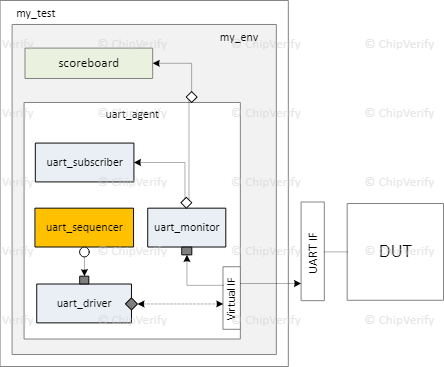
Sequencer란 무엇인가요?
 사진, 코드 출처: chipverify
사진, 코드 출처: chipverify
Sequence와Driver간의 데이터 트랜잭션 전달을 제어하는 중요한 컴포넌트입니다.uvm_sequencer라는 UVM 라이브러리 클래스를 상속받아 사용되는 것이 권장되며,- 이 클래스는 sequence가 driver와 통신할 수 있도록 필요한 모든 기능을 포함하고 있습니다.
어떻게 사용하나요?
Sequencer에는 2가지 타입이 존재합니다.
// class uvm_sequencer #(type REQ = uvm_sequence_item, RSP = REQ) extends uvm_sequencer_param_base #(REQ, RSP);
uvm_sequencer #(my_data, data_rsp) seqr0; // with RSP
uvm_sequencer #(my_data) seqr0; // without RSPmy_data: Sequence가 생성하는 request transaction 타입(item).
data_rsp: Driver가 반환하는 response transaction 타입.
위에는 response가 있는 type, 아래는 response가 없는 type인데, 보통 아래 type의 sequencer을 주로 사용합니다. Driver의 반환값보다는 그냥 monitor를 통해 검증을 하기 때문인 것으로 추정됩니다.
사용법으로는 UVM library에 작성된 sequencer를 상속받아 custom sequencer을 만들어서 사용하거나, 그냥 따로 sequencer를 만들 필요 없이 uvm_sequencer 그 자체를 활용하는 방법이 있습니다.
사용법 1. Custom sequencer 만들어서 사용
//sequencer 생성
class my_sequencer extends uvm_sequencer #(my_data);
`uvm_component_utils (my_sequencer)
function new (string name, uvm_component parent);
super.new (name, parent);
endfunction
endclass
//agent에서 활용
class agent extends uvm_agent;
`uvm_component_utils(agent)
function new(string name="agent", uvm_component parent=null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
driver d0; // Driver handle
monitor m0; // Monitor handle
my_sequencer s0; // Sequencer Handle
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
s0 = my_sequencer::type_id::create("s0", this);
d0 = driver::type_id::create("d0", this);
m0 = monitor::type_id::create("m0", this);
endfunction
virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
d0.seq_item_port.connect(s0.seq_item_export);
endfunction
endclass단순히 uvm_sequencer를 상속받고 특별한 기능을 추가적으로 수행하지는 않습니다. 추가적인 기능을 추가해도 되지만 그렇게 사용하는 경우는 잘 보지 못했습니다.
중요한 부분은 #(my_data)입니다. Sequencer의 type을 item(여기선 my_data)으로 해줘야합니다. 기본적인 uvm_sequencer는 type이 정해져있지 않기 때문이죠.
사용법 2. 기본적인 uvm_sequencer를 사용
딱히 추가적인 기능을 추가하고 싶지 않다면 그냥 uvm_sequencer를 사용해도 됩니다. 단 인스턴스할 때, 위에처럼 type을 item으로 해주세요.
class agent extends uvm_agent;
`uvm_component_utils(agent)
function new(string name="agent", uvm_component parent=null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
driver d0; // Driver handle
monitor m0; // Monitor handle
uvm_sequencer #(my_data) s0; // Sequencer Handle
virtual function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
s0 = uvm_sequencer#(my_data)::type_id::create("s0", this);
d0 = driver::type_id::create("d0", this);
m0 = monitor::type_id::create("m0", this);
endfunction
virtual function void connect_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.connect_phase(phase);
d0.seq_item_port.connect(s0.seq_item_export);
endfunction
endclass그냥 라이브러리 내장 uvm_sequencer를 사용했습니다. 인스턴스할 때, my_data 타입으로 선언해주었습니다.
어떤 기업에서 사용하는 AMBA BUS Verification IP를 봤는데, 사용법 1을 많이 사용하더라구요. 추가적인 기능구현은 없었는데도 불구하고 말이죠. 어떤 방식을 쓰던 자유인 것 같습니다.
😍읽어주셔서 감사합니다~
댓글, 지적, 하트 환영합니다.🌈
