panel content를 별도의 view로 처리하면 응용 프로그램 구조를 훨씬 쉽게 이해할 수 있으며 재사용이 가능하다.
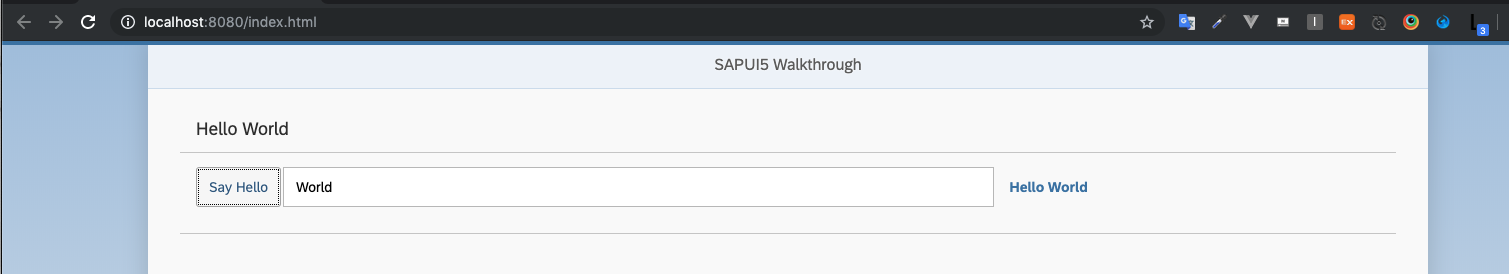
Preview
Coding
webapp/view/App.view.xml
<mvc:View
controllerName="sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.App"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc"
displayBlock="true">
<Shell>
<App class="myAppDemoWT">
<pages>
<Page title="{i18n>homePageTitle}">
<content>
<mvc:XMLView viewName="sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.view.HelloPanel"/>
</content>
</Page>
</pages>
</App>
</Shell>
</mvc:View>panel과 그 content를 App view에 직접 저장하는 대신 HelloPanel view로 옮길 것이다.
panel의 content aggregation에서 XMLView 태그를 사용한다.
webapp/view/HelloPanel.view.xml (New)
<mvc:View
controllerName="sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.HelloPanel"
xmlns="sap.m"
xmlns:mvc="sap.ui.core.mvc">
<Panel
headerText="{i18n>helloPanelTitle}"
class="sapUiResponsiveMargin"
width="auto" >
<content>
<Button
text="{i18n>showHelloButtonText}"
press=".onShowHello"
class="myAppDemoWT myCustomButton"/>
<Input
value="{/recipient/name}"
valueLiveUpdate="true"
width="60%"/>
<FormattedText
htmlText="Hello {/recipient/name}"
class="sapUiSmallMargin sapThemeHighlight-asColor myCustomText"/>
</content>
</Panel>
</mvc:View>panel의 전체 내용을 HelloPanel.view.xml 파일에 추가한다.
또한 XML view의 controllerName 속성을 설정하여 view에 대한 컨트롤러를 지정한다.
webapp/controller/HelloPanel.controller.js (New)
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller",
"sap/m/MessageToast"
], function (Controller, MessageToast) {
"use strict";
return Controller.extend("sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.HelloPanel", {
onShowHello : function () {
// read msg from i18n model
var oBundle = this.getView().getModel("i18n").getResourceBundle();
var sRecipient = this.getView().getModel().getProperty("/recipient/name");
var sMsg = oBundle.getText("helloMsg", [sRecipient]);
// show message
MessageToast.show(sMsg);
}
});
});onShowHello 메서드를 HelloPanel controller에 지정하면 해당 메서드는 재사용이 가능하다.
webapp/controller/App.controller.js
sap.ui.define([
"sap/ui/core/mvc/Controller"
], function (Controller) {
"use strict";
return Controller.extend("sap.ui.demo.walkthrough.controller.App", {
});
});이전 App.controller에 정의된 모든 것들을 다른 파일로 옮겼다. 따라서 앱 app controller는 지금은 빈 스텁으로 남는다.
