구현전 테스트 결과
FAIL tests/userprog/args-none
FAIL tests/userprog/args-single
FAIL tests/userprog/args-multiple
FAIL tests/userprog/args-many
FAIL tests/userprog/args-dbl-space
FAIL tests/userprog/halt
FAIL tests/userprog/exit
FAIL tests/userprog/create-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/create-empty
FAIL tests/userprog/create-null
FAIL tests/userprog/create-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/create-long
FAIL tests/userprog/create-exists
FAIL tests/userprog/create-bound
FAIL tests/userprog/open-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/open-missing
FAIL tests/userprog/open-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/open-empty
FAIL tests/userprog/open-null
FAIL tests/userprog/open-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/open-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/close-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/close-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/close-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/read-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/read-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/read-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/read-zero
FAIL tests/userprog/read-stdout
FAIL tests/userprog/read-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/write-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/write-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/write-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/write-zero
FAIL tests/userprog/write-stdin
FAIL tests/userprog/write-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-once
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-multiple
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-recursive
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-read
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-close
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-once
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-arg
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-missing
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-read
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-killed
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-bad-pid
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-recurse
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-child-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-child
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-multichild
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-read
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-write
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-read2
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-write2
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-jump
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-jump2
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-create
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-full
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-create
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-full
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-read
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-write
FAIL tests/userprog/no-vm/multi-oom
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-single
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-multiple
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-priority
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-zero
FAIL tests/threads/alarm-negative
FAIL tests/threads/priority-change
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-one
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
FAIL tests/threads/priority-fifo
FAIL tests/threads/priority-preempt
FAIL tests/threads/priority-sema
FAIL tests/threads/priority-condvar
FAIL tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
95 of 95 tests failed.intr_context 오류 수정
../userprog/에서 make check를 하니까
기존에 ../threads/에서 해결한 테스트 케이스도 fail이 나오길래
오류메시지를 읽어보니 thread.c의 thread_yield() 함수에서
intr_context() fail이 나왔다. 그래서 thread_yield 내부 실행코드를
외부 인터럽트가 실행 중이면 실행하지 않도록 변경했다.
내장함수인 intr_context()를 사용했는데
이 함수는 외부 인터럽트가 실행 중이면 true를 반환하고
그 이외에 경우에는 false를 반환한다.
그래서 if(!intr_context())으로 감싸면 외부 인터럽트가 실행 중이
아닐 때에만 thread_yield의 함수를 실행하겠다는 의미다.
../threads/thread.c

/* Yields the CPU. The current thread is not put to sleep and
may be scheduled again immediately at the scheduler's whim. */
void
thread_yield (void) {
if(!intr_context()){
struct thread *curr = thread_current ();
enum intr_level old_level;
ASSERT (!intr_context ());
old_level = intr_disable ();
if (curr != idle_thread)
list_insert_ordered(&ready_list, &curr->elem,
get_higher_priority, NULL);
do_schedule (THREAD_READY);
intr_set_level (old_level);
}
}FAIL tests/userprog/args-none
FAIL tests/userprog/args-single
FAIL tests/userprog/args-multiple
FAIL tests/userprog/args-many
FAIL tests/userprog/args-dbl-space
FAIL tests/userprog/halt
FAIL tests/userprog/exit
FAIL tests/userprog/create-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/create-empty
FAIL tests/userprog/create-null
FAIL tests/userprog/create-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/create-long
FAIL tests/userprog/create-exists
FAIL tests/userprog/create-bound
FAIL tests/userprog/open-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/open-missing
FAIL tests/userprog/open-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/open-empty
FAIL tests/userprog/open-null
FAIL tests/userprog/open-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/open-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/close-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/close-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/close-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/read-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/read-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/read-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/read-zero
FAIL tests/userprog/read-stdout
FAIL tests/userprog/read-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/write-normal
FAIL tests/userprog/write-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/write-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/write-zero
FAIL tests/userprog/write-stdin
FAIL tests/userprog/write-bad-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-once
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-multiple
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-recursive
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-read
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-close
FAIL tests/userprog/fork-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-once
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-arg
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-boundary
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-missing
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-bad-ptr
FAIL tests/userprog/exec-read
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-twice
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-killed
FAIL tests/userprog/wait-bad-pid
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-recurse
FAIL tests/userprog/multi-child-fd
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-simple
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-child
FAIL tests/userprog/rox-multichild
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-read
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-write
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-read2
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-write2
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-jump
FAIL tests/userprog/bad-jump2
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-create
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-full
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-block
FAIL tests/filesys/base/lg-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-create
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-full
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-block
FAIL tests/filesys/base/sm-seq-random
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-read
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-remove
FAIL tests/filesys/base/syn-write
FAIL tests/userprog/no-vm/multi-oom
pass tests/threads/alarm-single
pass tests/threads/alarm-multiple
pass tests/threads/alarm-simultaneous
pass tests/threads/alarm-priority
pass tests/threads/alarm-zero
pass tests/threads/alarm-negative
pass tests/threads/priority-change
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-one
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-multiple2
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-nest
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-lower
pass tests/threads/priority-fifo
pass tests/threads/priority-preempt
pass tests/threads/priority-sema
pass tests/threads/priority-condvar
pass tests/threads/priority-donate-chain
77 of 95 tests failed.thread_yield()함수를 외부 인터럽트가 실행 중이지 않은 경우에만
동작하도록 구현하니 기존 Project 1에서 통과했던 테스트들이 전부 pass했다.
구현 step 1
그러면 이제 본격적으로 Project 2를 차근차근 구현해보자.
테스트 코드 실행해보기
pintos --fs-disk=10 -p tests/userprog/args-
single:args-single -- -q -f run 'args-single one(root는 PintOS 깃을 클론한 루트 디렉토리를. 이름에 맞게 바꿔주자)
../root/userprog/$ make
위 명령어로 빌드를 하면 userprog/build 디렉토리가 생성된다.
../root/userprog$ cd build
../root/userprog/build$ pintos --fs-disk=10 -p tests/userprog/args-
single:args-single -- -q -f run 'args-single one
-> 테스트를 해주자.
테스트 결과
qemu-system-x86_64: warning: TCG doesn't support requested feature: CPUID.01H:ECX.vmx [bit 5]
Kernel command line: -q -f put args-single run 'args-single onearg'
0 ~ 9fc00 1
100000 ~ ffe0000 1
Pintos booting with:
base_mem: 0x0 ~ 0x9fc00 (Usable: 639 kB)
ext_mem: 0x100000 ~ 0xffe0000 (Usable: 260,992 kB)
Calibrating timer... 314,163,200 loops/s.
hd0:0: detected 313 sector (156 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00001"
hd0:1: detected 20,160 sector (9 MB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00002"
hd1:0: detected 102 sector (51 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00003"
Formatting file system...done.
Boot complete.
Putting 'args-single' into the file system...
Executing 'args-single onearg':
Execution of 'args-single onearg' complete.
Timer: 58 ticks
Thread: 33 idle ticks, 25 kernel ticks, 0 user ticks
hd0:0: 0 reads, 0 writes
hd0:1: 34 reads, 232 writes
hd1:0: 102 reads, 0 writes
Console: 821 characters output
Keyboard: 0 keys pressed
Exception: 0 page faults
Powering off...테스트 출력 결과 중에서 크게 3가지 포인트가 인상적이었다.
Putting 'args-single' into the file system...
Executing 'args-single onearg':
Execution of 'args-single onearg' complete.
뭔가 printf을 실행하면서
Putting '%s'
Executing '%s'
Execution '%s'
이런 모양으로 나올 것 같아서 cmd+shift+F로 전체 검색해봤다.
../root/filesys/fsutil.c 파일 안에서 fsutil_put()에서
printf ("Putting '%s' into the file system...\n", file_name);가 있었고
../root/threads/init.c 파일 안에서 run_task()안에서
printf ("Executing '%s':\n", task);
printf ("Execution of '%s' complete.\n", task);가 있었다.
process_wait 수정하고 테스트
int
process_wait (tid_t child_tid UNUSED) {
/* XXX: Hint) The pintos exit if process_wait (initd), we recommend you
* XXX: to add infinite loop here before
* XXX: implementing the process_wait. */
while(1){};
return -1;
}-> 주석을 읽어보니까 일단은 무한루프를 추가하라는 의미로 받아들여서
무한루프가 되도록 변경해주고 테스트를 해봤다.
테스트 1: process_wait에 무한루프 추가
qemu-system-x86_64: warning: TCG doesn't support requested feature: CPUID.01H:ECX.vmx [bit 5]
Kernel command line: -q -f put args-single run 'args-single onearg'
0 ~ 9fc00 1
100000 ~ ffe0000 1
Pintos booting with:
base_mem: 0x0 ~ 0x9fc00 (Usable: 639 kB)
ext_mem: 0x100000 ~ 0xffe0000 (Usable: 260,992 kB)
Calibrating timer... 314,163,200 loops/s.
hd0:0: detected 313 sector (156 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00001"
hd0:1: detected 20,160 sector (9 MB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00002"
hd1:0: detected 102 sector (51 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00003"
Formatting file system...done.
Boot complete.
Putting 'args-single' into the file system...
Executing 'args-single onearg':
load: args-single onearg: open failed
Kernel PANIC at ../../userprog/process.c:71 in initd(): Fail to launch initd
Call stack: 0x800421877e 0x800421bdef 0x8004207b09.
The `backtrace' program can make call stacks useful.
Read "Backtraces" in the "Debugging Tools" chapter
of the Pintos documentation for more information.
Timer: 129 ticks
Thread: 31 idle ticks, 98 kernel ticks, 0 user ticks
hd0:0: 0 reads, 0 writes
hd0:1: 51 reads, 232 writes
hd1:0: 102 reads, 0 writes
Console: 1100 characters outputprocess_wait()함수에 무한루프를 추가했을 때랑 안 했을 때 테스트 결과를 비교해봤다.
무한루프를 추가하니 커널 패닉이 발생했다.

static bool load(...)
/* Open executable file. */
file = filesys_open (file_name);
if (file == NULL) {
printf ("load: %s: open failed\n", file_name);
goto done;
}즉 다시 말해서 아까 얘기한 테스트는
load: args-single onearg: open failed 메시지가 나타나며
file_name에 "args-single onearg"가
들어가고 있었다. 근데 "args-single"은 파일 이름이고 "onearg"는 인자이므로
file_name에 "args-single"만 들어가도록 해줘야한다.
어떻게 문자열을 파싱할까 고민하니 마침 pdf에 어떤 라이브러리를 써야하는지 적혀있었다.
바로 'strtok_r'라는 "lib/string.c"라이브러리다.
이번 글에서는 load()를 따로 수정하지는 않는다.
다만 int process_exec()속에서 success = load (parse[0], &_if);
에서 load() 첫번째 인자에 "args-single"만 들어가야한다는 점이 중요하다.
Parameter passing
• User strtok_r in lib/string.c to break “char *file_name” into command line and arguments
• /bin/ls –l foo bar à “/bin/ls”, “-l”, “foo”, ”bar” • Put the arguments onto the user-level stack
• You must follow calling convention (ABI)아래는 이 함수의 전체 코드이다.
static bool
load (const char *file_name, struct intr_frame *if_) {
struct thread *t = thread_current ();
struct ELF ehdr;
struct file *file = NULL;
off_t file_ofs;
bool success = false;
int i;
/* Allocate and activate page directory. */
t->pml4 = pml4_create ();
if (t->pml4 == NULL)
goto done;
process_activate (thread_current ());
/* Open executable file. */
file = filesys_open (file_name);
if (file == NULL) {
printf ("load: %s: open failed\n", file_name);
goto done;
}
/* Read and verify executable header. */
if (file_read (file, &ehdr, sizeof ehdr) != sizeof ehdr
|| memcmp (ehdr.e_ident, "\177ELF\2\1\1", 7)
|| ehdr.e_type != 2
|| ehdr.e_machine != 0x3E // amd64
|| ehdr.e_version != 1
|| ehdr.e_phentsize != sizeof (struct Phdr)
|| ehdr.e_phnum > 1024) {
printf ("load: %s: error loading executable\n", file_name);
goto done;
}
/* Read program headers. */
file_ofs = ehdr.e_phoff;
for (i = 0; i < ehdr.e_phnum; i++) {
struct Phdr phdr;
if (file_ofs < 0 || file_ofs > file_length (file))
goto done;
file_seek (file, file_ofs);
if (file_read (file, &phdr, sizeof phdr) != sizeof phdr)
goto done;
file_ofs += sizeof phdr;
switch (phdr.p_type) {
case PT_NULL:
case PT_NOTE:
case PT_PHDR:
case PT_STACK:
default:
/* Ignore this segment. */
break;
case PT_DYNAMIC:
case PT_INTERP:
case PT_SHLIB:
goto done;
case PT_LOAD:
if (validate_segment (&phdr, file)) {
bool writable = (phdr.p_flags & PF_W) != 0;
uint64_t file_page = phdr.p_offset & ~PGMASK;
uint64_t mem_page = phdr.p_vaddr & ~PGMASK;
uint64_t page_offset = phdr.p_vaddr & PGMASK;
uint32_t read_bytes, zero_bytes;
if (phdr.p_filesz > 0) {
/* Normal segment.
* Read initial part from disk and zero the rest. */
read_bytes = page_offset + phdr.p_filesz;
zero_bytes = (ROUND_UP (page_offset + phdr.p_memsz, PGSIZE)
- read_bytes);
} else {
/* Entirely zero.
* Don't read anything from disk. */
read_bytes = 0;
zero_bytes = ROUND_UP (page_offset + phdr.p_memsz, PGSIZE);
}
if (!load_segment (file, file_page, (void *) mem_page,
read_bytes, zero_bytes, writable))
goto done;
}
else
goto done;
break;
}
}
/* Set up stack. */
if (!setup_stack (if_))
goto done;
/* Start address. */
if_->rip = ehdr.e_entry;
/* TODO: Your code goes here.
* TODO: Implement argument passing (see project2/argument_passing.html). */
success = true;
done:
/* We arrive here whether the load is successful or not. */
file_close (file);
return success;
}process.c
tid_t process_create_initd (...)
thread_create (file_name,...)에서 file_name에
입력이 "args-single onearg"이면 file_name에 "args-single"이 들어가도록 실행해줘야한다. Instruction에서 권장하는대로 strtok_r() 함수를 사용해서 file_name에 " "로 구분한 토큰 "args-single"을 넣어줬다.
file_name = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &save_ptr);
/* Create a new thread to execute FILE_NAME. */
tid = thread_create (file_name, PRI_DEFAULT, initd, fn_copy);
여기서 file_name에는 "args-single"이 들어가고
initd에 fn_copy가 들어가게 된다.
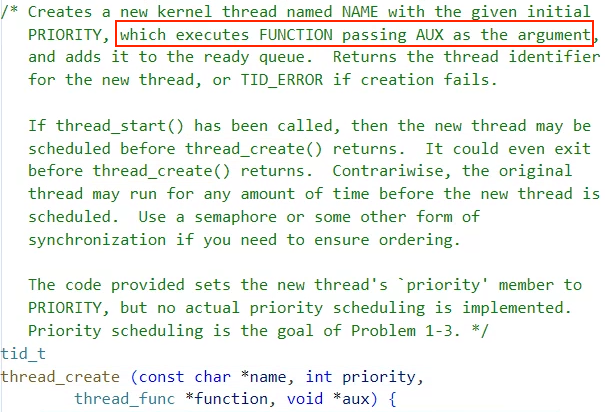
그 근거가 함수 설명에 나와있는데 function==initd이고 AUX가 fn_copy이고
이게 AUX가 FUNCTION의 인자로 들어가서 실행한다고 한다.
/* 프로세스(스레드) 생성 함수를 호출하고 tid 리턴
pdf의 process_execute와 같다.*/
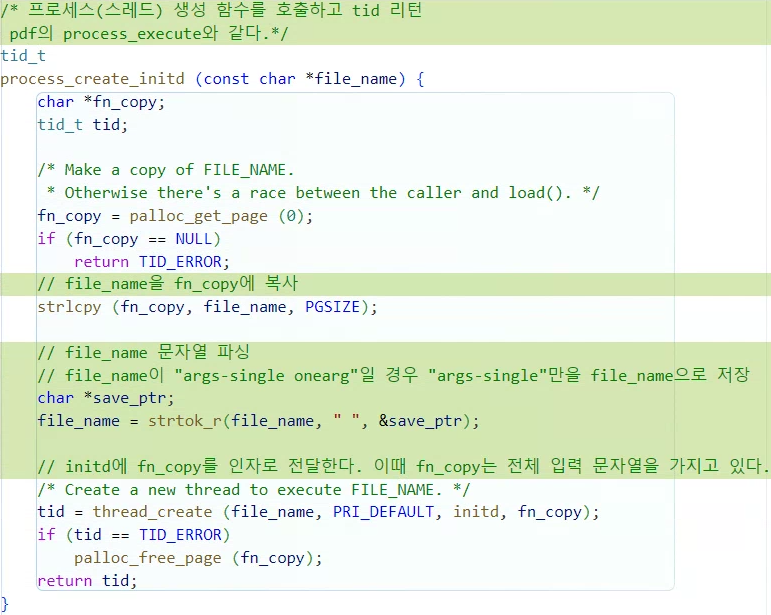
tid_t
process_create_initd (const char *file_name) {
char *fn_copy;
tid_t tid;
/* Make a copy of FILE_NAME.
* Otherwise there's a race between the caller and load(). */
fn_copy = palloc_get_page (0);
if (fn_copy == NULL)
return TID_ERROR;
// file_name을 fn_copy에 복사
strlcpy (fn_copy, file_name, PGSIZE);
// file_name 문자열 파싱
// file_name이 "args-single onearg"일 경우 "args-single"만을 file_name으로 저장
char *save_ptr;
file_name = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &save_ptr);
// initd에 fn_copy를 인자로 전달한다. 이때 fn_copy는 전체 입력 문자열을 가지고 있다.
/* Create a new thread to execute FILE_NAME. */
tid = thread_create (file_name, PRI_DEFAULT, initd, fn_copy);
if (tid == TID_ERROR)
palloc_free_page (fn_copy);
return tid;
}int process_exec (...)
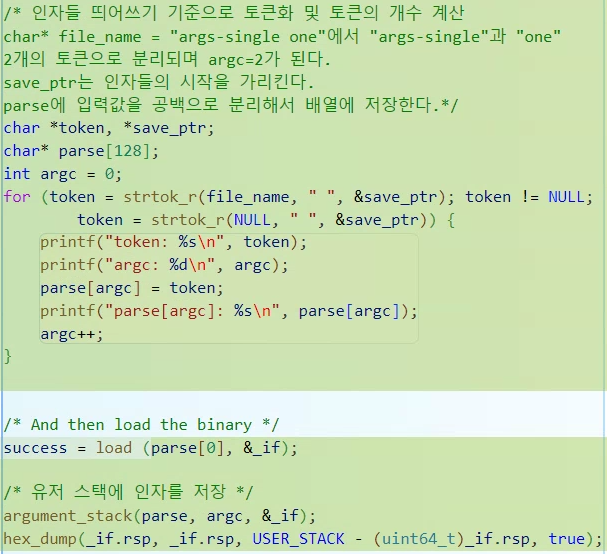
추가한 부분은 입력한 태스크를 분리해서 "args-single onearg"을 파싱해서
" "으로 분리한 토큰들을 parse[128]에 저장하고, argc에 토큰의 갯수를 저장해준다.
이렇게 저장했을 때 parse[0]은 파일 이름인 "args-single"을 가리키게 된다.
파일 이름을 load()에 넣어서 불러오고
argument_stack(parse, argc, &_if);
-> 유저 스택에 인자를 저장하는 함수이다.
hex_dump(_if.rsp, _if.rsp, USER_STACK - (uint64_t)_if.rsp, true);
-> USER_STACK에 저장한 데이터를 출력하는 함수로 런타임 디버그를 하는데 사용된다.
int
process_exec (void *f_name) { // pdf의 start_process와 같다.
char *file_name = f_name;
bool success;
/* We cannot use the intr_frame in the thread structure.
* This is because when current thread rescheduled,
* it stores the execution information to the member. */
struct intr_frame _if;
_if.ds = _if.es = _if.ss = SEL_UDSEG;
_if.cs = SEL_UCSEG;
_if.eflags = FLAG_IF | FLAG_MBS;
/* We first kill the current context */
process_cleanup ();
/* 인자들 띄어쓰기 기준으로 토큰화 및 토큰의 개수 계산
char* file_name = "args-single one"에서 "args-single"과 "one"
2개의 토큰으로 분리되며 argc=2가 된다.
save_ptr는 인자들의 시작을 가리킨다.
parse에 입력값을 공백으로 분리해서 배열에 저장한다.*/
char *token, *save_ptr;
char* parse[128];
int argc = 0;
for (token = strtok_r(file_name, " ", &save_ptr); token != NULL;
token = strtok_r(NULL, " ", &save_ptr)) {
printf("token: %s\n", token);
printf("argc: %d\n", argc);
parse[argc] = token;
printf("parse[argc]: %s\n", parse[argc]);
argc++;
}
/* And then load the binary */
success = load (parse[0], &_if);
/* 유저 스택에 인자를 저장 */
argument_stack(parse, argc, &_if);
hex_dump(_if.rsp, _if.rsp, USER_STACK - (uint64_t)_if.rsp, true);
/* If load failed, quit. */
palloc_free_page (file_name);
if (!success)
return -1;
/* Start switched process. */
do_iret (&_if);
NOT_REACHED ();
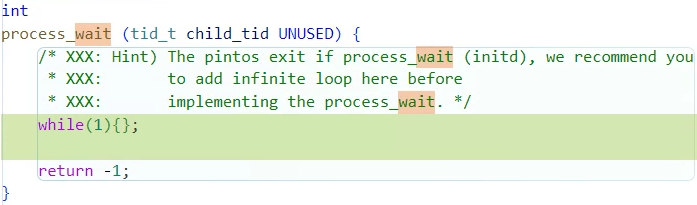
}int process_wait (...)
자식 프로세스가 종료될 때까지 대기하는 함수다.
주석에 적힌대로 일단은 무한루프로 구현해두고 테스트를 진행했다.
이렇게 되어있으면 한 번 실행하고 무한루프가 되지만 일단 테스트는 진행된다.
int
process_wait (tid_t child_tid UNUSED) {
/* XXX: Hint) The pintos exit if process_wait (initd), we recommend you
* XXX: to add infinite loop here before
* XXX: implementing the process_wait. */
while(1){};
return -1;
}static void argument_stack(...)
유저 스택에 파싱된 토큰을 저장하는 함수로 새로 만들어줘야한다.
이 함수가 하는 일을 쉽게 말하면 유저프로그램 스택에 데이터를 넣어주는 일인데
- 인자의 문자열을 넣어준다.
- 문자열을 가리키는 주소를 넣는다.
- 인자들의 갯수 argc와 인자들의 배열을 가리키는 포인터 argv를 담는다.
- 실행을 마치고 되돌아갈 함수의 주소를 적는다.
여기서 실행하는 함수는 main()이므로 fake address인 NULL 또는 0을 적어준다.
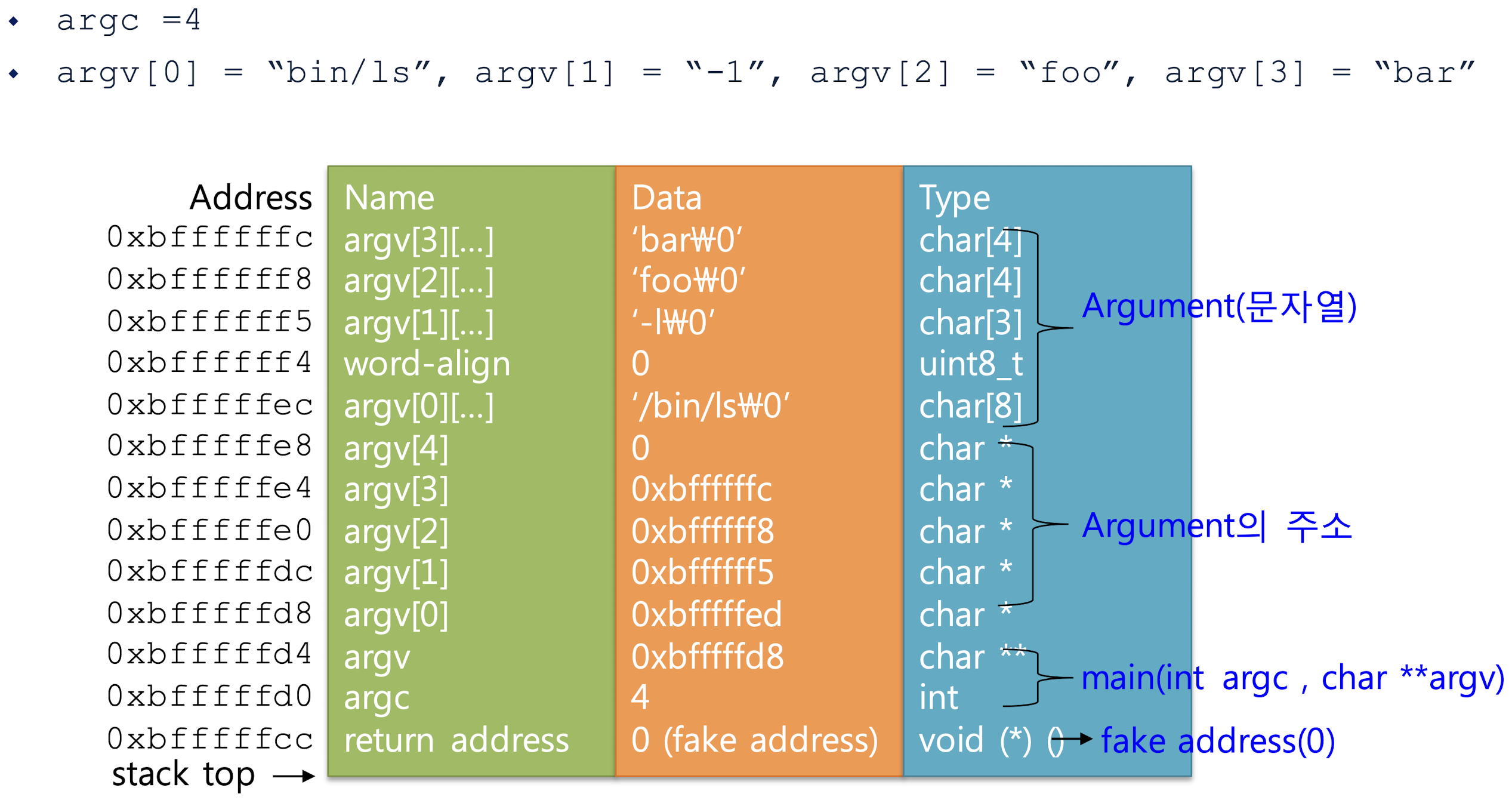
ABI Code Convention에 따라 64비트 레지스터 rdi, rsi에 각각 argc, argv를 저장해주자.여기서 argc = argument count, argv = argument vector를 뜻한다.
함수 원형 static void argument_stack(char** argv, int argc, struct intr_frame* _if)도 맨위에 적어주자.
/* 유저 스택에 파싱된 토큰을 저장하는 함수 구현*/
static void
argument_stack(char** argv, int argc, struct intr_frame* _if){
char *arg_address[128];
/* 인자들을 스택에 삽입*/
for(int i=argc-1;i>-1;i--){
//스택 주소 감소
int input_argv_length = strlen(argv[i])+1; // memcpy에서 종료문자"\0"까지 포함하기 위해 +1
_if->rsp -= input_argv_length;
// 스택 데이터 넣기
memcpy(_if->rsp, argv[i], input_argv_length); // rsp에 argv[i] 복사 (input_argv_length만큼)
arg_address[i] = _if->rsp; // arg_address[i]에 인자의 시작주소 저장
}
/* WORD 크기에 맞도록 8배수의 크기를 만족하는 padding 추가 */
int padding = (_if->rsp)%8; // rsp가 8의 배수가 되도록 padding 계산
for(int i=padding;i>=0;i--){
_if->rsp -= sizeof(char); // rsp를 1바이트씩 감소
*(uint8_t*)_if->rsp = 0; // 데이터 0을 넣어서 padding
}
/* 줄바꿈 문자(sentinel) "\n"를 포함한 문자열의 주소를 삽입 */
for(int i=argc-1;i>=0;i--){
_if->rsp -= sizeof(char*); // rsp를 8바이트씩 감소
*(char**)_if->rsp = arg_address[i]; // rsp에 arg_address[i] 저장
}
/* fake address 삽입: argv의 끝을 나타낸다. */
_if->rsp -= sizeof(char*); // rsp를 8바이트씩 감소
*(char**)_if->rsp = 0; // rsp에 0 저장
/* argv 주소 삽입 */
_if->R.rdi = argc; // Code Convention ABI에 따라 rdi에 argc 저장
_if->R.rsi = _if->rsp + sizeof(char*); // rsp에 저장된 주소를 rsi에 저장
}테스트 2
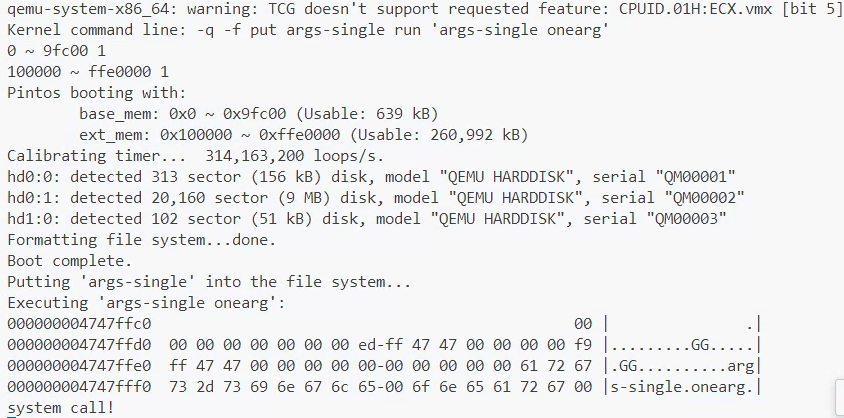
pintos --fs-disk=10 -p tests/userprog/args-single:args-single -- -q -f run 'args-single onearg'를 실행해서 테스트 결과를 확인하자.
qemu-system-x86_64: warning: TCG doesn't support requested feature: CPUID.01H:ECX.vmx [bit 5]
Kernel command line: -q -f put args-single run 'args-single onearg'
0 ~ 9fc00 1
100000 ~ ffe0000 1
Pintos booting with:
base_mem: 0x0 ~ 0x9fc00 (Usable: 639 kB)
ext_mem: 0x100000 ~ 0xffe0000 (Usable: 260,992 kB)
Calibrating timer... 314,163,200 loops/s.
hd0:0: detected 313 sector (156 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00001"
hd0:1: detected 20,160 sector (9 MB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00002"
hd1:0: detected 102 sector (51 kB) disk, model "QEMU HARDDISK", serial "QM00003"
Formatting file system...done.
Boot complete.
Putting 'args-single' into the file system...
Executing 'args-single onearg':
000000004747ffc0 00 | .|
000000004747ffd0 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 ed-ff 47 47 00 00 00 00 f9 |.........GG.....|
000000004747ffe0 ff 47 47 00 00 00 00 00-00 00 00 00 00 61 72 67 |.GG..........arg|
000000004747fff0 73 2d 73 69 6e 67 6c 65-00 6f 6e 65 61 72 67 00 |s-single.onearg.|
system call!hex_dump()로 인자들이 제대로 담겨서 출력되고
system call!이 출력되며 무한루프가 발생하면 제대로 구현이 된 것이다.
다음장에서는 system call!