B-TREE
전산학에서 B-트리(B-tree)는 데이터베이스와 파일 시스템에서 널리 사용되는 트리 자료구조의 일종으로, 이진 트리를 확장해 하나의 노드가 가질 수 있는 자식 노드의 최대 숫자가 2보다 큰 트리 구조이다. -위키백과
쉽게 말하자면 B-TREE는 기존의 이진트리와는 달리 2개 이상의 자식을 가질 수 있는 이진트리이다.
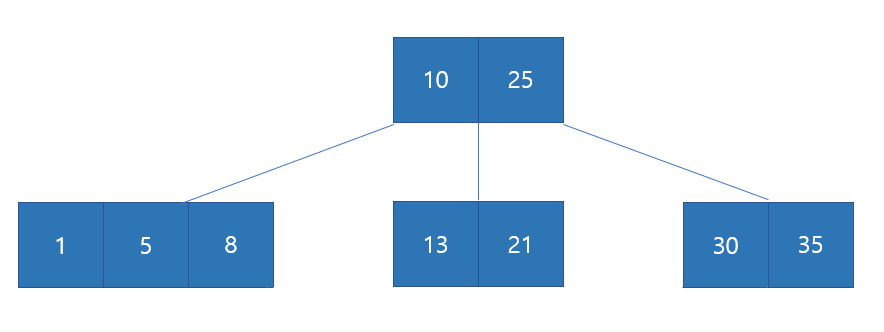
*아래의 내용은 'INTRODUCTION TO ALGORITHMS 3rd Edition'을 참고했습니다.
디스크에 저장되어 있는 정보에 접근하는 시간이 디스크에서 얻은 정보를 메인메모리에서 처리하는 데 걸리는 시간보다 긴 경우가 종종 있기 때문에 디스크에 접근하는 횟수를 최대한 줄여야 한다.
최악의 경우에 트리의 높이만큼 디스크에 접근을 하게 되는데 B-TREE는 하나의 노드에 여러 개의 키를 저장할 수 있기 때문에 허용하는 키의 개수에 따라 트리의 높이가 크게 줄기에 디스크 접근 횟수에 있어서 유리하다.
B-TREE의 특징
- B-TREE는 루트노드, 리프노드와 내부노드로 구성되어있다.
- 모든 노드 x의 n개의 키들은 오름차순으로 정렬이 되어있다.
- 각 내부노드 x는 자식 노드를 가리키는 x.n + 1개의 포인터를 가진다. 리프노드는 자식이 없으므로 포인터값을 갖지않는다.
- 노드의 키들은 서브 트리에 저장되는 키들의 범위를 분할한다.
ex) k1 <= x.key1 <= k2 <= x.key2 <= k3 ... - 모든 리프 노드는 트리 높이 h와 같은 깊이를 가진다.
- 노드는 그들이 포함할 수 있는 키의 개수에 대해 상한과 하한을 가진다. 이런 한계를 B-트리의 최소 차수(minimum degree)라고 하는 일정한 정수 t >= 2을 이용해 표현한다.
a. 루트를 제외한 모든 노드는 t - 1개 이상의 키를 가진다. 따라서 루트를 제외한 모든 내부 노드는 자식 노드를 적어도 t개 이상 가진다. 트리가 비지않았다면 루트는키를 적어도 하나 가진다.
b. 모든 노드는 2t - 1개 이하의 키를 가진다. 따라서 하나의 내부 노드는 자식 노드를 최대 2t개 가진다. 어떤 노드가 키를 정확히 2t - 1개 갖는 경우, 그 노드를 가득 차있다고 한다.
코드
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#define MIN_DEGREE 3
#define MAX_KEY (MIN_DEGREE*2 - 1)
typedef struct _node {
bool is_leaf;
int key[MAX_KEY + 1], key_count;
struct _node *linker[MAX_KEY + 2];
} node;
node *node_create();
void b_tree_create(node **root);
void b_tree_insert(node **root, int k);
void b_tree_delete(node *sub_root, node **root, int k);
void b_tree_search(node *sub_root, int k);
void node_insert(node *sub_root, int k);
void node_split(node *parent, int child_index);
void node_delete(node *sub_root, int k);
void move_key_right_to_left(node *left_child, node *right_child, int *parent_key);
void move_key_left_to_right(node *left_child, node *right_child, int *parent_key);
void merge_node(node *parent, node *left_child, node *right_child, int index);
void display(node *cur_node, int blanks);
void test_case(node **root);
int PRED(node *pred_child);
int SUCC(node *succ_child);
int main() {
node *root;
b_tree_create(&root);
test_case(&root);
display(root, 0);
}
void test_case(node **root) {
int* out_arr = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * 1000000);
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
out_arr[i] = i;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++)
{
int j = i + rand() / (RAND_MAX / (1000000 - i) + 1);
int t = out_arr[j];
out_arr[j] = out_arr[i];
out_arr[i] = t;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
int r = out_arr[i];
b_tree_insert(root, r);
}
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
int r = out_arr[i];
b_tree_delete(*root, root, r);
}
}
node *node_create() {
node *new_node = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
if (new_node == NULL) {
perror("Record creation.");
exit(EXIT_FAILURE);
}
new_node->is_leaf = true;
new_node->key_count = 0;
return new_node;
}
void b_tree_create(node **root) {
node *new_node = node_create();
*root = new_node;
}
void node_split(node *parent, int child_index) {
node *right_child = (node *)malloc(sizeof(node));
node *left_child = parent->linker[child_index];
right_child->is_leaf = left_child -> is_leaf;
right_child->key_count = MIN_DEGREE - 1;
for (int i = 1; i <= MIN_DEGREE - 1; i ++) {
right_child->key[i] = left_child->key[i + MIN_DEGREE];
}
if (!left_child->is_leaf) {
for (int i = 1; i <= MIN_DEGREE; i++) {
right_child->linker[i] = left_child->linker[i + MIN_DEGREE];
}
}
right_child->linker[0] = parent;
left_child->key_count = MIN_DEGREE - 1;
for (int i = parent->key_count + 1; i >= child_index + 1; i--) {
parent->linker[i + 1] = parent->linker[i];
}
parent->linker[child_index + 1] = right_child;
for (int i = parent->key_count; i >= child_index; i--) {
parent->key[i + 1] = parent->key[i];
}
parent->key[child_index] = left_child->key[MIN_DEGREE];
parent->key_count += 1;
}
void b_tree_insert(node **root, int k) {
node *curr_root = *root;
if((*root)->key_count == MAX_KEY) {
node *new_root = node_create();
*root = new_root;
new_root->is_leaf = false;
new_root->linker[1] = curr_root;
curr_root->linker[0] = new_root;
node_split(new_root, 1);
node_insert(new_root, k);
}
else {
node_insert(curr_root, k);
}
}
void node_insert(node *sub_root, int k) {
int i = sub_root->key_count;
if (sub_root->is_leaf){
while (i >= 1 && k < sub_root->key[i]) {
sub_root->key[i + 1] = sub_root->key[i];
i -= 1;
}
sub_root->key[i + 1] = k;
sub_root->key_count += 1;
}
else {
while (i >= 1 && k < sub_root->key[i]) {
i -= 1;
}
i += 1;
if (sub_root->linker[i]->key_count == MAX_KEY) {
node_split(sub_root, i);
if (k > sub_root->key[i]) {
i += 1;
}
}
node_insert(sub_root->linker[i], k);
}
}
void b_tree_search(node *sub_root, int k){
int i = 1;
while(i < sub_root->key_count && k > sub_root->key[i]) {
i = i + 1;
}
if (i <= sub_root->key_count && k == sub_root->key[i]) {
printf("success find %d\n", k);
} else if(sub_root->is_leaf == true) {
printf("fail find %d\n", k);
} else {
b_tree_search(sub_root->linker[i], i);
}
}
void b_tree_delete(node *sub_root, node **root, int k) {
if ((*root)->key_count == 0) {
if ((*root)->is_leaf) {
printf("tree is empty\n");
return;
}
}
node_delete(sub_root, k);
if ((*root)->key_count == 0) {
if ((*root)->is_leaf) {
printf("tree is empty\n");
free(*root);
b_tree_create(root);
return;
}
else {
node *old_root = *root;
*root = (*root)->linker[1];
free(old_root);
return;
}
}
}
void node_delete(node *sub_root, int k) {
if (sub_root->is_leaf){
int original_key_count = sub_root->key_count;
for (int i = 1; i <= sub_root->key_count; i ++) {
if (sub_root->key[i] == k){
for (int j = i; j < sub_root->key_count; j ++) {
sub_root->key[j] = sub_root->key[j + 1];
}
sub_root->key_count -= 1;
}
}
if (original_key_count == sub_root->key_count) {
printf("%d not in b-tree\n", k);
}
return;
}
int i = 1;
while(sub_root->key[i] < k && i <= sub_root->key_count) {
i += 1;
}
if (sub_root->key[i] == k && i <= sub_root->key_count) {
node *left_child = sub_root->linker[i];
node *right_child = sub_root->linker[i + 1];
if (left_child->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
int pred = PRED(left_child);
sub_root->key[i] = pred;
node_delete(left_child, pred);
return;
}
else if (right_child->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
int succ = SUCC(right_child);
sub_root->key[i] = succ;
node_delete(right_child, succ);
return;
} else {
merge_node(sub_root, left_child, right_child, i);
node_delete(left_child, k);
return;
}
return;
}
if (i == sub_root->key_count + 1) {
node *left_child = sub_root->linker[i - 1];
node *right_child = sub_root->linker[i];
if (sub_root->linker[i]->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
node_delete(sub_root->linker[i], k);
return;
}
if (sub_root->linker[i - 1]->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
move_key_left_to_right(left_child, right_child, &(sub_root->key[i - 1]));
node_delete(right_child, k);
return;
}
else {
merge_node(sub_root, left_child, right_child, i - 1);
node_delete(left_child, k);
return;
}
return;
}
else {
node *left_child = sub_root->linker[i];
node *right_child = sub_root->linker[i + 1];
if (sub_root->linker[i]->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
node_delete(sub_root->linker[i], k);
return;
}
if (sub_root->linker[i + 1]->key_count >= MIN_DEGREE) {
move_key_right_to_left(left_child, right_child, &(sub_root->key[i]));
node_delete(left_child, k);
return;
}
else {
merge_node(sub_root, left_child, right_child, i);
node_delete(sub_root->linker[i], k);
return;
}
return;
}
}
void move_key_right_to_left(node *left_child, node *right_child, int *parent_key) {
left_child->key[MIN_DEGREE] = *parent_key;
left_child->key_count += 1;
*parent_key = right_child->key[1];
right_child->key_count -= 1;
left_child->linker[MIN_DEGREE + 1] = right_child->linker[1];
for (int j = 1; j <= right_child->key_count; j++) {
right_child->key[j] = right_child->key[j + 1];
}
if (!left_child->is_leaf) {
for (int j = 1; j <= (right_child->key_count) + 1; j++ ) {
right_child->linker[j] = right_child->linker[j + 1];
}
}
}
void move_key_left_to_right(node *left_child, node *right_child, int *parent_key) {
for (int j = right_child->key_count; j >= 1; j--) {
right_child->key[j + 1] = right_child->key[j];
}
int left_sibling_key_count = left_child->key_count;
if (!right_child->is_leaf){
for (int j = (right_child->key_count) + 1; j >= 1; j--) {
right_child->linker[j + 1] = right_child->linker[j];
}
right_child->linker[1] = left_child->linker[left_sibling_key_count + 1];
}
right_child->key_count += 1;
right_child->key[1] = *parent_key;
*parent_key = left_child->key[left_sibling_key_count];
left_child->key_count -= 1;
}
void merge_node(node *parent, node *left_child, node *right_child, int index) {
left_child->key[left_child->key_count + 1] = parent->key[index];
for (int j = index; j < parent->key_count; j++) {
parent->key[j] = parent->key[j + 1];
}
for (int j = index + 1; j <= parent->key_count; j++) {
parent->linker[j] = parent->linker[j + 1];
}
parent->key_count -= 1;
for (int j = 1; j <= right_child->key_count; j++) {
left_child->key[MIN_DEGREE + j] = right_child->key[j];
}
if (!left_child->is_leaf) {
for (int j = 1; j <= (right_child->key_count) + 1; j++) {
left_child->linker[MIN_DEGREE + j] = right_child->linker[j];
}
}
left_child->key_count += (right_child->key_count + 1);
free(right_child);
}
int PRED (node *pred_child) {
if (pred_child->is_leaf) {
return pred_child->key[pred_child->key_count];
} else {
return PRED(pred_child->linker[(pred_child->key_count) + 1]);
}
}
int SUCC (node *succ_child) {
if (succ_child->is_leaf) {
return succ_child->key[1];
} else {
return SUCC(succ_child->linker[1]);
}
}
void display(node *cur_node, int blanks) {
int i;
if (cur_node->key_count == 0) {
printf("tree is empty\n");
return;
}
if (cur_node->is_leaf) {
for (i = 1; i <= cur_node->key_count; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= blanks; j ++)
printf("---!");
printf("%d\n", cur_node->key[i]);
}
return;
}
for (i = 1; i <= cur_node->key_count; i++) {
display(cur_node->linker[i], blanks + 1);
for (int j = 1; j <= blanks; j ++)
printf("---!");
printf("%d\n", cur_node->key[i]);
}
display(cur_node->linker[i], blanks + 1);
return;
}
3일 동안 b-tree를 잡고 있으니 이제 어떤 구조인지 조금 감이 오는 것 같다.
특히 거의 처음써보는 C언어와 포인터에 조금은 익숙해진 것 같다.
역시 부딪혀보는게 가장 빨리 배우는 방법인 것 같다.
다음 포스팅은 위 코드를 간단히 설명해보도록 하겠습니다.
피드백 환영합니다.
-끝-
