1. CSV
- Comma Seperated Value의 약자로, 쉼표로 구분된 파일을 말한다.
CSV 파일과 Pandas
- Pandas의 DataFrame은 to_csv 메서드를 지원한다. 이 메서드를 이용하면 손쉽게 csv 파일로 저장할 수 있다.
import pandas as pd
df=pd.DataFrame(rows, columns=fields)
df.to_csv('pandas.csv',index=False)
df = pd.read_csv('pandas.csv')
df.head()
2. XML
- Extensible Markup Language의 약자로, 다목적 마크업 언어이다.
- API에서 데이터를 저장하고 요청할 때 XML이나 JSON 형식을 사용한다.

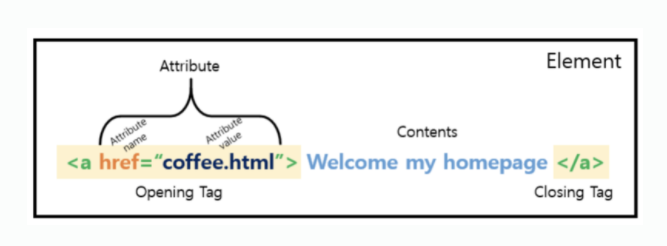
- 마크업 언어는 태그(tag)로 이루어진 언어를 말하며, 상위 태그- 하위 태그의 계층적 구조로 되어 있다.
- XML은 요소(element)로 이루어져 있다.
- 요소는
<열린 태그> 내용 </닫힌 태그>가 기본적인 구조이며, 속성(attribute)값을 가질 수도 있다.
XML 파일 만들기
- 파이선 표준라이브러리인 ElementTree를 이용
- Element() : 태그 생성
- SubElement() : 자식 태그 생성
- tag : 태그 이름
- text : 텍스트 내용 생성
- attrib : 속성 생성
XML 파싱하기
- 파싱(parsing, 구문 분석)이란, 어떤 문자열을 의미있는 토큰(token)으로 분해해, 문법적 의미와 구조를 반영한 파스 트리(parse tree)를 만드는 과정이다.
BeautifulSoup를 이용해 파싱하기
from bs4 import BeautifulSoup
import os
path = os.getenv("HOME") + "/aiffel/ftext/data/books.xml"
with open(path, "r", encoding='utf8') as f:
booksxml = f.read()
soup = BeautifulSoup(booksxml,'lxml')
for title in soup.find_all('title'):
print(title.get_text())
print(title)
3. JSON
- JavaScript Object Notation의 약자로, 웹 언어인 JavaScript의 데이터 객체 표현 방식이다.
person = {
"first name" : "Yuna",
"last name" : "Jung",
"age" : 33,
"nationality" : "South Korea",
"education" : [{"degree":"B.S degree", "university":"Daehan university",
"major": "mechanical engineering",
"graduated year":2010}]
}
- 장점: CSV 파일에 비해 좀 더 유연하게 데이터를 표현할 수 있고 XML 파일보다 파일을 쉽게 읽고 쓸 수 있다.
- 장점: JavaScript에서 작성된 프로그램에서 쉽게 다룰 수 있다.
JSON 파싱
- JSON 파일 저장
import json
person = {
"first name" : "Yuna",
"last name" : "Jung",
"age" : 33,
"nationality" : "South Korea",
"education" : [{"degree":"B.S degree", "university":"Daehan university", "major": "mechanical engineering", "graduated year":2010}]
}
with open("person.json", "w") as f:
json.dump(person , f)
- JSON 파일 읽기
import json
with open("person.json", "r", encoding="utf-8") as f:
contents = json.load(f)
print(contents["first name"])
print(contents["nationality"])
Yuna
South Korea


