조인
- 조인: 두 개 이상의 테이블을 특정 컬럼을 기준으로 연결하여, 마치 처음부터 하나의 테이블이었던 것처럼 보여주는 기능이다
조인이 필요한 이유
- 하나의 테이블에 다 저장을 하게 된다면 편하겠지만 심각한 문제들이 발생한다
- 데이터 중복
- 갱신 이상: 주소를 업데이트를 하는데 하나라도 누락하면 데이터의 일관성이 깨져버린다
- 삽입 이상
- 삭제 이상
이러한 문제들로 인해 정규화라는 과정을 거친다
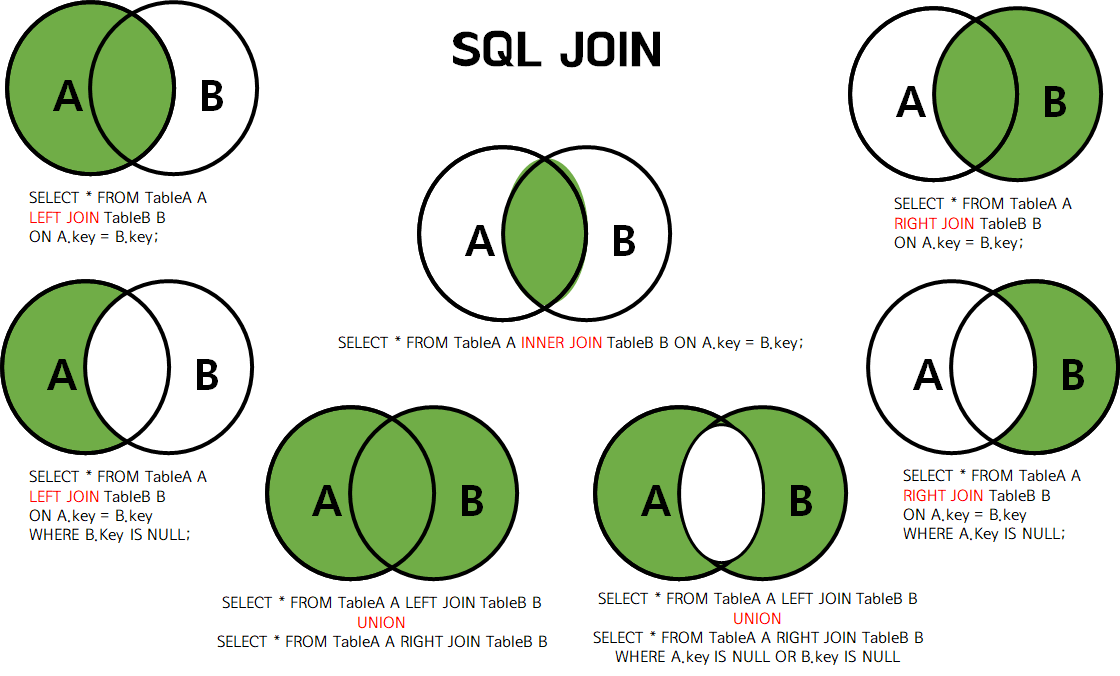
1. 내부조인
- 양쪽 테이블에 공통으로 존재하는 데이터만을 결과로 보여준다.
- 내부 조인은 결과가 같으므로 순서는 무관하나, 쿼리를 읽는 사람의 입장에서 어떤 데이터가 중심이 되는가에 따라 순서를 정하면 가독성이 높아진다
select *
from orders
inner join users on orders.user_id = users.user_id;
select u.name, sum(o.quantity * p.price) as total_purchase_amount
from orders o
join users u on u.user_id = o.user_id
join products p on p.product_id = o.product_id
group by u.name
order by total_purchase_amount desc;
2. 외부조인
LEFT JOIN은 구문의 왼쪽에 있는 테이블이 기준이 된다
- 일단 왼쪽 테이블의 모든 데이터를 결과에 포함시킨다
- 오른쪽 테이블에 짝이 맞는 데이터가 없다면 그 자리는
NULL값으로 채워진다
select *
from products p
left join orders o on p.product_id = o.product_id
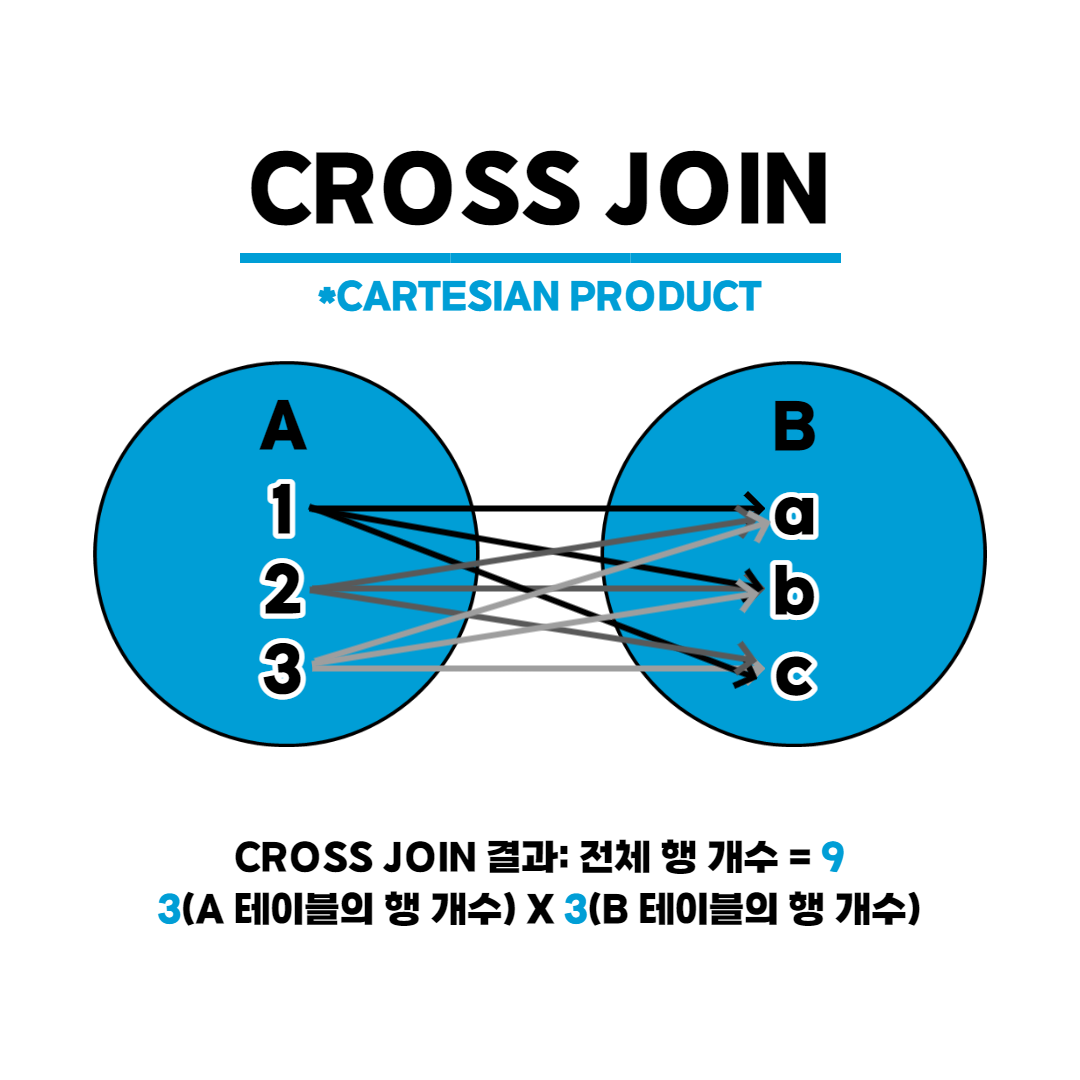
3. Cross Join
- A 테이블의 모든 행을 B 테이블의 모든 행과 하나씩 전부 연결하는 방식이다
- 카테시안 곱으로 나타나며 m * n개의 행을 갖게 된다
select
concat('기본티셔츠-', c.color, '-', s.size) as product_name,
s.size,
c.color
from sizes s
cross join colors c;
insert into product_options(product_name, size, color)
select
concat('기본티셔츠-', c.color, '-', s.size) as product_name,
s.size,
c.color
from sizes s
cross join colors c;
서브쿼리
- 하나의 SQL 쿼리문 안에 포함된 또 다른
SELECT쿼리를 의미한다
- 바깥쪽 메인쿼리가 실행되기 전에 괄호안에 있는 서브쿼리가 먼저 실행된다
- 서브쿼리의 실행결과를 바깥쪽 메인쿼리에게 전달하여, 메인쿼리가 그 결과를 사용해서 최종 작업을 수행하게 된다
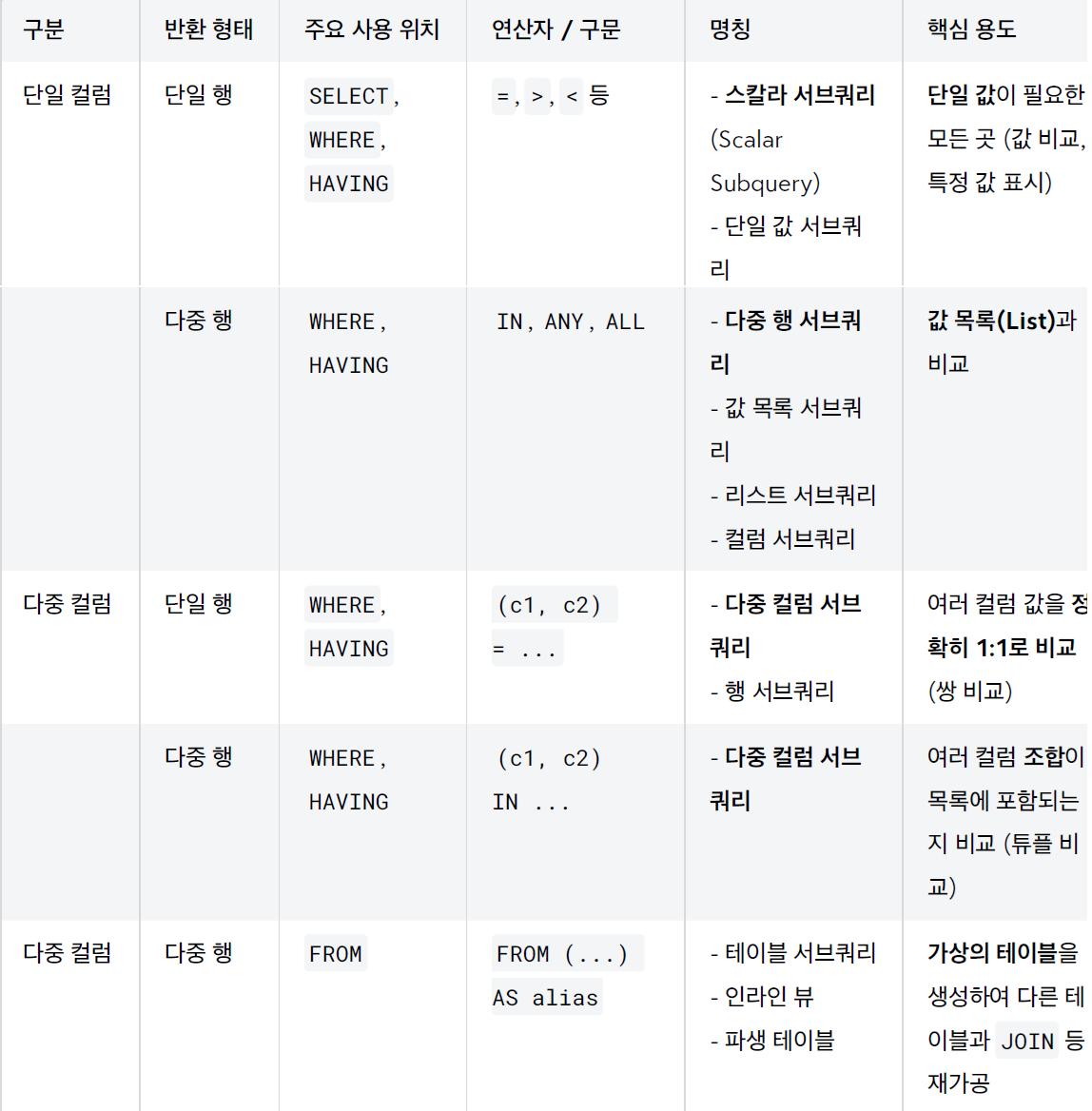
1). 스칼라 서브쿼리
- 단일 컬럼, 단일행
- 서브쿼리를 실행했을 때 결과가 오직 하나의 행, 하나의 컬럼으로 나오는 경우를 말한다
select u.name, u.address
from users u
where address = (select u.address
from orders o
join users u on o.user_id = u.user_id
where o.order_id = 1);
2). 다중 행 서브쿼리
- 두 개 이상의 행을 반환할 때 사용한다
- 다중 행 서브쿼리 결과를 처리하기 위한
IN, ANY, ALL같은 연산자가 존재한다
select * from orders
where product_id in(
select product_id
from products
where category = '전자기기'
)
order by order_id;
WHERE price > any (100, 200, 300)
WHERE price > all (100, 200, 300)
3). 다중 컬럼 서브쿼리
select user_id, status
from orders
where (user_id, status) = (select user_id, status
from orders
where order_id = 3);
4). 상관 서브쿼리
- 메인쿼리와 서브쿼리가 서로 영향을 준다는 뜻이다
- 상관 서브쿼리
- 메인쿼리가 먼저 한 행을 읽는다
- 읽혀진 행의 값을 서브쿼리에 전달하여, 서브쿼리가 실행된다
- 서브쿼리 결과를 이용해 메인쿼리의
WHERE조건을 판단한다
- 메인쿼리의 다음 행을 읽고, 2-3 과정을 반복한다
select *
from products p1
where price >= (select avg(p2.price)
from products p2
where p1.category = p2.category
);
select
product_id,
name,
price
from products p
where exists (
select 1
from orders o
where o.product_id = p.product_id
);
5). 테이블 서브쿼리
FROM절에 위치하는 서브쿼리로, 하나의 독립된 가상 테이블처럼 사용되기 때문에 테이블 서브쿼리라 한다- 인라인으로 즉석에서 정의되는 뷰와 같다고 해서 인라인 뷰라고도 부른다
select
p.product_id,
p.name,
p.price
from products p
join (
select category, max(price) as max_price
from products
group by category
) as cmp on p.category = cmp.category and p.price = cmp.max_price
UNION
- 여러 개의 결과집합을 아래로(수직으로)이어 붙여서 더 많은 행을 가진 하나의 집합으로 만드는 기술이다
- 즉 데이터를 합쳐서 하나의 테이블로 만드는 작업이다
select name, email from users
union
select name, email from retired_users;
핵심규칙
UNION으로 연결되는 모든 SELECT문은 컬럼의 개수가 동일해야 한다- 각
SELECT문의 같은 위치에 있는 컬럼들은 서로 호환 가능한 데이터 타입이어야 한다
- 최종 결과의 컬러 이름은 첫번째
SELECT문의 컬럼 이름을 따른다
1). UNION ALL
UNION은 중복을 제거하지만 UNION ALL은 중복을 제거하지 않는다- 중복제거는 중복을 찾아내는 과정을 거쳐서 엄청난 비용과 시간을 소모한다
- 특별한 요구사항이 없을 경우에는
UNION ALL을 사용하자
select u.name, u.email
from users u
join orders o on u.user_id = o.user_id
join products p on p.product_id = o.product_id
where p.category = '전자기기'
UNION ALL
select name, email
from users
where address like '서울%';
CASE문
- IF문 처럼 특정 조건에 따라 다른 값을 출력하게 만드는 강력한 조건부 도구이다
select
order_id,
user_id,
product_id,
quantity,
status,
CASE status
WHEN 'PENDING' THEN '주문 대기'
WHEN 'COMPLETED' THEN '결제 완료'
WHEN 'SHIPPED' THEN '배송'
WHEN 'CANCELLED' THEN '주문 취소'
ELSE '알 수 없음'
END AS status_korean
from orders;
select
name,
price,
CASE
WHEN price >= 100000 then '고가'
WHEN price >= 30000 then '중가'
ELSE '저가'
END AS price_label,
CASE
WHEN price >= 100000 then 1
WHEN price >= 30000 then 2
ELSE 3
END as sort
from products
order by
CASE
WHEN price >= 100000 then 1
WHEN price >= 30000 then 2
ELSE 3
END;
1). 그룹핑
select
case
when year(birth_date) >= 1990 then '1990년대생'
when year(birth_date) >= 1980 then '1980년대생'
else '그 이전 출생'
end as birth_decade,
count(*) as customer_count
from users
group by
case
when year(birth_date) >= 1990 then '1990년대생'
when year(birth_date) >= 1980 then '1980년대생'
else '그 이전 출생'
end
select
case
when year(birth_date) >= 1990 then '1990년대생'
when year(birth_date) >= 1980 then '1980년대생'
else '그 이전 출생'
end as birth_decade,
count(*) as customer_count
from users
group by birth_decade;
select
count(*) as total_orders,
sum(case when status = 'COMPLETED' then 1 else 0 end) as completed_count,
sum(case when status = 'SHIPPED' then 1 else 0 end) as shipped_count,
sum(case when status = 'PENDING' then 1 else 0 end) as pending_count
from orders;
select
count(*) as total_orders,
sum(case when status = 'COMPLETED' then 1 else 0 end) as completed_count,
sum(case when status = 'SHIPPED' then 1 else 0 end) as shipped_count,
sum(case when status = 'PENDING' then 1 else 0 end) as pending_count
from orders o
join products p on o.product_id = p.product_id
group by p.category;
View
- 실제 데이터를 가지고 있지 않는 가상의 테이블이다
- 바로가기 아이콘이라고 생각하면 된다
- 데이터를 저장하는 테이블이 아니라
SELECT 쿼리문 자체를 저장하고 있어 select * from 나의_바로가기_뷰;라는 명령만으로 쿼리의 결과를 얻을 수 있다
- 뷰는 데이터를 저장하지 않기 때문에 최신 상태의 원본 테이블을 기준으로 쿼리가 실행된다
create view v_category_order_status as
select
count(*) as total_orders,
sum(case when status = 'COMPLETED' then 1 else 0 end) as completed_count,
sum(case when status = 'SHIPPED' then 1 else 0 end) as shipped_count,
sum(case when status = 'PENDING' then 1 else 0 end) as pending_count
from orders o
join products p on o.product_id = p.product_id
group by p.category;
select * from v_category_order_status;
select * from v_category_order_status
where category = '전자기기';
alter view v_category_order_status
select
u.name as user_name,
count(o.order_id) as total_orders,
sum(case when p.category = '전자기기' then 1 else 0 end) as electoronics_orders,
sum(case when p.category = '도서' then 1 else 0 end) as electoronics_orders,
sum(case when p.category = '패션' then 1 else 0 end) as electoronics_orders
from users u
left join orders o on u.user_id = o.user_id
left join products p on o.product_id = p.product_id
group by u.name
drop view v_category_order_status
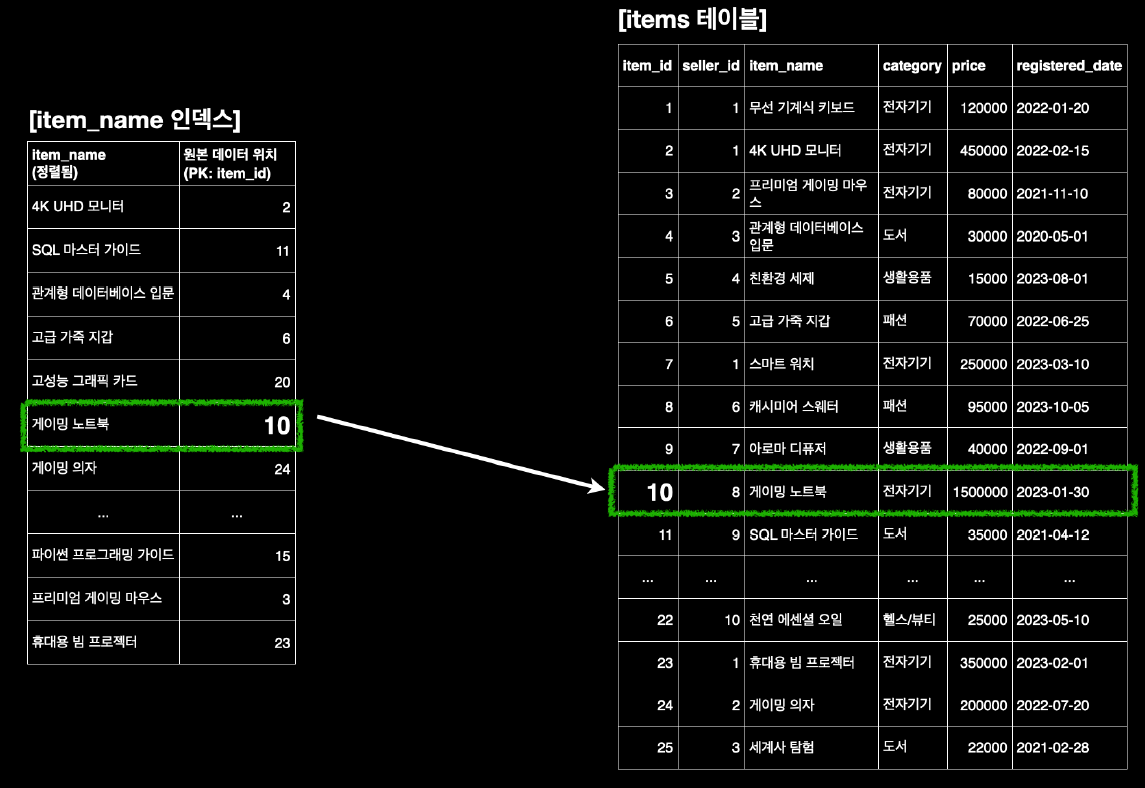
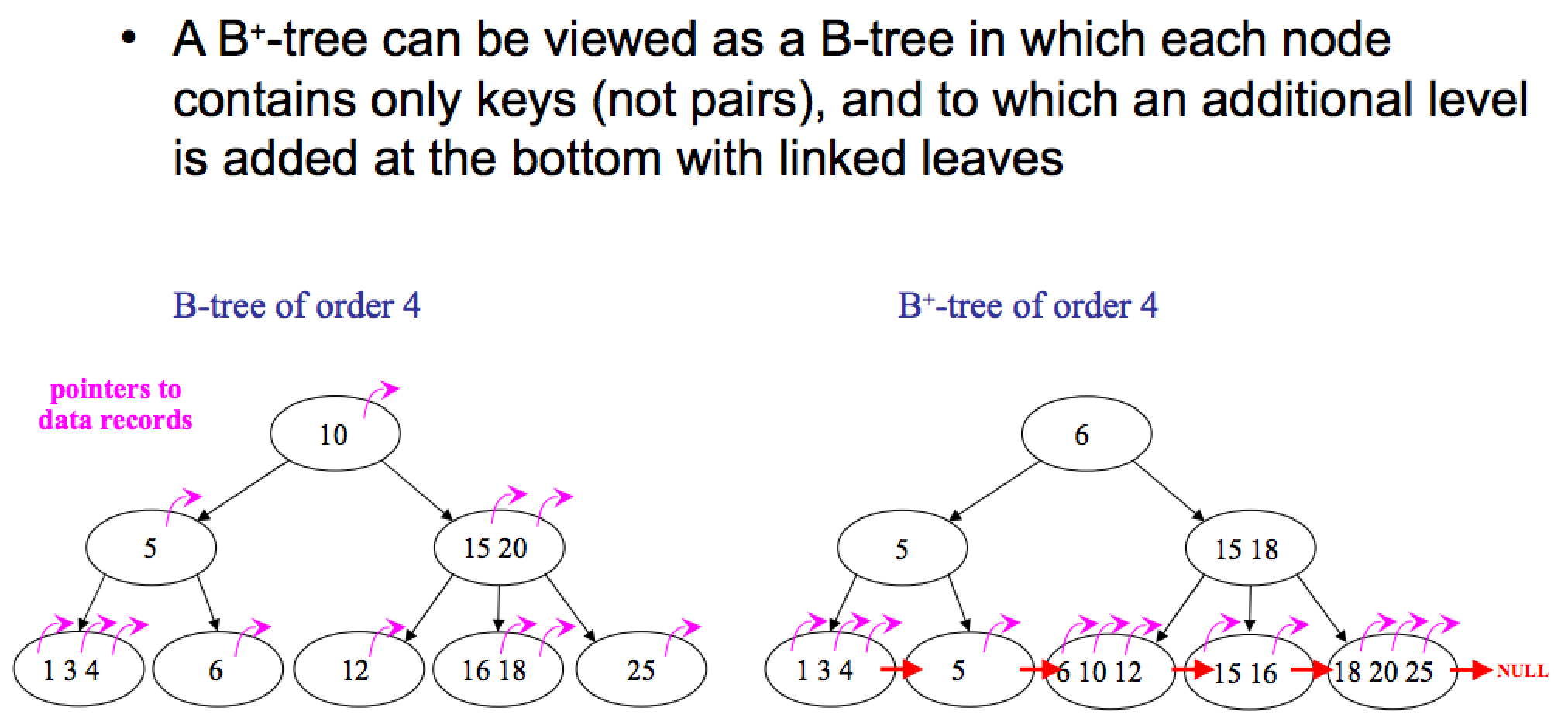
Index
- 특정 컬럼의 데이터를 기반으로 생성되는, 원본 데이블과는 별개의 특수한 자료구조이다
- 인덱스는 이진트리 중 하나인 B-Tree+를 사용하고 있다
- 이로 인해 시간 복잡도가 O(log N)으로 줄어든다."
create index idx_items_item_name on items(item_name);
show index from items
drop index idx_items_item_name on items;




