ITPM - 04. Project Scope Management
What is Project Scope Management?
Scope
- All the work(activities) involved in creating the products of the project
- All the processes used to create them
Main Purpose
1) Planning scope management : Determining how the project's scope and requirements will be managed
2) Collecting requirements : Defining and documenting the features and functions of the products as well as the processes
3) Defining scope : reviewing documents to create a scope statement
4) Createing the WBS : subdividing the major project deliverables into smaller, more manageable components
5) Validating scope : formalizaing acceptance of the project deliverables
6) Controllling scope : controlling changes
1. Planning scope management
Input
- Project Charter
- Project management plan
Output
- Scope management plan
plans for
-> 1. Preparing a detailed project scope statement
-> 2. Creating a WBS
-> 3. Maintaining and approving the WBS
-> 4. Obtaining formal acceptance of the completed project deliverables
-> 5. Controlling requests for changes to the project scope - Requirements management plan
-> How we collect and trace the requirements from stakeholders
포함 요소
- How to collect requirements
- How to prioritize requirements
- How to plan, decide, track, and report requirements
- How to perform Configuration management activities
- How to trace and capture attrivutes of requirements
-> Iterative approach 의 중요성 : 초기에는 requirements가 unclear하기 때문에 점진적으로 정의하는 방식이 중요하다.
2. Collecting Requirements
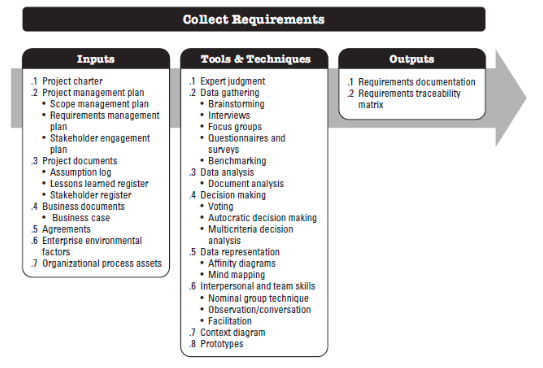
Inputs
- Project Charter
- Project Management Plan
- Scope management plan
- Requirement management plan
- Stackeholder management plan
- Project Documents
- Assumption log
- Lessons learned register
- Stackeholder register
- Business documents
- Business Case
- Agreements
- Enterprise environmental factors
- Organizational process assets
Tools & Techniques
- Expert judgement
- Data Gathering
- Brainstorming
- Interviews -> Effective but expensive and time consuming
- Focus groups -> Faster and less expensive than interviews
- Questionnaires and Surveys -> Efficient way
- Benchmarking
- Data Analysis
- document analysis
- Decision making
- Affinity Diagrams
- Mind mapping
- Interpersonal and team skills
- Nominal group technique
- Observation/Conversation
- Facilitation
- Context Diagram
- Prototypes
Ouputs
- Requirements documentation
- Requirements traceability matrx (RTM)
: A table that lists requirements, various attributes of each requirement, and the status of the requirements to ensure that all requirements are addressed
: Requirement ID, Name, Category, Source, Status, Description
3. Defining Scope
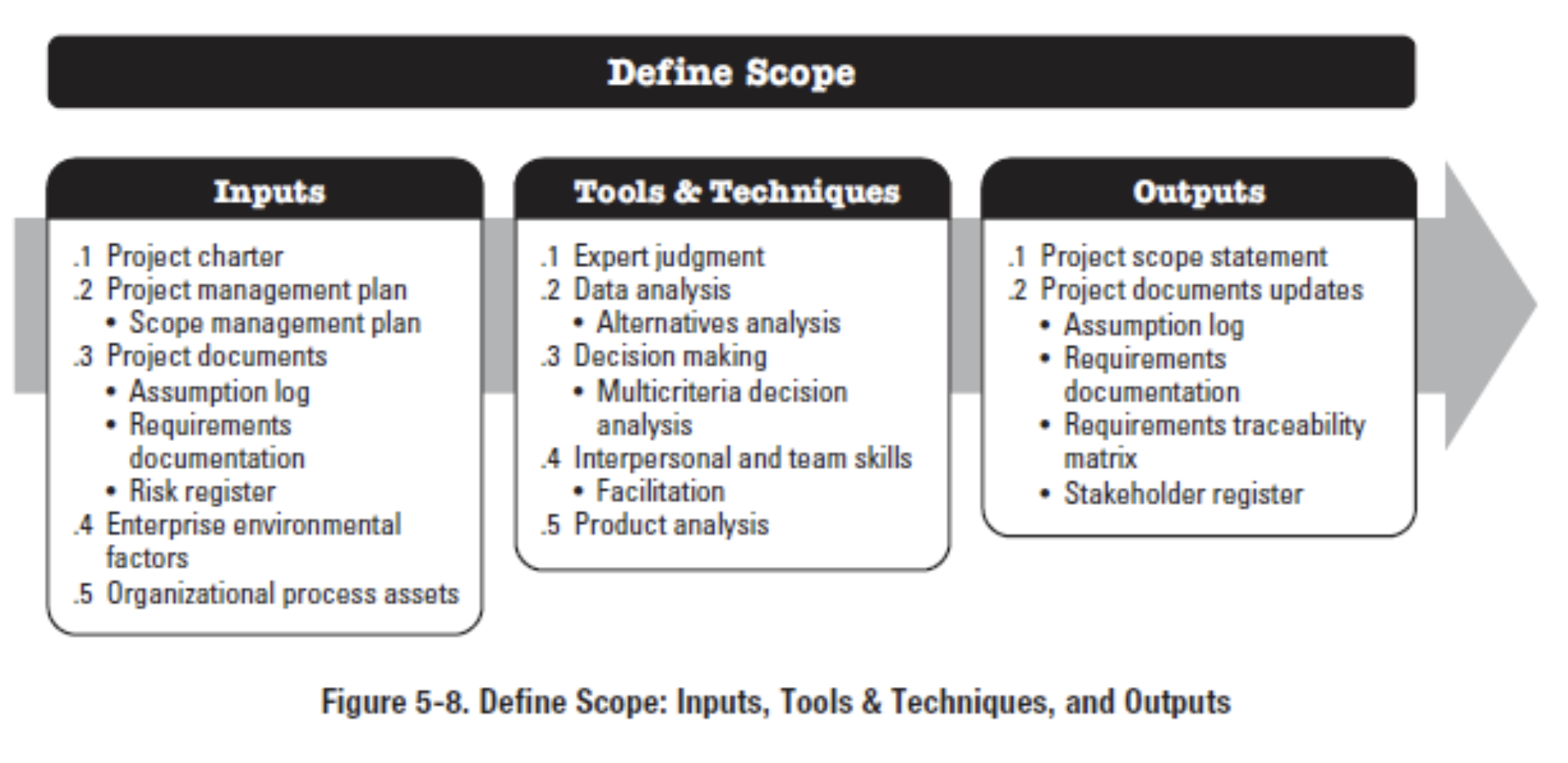
Tools & Techniques
- Decision making -> Multicriteria decision analysis
- Interpersonal and team skills -> Facilitation
- Product analysis
Output
- Project scope statement
-> Product scope description
-> Detailed information on all project Deliverables (including user manual, meeting min, etc.)
-> Acceptance criteria
-> Project exclusions - Project documents updates
Project scope statement
- 더 진행될 수록 become clearer and more specific
4. Create WBS (Work Break Down)
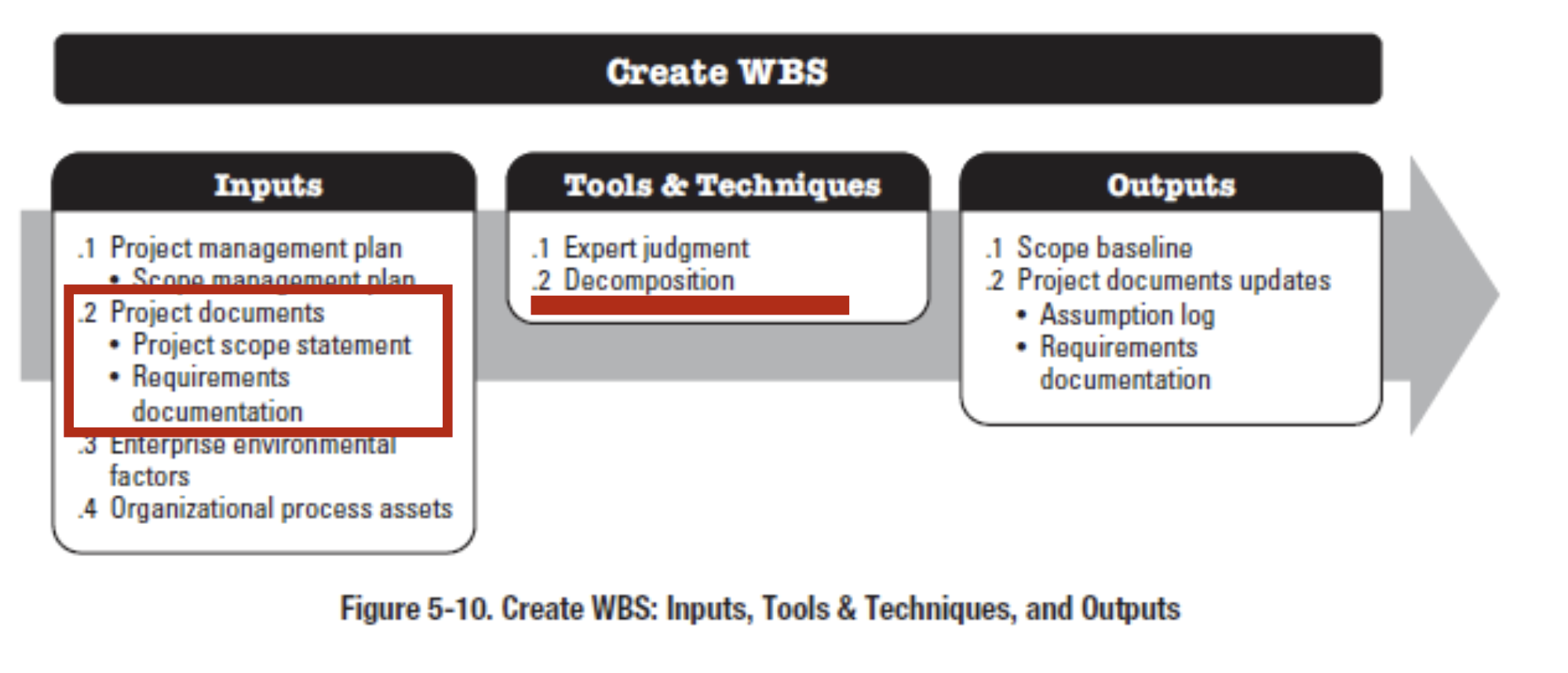
Input
- Project documents -> Project scope statement, Requirements documentation
Tools & Techniques
- Decomposition
Output
- Scope baseline -> includes the "approved" project scope statement / WBS, WBS Dictionary
Work Breakdown Structure
- a deliverable - oriented grouping of the work
- important to organize and divide the work into logical parts
~ Work Package : Lowest lebel tasks of WBS
- Top-down approach
- Botton-up approac
WBS Dictionary
- a document that describes detailed information about each WBS item
- responsibility of only one individual, even though many pepople may be working on it
Scope Baseline
- Scope statement + WBS + WBS Dictionary
- requires several iterations
5. Validating Scope
- to verify the project scope and minimize scope changes는 어렵다
- Scope validation involves formal acceptance of the completed project deliverables (프로젝트의 완료된 산출물에 대해 공식적인 승인을 받는 과정)
6. Controlling Scope
- Scope control invovles controlling changes to the project scope
오답 정리
📘 Q5. Assume that you have a project with major categories called planning, analysis, design, and testing.
What level of the WBS would these items fall under?
정답: c. 2
🧠 해설:
WBS는 계층 구조로 되어 있음.
Level 0: 전체 프로젝트
Level 1: 주요 산출물 또는 프로젝트 단계
Level 2: 그 하위의 중요 활동 or 프로세스 그룹들 (여기서 말하는 planning, analysis, design, testing)
따라서, planning, analysis, design, testing은 Level 2에 해당하는 항목이다.
📘 Q6. Which is NOT a good practice for successful projects?
보기:
a. Keep the scope realistic.
b. Use off-the-shelf hardware and software whenever possible.
c. Follow good project management processes.
d. Don’t involve too many users in scope management.
정답: d. Don’t involve too many users in scope management.
🧠 해설:
사용자 참여를 제한하는 건 좋지 않은 관행이다.
특히 요구사항 수집과 범위 검증 단계에서는 핵심 이해관계자와의 지속적 협업이 필수.
나머지 선택지는 다 좋은 실천 방법이 맞음!
📘 Q7. What constitutes requirements for agile projects?
정답: b. The backlog
🧠 해설:
애자일 환경에서는 요구사항이 product backlog로 관리됨.
backlog는 고객이 원하는 기능, 변경 사항, 요구사항 등을 정리한 목록.
Scrum은 프레임워크, sprint는 개발 주기, requirements list는 전통적인 접근 방식에 더 가까움.

Scope 정의를 산출물과 작업 관점으로 함께 풀어주셔서 실무 적용 포인트가 분명했습니다. 30년 넘게 개발자로 일하면서 일정 지연의 시작은 대부분 모호한 범위 정의에서 시작된다는 걸 많이 봤습니다. 그래서 Plexo를 개발했고 AI Task Breakdown으로 기능 설명만 입력하면 WBS/예상시간/우선순위를 자동 생성해 초기 범위 정렬 속도를 높이고 있습니다. https://plexo.work 범위 고정이 어려운 프로젝트에서는 어떤 기준으로 변경 요청을 수용하시는지 궁금합니다.