Understanding the premise
: 학습은 인공지능에서 가장 기본적인 요소로 기계가 스스로 학습할 수 있도록 기계에게 학습 방법을 가르치는 것을 의미한다. 강화 학습은 주어진 상황에 대해 취할 행동을 보상으로 극대화하는 방향으로 결정하는 방법을 학습한다. 강화학습이 다른 학습과 뚜렷이 구분되는 대표적인 특징은 시행 착오 학습과 지연 보상이다.
Reinforcement learning vs. supervised learning
: 지도학습은 별도로 제공된 레이블이 달린 샘플을 통해 학습한다. 그렇기 때문에 사전에 주어진 학습용 샘플 데이터가 없는 처음 마주하는 문제를 해결할 때 지도 학습 기법을 적용할 수 없다. 강화학습은 바로 이러한 종류의 문제에서 힘을 발휘한다.
강화 학습은 좀 더 주변 상황을 탐색하고 행동해야 하는가, 아니면 제한된 경험만을 가지고 학습해야 하는가, 즉 탐색과 이용의 상충관계에 대한 연구가 필요하다.
Real world examples of reinforcement learning
- 게임: 바둑이나 체스 같은 최적의 수를 결정하기 위해 수많은 요인을 검토해야 하는 게임
- 로보틱스: 처음 본 건물을 탐사하는 로봇
- 산업용 제어기: 엘리베이터를 제어하는 스케줄러
- 아기: 갓 태어난 아기의 걸음마
--> 공통적인 특징이 있따. 환경과 상호작용하며, 학습 에이전트는 환경에 대한 불확실성이 어느 정도 있더라도 주어진 목적을 달성하기 위해 노력한다. 나중에 환경이 달라진다면 에이전트가 취하는 행동 또한 달라질 것이다.
Building blocks of reinforcement learning
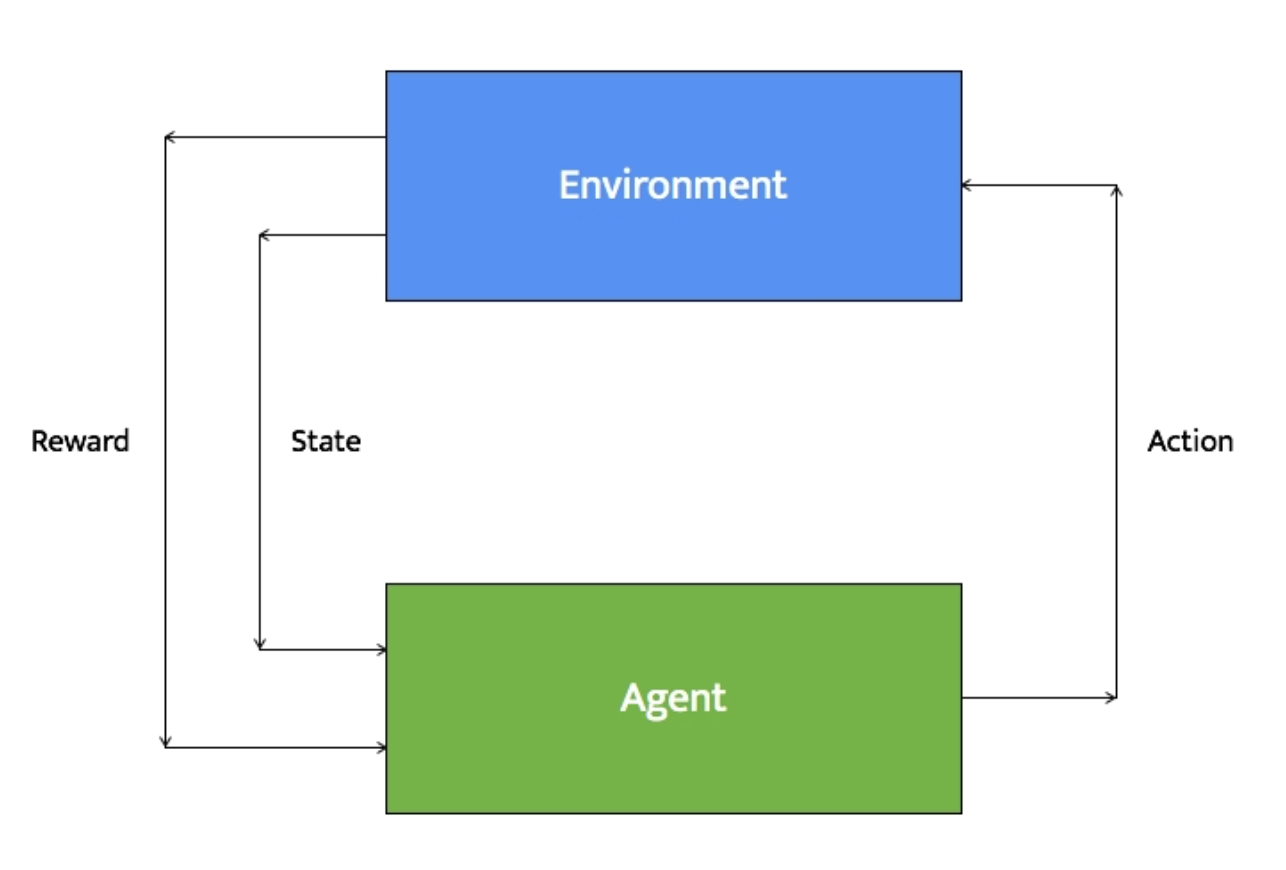
- 에이전트와 환경에 대해 몇 가지 상태가 정의되어 있다. 특정 시점에 에이전트는 주변 환경에 대한 정보가 담긴 상태를 입력 받는다.
- 에이전트가 취할 동작에 관련된 정책이 정의되어 있다. 이러한 정책은 의사 결정 기능을 수행한다. 입력 상태에 대해 에이전트가 취할 동작은 이러한 정책에 따라 결정한다.
- 에이전트는 이전 단계의 결정에 따라 동작을 수행한다.
- 환경은 에이전트가 취한 동작에 따라 반응한다. 에이전트는 환경으로부터 보상을 받는다.
- 에이전트는 보상에 대한 정보를 기록한다. 이때 동작과 상태에 대해 어떤 보상이 주어졌는지 기록한다.
Creating an environment
- 터미널
$ pip3 install gym- 파이썬 코드
import argparse
import gym
def build_arg_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Run an environment')
parser.add_argument('--input-env', dest='input_env', required=True,
choices=['cartpole', 'mountaincar', 'pendulum', 'taxi', 'lake'],
help='Specify the name of the environment')
return parser
if __name__=='__main__':
args = build_arg_parser().parse_args()
input_env = args.input_env
name_map = {'cartpole': 'CartPole-v0',
'mountaincar': 'MountainCar-v0',
'pendulum': 'Pendulum-v0',
'taxi': 'Taxi-v1',
'lake': 'FrozenLake-v0'}
# Create the environment and reset it
env = gym.make(name_map[input_env])
env.reset()
# Iterate 1000 times
for _ in range(1000):
# Render the environment
env.render()
# take a random action
env.step(env.action_space.sample()) Building a learning agent
import argparse
import gym
def build_arg_parser():
parser = argparse.ArgumentParser(description='Run an environment')
parser.add_argument('--input-env', dest='input_env', required=True,
choices=['cartpole', 'mountaincar', 'pendulum'],
help='Specify the name of the environment')
return parser
if __name__=='__main__':
args = build_arg_parser().parse_args()
input_env = args.input_env
name_map = {'cartpole': 'CartPole-v0',
'mountaincar': 'MountainCar-v0',
'pendulum': 'Pendulum-v0'}
# Create the environment
env = gym.make(name_map[input_env])
# Start iterating
for _ in range(20):
# Reset the environment
observation = env.reset()
# Iterate 100 times
for i in range(100):
# Render the environment
env.render()
# Print the current observation
print(observation)
# Take action
action = env.action_space.sample()
# Extract the observation, reward, status and
# other info based on the action taken
observation, reward, done, info = env.step(action)
# Check if it's done
if done:
print('Episode finished after {} timesteps'.format(i+1))
break 