A Mazing Problem:
- a maze is represented as a two-dimensional array
- The location of the rat in the maze can at any time be descrived by the row and column position.
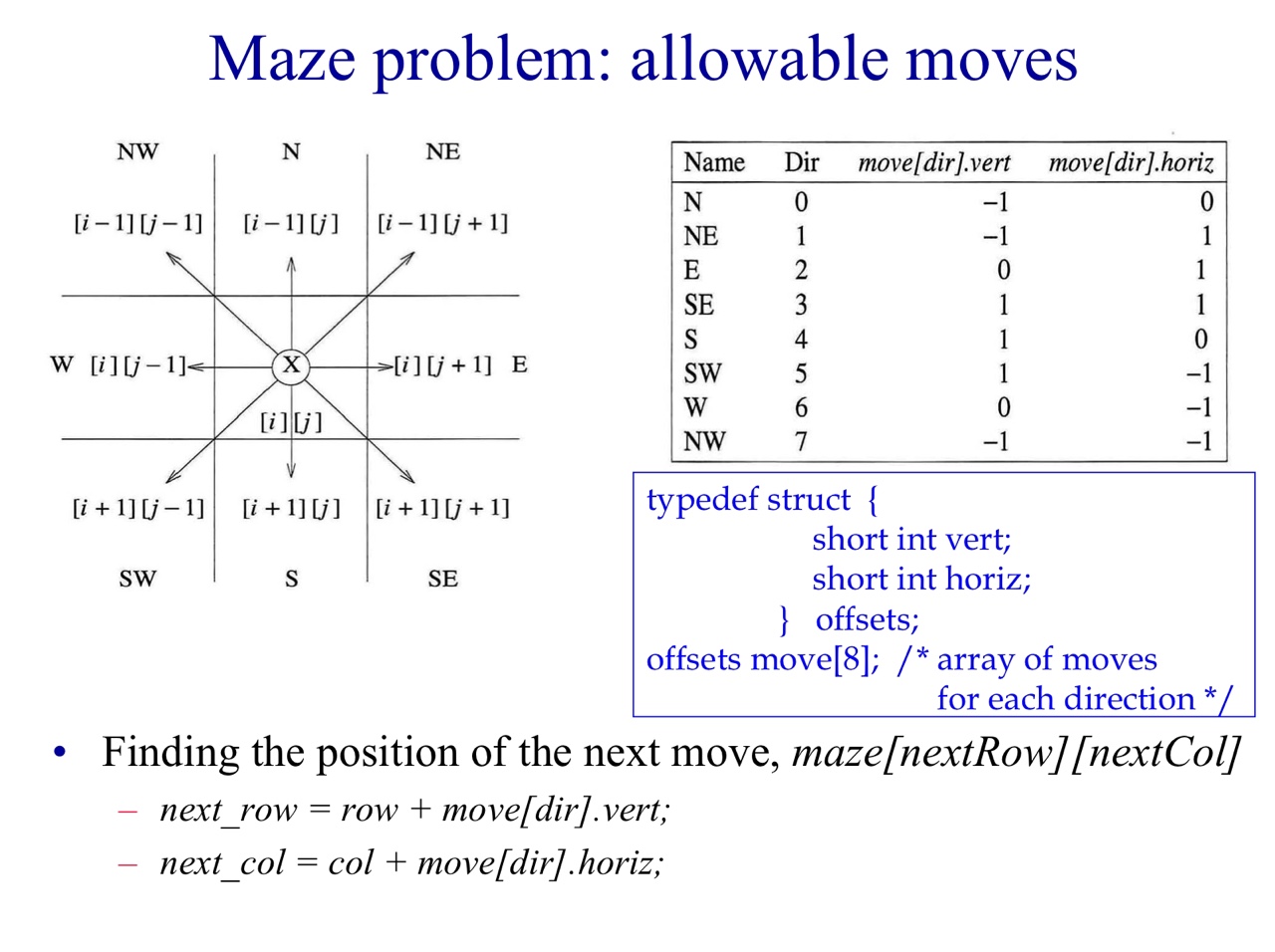
- We use compass points to specify the eight directions of movement.
N, NE, E, SE, S, SW, W, NW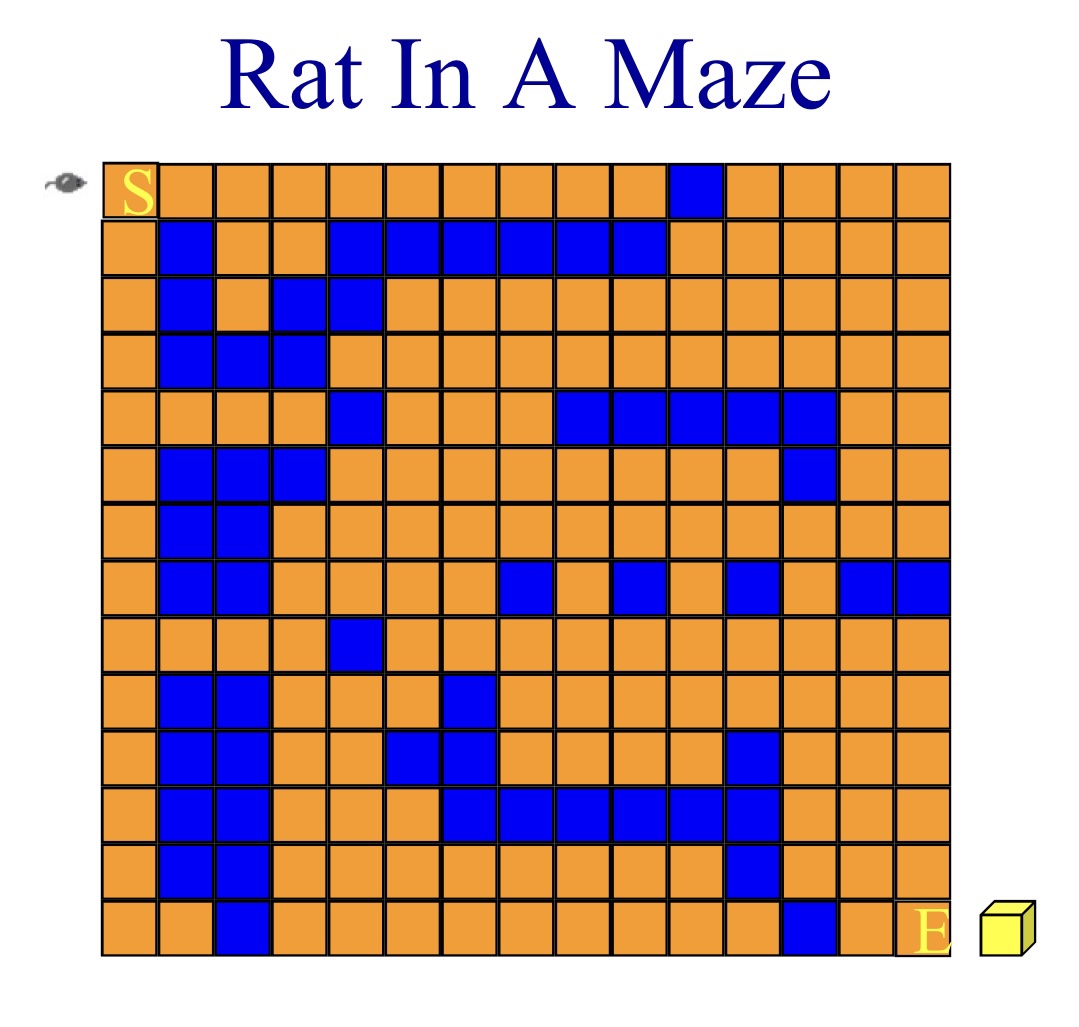
움직임 순서(Move order): 오른쪽, 아래, 왼쪽, 위
#include <iostream>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <string>
#define MAX_STACK_SIZE 100
using namespace std;
FILE* fp = NULL;
int top = 0;
typedef struct {
short int vert;
short int horiz;
} offsets;
offsets mv[8];
void assign(offsets move[]) { //방향 할당하는 매서드
move[0].vert = -1; move[0].horiz = 0;
move[1].vert = -1; move[1].horiz = 1;
move[2].vert = 0; move[2].horiz = 1;
move[3].vert = 1; move[3].horiz = 1;
move[4].vert = 1; move[4].horiz = 0;
move[5].vert = 1; move[5].horiz = -1;
move[6].vert = 0; move[6].horiz = -1;
move[7].vert = -1; move[7].horiz = -1;
}
typedef struct {
short int row;
short int col;
short int dir;
}element;
element stack[MAX_STACK_SIZE];
void stackFull() {
fprintf(stderr, "Stack is Full, cannot add element");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
element stackEmpty() {
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
void push(element item) {
if (top >= MAX_STACK_SIZE - 1)
stackFull();
stack[++top] = item;
}
element pop(element stack[]) {
if (top == -1)
return stackEmpty();
return stack[top--];
}
void path(int s, int t, int EXIT_ROW, int EXIT_COL){
/* output a path through the maze if such a path
exists */
/* mark[][] are initialized with 0 */
int i, row, col, next_row, next_col, dir; bool found = false;
int maze[7][7]; int mark[5][5]; string output[7][7];
assign(mv);
fopen_s(&fp, "in.txt", "r");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
mark[i][j] = 0;
}
} //mark 초기화
for (int i = 0; i < 7; i++) {
maze[0][i] = 1; maze[6][i] = 1;
maze[i][0] = 1; maze[i][6] = 1;
}//maze 테두리 초기화
for (int i = 1; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 6; j++) {
fscanf_s(fp, "%d", &maze[i][j]);
output[i - 1][j - 1] = to_string(maze[i][j]);
}
}//maze 초기화
maze[s][t] = 0; maze[EXIT_ROW][EXIT_COL] = 0;
element position;
mark[s - 1][t - 1] = 1;
stack[0].row = s; stack[0].col = t; stack[0].dir = 0;
while (top > -1 && !found) {
position = pop(&stack[top]); // stack은 maze 주소
row = position.row;
col = position.col;
dir = position.dir;
while (dir < 8 && !found) {
/* move in direction dir */
next_row = row + mv[dir].vert;
next_col = col + mv[dir].horiz;
if (next_row == EXIT_ROW && next_col == EXIT_COL) {
mark[next_row - 1][next_col - 1] = 1;
position.row = row; position.col = col;
position.dir = ++dir; push(position);
row = next_row; col = next_col; dir = 0;
found = true;
}
else if (!maze[next_row][next_col] && !mark[next_row - 1][next_col - 1]) {
mark[next_row - 1][next_col - 1] = 1;
position.row = row; position.col = col;
position.dir = ++dir; push(position);
row = next_row; col = next_col; dir = 0;
}
else ++dir;
}
}
if (found) {
for (i = 0; i <= top; i++)
output[stack[i].row -1][stack[i].col - 1] = 'x';
output[EXIT_ROW-1][EXIT_COL-1]='x';
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++) {
cout << output[i][j] << " ";
}
printf("\n");
}
}
else printf("no path");
}
int main() {
int s = 0; int t = 0; int u = 0; int v = 0;
scanf_s("%d %d %d %d", &s, &t, &u, &v);
path(s, t, u, v); // 5 1 2 5
}


