ITPM - 08. Project Quality Management
What is Project Quality Management?
Scope vs Quality
- Scope is a starting point.
- Quality is the finish line
Project Quality Management
- ensures the project will satisfy the needs
Process Group
- Plan Quality Management
- Manage Quality
- Control Quality
1. Planning Quality Management
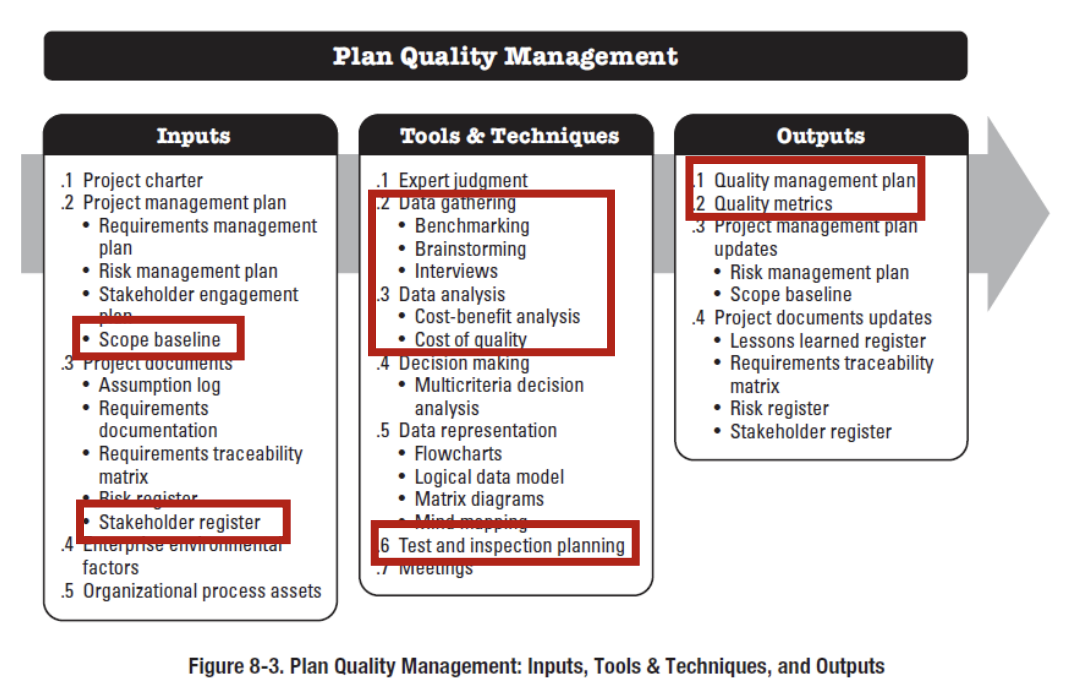
- It implies the ability to anticipate situations and prepare actions to bring about the desired outcome
Some major elements of IT projects
- Functionality : degree to which a system perform its intended function (what - 시스템이 의도한대로 작동하는가)
- Features : system's special characteristics that appeal to users (how)
- System outputs (templates) : screens and reports the system generates
- Perfomance addresses : how well a product or service performs the customer's intended use (고객이 기대한 용도에 맞춰 얼마나 잘 작동하는가)
- Reliability : ability of a product or service to perform as expected under normal conditions (신뢰성 - 정상적인 조건에서 예상한대로 작동하는 능력)
- Maintainability : ease of performing maintenance on a product (유지보수성)
- Scalability : delivering performance with an increased load (확장성 - 사용량이 늘어도 성능이 유지되는지)
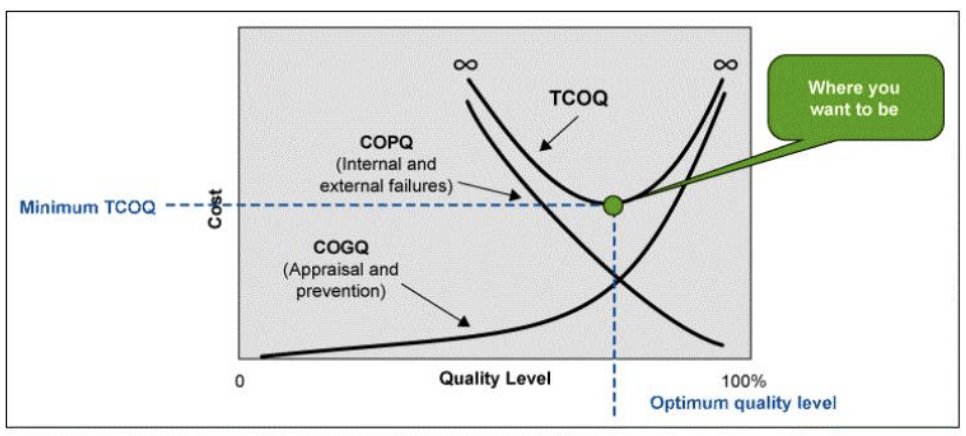
Cost of Quality
- Prevention Cost : cost of planning and executing a project so it is error-free or within an acceptable error range
- Appraisal Cost : cost of evaluating processes and their outputs to ensure quality (Testing Cost)
- Internal Failure Cost : cost incurred to correct an identified defect before the customer receives the product
- External Failure Cost : cost that relates to all errors not detected and corrected before delivery to the customer
-
COPQ (Cost of Poor Quality) : Internal / External failure cost
-
COGQ (Cost of Good Quality) : Prevention / Appraisal Cost
-
TCOQ (Total Cost of Quality)
-
이 그래프는 Traditional Approach로 Optimum quality level 찾음
-
COGQ가 커지면 COPQ가 작아짐 (예방 및 테스트를 많이하면 실패가 줄어듦)
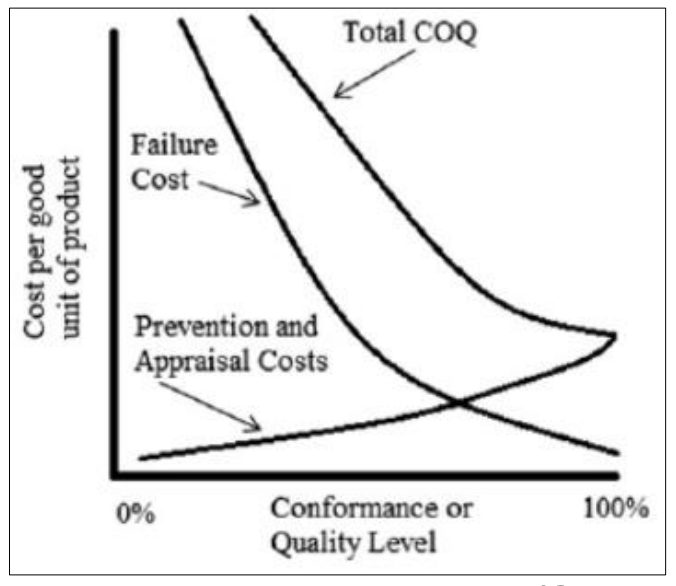
- 이 그래프는 modern view approach
- 차이점 : 예방과 검사에 투자할수록 TCOQ가 계속 감소 / High Quality를 지향하는 것이 장기적으로 비용 효율적
2. Managing Quality
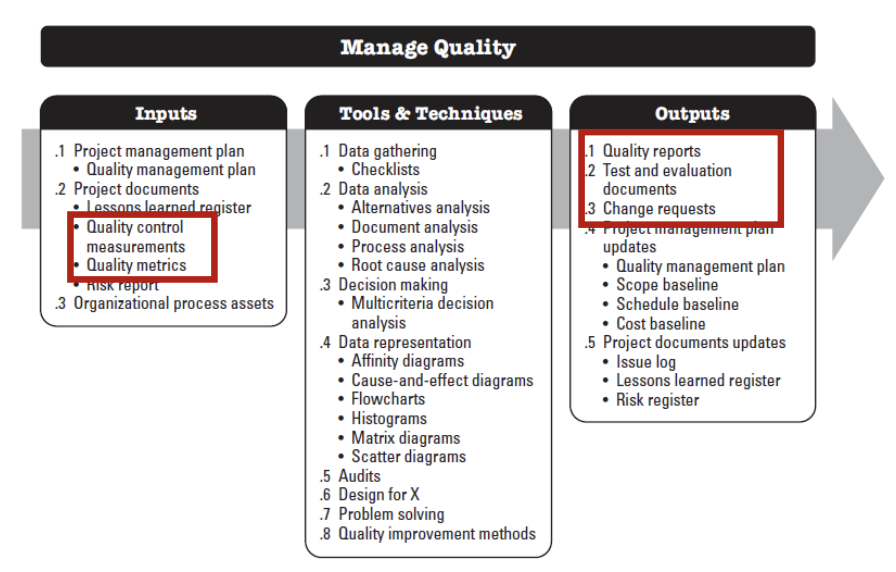
3. Controlling Quality
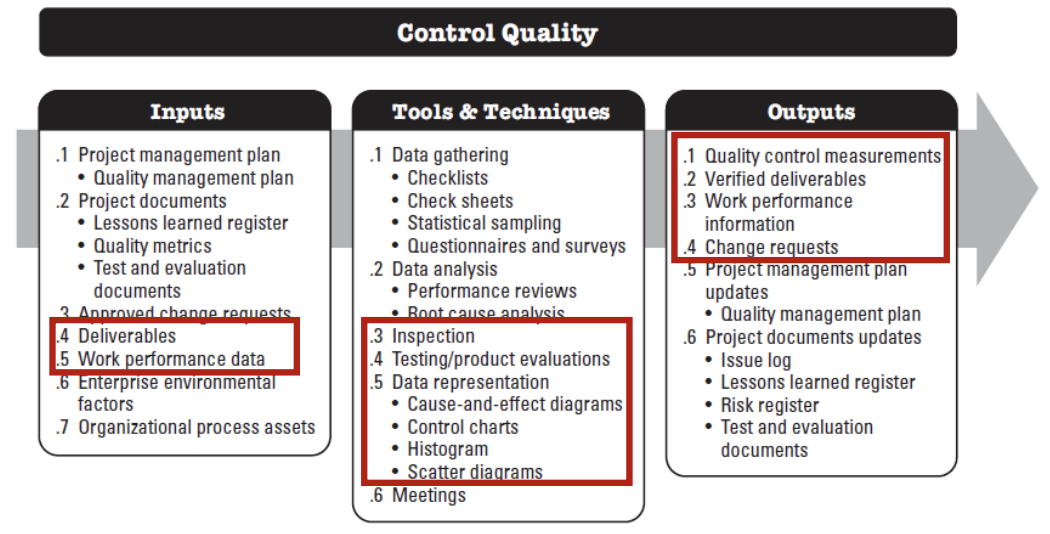
Tool - Cause and Effect Diagrams
- 가지들 화살표가 Cause / 중앙 줄기 Problem 이 Effect
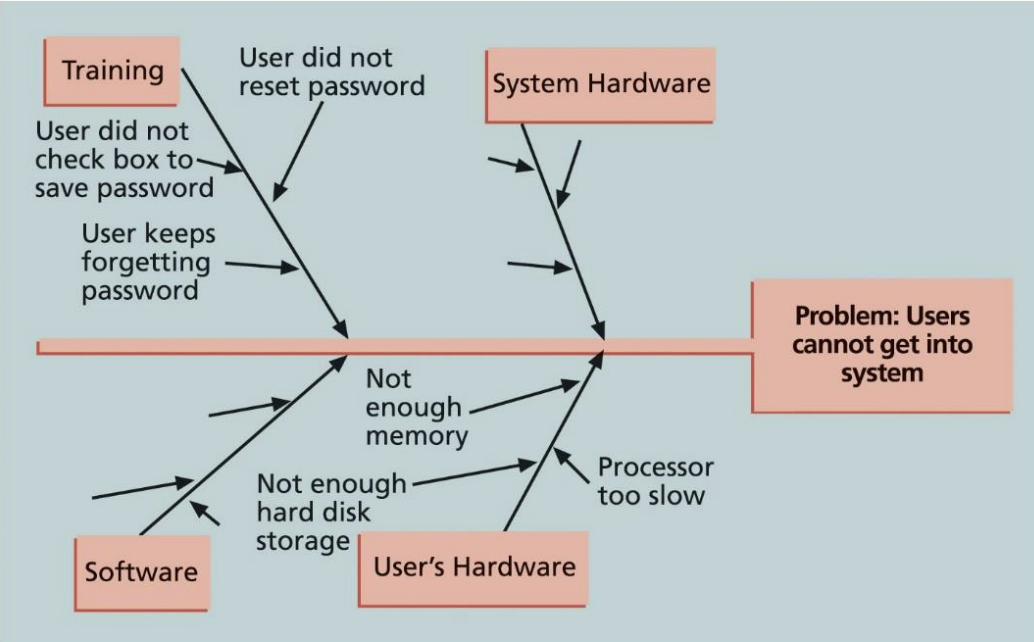
Tool - Control Chart
- Mean (Criteria) 보다 낮게 찍히면 올려야한다.
- 가로는 Time demention
- Keep tracking
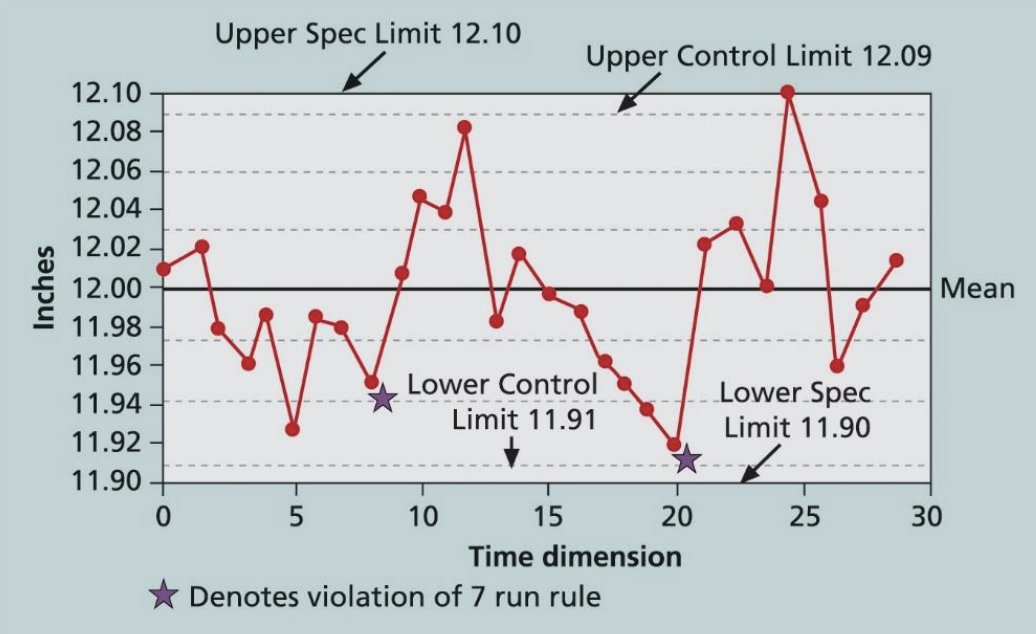
Tool - Checksheet
- 예시 사용처 : complain 횟수 표시
Tool - Scatter diagram
Tool - Histogram / Pareto chart
Tool - Flowcharts
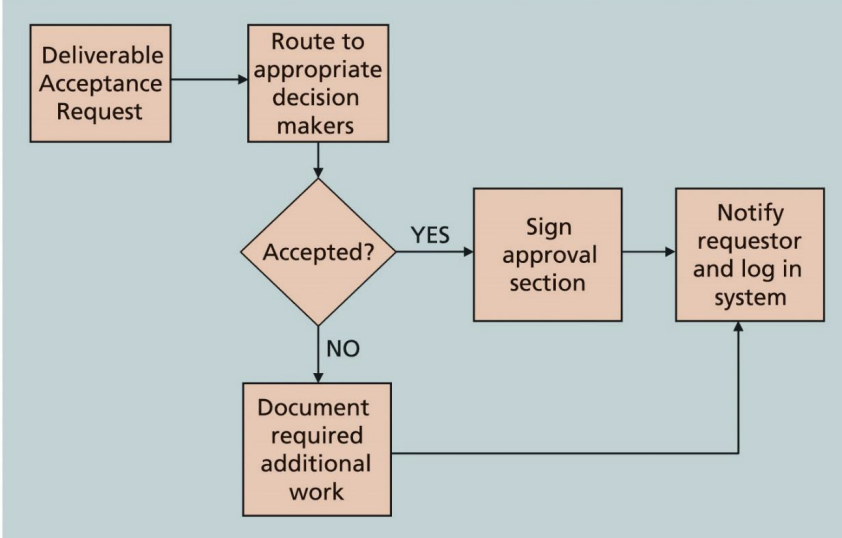
- Cause and Effect Diagrams와 다르게 sequential 하다.
Tool - Run charts(Control Chart)
Tool - Statistical Sampling
-
Choosing part of a population of interest for inspection (전체 집단에서 일부를 뽑아 검사)
-
전수 검사는 cost가 많이 들기 때문에 샘플링을 한다.
-
Sample size = 0.23 * (certainty factor / acceptable error)^2
-
certainty factor : 신뢰계수
-
acceptable error : 허용 오차
Six Sigma
- 얼마나 Exceptional case를 deal with 할 수 있는지
- Six Sigma is uniquely driven by close understanding of customer needs, disciplined use of facts, data, and statistical analysis, and diligent attention to managing, improving, and reinventing business processes.
(고객 니즈 깊이 이해, 사실/데이터/통계 분석 활용, 비즈니스 프로세스 관리/개선/재설계 집중)
Purpose
- Improve quality
- Decrease costs
- Better meet customer needs
DMAIC Process
- 과학적이고 사실 기반의 체계적인 반복 개선 프로세스
| 단계 | 설명 | 영어 설명 |
|---|---|---|
| Define | 문제/기회, 프로세스, 고객 요구사항 정의 | Define the problem/opportunity, process, and customer requirements |
| Measure | 측정 항목 정의, 데이터 수집/정리/표현 | Define measures, then collect, compile, and display data |
| Analyze | 프로세스 세부사항 분석하여 개선 기회 탐색 | Scrutinize process details to find improvement opportunities |
| Improve | 문제를 개선하기 위한 아이디어 및 솔루션 생성 | Generate solutions and ideas for improving the problem |
| Control | 개선이 안정적으로 유지되는지 추적하고 검증 | Track and verify the stability of the improvements and the predictability of the solution |
적용할 수 있는 문제 조건
- Must be a quality problem or gap between the current and desired performance (품질 문제가 있고, 현재 성과와 기대 성과 사이에 차이가 존재해야함)
- Project should not have a clearly understood problem (문제가 명확하지 않은 상태여야 함 - 즉, 원인 분석이 필요한 경우 적합)
- Solution should not be predetermined, and an optimal solution should not be apparent (해결책이 미리 정해져 있거나 명확하면 안됨)
Testing
-
Wrong Approach : testing as a stage comes near the end of IT product development
- Fixing 하기 어렵고, Cost도 많이 들어감 -
Correct Approach : Testing needs to be done during almost every phase of the systems development life cycle, not just before the organization ships or hands over a product to the customer
Types of Testing
- Uniting Testing : testing each individual component
- Integration Testing : occurs between unit and system testing to test functionally grouped components
- System Testing : tests the entire system as one entity
- User Acceptance Testing : independent test performed by end users prior to accepting the delivered system
- Alpha & Beata Testing, Performance Testing, Scalability Testing
- But code -> test -> fix 사이클 만으로는 충분하지 않다. 코드가 복잡해질수록, 테스트로 놓치는 결함이 늘어남
- 그래서 개발 프로세스를 재설계, 개발자에게 책임 부여, 오류 추적 및 개선, 동기부여 및 자율성 부여가 중요해졌다.
Modern Quality Management
주요 특징
- Requires customer satisfaction
- Prefers prevention to inspection
- Recognizes management responsibility for quality (경영진 책임이다)
ISO standards
- three-part : planning -> controlling -> ducumenting
- provid minimum requirements
- customer needs and expectations
Improving IT Project Quality
- Establish leadership that promotes quality
- Understand the cost of quality
- Provide a good workplace to enhance quality
- Work toward improving the organization's overall maturity level (조직의 전반적인 성숙도 수준 향상을 목표로 노력)
Leadership
- 품질 문제는 기술 문제가 아니라 관리 문제인 경우가 많다
- 이를 해결하기 위해서, 최고 경영진의 책임과 역할이 중요하다.
Cost of Quality
- Cost of Conformance (예방 비용): internal cost, prevention cost -> 품질을 확보하기 위한 비용
- Cost of NonConformance (수습 비용) : external failure cost -> 품질 실패로 인해 발생하는 비용
- 개발 비용의 절반이 테스트 및 디버깅에 쓰인다.
- 품질 실패 비용의 주범 경영진이다.
- 기술보다 조직이 생산선에 더 큰 영향을 미친다. -> 조직 분위기나 구조, 정책에 따라 퀄리티가 크게 달라진다.
Expectations and Cultural Differences in Quality
- PM은 stakeholder의 expectation을 잘 파악하고 관리해야한다.
- expectation은 사람마다 다르며, 조직 문화 및 지리적 위치의 영향을 받는다.
