router | numerical |
| advert_int | specify the advertisement interval in seconds (set to 1) | numerical |
| smtp_alert | Activate the SMTP notification for MASTER state transition | |
| authentication | identify a VRRP authentication definition block | |
| auth_type | specify which kind of authentication to use (PASS | AH) |
| auth_pass | specify the password string to use | string |
| virtual_ipaddress | identify a VRRP VIP definition block | |
| virtual_ipaddress_excluded | identify a VRRP VIP excluded definition block (not protocol VIPs) | |
| notify_master | specify a shell script to be executed during transition to master state | path |
| notify_backup | specify a shell script to be executed during transition to backup state | path |
| notify_fault | specify a shell script to be executed during transition to fault state | path |
| vrrp_sync_group | Identify the VRRP synchronization instances group | string |
