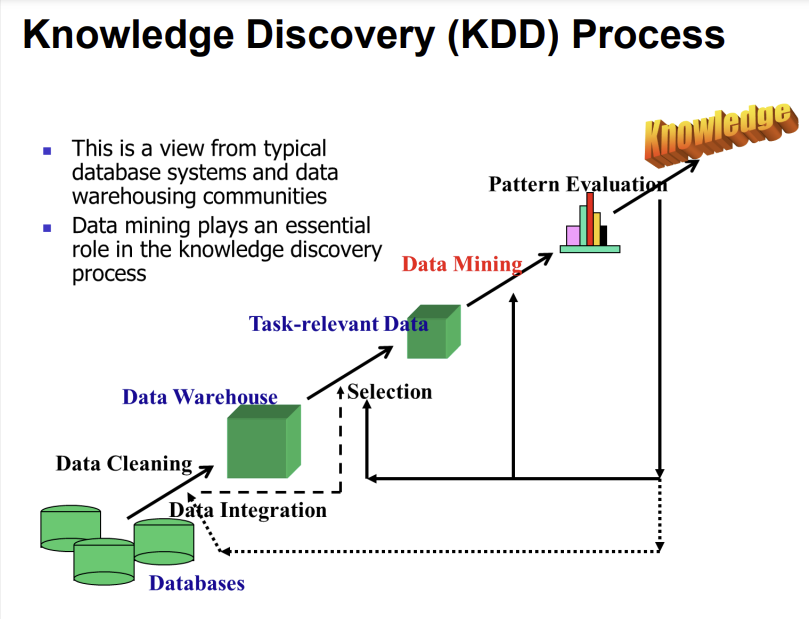
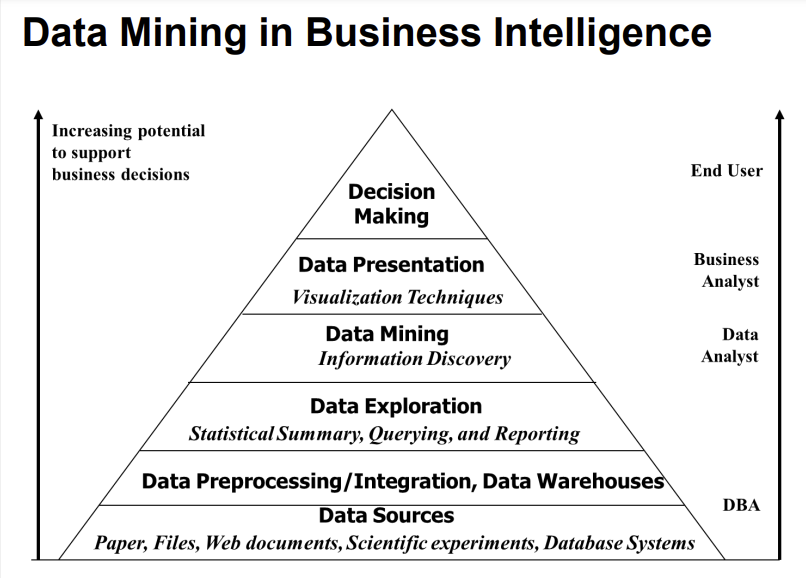
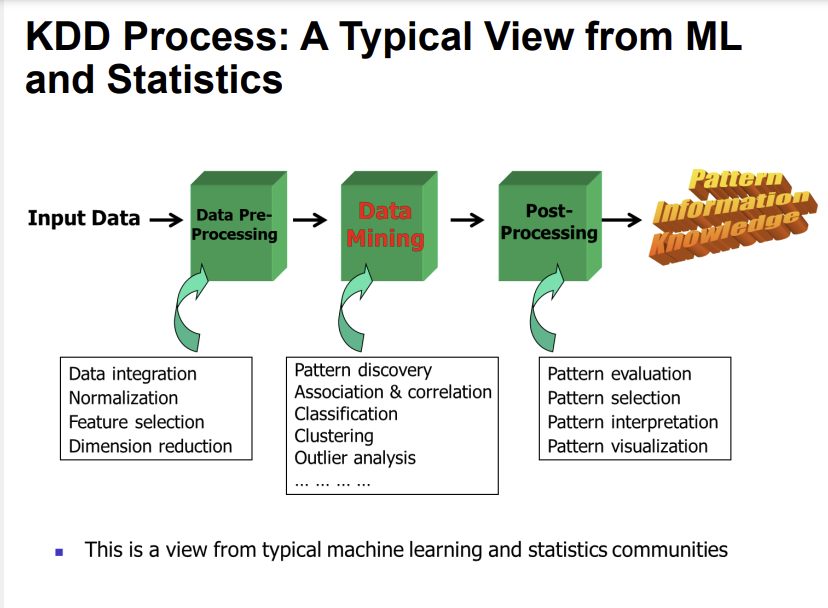
데이터마이닝의 chapter는 고려대 세종캠퍼스 해당 강의자료 챕터대로 정리했음을 알린다.
또한, 해당 강의자료에 대한 저작권 동의는 해당 교수님으로부터 승인을 받았음을 알린다.
Chapter 1. Introduction to Data Mining
Q.What is data mining?
Data Mining is the use of efficient techniques for the 'analysis' of 'very large collection of data' and the 'extraction' of 'useful and possibly unexpected patterns in data'.
->데이터마이닝은 매우 큰 양의 데이터들 모음집의 분석에 관한 효율적인 기술들을 의미하고 데이터에서 쓸모있고 가능한 예측되지 않은 패턴들의 추출을 의미한다.Big data==Data mining==Artificially Intelligence==Machine Learning==Statistical analysis
Q.Why do we need data mining?
Need to analyze the a lot of raw data to extract knowledgeThe data is the computer -> Large amounts of data can be more powerful than complex algorithms and models.
->Google has solved many Natural Language Processing problems, simply by looking at the data.Data is power! -> Today, the collected data is one of the biggest assets of an online company.
We need a way to harness the 'collective intelligence'.
The data is also very 'complex'.
-> Multiple types of data: tables,time series(시간에 흐름에 따라 기록된 데이터의 연속),images,graphs,etc...
->Spatial(공간의) and temporal(시간의) aspects.
->Interconnected data of different types.
Examples of data
1.transaction data(거래내역 데이터) -> WALMART:20M transactions per day
2.document data -> Wikipedia: 4 million articles(and counting)
3.network data -> Facebook: 500 million users
4.genomic data -> 3 10^9 nucleotides per person -> 3 10^12 nucleotides(DNA와 RNA의 기본 구성 요소 중 하나, 세가지 부분으로 이루어진 분자)
5.Environmental data -> 6000 temperature stations, 7500 precipitation stations, 2000 pressure stations -> Spatiotemporal data(공간적,시간적 정보가 함께 포함된 데이터)
->station: 기상 관측을 위한 측기 장비의 설치 지점
6.Behavior data -> Mobile phones today record a large amount of information about the user behavior.
Q.What is data?
Collection of data 'objects' and their 'attributes'.An attribute is a property or characteristic of an object.
->Examples: eye color of a person,temperature,etc..
->Object is also known as 'record','point','case','sample','entity',or,'instance'.
->Attribute is also known as 'variable','field','characteristic',or,'feature'.
->보통 2차원 행렬로 생각하면, 가로(행)가 objects, 세로(열)가 'attributes'이다.
->size: number of objects
->Dimensionality: Number of attributes
->Sparsity(희소성): Number of populated object-attribute pairs
->populated: 해당 데이터의 특정 필드에서 실제로 값이 존재하는 것. 즉, 실제로 존재하는 것.
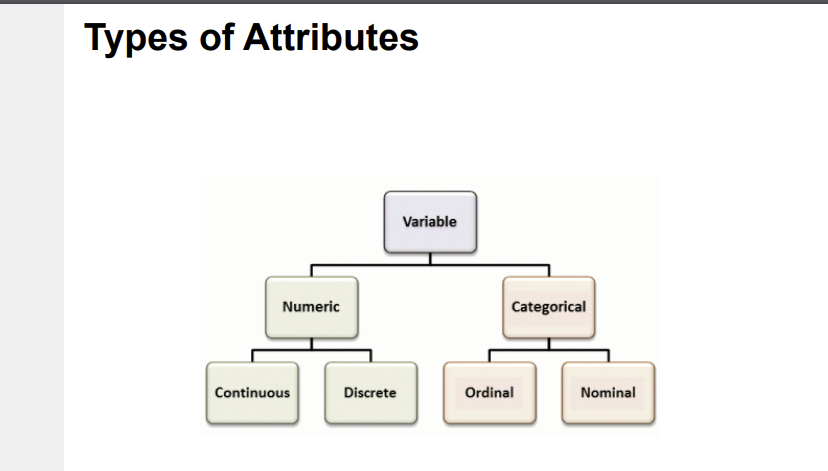
Types of Attributes
'Categorical' vs 'Numeric'*Categorial(범주형): Nominal(no order or comparision) vs Ordinal(order but not comparable).
->Nominal:명목형 데이터, ex)색상,동물 종류,혈액형 등
->Ordinal:순서형 데이터, ex)학점,만족도,등급 등
->Special case: Binary attributes(yes/no, exists,not exists)*Numeric(수치형): Discrete(counts,이산형) vs Continuous(연속형)
->Discrete: ex) 주사위 던지기 등
->Continuous: ex) 신장,체중,온도 등
Q.Why data mining?
1.Commercial point of view
->Data has become the key competitive advantage of companies.
->Being able to extract useful information out of data is key for exploiting them commercially.2.Scientific point of view
->Scientists are at an unprecedented(전례 없는) position where they can collect TB of information.
->We need the tools to analyze such data to get better understanding of the world and advance science.3.Scale(in data size and feature dimension)
->Why not use traditional analytic methods?
->Enormity of data(데이터 양의 막대함), curse of dimensionality(차원의 저주, 데이터의 차원이 늘어남에 따라 발생하는 문제).
->The amount and the complexity of data does not allow for manual processing of the data. We need 'automated' techniques.Data mining is the analysis of (often large)observation data sets to find 'unsuspected relationships(예상치 못했던 관계들)' and to 'summarize' the data in novel ways(새로운 방식으로) that are both 'understandable and useful' to the data analyst.
Data mining is the discovery of 'models' for data.
->Models that 'explain' the data
->Models that 'predict' the future data instances
->Models that 'summarize' the data
->Models that 'extract' the most prominent(중요한) 'features' of the data.
Q.What can we do with data mining?
Some examples:
->Frequent itemsets and Association Rules extraction -> 데이터셋에서 자주 나타나는 항목 집합을 식별하는 것과 frequent itemsets을 기반으로, 항목 간의 연관성 분석하는 것(두 개 이상의 항목이 얼마나 자주 함께 나타나는지,그리고 이를 이용하여 추천 시스템 등 다양한 분아에서 활용됨.)
->Feature extraction & selection
->Clustering
->Classfication
->Ranking
->Exploratory analysis
->Hypothesis testing(Decision making)
Example: A web Mining Framework
Web Mining usually involves:
->Data Cleaning
->Data integration from multiple sources
->Warehousing the data(데이터 웨어하우스를 구축하는 것. 데이터 웨어하우스: 기업에서 사용되는 대규모 데이터를 저장하고 관리하는 중앙 저장소)
->Data cube construction
->Data selection for data mining
->Data Mining
->Presentation of the mining results
->Patterns and knowledge to be used or stored into knowledge-base
Major issues in Data Mining
*Mining Methodology
->Mining various and new kinds of knowldege
->Mining knowlegde in multi-dimensional space
->Data Mining: An interdisciplinary effort(다양한 학문 분야들이 상호 작용하거나 협력하여 문제를 해결하는 것)
->Boosting the power of discovery in a networked environment.
->Handling noise,uncertainty,and incompleteness of data.
->Pattern evaluation and pattern- or constraint-guided(제약 조건) mining.*User Interaction
->Interactive Mining
->Incorporation of background knowledge(선행 지식을 활용하여 분석의 효율성을 높이는 것)
->Presentation and visualization of data mining results.
Major issues in Data Mining(Cont.)
*Efficiency and Scalability
->Efficiency and scalability(확장성) of data mining algorithms.
->Parallel,distributed,stream(데이터가 순차적으로 입력되는 경우),and incremental(데이터가 지속적으로 증가하는 경우) mining methods.*Diversity of data types
->Handling complex types of data
->Mining dynamic,networked,and global data repositories.*Data Mining and society
->Social impacts of data mining
->Privacy-preserving data mining
->Invisible data mining