1. 데이터 읽기
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from mpl_toolkits.mplot3d import Axes3D
%matplotlib inline
# raw data
raw_data = np.genfromtxt('./data/x09.txt', skip_header=36)
# 그래프
xs = np.array(raw_data[:,2], dtype=np.float32)
ys = np.array(raw_data[:,3], dtype=np.float32)
zs = np.array(raw_data[:,4], dtype=np.float32)
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs)
ax.set_xlabel('Weight')
ax.set_ylabel('Age')
ax.set_zlabel('Blodd fat')
plt.show()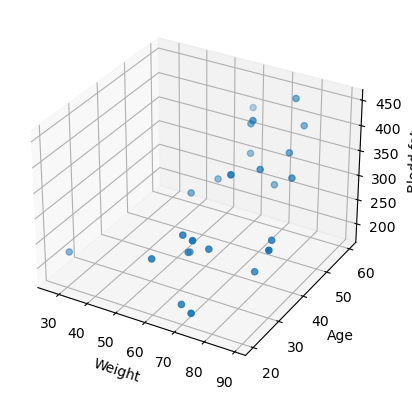
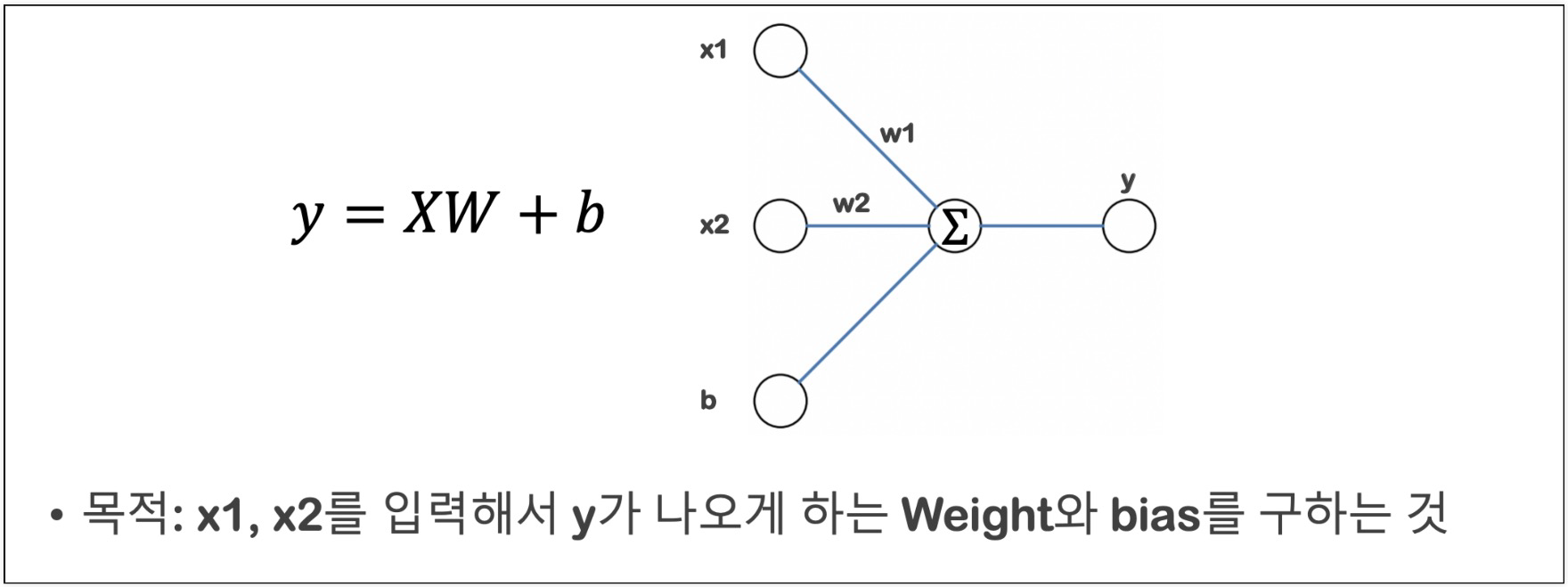
2. 목표
- 목적: input - age & weight / output - blood fat
- Linear Regression (y = Wx + b)
- 뉴런 하나만 사용
3. 학습 대상 데이터
- X: age, weight 데이터만 선택 행렬 (25, 2) & W (2, 1) → (25, 1)
- y: blood fat 데이터, 행렬 (25, ) → (25, 1) 되도록 reshape
x_data = np.array(raw_data[:,2:4], dtype=np.float32)
y_data = np.array(raw_data[:,4], dtype=np.float32)
y_data = y_data.reshape((25, 1))4. 모델
- 뉴런 1개 사용, input 2개
loss(cost)function: 정답까지 얼마나 멀리 있는지 측정하는 함수(에러)loss='mse': mean square error 오차 제곱의 평균optimizer: loss 함수를 최소화하는 가중치를 찾아가는 과정에 대한 알고리즘(loss를 어떻게 줄일 것인지를 결정하는 방법을 선택)rmsprop: Root Mean Square Propagation- 경사(gradient)의 크기를 지수 이동 평균(exponential moving average)을 사용하여 조절하며, 경사의 크기에 따라 각각의 파라미터를 업데이트한다. rmsprop 이동 평균을 사용하여 경사의 크기를 조절하기 때문에, 이전 기울기의 크기와 현재 기울기의 크기를 비교하여 기울기의 크기가 크게 변하는 경우 더 작은 학습률을 적용하여 안정적인 학습을 할 수 있다.
import tensorflow as tf
model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1, input_shape=(2, ))
])
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='mse')
5. fit 학습
- loss가 떨어진다
epochs모든 데이터셋을 학습시키는 횟수(ex) epochs=5000 > loss를 떨어뜨리면서 5000번)
hist = model.fit(x_data, y_data, epochs=5000)
plt.plot(hist.history['loss'])
plt.title('model loss')
plt.ylabel('loss')
plt.xlabel('epochs')
plt.show()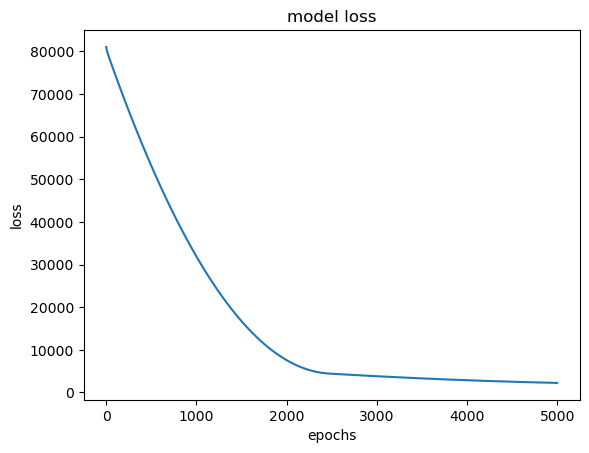
6. predict
model.predict(np.array([100, 44]).reshape(1,2))
# array([[393.3943]], dtype=float32)7. 가중치 & bias
w_, b_ = model.get_weights()
print('wieght is : ', w_)
print('bias is : ', b_)
'''
wieght is : [[2.1139164]
[4.0235105]]
bias is : [4.96821]
'''8. 그래프
x = np.linspace(20, 100, 50).reshape(50, 1)
y = np.linspace(10, 70, 50).reshape(50, 1)
X = np.concatenate((x,y), axis=1)
Z = np.matmul(X, w_) + b_
fig = plt.figure(figsize=(12, 12))
ax = fig.add_subplot(111, projection='3d')
ax.scatter(xs, ys, zs)
ax.scatter(x, y, Z)
ax.set_xlabel('Weight')
ax.set_ylabel('Age')
ax.set_zlabel('Blodd fat')
ax.view_init(15, 15)
plt.show()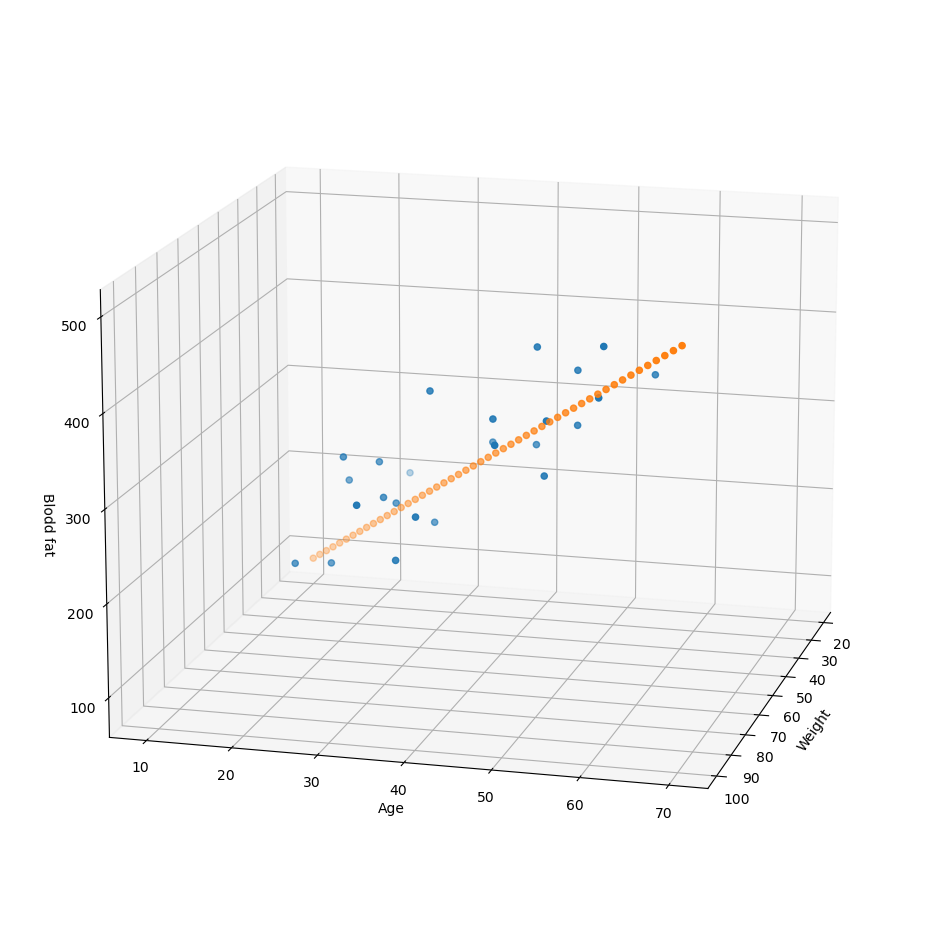
Reference
1) 제로베이스 데이터스쿨 강의자료
2) https://wikidocs.net/195016
