int p = 100;
double d = 3.14;
float f = 3.14F;
char c = 'A';
String s = "Hello";
printf(" %d %% %f %c %s " , p , d/f , c , s)
package ⓒ____;
import java.util.Scanner;public class ⓒ____{
📝main ↩ {

public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in); System.out.print("정수:");
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
int d = sc.nextInt();
int e = sc.nextInt();
int result = (a*a+b*b+c*c+d*d+e*e)%10;
System.out.println(result); System.out.print("문자열:");
String str = sc.next();
System.out.println(str+"??!");💡반복문 (조건문)
if🗝else if🗝else문
int n = 20;
int m = 30;
if (n>m) { // printf("%s %%d",변수,변수);
System.out.printf("%d이 큽니다.",n);
}else if (n<m) {
System.out.printf("%d이 작습니다.",n);
}else{
System.out.printf("%d와 %d는 같습니다.",n,m);
}
-----------------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int age = sc.nextInt();
if (age>=20) {
System.out.println("성인");
} else if (age>=17) {
System.out.println("고등학생");
} else if (age>=14) {
System.out.println("초등학생");
} else {
System.out.println("미취학 아동");
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int max = (a>b) ? a:b ; // 삼항연산자
=======================
int max = 0;
if (a>b)
max = a;
else
max = b;
=======================
System.out.println(max);
}
}
------------------------- 윤년/평년 ------------------------
/* 윤년은 연도가 4의 배수이면서,
100의 배수가 아닐 때 또는 400의 배수일 때이다.
예를 들어, 2012년은 4의 배수이면서 100의 배수가 아니라서 윤년이다.
1900년은 100의 배수이고 400의 배수는 아니기 때문에 윤년이 아니다.
하지만, 2000년은 400의 배수이기 때문에 윤년이다.
연도는 1보다 크거나 같고, 4000보다 작거나 같은 자연수이다.
연도가 윤년이면 1,아니면 0을 출력하는 프로그램을 작성하시오. */
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int s = sc.nextInt();
if (s%4 == 0 && s%100 != 0 || s%400 == 0) {
System.out.println("1");
}else {
System.out.println("0");
}
}
}
--------------------- 4분면 좌표 ------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int x = sc.nextInt();
int y = sc.nextInt();
if (x>=0 && y>=0) {
System.out.println("Quadrant 1");
}else if (x<=0 && y>=0) {
System.out.println("Quadrant 2");
}else if (x<=0 && y<=0) {
System.out.println("Quadrant 3");
}else{
System.out.println("Quadrant 4");
}
}
}
-------------------- 알람문제 --------------------
/* 알람을 45분 앞서는 시간으로 바꾸기
(0 ≤ H ≤ 23, 0 ≤ M ≤ 59)
입력 시간은 24시간 표현을 사용한다.
24시간 표현에서 하루의 시작은 0:0(자정)이고,
끝은 23:59(다음날 자정 1분 전)이다.
시간을 나타낼 때, 불필요한 0은 사용하지 않는다. */
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int H = sc.nextInt();
int M = sc.nextInt();
M -= 45;
if (M<0) {
M += 60;
H -= 1;
if (H<0) {
H += 24;
}
}
System.out.printf("%d : %d",H,M);
}
}
------------------- 오븐문제 ---------------------
/* 현재시각은 (0 ≤ H ≤ 23)와(0 ≤ M ≤ 59)
정수로 빈칸을 사이에 두고 순서대로 주어진다.
요리하는데 필요한 시간은 (0 ≤ C ≤ 1,000)
23시59분에서 1분이 지나면 0시0분이 된다. */
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int A = sc.nextInt();
int B = sc.nextInt();
int C = sc.nextInt();
B += C;//48+25
A += B/60;//23+25
B %= 60;//73%60==13
if (A >= 24)
A -= 24;
System.out.printf("%d : %d",A,B);
}
}
-------------------- 주사위 문제 --------------------
/* 1~6개의 눈을 가진 3개의 주사위를 던져서 상금을 받는다.
⊙ 같은 눈이 3개가 나오면 10,000원+(같은 눈)×1,000원
⊙ 같은 눈이 2개만 나오는 경우에는 1,000원+(같은 눈)×100원
⊙ 모두 다른 눈이 나오는 경우에는 (그중 가장 큰 눈)×100원 */
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt();
int b = sc.nextInt();
int c = sc.nextInt();
int s = 0;
if(a==b && b==c){
s = 10000 + a*1000;
}else if(a!=b && a!=c && b!=c){
if(a>b && a>c){
s = a*100;
}else if(b>a && b>c){
s = b*100;
}else{
s = c*100;
}
}else{
if(a==b || a==c){
s = 1000 + a*100;
}else{
s = 1000 + b*100;
}
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}switch🗝case문
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n = 3;
switch(n) {
case 1:
System.out.println("simple java!");
case 2:
System.out.println("funny java!");
case 3:
System.out.println("exciting java!");
default:
System.out.println("Do you like java?");
}
}
----------------------- 학점출력 --------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
switch(n/10){
case 10:
case 9:
System.out.println("A");
break;
case 8:
System.out.println("B");
break;
case 7:
System.out.println("C");
break;
case 6:
System.out.println("D");
break;
default :
System.out.println("F");
break;
}
}
}do🗝while문
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Loop {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int month;
do{//처음한번은 무조건 실행 ▶ 중복제거
System.out.print("올바른 월을 입력하시오.[1-12]: ");
month = sc.nextInt();
}while(month<1 || month>12);//OUT
System.out.println("사용자는 "+month+"월을 입력 하셨습니다.");
}
}while🗝문
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int s = 0;
========================
int i = 1;
while(i<=10) {
s += i;
i++;
}
========================
for(int i=1;i<=10;i++) {
s += i;
}
========================
System.out.print(s);
}
}
--------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n= 0;
int i = 1;
while(i<=5) {
System.out.print("input :");
n = sc.nextInt();
if(n%5==0) continue;
System.out.println("output :"+ n);
i++;
}
}
}
----------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int i = 1;
int s = 0;
while(i<=n) {
if (i%3==0) {
s += i;
}
i++;
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}
---------------------------------------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int cnt = 0;
==================
while(n!=0) {
n=n/10;
cnt++;
}
==================
while(true){
n=n/10;
cnt++;
if n==0 break;
}
==================
System.out.println(cnt);
}
}
------------------ 자리수 합 ----------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int s = 0;
while(n!=0) {
s += n%10;
n=n/10;
}
System.out.println(s);
}
}for🗝문
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println("");
}
}
}
* *
** **
*** ***
**** ****
***** *****
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
for(int j=1;j<=5-i;j++) {
System.out.print(" ");
}
for(int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print("*");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
---------------- 행&열 출력하기 ---------------
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
System.out.println();
for(int j=1;j<=5;j++) {
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
}
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5
---------------------------------------------
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
//System.out.println();
for (int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
////////////////////////////////////////////
1 1 2 3 4 5
1 2 1 2 3 4
1 2 3 1 2 3
1 2 3 4 1 2
1 2 3 4 5 1
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
//System.out.println();
for (int j=1;j<=6-i;j++) {
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
--------------------------------------------
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
for (int j=1;j<=5-i;j++) {
System.out.print("__");
}
for (int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
System.out.print(j+"_");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1 5
1 2 4 5
1 2 3 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 1 2 3 4 5
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=5;i++) {
for (int j=1;j<=5-i;j++) {
System.out.print("__");
}
for (int j=6-i;j<=5;j++) {
System.out.print(j+"_");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
---------------- 소수 출력하기 ---------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("소수를 출력하세요>>>");
int n = sc.nextInt();
for (int i=1;i<=n;i++) {
int cnt = 0;
for (int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
if (i%j==0) {
cnt++;
}
}
if (cnt==2) {
System.out.print(i+" ");
}
}
}
}
소수를 출력하세요>>>20
2 3 5 7 11 13 17 19
------------------ 100까지 소수 --------------
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i=1;i<=100;i++) {
System.out.printf("%d : ",i);
for (int j=1;j<=i;j++) {
if (i%j == 0) {
System.out.print(j+" ");
}
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1 : 1
2 : 1 2
3 : 1 3
4 : 1 2 4
5 : 1 5
6 : 1 2 3 6
7 : 1 7
8 : 1 2 4 8
9 : 1 3 9
10 : 1 2 5 10
11 : 1 11
12 : 1 2 3 4 6 12
13 : 1 13
14 : 1 2 7 14
15 : 1 3 5 15
16 : 1 2 4 8 16
17 : 1 17
18 : 1 2 3 6 9 18
19 : 1 19
20 : 1 2 4 5 10 20
...
100 : 1 2 4 5 10 20 25 50 100
------------- n까지 k번째(약수n) -------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int n,k;
Scanner sc =new Scanner(System.in);
n = sc.nextInt();
k = sc.nextInt();
int cnt = 0;
int res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i<=n; i++) {
if (n%i == 0) {
cnt++;
if(cnt == k){
res = i;
}
}
}
System.out.println(res);
}
}
------------- 최대값 & 최대값_자리 -------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int max=0, max_idx=0;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n=0;
for(int i=0;i<9;i++) {
n = sc.nextInt();
if (n>max) {
max = n;
max_idx = i+1;
}
}
System.out.printf("%d\n%d",max,max_idx);
}
}
-------------- 7개~100 홀수합:-1 ---------------
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int min = 100;
int sum = 0;
int n;
for (int i=0;i<7;i++) {
n = sc.nextInt();
if (n % 2 == 1) {
sum += n;
if (min >= n) {
min = n;
}
}
}
if (sum == 0) {
System.out.println("-1");
System.out.printf("%d\n%d",sum,min);
}
}
>>>24 82 46 58 42 8 14
홀수가 존재하지 않음 : -1
=======================
>>>12 77 38 41 53 92 85
77 + 41 + 53 + 85 = 256
최솟값:41 < 53 < 77 < 85
----------------------- 윷놀이 ---------------------
⊙ - : 배0 등1
⊙도A : 배1 등3
⊙개B : 배2 등2
⊙걸C : 배3 등1
⊙윷D : 배4 등0
⊙모E : 배0 등4
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a,b,c,d;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System,in);
for (int i=0;i<3;i++){
a = sc.nextInt();
b = sc.nextInt();
c = sc.nextInt();
d = sc.nextInt();
sum = a+b+c+d;
if (sum == 3)
System.out.println('A');
else if (sum == 2)
System.out.println('B');
else if (sum == 1)
System.out.println('C');
else if (sum == 0)
System.out.println('D');
else
System.out.println('E');
}
}
}✏️1차원 배열
1차원배열 : 타입[] 배열이름 = new 타입[크기];
2차원배열 : 타입[][] 배열이름 = new 타입[행][열];
int[] arr = new int[10];
System.out.printf("%d %d %d %d %d",arr[0],arr[1],arr[2],arr[3],arr[4]);
---------------------- 기본타입 배열은 0으로 초기화 -----------------------
arr[0] = 1;
arr[1] = 2;
arr[2] = 3;
arr[3] = arr[0] + arr[1];
System.out.println(arr[0] + " " + arr[1] + " " + arr[2] + " " + arr[3]);
----------------------- 배열의 모든요소 값 할당하기 -----------------------
//참조변수 배열은 null로 초기화
String[] str = new String[10];
//배열생성 & 초기화 1(배열크기X)
int[] arr = new int[] {1,2,3};
//배열생성 & 초기화 2
int[] arr = {1,2,3};
int[] arr = new int[5];
Array.fill(arr,-1);
============== for문 ==============
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
============ for - each ===========
for(int i : arr){
System.out.print(i);
}
============== toString() ==============
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr))
----------------- 10자리 배열합 ---------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int sum = 0;
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[10];
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
sum+=arr[i];
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
---------- 배열 최대값 & 최대값_자리 -----------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arr = new int[10];
int n = 0;
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
arr[i] = sc.nextInt();
}
int max = 0, max_idx = 0;
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
if (arr[1]>max) {
max = arr[i];
max_idx = i;
}
}
System.out.println(max+" "+max_idx);
}
}
------------ 10진수 => 2진수로 출력 ------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int n = sc.nextInt();
int[] arr = new int[10000];
int idx= 0;
while(n!=0) {
arr[idx++] = n%2;
//arr[idx] = n%2;
n /= 2;
//idx++;
}
for(int i=idx-1;i>=0;i--) {
System.out.print(arr[i]);
}
}
}
-------------- 배열비교 & 무승부 -------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[] arrA = new int[10];
int[] arrB = new int[10];
int A_cnt=0, B_cnt=0;
for (int i=0;i<10;i++) {
arrA[i] = sc.nextInt();
arrB[i] = sc.nextInt();
if (arrA[i] > arrB[i]) A_cnt++;
else if (arrA[i] < arrB[i]) B_cnt++;
}
if (A_cnt > B_cnt) {
System.out.print("A");
}else if(A_cnt < B_cnt) {
System.out.print("B");
}else {
System.out.print("D");
}
}
}
>>>7 1 6 5 2 8 9 0 3 4
>>>6 2 3 5 7 9 1 0 4 8
승패 : D
------------------ 10의배수 10개 ---------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int sum = 0;
int[] arr = new int[101];
int n = 0;
int max = 0,max_idx = 0;
for(int i=0;i<10;i++) {
n = sc.nextInt();
sum += n;
arr[n/10]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<101;i++) {
if(arr[i] > max) {
max = arr[i];
max_idx = i;
}
}
System.out.printf("%d\n%d",sum/10,max_idx*10);
}
}
>>>10 30 50 70 90 40 60 80 20 100
평균값 : 55
최대값_자리 : 10✏️2차원 배열
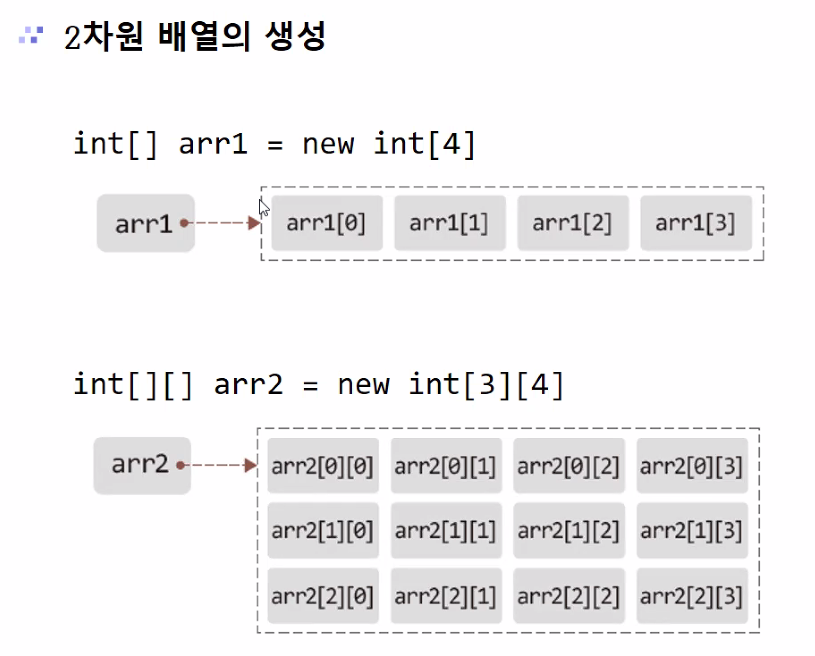
int[][] arr = new int[3][3]
===========================
int[][] arr = {
{1,2,3},
{4,5,6},
{7,8,9}
};
===============
arr[0][0] = 1;
arr[0][1] = 2;
arr[0][2] = 3;
arr[1][0] = 4;
arr[1][1] = 5;
arr[1][2] = 6;
arr[2][0] = 7;
arr[2][1] = 8;
arr[2][2] = 9;
===================
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[3][3];
int num = 1;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++){
for(int j=0;j<3;j++){
arr[i][j] = num;
num++;
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
------------------ 4행 5열 ------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[4][5];
int num = 1;
for(int i=0;i<4;i++){
for(int j=0;j<5;j++){
arr[i][j] = num;
num++;
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1 2 3 4 5
6 7 8 9 10
11 12 13 14 15
16 17 18 19 20
--------------------------------------------------
//첫번째 행과 열은 모두 1로 초기화
//두번째 행부터 위의 값과 바로 왼쪽의 값을 더한 값을 저장
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[][] arr = new int[5][5];
for(int i=0;i=<5;i++){
for(int j=0;j=<5;j++){
if(i==0 || j==0) {
arr[i][j] = 1;
}else {
arr[i][j] = arr[i-1][j]+arr[i][j-1];
}
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
1 1 1 1 1
1 2 3 4 5
1 3 6 10 15
1 4 10 20 35
1 5 15 35 70
--------------------- 파스칼 삼각형 ----------------------
1 5 10 10 5 1
↑ ↑ ↑ ↑
1 + 4 + 6 + 4 + 1
↑ ↑ ↑
1 + 3 + 3 + 1
↑ ↑
1 + 2 + 1
↑
1 + 1
1
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] arr = new int[10][10];
int n = sc.nextInt();
for(int i=n-1;i>=0;i--) {
for(int j=0;j<n;j++) {
if(j==0) {
arr[i][j] = 1;
}else {
arr[i][j] = arr[i+1][j]+arr[i+1][j-1];
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
for(int j=0;j<n-i;j++) {
System.out.print(arr[i][j]+"\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
---------------- 승리한☆요리사 ----------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] arr = new int[5][4];
int sum=0,max=0,idx=0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++) {
sum = 0; // 잊지말기!
for(int j=0;j<4;j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
sum += arr[i][j];
}
if(sum > max) {
max = sum;
idx = i+1;
}
}
System.out.printf("승자 : %d 행\n승점 : %d점",idx,max);
}
}
>>>5 4 2 5
>>>4 3 5 5
>>>2 5 3 5
>>>3 5 4 4
>>>5 5 1 2
승자 : 2 행
승점 : 17점
--------------- 행의합 & 최대행 ---------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int[][] arr = new int[3][5];
int sum=0,max=0,idx=0;
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
sum = 0;
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
arr[i][j] = sc.nextInt();
sum += arr[i][j];
if(sum > max) {
max = sum;
idx = i+1;
}
}
}
for(int i=0;i<3;i++) {
System.out.printf("%d행의 합 : %d\n",i,sum);
}
System.out.print("최 대 행 : ");
for(int j=0;j<5;j++) {
System.out.print(arr[idx-1][j]+" ");
}
}
}
>>>12 56 32 16 98
>>>99 56 34 34 3
>>>65 3 87 78 21
0행의 합 : 214
1행의 합 : 226
2행의 합 : 254
최 대 행 : 65 3 87 78 21
------------------- 방배정 ------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("학생수:");
int N = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("정원수:");
int K = sc.nextInt();
int[][] arr = new int[2][7];//넉넉히
int S,Y;
System.out.println("S/Y");
for (int i=0;i<N;i++) {
S = sc.nextInt();
Y = sc.nextInt();
arr[S][Y]++;
}
int cnt = 0;
for (int i=0;i<2;i++) {//보통은<크기
for (int j=1;j<=6;j++) {//=조심
cnt += arr[i][j]/K;
if (arr[i][j]%K != 0)
cnt++;
}
}
System.out.print("방갯수:"+cnt);
}
}
학생수:16 학생수:3
정원수:2 정원수:3
S/Y S/Y
1 1 0 3
0 1 1 5
1 1 0 6
0 2 방갯수:3
1 2
0 2
0 3
1 3
1 4
1 3
1 3
0 6
1 5
0 5
1 5
1 6
방갯수:12🗝 String객체
package ex1_string;
import java.util.*;
public class Ex1_String {
public static void main(String[] args) {
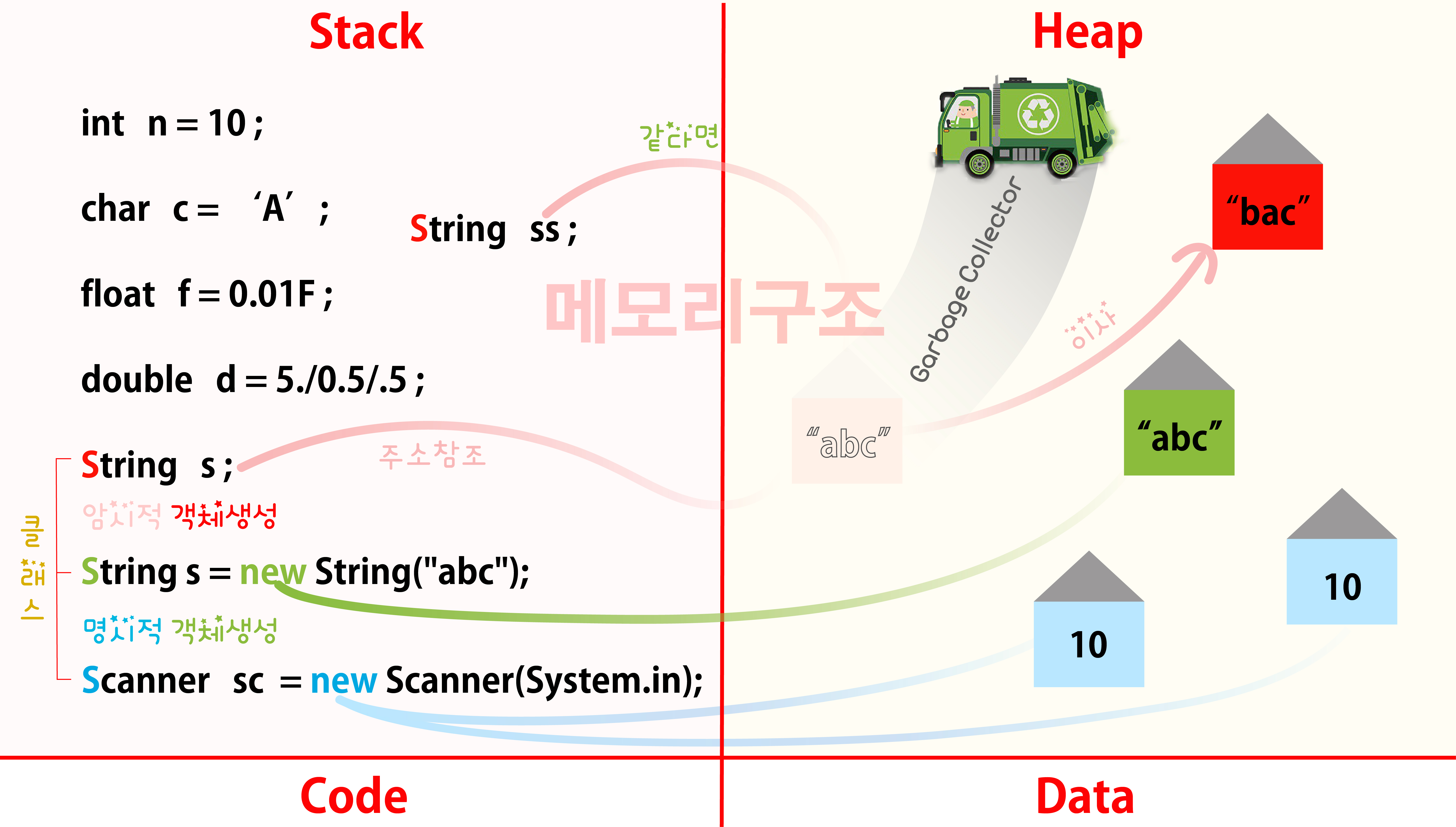
//String 클래스 2가지 특징:
//객체생성 방법:(암시적,명시적)
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
//암시적 객체생성:
//이미 만들어져 있는 heap메모리의 주소를
//다른 String객체가 공유하여 사용하는 것.
//클래스를 통해 만들어진 s1변수는 사실 '객체'다.
String s1 = "abc";//암시적 객체생성
String s2 = "abc";//같은 집을 공유
//한번 생성된 문자열의 내용은 변하지 않는다.
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
//String s2 = "bca"; (불변의 특징)
//s2 = "abc";이사간다. (immutable)
String greet = "hi";//쓰레기 값(Garbage Collector 순회 => 날림)
greet += "hello";//새로운 집이사(원치않을때 원래 주소값이 변치않도록)
System.out.println(greet);//불변의 특징 => 커지거나 달라지지 않음.
String s3 = new String("abc");//명시적 객체생성
String s4 = new String("abc");//서로다른 주소값
//new를 통해 만들어지는 클래스들은 모두 명시적 객체생성
//명시적 객체생성은 메모리에 동일한 값의 유무와 상관없이
//나의 영역을 개별적으로 생성하는 것.
//일반 변수들간의 ==은 값을 비교
//객체들간의 ==은 주소를 비교(위험!)
if (s1 == s3) {//값이 아닌 주소가?
System.out.println("같습니다");
}else {
System.out.println("다릅니다");✔️
}
if (s1.equals(s3)) {//훨씬 효율적!
System.out.println("값이 같습니다");✔️
}
}
}Scanner명시적 객체생성:같은주소를 절대로 공유않함
class중에서도 String만 유일하게 암시적 객체생성
==로 주소를 비교하고 값이 같은지 는equals()
package ex1_string;
public class Ex2_StringMethod {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//String클래스의 메서드들
//메서드란? 어떤 작업을 수행하기 위한 명령문들의 집합
//자주 사용되는 코드를 메서드를 통해 재활용 함으로써 코드의 재사용성을 높일 수 있다.
String name = "Hong Gil Dong";
int index = name.length();//모든 메서드는 (|Ctrl+Space)를 가지고 있음.
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("name의 길이 :"+index);//13
index = name.indexOf('o');//(|)기능 설명나옴.
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("맨처음 o의 위치:"+index);//1
index = name.lastIndexOf('o');
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("마지막 o의 위치:"+index);//10
char res = name.charAt(5);//|charAt(int index) : char String
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("5번째 위치의 문자(하나만):"+res);//G
String fruit = " apple ";
String t_fruit = fruit.trim();//문자열 앞뒤의 의미없는 공백을 제거
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
t_fruit.length();//5▼
fruit.length();//7 한번 공백제거 계속X
boolean bb = fruit.equals("apple");
if (bb) {
System.out.println("값이 달라요");✔️
}
if (t_fruit.equals("Apple")) {
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("대소문자 구분해주세요.");✔️
}
if (t_fruit.equalsIgnoreCase("Apple")) {
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println("대소문자 상관없이 알파벳만 같으면 인정!");✔️
}
//String클래스의 기능은 아니지만, 알아두면 좋은 메서드
String number = "100";//"100a"는 오류난다.
int num = Integer.parseInt(number) + 10;
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
//정수형식의 문자열을 연산이 가능한 실제정수로 바꿔준다.
System.out.println(num);
}
}import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex3_StringWork {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("입력>>>");
String str = sc.next();
int count = 0;
for(int i = 0;i<str.length();i++) {
if(str.charAt(i) == 'a') {
count++;
}
}
System.out.println("a의 갯수 : "+count);
}
}
>>>asdfgWERTYUb.j-[8f907a
a의 갯수 : 2
>>>aassasaasas
a의 갯수 : 6
------------------------ 주민번호 -------------------------
package ex1_string;
import java.util.*;
public class Ex4_HomeWork {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("주민등록 번호 : ");
String s = sc.nextLine();//공백받음
String y = s.substring(0,2);
String m = s.substring(2,4);
String d = s.substring(4,6);
String r = s.replace("-","");
char g = r.charAt(6);
if ( g == '1' ){
System.out.printf("당신은 %s년 %s월 %s일에 태어난 남자입니다.",y,m,d);
}else if( g == '2'){
System.out.printf("당신은 %s년 %s월 %s일에 태어난 여자입니다.",y,m,d);
}else {
System.out.println("잘못된 입력입니다.");
}
}
}
주민등록 번호 : 991122-1234567
당신은 99년 11월 22일에 태어난 남자입니다.
주민등록 번호 : 981020 2234567
잘못된 입력입니다.
주민등록 번호 : 9202122234567
당신은 92년 02월 12일에 태어난 여자입니다.
------------------------ 그릇 -------------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// (((( 10+5+5+5 = 25 차곡차곡
// ()()((( 10+10+10+10+10+5+5
// () 20 반대
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String s = sc.nextLine();//"((((";
String[] arr = s.split("");//"(" "(" "(" "("
int h = 10;
for(int i=1;i<s.length();i++) {
if (arr[i].equals(arr[i-1])) {
h += 5;
}else {
h += 10;
}
}
System.out.println(h);
}
}
>>>()()((((
65
------------------- ox퀴즈 ------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// O O X X O X X O O O
// 1+2+0+0+1+0+0+1+2+3 = 10점
System.out.print("ox테스트 개수 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();//입력보다 1크다
String s;//데이터 잡아먹으니 밖에 선언
String[] arr;
for (int i=0;i<=n;i++) {
s = sc.next();
arr = s.split("");
int score = 0;
int sum = 0;
for(int j=0;j<s.length();j++) {
if (arr[j].equals("o")) {
score += 1;
} else if (arr[j].equals("x")) {
score = 0;
} else {
System.out.println("잘못 입력하셨습니다.");
}
sum += score;
System.out.print(score);
}
System.out.println(sum);
}
}
}
ox테스트 개수 : 5
oxoooxooxo
1012301201=11
oxooxo
101201=5
oooxoxooooxx
123010123400=17
oooxooxoxoo
12301201012=13
ooooxoooxxo
12340123001=17
ooxoxxxooo
1201000123=10
------------------------- baekjoon ---------------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
//_ _ _ _ _ _ _
//a b c d e f g h i j k l m n o p q r s t u v w x y z
//1 0-1-1 2-1-1-1-1 4 3-1-1 7 5-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1-1
//b0 a1 e2 k3 j4 o5o6 n7
int[] res = new int[26];
String s = sc.next();
//res -1로 초기화
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
res[i] = -1;
//문자열 탐색 -> idx 추출
for(int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
if(res[s.charAt(i)-97] == -1)
res[s.charAt(i)-97] = i;
}
for(int i=0;i<26;i++) {
System.out.print(res[i]+" ");
}
}
}
>>>baekjoon
1 0 -1 -1 2 -1 -1 -1 -1 4 3 -1 -1 7 5 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1 -1
----------------- 세로단어 ------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
String[] str = new String[5];
int max_len = 0;
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
str[i] = sc.nextLine();
if(max_len < str[i].length()) {
max_len = str[i].length();
}
}
for(int i=0;i<max_len;i++)
{
for(int j=0;j<5;j++)
{
if(str[j].length()>i)
System.out.print(str[j].charAt(i));
}
}
}
}
>>>ABCDE
>>>abcde
>>>01234
>>>FGHIJ
>>>fghij
Aa0FfBb1GgCc2HhDd3IiEe4Jj
----------------- 최?대문자 ----------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
// 문자열 -> 대문자로 변환 'A'=65
String str = sc.next().toUpperCase();
int max_value=0; //최대값
int max_index=0; //최대값의 index
int[] arr = new int[26];
for(int i=0;i<str.length();i++) {
arr[str.charAt(i)-65]++;
}
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
{
if(max_value < arr[i]) {
max_value = arr[i];
max_index = i;
}
}
int cnt=0;
for(int i=0;i<26;i++)
{
if(max_value==arr[i])
cnt++;
}
if(cnt==1)
System.out.println((char)(max_index+65));
else
System.out.println("?");
}
}
>>>Mississipi
?
>>>Zza
Z
>>>z
Z🗝 재귀함수()
---------------- 계산기 만들기 ----------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
public static int sub(int a, int b) {
return a-b;
}
public static int mul(int a, int b) {
return a*b;
}
public static int div(int a, int b) {
return a/b;
}
public static int rem(int a, int b) {
return a%b;
}
public static void MENU() {
System.out.println("========== MENU ==========");
System.out.println("1:덧셈");
System.out.println("2:뺄셈");
System.out.println("3:곱셈");
System.out.println("4:나눗셈");
System.out.println("5:나머지");
System.out.print("6.(1-5)메뉴를 선택하세요:");
}
public static void cal() {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
MENU();
int n = sc.nextInt();
int a = sc.nextInt(),b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("7.숫자 2개를 입력하시요.>>>");
int res = 0;
switch(n) {
case 1:
res = add(a,b);
break;
case 2:
res = sub(a,b);
break;
case 3:
res = mul(a,b);
break;
case 4:
res = div(a,b);
break;
case 5:
res = rem(a,b);
break;
}
System.out.printf("8.완산 결과 : %d",res);
System.out.print("9.계속 하려면 1을 누르시오 :");
int e = sc.nextInt();
if (e == 1) {
cal();//재귀함수
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
cal();
}
}import java.util.*;
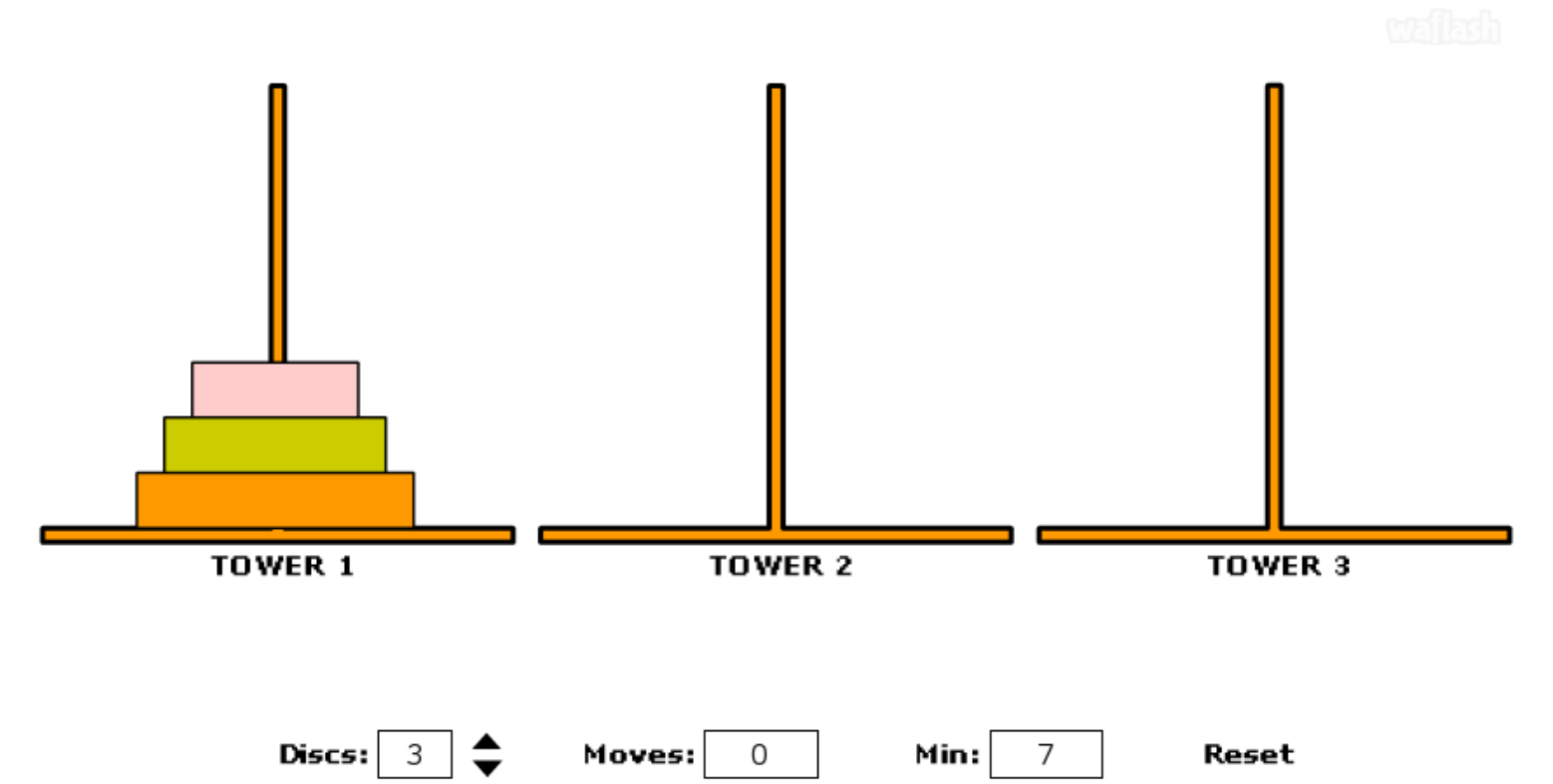
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print(">>>Discs : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();
hanoi(1,2,3,n);
System.out.print("min_step : ");
System.out.print((int)(Math.pow(2, n))-1);
}
public static void hanoi(int from,int tmp,int to,int n){//from->to로 (n)이 이동
if(n==0)
return;
hanoi(from,to,tmp,n-1); // (n-1)은 from->tmp로 이동
System.out.printf("(%d) : %d -> %d\n",n,from,to);//실제 (n)이 from->to 이동
hanoi(tmp,from,to,n-1); // (n-1)이 tmp->to로 이동
}
}
>>>Discs : 5 >>>Discs : 4 >>>Discs : 3
(1) : 1 -> 3 (1) : 1 -> 2 (1) : 1 -> 3
(2) : 1 -> 2 (2) : 1 -> 3 (2) : 1 -> 2
(1) : 3 -> 2 (1) : 2 -> 3 (1) : 3 -> 2
(3) : 1 -> 3 (3) : 1 -> 2 (3) : 1 -> 3
(1) : 2 -> 1 (1) : 3 -> 1 (1) : 2 -> 1
(2) : 2 -> 3 (2) : 3 -> 2 (2) : 2 -> 3
(1) : 1 -> 3 (1) : 1 -> 2 (1) : 1 -> 3
(4) : 1 -> 2 (4) : 1 -> 3 min_step : 7
(1) : 3 -> 2 (1) : 2 -> 3
(2) : 3 -> 1 (2) : 2 -> 1
(1) : 2 -> 1 (1) : 3 -> 1
(3) : 3 -> 2 (3) : 2 -> 3
(1) : 1 -> 3 (1) : 1 -> 2
(2) : 1 -> 2 (2) : 1 -> 3
(1) : 3 -> 2 (1) : 2 -> 3
(5) : 1 -> 3 min_step : 15
(1) : 2 -> 1
(2) : 2 -> 3
(1) : 1 -> 3
(3) : 2 -> 1
(1) : 3 -> 2
(2) : 3 -> 1
(1) : 2 -> 1
(4) : 2 -> 3
(1) : 1 -> 3
(2) : 1 -> 2
(1) : 3 -> 2
(3) : 1 -> 3
(1) : 2 -> 1
(2) : 2 -> 3
(1) : 1 -> 3
min_step : 31⏱ class ⓒ____{

package first;
public class Main{
public static void Std_info(String name,String dept,String phone,String address,String grade){
System.out.println(name);
System.out.println(dept);
System.out.println(phone);
System.out.println(address);
System.out.println(grade);
}
public static void main(String[] args){
String name = "OOO";
String department = "Computer Science";
String phone = "010-1111-1234";
String address = "Seoul";
String grade = "A";
Stu_info(name,department,phone,address,grade);
String name = "XXX";
String department = "Fashion Design";
String phone = "010-2222-1234";
String address = "Busan";
String grade = "B";
Stu_info(name,department,phone,address,grade);
}
}
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
① System.out.println("start!");
② message();//메소드 호출 ↩ ⑥
⑦ System.out.println("-end-");
}
public static void message(){ ③
④ System.out.println("Hello~");
⑤ return;//있으면 (생략가능)
}
}start!
Hello~
-end-
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
① System.out.print("주사위 눈은 ");
② dice();//메소드 호출↩ ⑥
⑦ System.out.print("입니다.");
}
public static void dice(){ ③
④ int r = (int)(Math.random()*6+1);
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
⑤ return;//있으면 (생략가능)
}
}주사위 눈은 5입니다.
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args){
① System.out.print("일기예보에 따르면 내일은 ");
② weather();//메소드 호출 ↩ ⑦
⑧ System.out.print("라고 합니다.");
}
public static void weather(){ ③
④ double r = Math.random();
⑤ if (r<0.3) System.out.print("비");
else if (r<0.6) System.out.print("흐림");
else System.out.print("맑음");
⑥ return;//있으면 (생략가능)
}
}일기예보에 따르면 내일은 비라고 합니다.
🗝 void 메소드()
public class Main{//함수 정의(매개변수 존재)
public static void add(int num1, int num2){
System.out.println(a+b);//(반환값❌)
}
public static void main(String[] args){
int a = 3 , b = 2;
add(a,b);//함수 호출
add(5,3);//함수 호출
}
}
----------------------------------------------
public class Main{ ▼반환형
public static int add(int a,int b){//동명
int a = 10 , b = 20;
던졌으니▶return a+b;
}
public static void main(String[] args){
받아주기▶int res =❌add(a,b)❌;//이인
System.out.println(res);
}
}
---------------- 사칙 연산 ----------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int add(int a, int b) {
return a+b;
}
public static int sub(int a, int b) {
return a-b;
}
public static int mul(int a, int b) {
return a*b;
}
public static int div(int a, int b) {
return a/b;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int a = sc.nextInt(), b = sc.nextInt();
System.out.printf("%d + %d = %d\n",a,b,add(a,b));
System.out.printf("%d - %d = %d\n",a,b,sub(a,b));
System.out.printf("%d * %d = %d\n",a,b,mul(a,b));
System.out.printf("%d / %d = %d\n",a,b,div(a,b));
}
}
>>>10
>>>5
10 + 5 = 15
10 - 5 = 5
10 * 5 = 50
10 / 5 = 2
---------------- 함수 응용 --------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int Sum(int n) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++)
sum += i;
return sum;//1~n
}
public static int Power(int n) {
return n*n;
}
public static int zariSum(int n) {
int s = 0;
while(n != 0) {
s += n%10;
n = n/10;
}
return s;//자리수 합
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Sum(10));//55
System.out.println(Power(5));//25
System.out.println(zariSum(12345));//15
}
}
------------------- 최소~최대합 -------------------
import java.util.*;
public class Main {
public static int max(int a, int b) {
if (a>b) return a;
else return b;
}
public static int min(int a, int b) {
if (a<b) return a;
else return b;
}
public static int ShowSum(int a, int b) {
int sum = 0;
for(int i = min(a,b);i<=max(a,b);i++) {
sum += i;
}
return sum;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(ShowSum(10,2));
}
}⚠ 매개변수
💫SPD : 메소드의 논리흐름
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
① System.out.println("안녕하세요~");
② greeting("홍길동",1);//실인수 ↩
⑦ greeting("성춘향",2);//실인수 ↩
⑫ System.out.println("반갑습니다!");
} ③ ⑧//가인수,형식인수
public static void greeting(String name,int sex){
④ if (sex==1) ⑤System.out.print(name+" 군");
⑨ else ⑩System.out.print(name+" 양");
⑥⑪return;
}
}안녕하세요~
홍길동 군
성춘향 양
반갑습니다!
package ex2_method;
public class Gugu { ❌ main전달했으면 하는값이 있으면(강제성)
public void result(int dan) {
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) {
System.out.printf("%d*%d=%d\n",dan,i,dan*i);
}
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_method;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class GuguMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("단 : ");
int n = sc.nextInt();//Gugu 클래스한테 전달할 값
/*
for(int i=1;i<=9;i++) {
System.out.printf("%d*%d=%d\n",dan,i,dan*i);
}유지보수 측면에서 소분화 하는것이 훨씬 더 효율적이다.
*/
Gugu gugu = new Gugu();//메모리에 할당받는 작업
gugu.result(n);
}
}
단 : 6
6*1=6
6*2=12
6*3=18
6*4=24
6*5=30
6*6=36
6*7=42
6*8=48
6*9=54package ex2_method;
public class MethodTest { ❌ main
//앞으로 test()메소드를 호출하려면
//반드시 int형태의 인자를 파라미터로 보내줘야 한다.
public void test2(int n){
✔️파라미터로 전달된 값은 사본이다.
n++;
System.out.println("n : "+n);
}
public void test1() {//메소드 정의
System.out.println("안녕하세요");
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_method;
public class MethodMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MethodTest mt = new MethodTest();
mt.test1();//메소드 호출
|//test1() : void MethodTest
int value = 200;
mt.test2(value);✏️201
|//test2(int n) : void MethodTes
🔻void로 지정되어 있는 메소드
int res = mt.test2(value);
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
❌특정 자료형에 값을 저장불가
✔️파라미터로 전달된 값은 사본이다.✏️200
System.out.println("value : "+value);
}
}↩ return ○;
package ex1_method;
public class MethodTest {
public int valueTest(int n) {
n += 50;
System.out.println("n : "+n);//100
//valueTest메서드가 호출되면
//최종적으로 return 값을 가지고
//나를 호출했던 곳으로 복귀한다.
return n;
//서로다른 클래스간에 값을 공유가능!
}
public int multi(int n) {
if (n>=1000) {
n *= 10;
return n;//값을 가지고 main으로 돌아갈꺼야
}else {
n *= 5;
return n;//값을 가지고 main으로 돌아갈꺼야
}
//보여주기만 할수 있고 main으로 가져와 쓸수 없으니까
}
}
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_method;
public class MethodMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MethodTest mt = new MethodTest();
int value = 50;//줄때는 파라미터 돌려받을 때 리턴
int res = mt.valueTest(value);//100
System.out.println(value);//50
System.out.println("---------------------------");
res = mt.multi(2000);
System.out.println(res);//20,000
res = mt.multi(500);
System.out.println(res);//2,500
}
}。내부접근자
package ex1_cpmputer;
public class Computer { ❌ main💻컴퓨터를 대량생산 하기위한 설계도
int ssd = 256;
int ram = 8;
float cpu = 2.0f;
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_cpmputer;
public class ComMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer c1 = new Computer();//명시적 객체생성
System.out.println("ssd: "+c1.ssd);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("ram: "+c1.ram);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("cpu: "+c1.cpu);//.내부접근자
=============================================
Computer c2 = new Computer();//명시적 객체생성
System.out.println("ssd: "+c2.ssd);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("ram: "+c2.ram);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("cpu: "+c2.cpu);//.내부접근자
--------------- 유지보수 가능하다 ---------------
Computer c3 = new Computer();//명시적 객체생성
c3.ssd = 512;//업그레이드
c3.ram = 32;//업그레이드
System.out.println("ssd: "+c3.ssd);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("ram: "+c3.ram);//.내부접근자
System.out.println("cpu: "+c3.cpu);//.내부접근자
}
}🗝접근제한자
package ex1_computer;
public class Computer { ❌ main 외부유출을 막기 위해서 [보안장치]
private String company = "apple";
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
int ssd = 256;
int ram = 8;
float cpu = 2.0f;접근제한자 종류 :
☑ public : 같은 프로젝트의 모든 클래스에서 사용을 허가
☑ private : 현재 클래스에서만 사용을 허가
☑ protected : 상속관계의 클래스에게만 사용을 허가
☑ default패키지의 클래스에서만 사용을 허가
void : 반환형 소___ : 메소드명 (파라미터,매개변수,아규먼츠,인자){
public void info() { //메소드가 호출됐을 때 실행되는 영역
System.out.println("제조사 : "+company);
System.out.println("ssd : "+ssd+"GB");
System.out.println("ssd : "+ram+"GB");
System.out.println("ssd : "+cpu+"GHz");
System.out.println("----------------");
}
}。메소드호출
class의 구성요소 :
☑ 변수, 멤버, 속성, 필드 . . .
☑ 메소드, 기능, 동작, 함수 . . .
• 메소드는 어떤 작업을 수행하기 위한 명령문들의 집합
• 반복적으로 사용되는 코드나 너무 긴 코드등을 정의해두고
• 필요할 때 가져다 씀으로써 재활용성이 높아진다는 장점이 있다.
package ex1_computer;
public class ComMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Computer c1 = new Computer();//객체생성
✔️ c1.info();//재활용 가능하다
Computer c2 = new Computer();//객체생성
✔️ c2.info();//재활용 가능하다
Computer c3 = new Computer();//객체생성
private로 지정된 변수는 타 클래스에서 접근불가
❌ c3.company = "samsung";//
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
c3.ssd = 512;//업그레이드
c3.ram = 32;//업그레이드
✔️ c2.info();//재활용 가능하다
}
}🗝 overload()
메소드 오버로드 : 메소드의 '중복정의'
하나의 클래스내에서 같은 이름을 가진 메소드가 여러개 정의되는것.
☑규칙 1) : 파라미터의 갯수 다르게 만든다.
☑규칙 2) : 파라미터의 갯수 같다면 타입을 다르게 만든다.
☑규칙 3) : 파라미터의 타입,갯수 같다면 순서를 다르게 만든다.
(파라미터 : 영역내변수명X변수명|변수명(만)다르면
package ex1_overload;
public class OverloadTest {
public void result() {
System.out.println("안녕하세요");
}
public void result(int n) {//번지에 사는 홍길동?
System.out.println("정수를 인자로 받는 메서드");
}
public void result(char n) {//A동에 사는 홍길동?
System.out.println("문자를 인자로 받는 메서드");
}
public void result(int n,String s) {//나이,제주도 사는 홍길동?
System.out.println("정수,문자열 순으로 인자로 받는 메서드");
}
public void result(String s,int n) {//서울에 살고,n번지 홍길동?
System.out.println("문자열,정수 순으로 인자로 받는 메서드");
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_overload;
public class OverMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
OverloadTest olt = new OverloadTest();
olt.result();//객체생성 후 메소드 호출
olt.result(10);//메서드 이름은 동일(파라미터 개수 다름)
olt.result('A');//메서드 이름은 동일(파라미터 타입 다름)
olt.result(10,"hi");//(int 변수명i , String 변수명j)
olt.result("hi",100);//(String 변수명i , int 변수명j)
System.out.println(10);//나두 오버로드중~
System.out.println("문장");//모르고도 씀!
}
}🍔bread
package ex2_overload;
public class Bread {
public void make() {
System.out.println("빵을 만들었습니다.");
}
public void make(int n) {
for(int i=0;i<n;i++) {
System.out.println("빵을 만들었습니다.");
}
System.out.println("빵을 "+n+"개 만들었습니다.");
}
public void make(String s,int m) {
for(int i=0;i<m;i++) {
System.out.println(s+"을 만들었습니다.");
}
System.out.println(s+"을 "+m+"개 만들었습니다.");
}
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_overload;
public class BreadMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bread bread = new Bread();
//메소드1 호출-->
bread.make();
//빵을 만들었습니다.
//메소드2 호출-->
bread.make(2);
//빵을 만들었습니다.
//빵을 만들었습니다.
//빵을 2개 만들었습니다.
//메소드3 호출-->
bread.make("크림빵",3);
//크림빵을 만들었습니다.
//크림빵을 만들었습니다.
//크림빵을 만들었습니다.
//크림빵을 3개 만들었습니다.
}
}
빵을 만들었습니다.
빵을 만들었습니다.
빵을 만들었습니다.
빵을 2개 만들었습니다.
크림빵을 만들었습니다.
크림빵을 만들었습니다.
크림빵을 만들었습니다.
크림빵을 3개 만들었습니다.ⓒonstructor
디폴트 생성자
인수가 없는 생성자로 java컴파일러가 암묵적으로 만듦.
프로그래머가 직접 생성자를 만들면 사용할 수 없게된다.
프로그래머가 생성자를 만들지 않았을 때에만 자동으로~
package ex3_constructor;
public class ConTest {
//생성자 : 객체가 만들어질때 [메모리 할당]을 위해
//'딱 한번' 메소드와 비슷한 실행영역에 호출된다.
//반환형이 없으면서 클래스와 똑같은 이름의 메소드 형태
"숨겨져있는 생성자를 호출하는 메소드"
public ConTest() { //일반 볼펜 만들때 => 원본(틀)
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
//System.out.println("기본생성자가 호출됨!");
}
private String brand = "monami";
private String color = "black";
private int price = 500;
최고장점 : setter의 역할을 대신하면서, -끝까지- 유지!
//한번 만들고 나면 그 누구도 값을 함부로 바꿀 수 없음!
public ConTest(String color,int price) {//프리미엄
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
this.color = color;
this.price = price;
}
public void myMonami() {//인스턴스 메소드
System.out.println("브랜드 : "+brand);
System.out.println("가격 : "+price);
System.out.println("색상 : "+color);
System.out.println("--------------");
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex3_constructor;
public class ConMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 새주소 내가만듦!빈공터 찾아봐~
ConTest ct = new ConTest();//객체생성
//ct.ConTest();생성자는 객체가 생성된 이후에 재호출 불가!
ct.myMonami(); // 메소드 호출
ConTest ct2 = new ConTest();//객체생성
ct2.myMonami();// 메소드 호출
//한정판 모나미 볼펜을 만들고 싶어졌다...
ConTest ct_pri = new ConTest("gold",20000);
ct_pri.myMonami(); // 프리미엄.메소드 호출
}
}
브랜드 : monami
가격 : 500
색상 : black
--------------
브랜드 : monami
가격 : 500
색상 : black
--------------
브랜드 : monami
가격 : 20000
색상 : gold이름 : 홍길동 나이 : 40
이름 : 박길동 나이 : 30
------------------------
package ex4_constructor;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
public Person(String name,int age) { //생성자 오버로딩
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void info() { // 인스턴스 메소드
System.out.println("이름 : "+name+"\t나이 : "+age);
}
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex4_constructor;
public class PersonMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Person p1 = new Person("홍길동",40);
Person p2 = new Person("박길동",30);
p1.info();
p2.info();
}
}package first;
class Car {
String model = "BMW";
String color = "White";
void speedChange(int v){ //인스턴스 메소드
System.out.printf("speed Change : %d", v);
int speed = v;
}
}
—————————————————————————————————————————————————
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Car bmw = new Car();//객체생성
System.out.println(bmw.model);
System.out.println(bmw.color);
bmw.speedChange(100);//메소드 호출
Car benz = new Car();//객체생성
benz.model = "benz";//업데이트
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
benz.color = "Black";//업데이트
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
System.out.println(bmw.model);
System.out.println(bmw.color);
bmw.speedChange(120);//메소드 호출
}
}♻ this.🗝
this .인스턴스 변수☞ 타입 ____;
클래스명 . 클래스 변수 ☞ static 타입 ____=0;
class Car{
String model;
String color;
/* void Car(){
this.model = null;
this.color = null;
}컴파일러가 자동으로《디폴트 생성자》추가해준다. */
=========================================
void setData(String model, String color){
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
} //인스턴스 메소드(setting)
=========================================
void info(){ //인스턴스 메소드(getting)
System.out.printf("Model : %s , Color : %s\n",this.model,this.color);
}
}
—————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
Car bmw = new Car(); // bmw 객체생성
bmw.setData("BMW", "white");
bmw.info();
--------------------------------------
Car benz = new Car(); // benz 객체생성
// 매개변수를 하나도 가지지 않을 때 //
benz.info();// null null《디폴트 생성자》
--------------------------------------
}
}
class TV{
boolean Power; "필드"
int channel; "필드"
int volume; "필드"
==================================
void setTV(boolean P,int C,int V){
this.Power = P;
this.channel = C;
this.volume = V;
} // setting 메소드
==================================
void info(){ // getting 메소드
System.out.println("Power : "+this.Power);
System.out.println("Channel : "+this.channel);
System.out.println("Volume : "+this.volume);
}
★전원버튼 기능★
void on_off(){
if(this.Power==true) {
System.out.println("○ Turn off");
this.Power = false;
}else {
System.out.println("● Turn on");
this.Power = true;
}
}
★채널변경 기능★
void set_channel(int c){
this.channel = c;
System.out.println("△ Channel : "+this.channel);
}
★볼륨변경 기능★
void set_volume(int v){
this.volume = v;
System.out.println("▲ Volume : "+this.volume);
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————
public class Main{
public static void main(String[] args){
TV tv = new TV();
====================
tv.setTV(true,1,16);
====================
tv.info();
--------------------
tv.on_off();
tv.on_off();
tv.set_channel(4);
tv.set_volume(24);
}
}Power : true
Channel : 1
Volume : 16
○ Turn off
● Turn on
△ Channel : 4
▲ Volume : 24
🧮계산기
package ex3_calculator;
public class Calculator {
public int getResult(String op,int su1,int su2) {
//return 0;없으면 오류
switch(op) {
case "+":
return su1 + su2;
//break; 대신에↩
case "-":
return su1 - su2;
//break; 대신에↩
case "*":
return su1 * su2;
//break; 대신에↩
case "/":
return su1 / su2;
//break; 대신에↩
case "%":
return su1 % su2;
//break; 대신에↩
default:
System.out.println("올바른 연산자를 넣어주세요.");
return 0;//반환형이 int로 지정되어 있기에 뭐라도 줘야함!
}
}
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
public /*int*/ getResult(String op,int su1,int su2) {
/*int*/ => void로 지정
/*return*/ => printf("%d+%d=%d",su1,su2,su1+su2); => break;
default : syso => /*return 0;*/
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex3_calculator;
public class CalMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calculator cal = new Calculator();
int res = cal.getResult("+", 10, 20);
System.out.println(res);
}
}💸ATM
package ex4_account;
public class ATM {
private int money;
//입금
public void deposit(int money) {
this.money += money;
System.out.println("입금 성공!");
//return X 다시 꺼낼필요 없음!
}
//출금
public int withdraw(int money) {
if(this.money - money < 0) {
System.out.println("잔액 부족!");
return 0;
}else {
System.out.println("출금 성공!");
this.money -= money;
return money;
}
}
//잔액
public void balance() {
System.out.println("잔액 : "+money);
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex4_account;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class AtmMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ATM atm = new ATM();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
outer : while(true) { //레이블 추가
System.out.println("1.입 금");
System.out.println("2.출 금");
System.out.println("3.잔액확인");
System.out.println("etc.종 료");
System.out.print(">>>");
int select = sc.nextInt();
switch(select) {
case 1://입금
System.out.println("--- 입금 ---");
System.out.print("입금액: ");
atm.deposit(sc.nextInt());
break;
case 2://출금
System.out.println("--- 출금 ---");
System.out.print("출금액: ");
atm.withdraw(sc.nextInt());
break;
case 3://잔액
System.out.println("--- 잔액확인 ---");
atm.balance();
break;
default:
System.out.println("종료");
break outer;
}//switch
System.out.println("---------");
}
}
}
1.입 금
2.출 금
3.잔액확인
etc.종 료
>>>1
--- 입금 ---
입금액: 1000
입금 성공!
---------
1.입 금
2.출 금
3.잔액확인
etc.종 료
>>>2
--- 출금 ---
출금액: 1500
잔액 부족!
---------
1.입 금
2.출 금
3.잔액확인
etc.종 료
>>>4
종료♻ static🗝
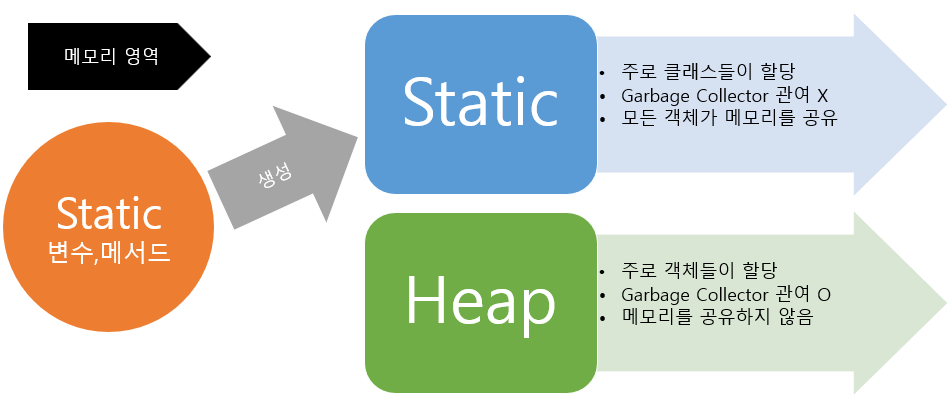
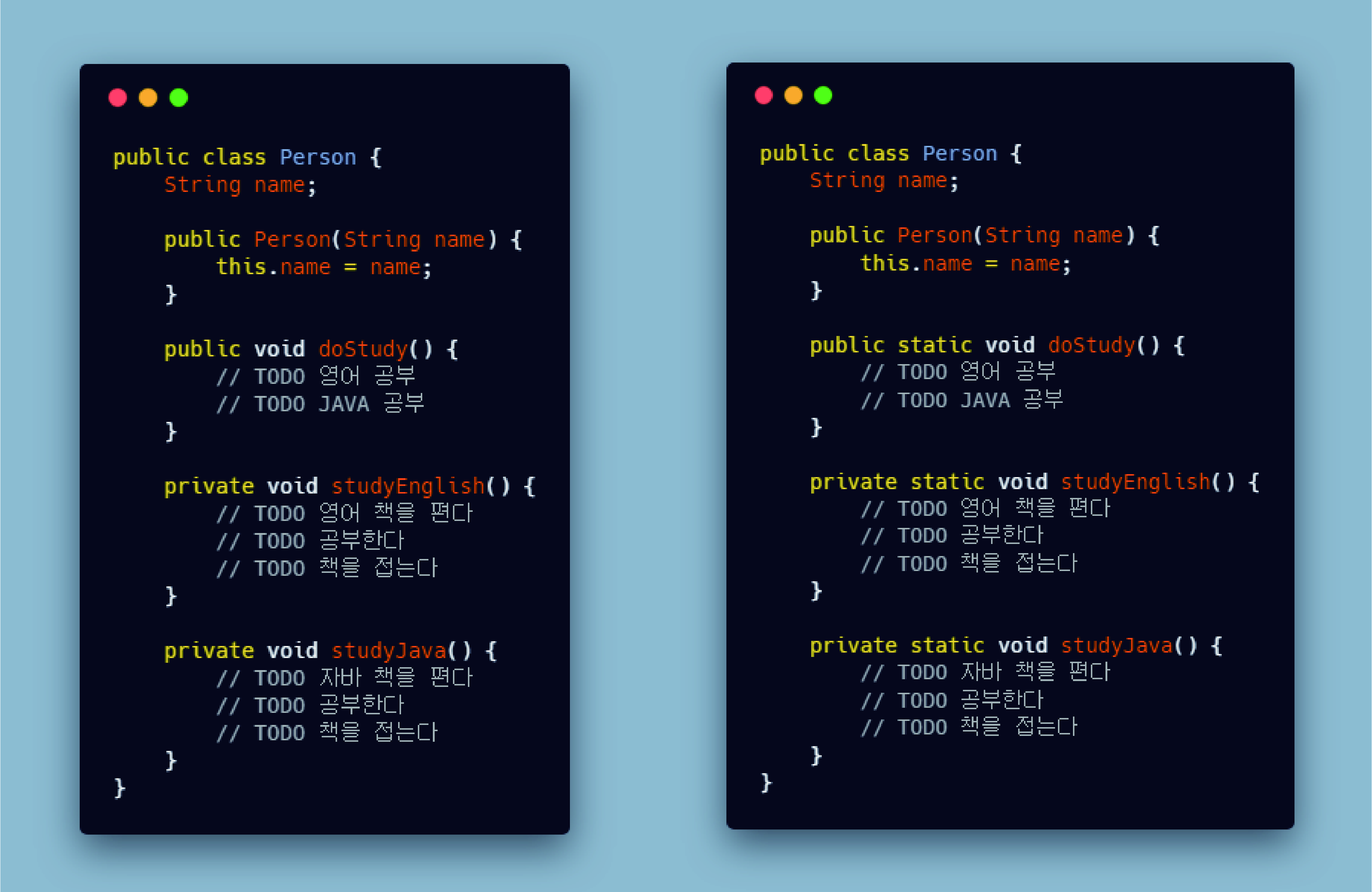
package ex1_static;
public class Bank {
private String point;
private String tel;
______________________
static float interest = 10 ;//동시다발
클래스명을 통해서 곧바로 메모리 할당 받는다.
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
"public Bank(){ }" // 디폴트 생성자(){}
--------------------------------------
public Bank(String point,String tel) {//오버로딩
this.point = point;
this.tel = tel;
}
public void getInfo() {//인스턴스 메소드
System.out.println("지점 : "+point);
System.out.println("전화 : "+tel);
System.out.println("이자율 : "+interest+"%");
System.out.println("---------------------");
}
}
———————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_static;
public class BankMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bank b = new Bank(); ()객체생성 => "수동"⚠
-----------------------------------------
/*생성자 오버로딩*/=>("값을 대입하지 않으면")⚠
Bank b1 = new Bank("홍대","02-111-1111");
Bank b2 = new Bank("서강대","02-222-2222");
Bank b3 = new Bank("이대","02-333-3333");
//b.interest = 0.1f;
--------------------
//b1.interest = 0.1f;
//b2.interest = 0.1f;
//b3.interest = 0.1f;
_____________
Bank.interest = 0.1f;
클래스명.스테틱변수/메서드
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
b.getInfo();
------------
b1.getInfo();
b2.getInfo();
b3.getInfo();
}
}
지점 : null
전화 : null
이자율 : 10.0% => 0.1%
---------------------
지점 : 홍대
전화 : 02-111-1111
이자율 : 10.0% => 0.1%
---------------------
지점 : 서강대
전화 : 02-222-2222
이자율 : 10.0% => 0.1%
---------------------
지점 : 이대
전화 : 02-333-3333
이자율 : 10.0% => 0.1%
---------------------🖱 S/Getter
setter & getter
private 변수에 값을 넣거나(setting) 꺼낼때(getting) 사용하기 위한 메서드 개념
package ex2_set_get;
public class S_Getter {
private String name;
//값이 안바뀌는 건 맞는데
//영원히 안바뀌는 건 확신할 수 없어서...
String hobby;
//setter
public void setName(String n) {
name = n;
//어느정도의 보안성을 유지할 수 있는 범위안에서~
//너무 어렵지도 쉽지도 않게 private에 접근가능!
}
//getter
public String getName() {
return name;
}
}
——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_set_get;
public class SGMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
S_Getter sg = new S_Getter();
sg.hobby = "낚시";
sg.hobby = "뉴스";
sg.setName("홍길동");////setter는 집어넣는 역할만!
//의도하지 않게 값이 바뀌는 상황을 미연에 방지할 수 있다.
//값이 바뀌거나 변경될 위험없이 그대로 가져오고 싶어
//getter 넣어놓은 그대로 이름을 돌려주면 좋겠어
String s = sg.getName();//알려주기만 해~
System.out.println(s);
}
}
============================================
private int age;
public void setAge(int age) {//나이설정
this.age = age;
}
public int getAge() {//궁금하면?(500원)
return age;
}
============================================
public void setInfo(String n,int a) {//한번에
// 더 가까운 파라미터 변수로 인식
//this : 현재 클래스 자신
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
//멤버 변수 = 파라미터 변수
}우🖱클릭 > source > Generate getters and setters > ☑ Select All
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public String getHobby() {
return hobby;
}
public void setHobby(String hobby) {
this.hobby = hobby;
}👑extends
package ex2_inheritance;
public class Parent {
private int money = 2000000000;
//protected형식의 변수는 자식에게만 사용허가
protected String str = "신촌";
protected String key = "금고열쇠";
}
————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_inheritance;
public class Child extends Parent{
//자바는 단일상속 개념으로 써 하나의 자식이
//반드시 하나의 클래스만을 부모로 지정할 있다.
//extends 키워드를 통해 Child클래스가 Parent클래스의 자식임을 명시
//상속 : 부모가 가진 재산의 일부를 자식이 물려받도록 하는 것.
String Car = "모닝";
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_inheritance;
public class ExtendsMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//상속관계에서 자식클래스가 메모리 할당 될때
//반드시 그의 부모클래스가 먼저 메모리할당을 받는다.
//자식클래스는 부모가 허용한 범위안에서 어떤
//속성이든 마음대로 가져다 사용할 수 있다.
Child c = new Child();
System.out.println(c.Car); 💬모닝
=>p."object"아직은 별로...
//부모클래스에서 private로 지정해둔 속성을 자식클래스에서도 가져다 쓸 수 없다.
//System.out.println(c.money);
System.out.println(c.str); 💬신촌
System.out.println(c.key); 💬금고열쇠
System.out.println("----------------------------------------");
//부모클래스는 객체가 생성되어도 자식클래스의 속성을 가져다 쓸 수 없다.
Parent p = new Parent();//부모는 자기 메모리만 할당받아요.
System.out.println(p.str);"부모 그 자체"이기에 접근가능! 💬신촌
System.out.println(p.key);"부모 그 자체"이기에 접근가능!💬금고열쇠
}
}@Override
package ex1_override;
public class Animal {
private int eye = 2;
private int leg = 4;
private int tail = 1;
🖱우클릭 => getter만!
----------------------
public int getEye() {
return eye;
}
public int getLeg() {
return leg;
}
public int getTail() {
return tail;
}
----------------------
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_override;
public class Lion extends Animal{
String hair = "풍~성";
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_override;
public class Cat extends Animal{
String balance = "균형감각이 좋다";
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_override;
public class Elephant extends Animal{
String nose = "코를 손처럼 쓴다.";
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_override;
public class Snake extends Animal{
String sensor = "밤에도 잘본다.";
/*
public int getSnakeLeg() {//왜나만~
return 0;
}
*/
get => "Ctrl+Space↩" 🟢getLeg()
//상속관계의 객체에서 부모의 메서드를 그대로 자식에게 물려주되,
//(현재 클래스의 사정에 맞게)내용만 자식사정에 맞도록 재정의!
@Override//매소드의 재정의
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
public int getLeg() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return super.getLeg();
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex1_override;
public class AnimalMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Lion lion = new Lion();
System.out.println("눈 : "+lion.getEye());
System.out.println("다리 : "+lion.getLeg());
System.out.println("꼬리 : "+lion.getTail());
System.out.println("장점 : "+lion.hair);
System.out.println("---------------------");
Cat cat = new Cat();
System.out.println("눈 : "+cat.getEye());
System.out.println("다리 : "+cat.getLeg());
System.out.println("꼬리 : "+cat.getTail());
System.out.println("장점 : "+cat.balance);
System.out.println("---------------------");
Elephant elephant = new Elephant();
System.out.println("눈 : "+elephant.getEye());
System.out.println("다리 : "+elephant.getLeg());
System.out.println("꼬리 : "+elephant.getTail());
System.out.println("장점 : "+elephant.nose);
System.out.println("---------------------");
Snake snake = new Snake();
System.out.println("눈 : "+snake.getEye());
System.out.println("다리 : "+snake.getLeg());
//System.out.println("다리 : "+snake.getSnakeLeg());
System.out.println("꼬리 : "+snake.getTail());
System.out.println("장점 : "+snake.sensor);
System.out.println("---------------------");
}
}
눈 : 2
다리 : 4
꼬리 : 1
장점 : 풍~성
---------------------
눈 : 2
다리 : 4
꼬리 : 1
장점 : 균형감각이 좋다
---------------------
눈 : 2
다리 : 4
꼬리 : 1
장점 : 코를 손처럼 쓴다.
---------------------
눈 : 2
다리 : 4 ????? => 0
꼬리 : 1
장점 : 밤에도 잘 본다.
---------------------package homework;
public class Calculator {
public void getResult(int n1,int n2) {
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package homework;
public class Minus extends Calculator{
@Override
public void getResult(int n1,int n2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//super.getResult();
System.out.println(n1-n2);
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package homework;
public class Plus extends Calculator{
@Override
public void getResult(int n1,int n2) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//super.getResult();
System.out.println(n1+n2);
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package homework;
public class CalMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Plus p = new Plus();
Minus m = new Minus();
p.getResult(10,30);//40
m.getResult(30,10);//20
}
}🗝 super✴
package ex1_super;
public class Parent {
int n = 100;
private int n2 = 200;
_________________________
public Parent(int n) {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
System.out.println("부모생성자");
}
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
public int getN2() {
return n2;
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_super;
public class Child extends Parent{
"Ctrl+Space↩" 🟢 Child() - Constructor
public Child() {
// TODO Auto-generated constructor stub
💡💢 ①super(2); //Parent();부모클래스 생성자 호출
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
🟢 Create construtor 'Parent(int)' => Parent💽
//(자식은 필요없지만)기본생성자 없이
//부모한테 파라미터 전달하라고...
System.out.println("자식생성자");
}
public void mySetting(int n) {
//Parent.n = n;
super.n = n;//부모님에게 전달(변수)
}
get => "Ctrl+Space↩"
🟢 getN2() : int - Override method in 'Parent'
@Override
 ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄ ̄
public int getN2() {//부모님꺼 껍데기 가져와
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
// Parent.getN2();
return super.getN2();//오류방지->방어막
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex2_super;
public class SuperMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Child c = new Child();
System.out.println(c.getN2());
}
}부모생성자
자식생성자
200
🗝 generic
package ex3_generic;
public class Ex1_Generic<T> {
T value;
//🖱우클릭 => Source => setters and getters
------------------------------------------
public T getValue() {
return value;
}
public void setValue(T value) {
this.value = value;
}
------------------------------------------
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex3_generic;
public class GenMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Generic 클래스:
//일반적인 코드를 작성하되,이 안의 변수나 메소드에게
//다양한 타입에 대해 재사용이 가능하도록 정의해서 만들어둔 클래스
Ex1_ => 🟢 Generic<T>
Ex1_Generic<String> v1 = new Ex1_Generic<String>();
v1.set => 🟢 setValue(String value)
//v1.setValue(null);
v1.setValue("문자열");
System.out.println(v1.getValue());
//Ex1_Generic<int> v2 = new Ex1_Generic<int>();
Ex1_Generic<Integer> v2 = new Ex1_Generic<Integer>();
//제네릭 타입으로 지정되는 형태는 반드시 클래스 구조여야 한다.
//모든 기본자료형들은 나를 기본 자료형으로써 동작할 수 있게
//대문자형태의 부모인 클래스형태를 가지고 있어요.(wrapper)
//기본 자료형은 제네릭타입으로 지정할 수 없으므로,
//그의 wrapper클래스를 통해 타입을 지정한다.
v2.setValue(100);
//int res = v2.getValue();
//System.out.println(res+100);
System.out.println(v2.getValue());
}
}Wrapper 클래스:
int : Integer
Sting : String
char : Character
boolean : Boolean
byte : Byte
short : Short
long : Long
double : Double
package ex4_generic;
public class Gen<T,G> {
//여러개의 제네릭 타입을 가진 클래스도 얼마든지 생성할 수 있다.
T v1;
G v2;
//🖱우클릭 => Source => setters and getters
------------------------------------------
public T getV1() {
return v1;
}
public void setV1(T v1) {
this.v1 = v1;
}
public G getV2() {
return v2;
}
public void setV2(G v2) {
this.v2 = v2;
}
------------------------------------------
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex4_generic;
public class GenMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Gen<Integer, Character> g1 = new Gen<>();
g1.setV1(100);
g1.setV2('A');
}
}try🗝catch


package ex1_try_catch;
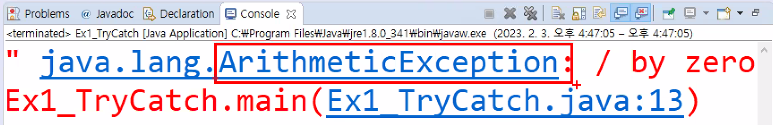
public class Ex1_TryCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int result = 0;
int[] arr = {0,1,2};//없는 index⚠
try {=>"Ctrl+Space"
result = 10/2;//여기 오류?
arr[3] = 100;//여기서 오류!
//try구문에서 오류가 발생하지 않았다면
//catch영역을 실행하지 않는다.
System.out.println("오류안남");
//} catch (Exception e) {//오류클래스 부모
} catch (ArithmeticException e) { (ari=>)
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("정수는 0으로 나눌 수 없습니다.");
//e.printStackTrace();??오류
//try구문에서 오류가 발생한 경우,
//catch구문을 실행하고 빠져나간다.
//System.out.println("오류발생");
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) { (arr=>)
System.out.println("배열에 존재하지 않는 index입니다.");
}
System.out.println("결과"+result);
}
}package ex1_try_catch;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex2_TryCatch {
public static void main(String<[] args) {
//Scanner를 통해 정수를 입력받아요.
//제대로 정수를 입력받은 경우에는 그대로 결과출력
//정수이외의 값을 입력받았다면 '정수만 입력하세요.'
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 : ");
try {
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("결과 : "+num);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
System.out.println("정수만 입력하세요.");
}
}
}package ex1_try_catch;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex3_TryCatch {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Scanner를 통해 정수를 입력받으세요.
//제대로 정수를 입력받은 경우에는 그대로 결과출력
//정수가 아니라면 "aaa(은)는 정수가 아닙니다.'
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("정수 : ");
/* 권장하지 않음!
try {
int num = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("결과 : "+num);
} catch (Exception e) {
String s = sc.next();
System.out.println(s+"은(는) 정수가 아닙니다.");
}
*/
String str = "";
try {
str = sc.next();//정수로 받아도됨.
int n = Integer.parseInt(str);
System.out.println("결과"+n);//}catch___?
} catch (NumberFormatException e) {
System.out.println(str+"은(는) 정수가 아닙니다.");
}
}
}
정수 : aaa
aaa은(는) 정수가 아닙니다.Collection
자바의 컬렉션(Collections)
데이터의 집합 or 그룹을 의미하며, 이를 구현하는 클래스들.
컬렉션의 종류: Set, Map, List
🗝Set
Set : 중복값이 허용안됨
HashSet: 정렬기능 XTreeSet:오름차순정렬
package ex1_set;
import java.util.HashSet;
public class Ex1_Set {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//hash => HashSet-java.util => import(자동)
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
hs.add(10);
hs.add(27);//★중복된 값은 메모리할당 받지않아요!
hs.add(15);
hs.add(17);
hs.add(27);//★중복된 값은 메모리할당 받지않아요!
hs.remove(17);//방자체 날림가능!
//[--]...[10]...[27]...[15]
//순차적으로 이어진다는 보장은 없다.
//index 번호를 가지고 있지 않아요.
System.out.println(hs);//hs[0] 불가능!
System.out.println(hs.size());
boolean b = hs.contains(10);//유무를 판단!
System.out.println(b);//true
//hs의 내용을 배열로 복사
Integer[] arr = hs.toArray(new Integer[0]);
for(int i : arr) {//개선된 루프 = 향상된 for문
System.out.println(i);//배열의 내용을 출력!
}//index에 대한 제어 어려움!
System.out.println("------- 원본 --------");
for(int i=0;i<arr.length;i++) {
System.out.println(arr[i]);
}
}
}package ex1_set;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Ex2_Set {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();
ts.add(150);
ts.add(120);
ts.add(200);
ts.add(50);
System.out.println(ts);//오름차순
System.out.println(ts.size());
System.out.println("---------------");
TreeSet<String> ts2 = new TreeSet<String>();
ts2.add("홍길동");
ts2.add("박말순");
ts2.add("bruce");
ts2.add("홍길동");
System.out.println(ts2);//오름차순
}
}package ex1_set;
"Ctrl + Shift + o"
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.HashSet;
import java.util.TreeSet;
public class Ex3_Set {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//난수 생성하기
//3~7사이의 난수
//ran => Random-java.util => import
Random rnd = new Random();
int n = rnd.nextInt(5)+3;//3~(5개)
//(발생할 난수의 범위)+시작수
System.out.println(n);
float f = rnd.nextFloat();
System.out.println(f);
System.out.println("------------------------");
//1~45 난수를 발생시켜서 그중 6개의
//겹치지 않는 숫자 만들기 (로또번호)
HashSet<Integer> hs = new HashSet<Integer>();
while(true) {//대문자 조심!!!
int number = rnd.nextInt(45)+1;
hs.add(number);//절대로 중복이 안되는
if(hs.size()==6) {//6개의 숫자 만들기
break;
}
}
System.out.println(hs);
System.out.println("------------------------");
TreeSet<Integer> ts = new TreeSet<Integer>();
while(true) {
int number = rnd.nextInt(45)+1;
ts.add(number);//오름차순으로 정렬된
if(ts.size()==6) {//6개의 숫자 만들기
break;
}
}
System.out.println(ts);
}
}
4
0.22683543
------------------------
[2, 34, 21, 41, 27, 45]
------------------------
[13, 17, 20, 23, 26, 45]🗝Map
Map : {키(key)=값(value)} 묶어서 하나로 저장
키를 통해 값을 검색하는 구조이기 때문에 많은 양의
데이터를 조회하는데 매우 뛰어난 성능을 발휘한다.
[1]... [2] ...[3]
[값]...[값]...[값]
package ex2_map;
import java.util.Collection;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Ex1_Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<Integer,Integer> map1 = new HashMap<Integer,Integer>();
map1.put(1,100);
map1.put(2,200);
map1.put(3,150);
System.out.println(map1.size());
System.out.println(map1);
map1.put(1,10);
System.out.println(map1);
//map은 키값이 중복되면 나중에 작성한 키값으로 value가 갱신
int n = map1.get(3);
System.out.println("n번째:"+n);
System.out.println(map1.get(1));
System.out.println("---------");
//map => 배열로 변환
💡💢 Collection<Integer> arr = map1.values();
Integer[] res = arr.toArray(new Integer[0]);
for(int i : res) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
3
{1=100, 2=200, 3=150}
{1=10, 2=200, 3=150}
n번째:150
10
---------
10
200
150package ex2_map;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class Ex2_Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
HashMap<String,Integer> map = new HashMap<String,Integer>();
map.put("k1",100);
map.put("k2",150);
map.put("k3",200);
map.put("k4",200);
map.remove("k1");//k1과 연결된 value
boolean b1 = map.containsKey("k1");
System.out.println("k1 있나요?"+b1);
boolean b2 = map.containsValue(200);
System.out.println("200 값은?"+b2);
System.out.println(map.get("k3"));
map.clear();//map을 완전히 비운다!
System.out.println(map.size());
}
}
k1 있나요?false
200 값은?true
150
0package ex2_map;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex3_Map {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
HashMap<String, Integer> map = new HashMap</*따로 기술안해도 됨*/>();
map.put("kim",1111);
map.put("lee",2222);
map.put("hong",3333);
while(true){
System.out.println("------ 로그인 ------");
System.out.print("id : ");
String id = sc.next();
System.out.print("pw : ");
int pw = sc.nextInt();
if(map.containsKey(id)) {
if(map.get(id) == pw) {
System.out.println("로그인 성공!");
break;
}else {
System.out.println("비밀번호 불일치!");
}
}else {
System.out.println("아이디가 없습니다.");
}
}
}
}
------ 로그인 ------
id : kim
pw : 2222
비밀번호 불일치!
------ 로그인 ------
id : park
pw : 3333
아이디가 없습니다.
------ 로그인 ------
id : hong
pw : 1111
비밀번호 불일치!
------ 로그인 ------
id : lee
pw : 2222
로그인 성공!🗝ArrayList
package ex3_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Ex1_ArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(100);
list.add(20);
list.add(150);
System.out.println(list.size());
System.out.println(list.get(2));
System.out.println(list);//index
//ArrayList는 index번호를 가지고 있기때문에
//특정값을 따로 추출하는 것이 간편하다
//(배열에 복사할 필요가 없다)
System.out.println("------- 원조 for문 ---");
for(int i =0;i<list.size();i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
System.out.println("------ 개선된 루프 -----");
for(int n : list) {
System.out.println(n);
}
}
}
3
150
[100, 20, 150]
------- 원조 for문 ---
100
20
150
------ 개선된 루프 -----
100
20
150package ex3_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Ex2_ArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<Integer> list = new ArrayList<>();
list.add(10);
list.add(50);
list.add(30);
list.add(20);
list.add(1,15);//오버로드(1번에,15를)새로운 방을 생성
// 0 ____ 1 2 3
//[10]-[15]->[50]->[30]->[10]
// 0 1 -> 2 -> 3 -> 4
//이빨이 빠지거나 겹치는 경우없음!
list.set(3,11);//(3번에,11로) 값을 변경
list.remove(2);//2번 index를 삭제
System.out.println(list);
System.out.println("크기 : "+list.size());
System.out.println("------------------");
ArrayList<String> list2 = new ArrayList<>();
list2.add("홍길동");//유비
list2.add("조조"); //관우
list2.add("조운"); //장비
list2.add("유비"); //조조
list2.add("허저"); //여포
list2.set(0,"유비");
list2.add(1,"관우");
list2.add(2,"장비");
list2.set(4,"여포");
list2.remove(5);
list2.remove(5);//6번 조심!
System.out.println(list2);
}
}
[10, 15, 11, 20]
크기 : 4
------------------
[유비, 관우, 장비, 조조, 여포]package ex3_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex3_ArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
while(true){
System.out.print("id : ");
String id = sc.next();
if(arr.contains(id)){//포함여부
System.out.println("중복된 아이디입니다.");
continue;
}else if(id.equals("exit")){
System.out.println("종료 되었습니다.");
break;
}
arr.add(id);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
}
id : aaa
[aaa]
id : bbb
[aaa, bbb]
id : aaa
중복된 아이디입니다.
id : bbb
중복된 아이디입니다.
id : ccc
[aaa, bbb, ccc]
id : exit
종료 되었습니다.package ex3_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Ex3_ArrayList {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList<String> arr = new ArrayList<>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
outer : while(true){//라벨붙이기
System.out.print("id : ");
String id = sc.next();
for(int i=0;i<arr.size();i++) {
if(id.equals(arr.get(i))){
System.out.println("중복된 아이디입니다.");
continue outer;
}
}
if(id.equals("exit")){
System.out.println("종료 되었습니다.");
break;
}
arr.add(id);
System.out.println(arr);
}
}
}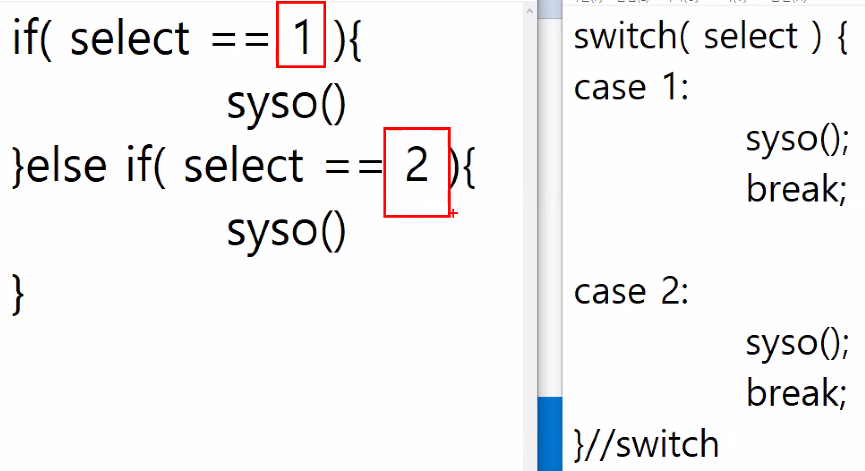
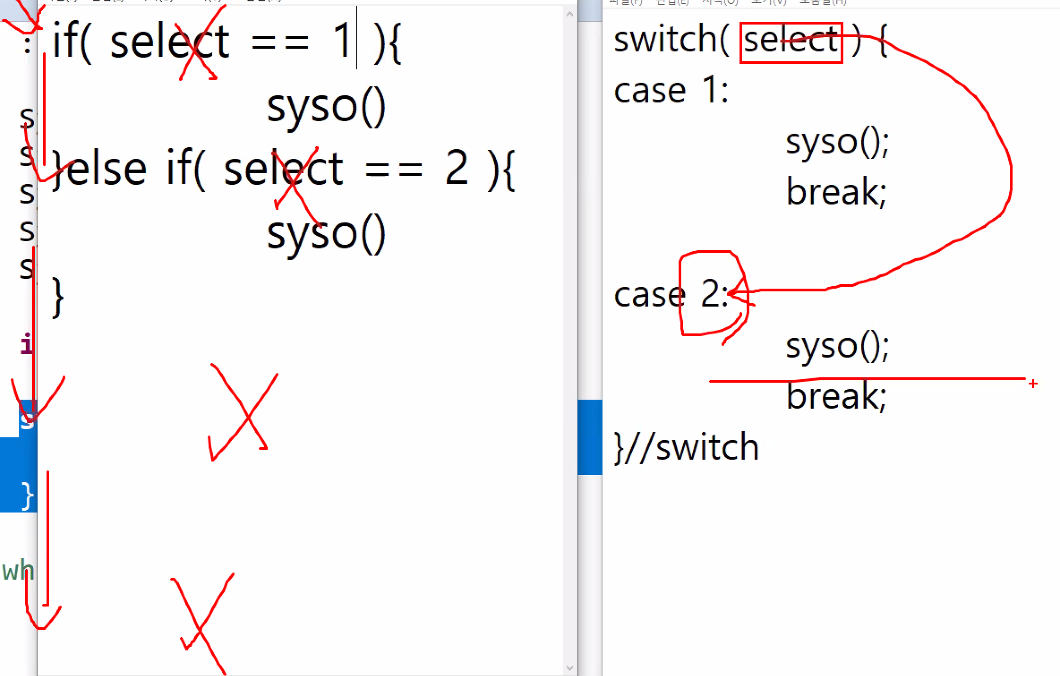
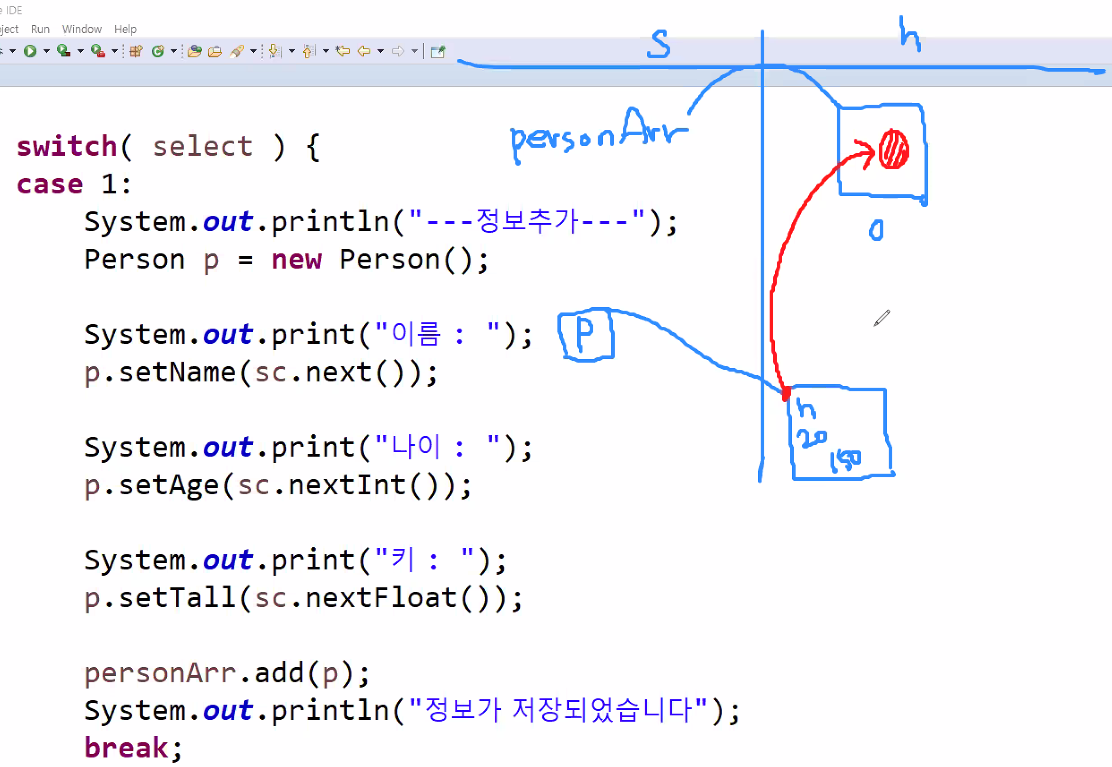
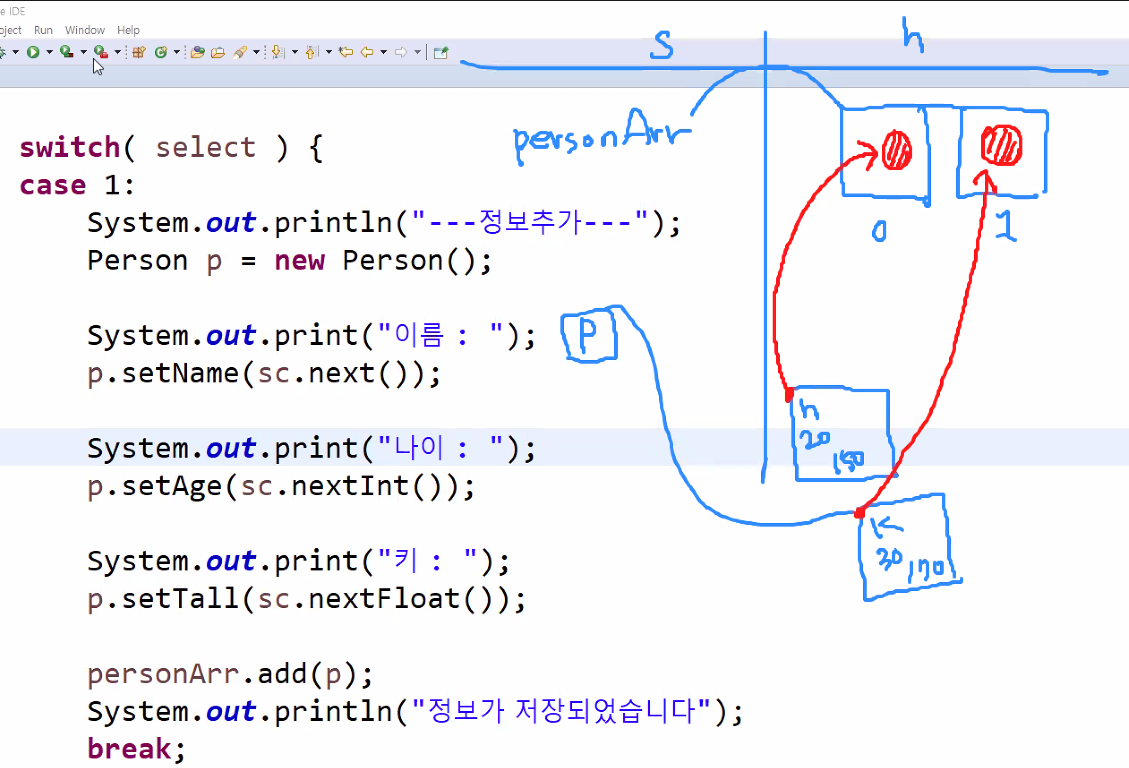
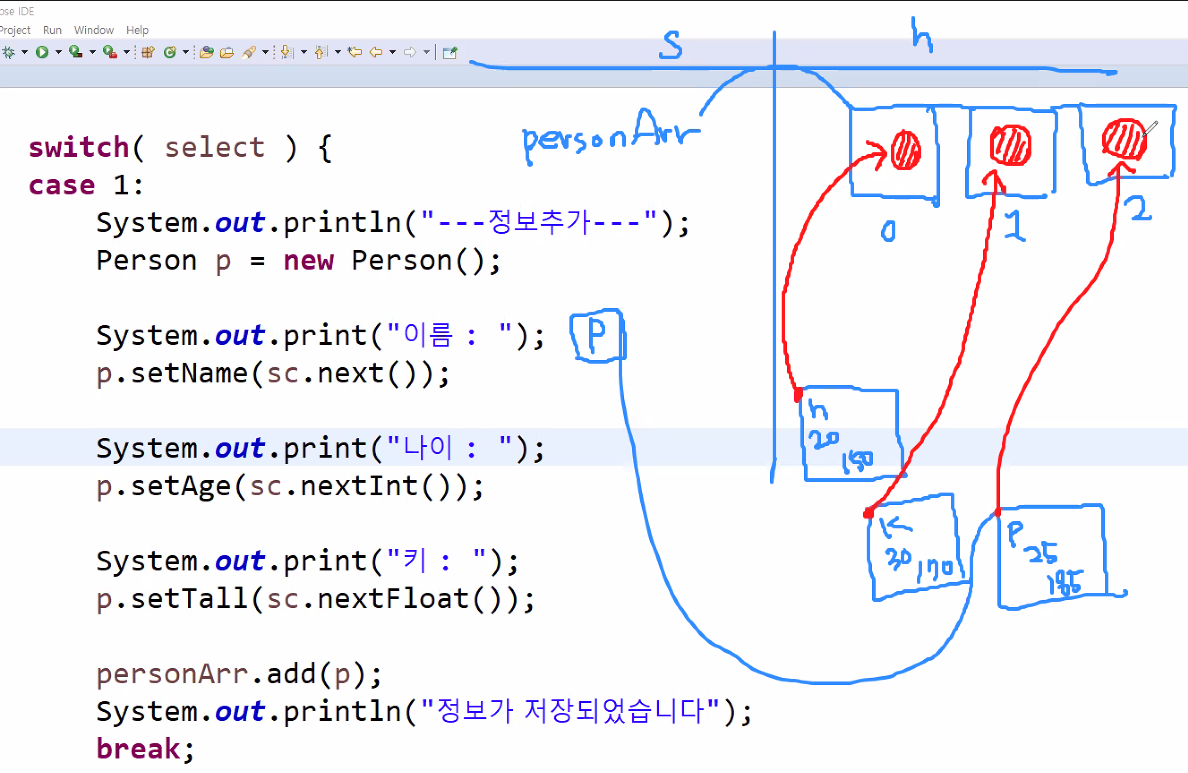
package ex4_list;
public class Person {
private String name;
private int age;
private float height;
public float getHeight() {
return height;
}
public void setHeight(float height) {
this.height = height;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
package ex4_list;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class PersonMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Person클래스로 만들어진 객체만 관리가 가능한 List
ArrayList<Person> personArr = new ArrayList<Person>();
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
out : while(true) {//Ctrl+Alt+↑↓
System.out.println("1.정보추가");
System.out.println("2.정보삭제");
System.out.println("3.전체정보");
System.out.println("etc.종 료");
System.out.print(">>> ");
int select = sc.nextInt();
switch(select){
case 1:
System.out.println("--정보추가--");
Person p = new Person();
System.out.print("이름 : ");
p.setName(sc.next());
System.out.print("나이 : ");
p.setAge(sc.nextInt());
System.out.print("키 : ");
p.setHeight(sc.nextFloat());
personArr.add(p);
System.out.println("정보가 저장되었습니다.");
break;
case 2:
System.out.println("--정보삭제--");
System.out.print("삭제할 이름 :");
String name = sc.next();
for(int i=0;i<personArr.size();i++) {
if(name.equals(personArr.get(i).getName())) {
personArr.remove(i);
System.out.println("삭제성공!");
continue out;
}
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.println("--전체조회--");
System.out.println("등록인원:"+personArr.size());
for(int i=0;i<personArr.size();i++) {
System.out.println(
personArr.get(i).getName()+"/"+
personArr.get(i).getAge()+"/"+
personArr.get(i).getHeight());
}
break;
default:
System.out.println("프로그램 종료");
break out;
}
System.out.println("------------------");
}
}
}
1.정보추가
2.정보삭제
3.전체정보
etc.종 료
>>> 1
--정보추가--
이름 : kim
나이 : 25
키 : 179.5
정보가 저장되었습니다.
------------------
1.정보추가
2.정보삭제
3.전체정보
etc.종 료
>>> 1
--정보추가--
이름 : hong
나이 : 30
키 : 168.2
정보가 저장되었습니다.
------------------
1.정보추가
2.정보삭제
3.전체정보
etc.종 료
>>> 3
--전체조회--
등록인원:2
kim/25/179.5
hong/30/168.2
------------------
1.정보추가
2.정보삭제
3.전체정보
etc.종 료
>>> 2
--정보삭제--
삭제할 이름 :hong
삭제성공!
1.정보추가
2.정보삭제
3.전체정보
etc.종 료
>>> 4
프로그램 종료📁FileClass
package ex1_file;
import java.io.File;
public class Ex1_File {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//IO(Input,Output)
//IO는 입출력 스트림을 의미한다.
//스트림 : 데이터를 입출력하기 위한 일종의 통로와 같은 개념
//JVM -> console : Output 스트림(eclipse 바깥으로)
//console -> JVM : Input 스트림(바깥에서 eclipse 안으로)
String path = "C:/pstudy/file_test.txt";
File f = new File(path);
//File 클래스의 접근경로가 폴더가 아닌 파일 구조일때
if(f.isFile()) {//(다른이름으로 저장)ANSI : 14
System.out.println(f.length()+"byte");
//내가 접근한 경로의 크기를 byte단위로 알아낼수 있다.
}
}
}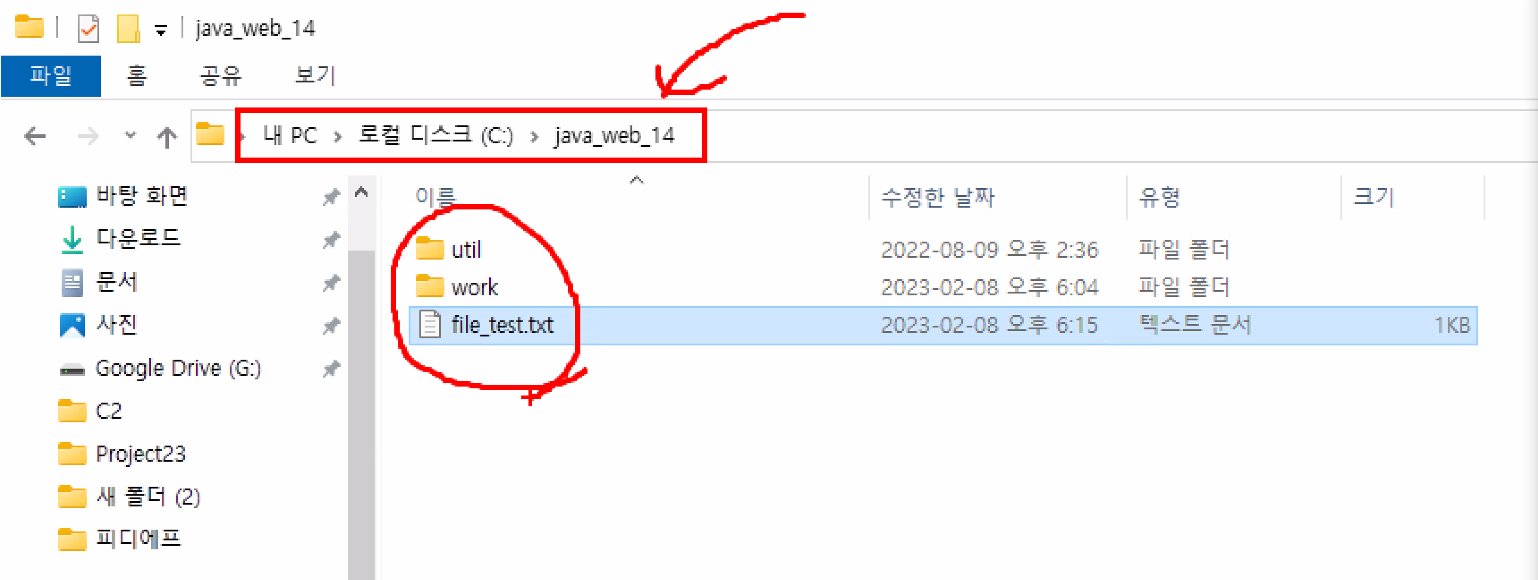
package ex1_file;
import java.io.File;
public class Ex2_File {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:/pstudy";//폴더여야함!
File f = new File(path);//경로로 접근해
if(f.isDirectory()) {//!f.isFile()
String[] names = f.list();//배열💾
//하위목록들...
for(String s : names) {
System.out.println(s);//세부파일
}
}
}
}
package ex1_file;
import java.io.File;
public class Ex3_ {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String path = "C:/pstudy/aaa/bbb";
File f = new File(path);
//f.exist() : 파일 클래스가 잡고있는 경로가
//실제로 존재한다면 true,없다면 false
if(!f.exists()) {//존재하지 않는다면
f.mkdirs();//make directory!
}
}
}